anatomy and function of female reproductive system
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
where are the ovaries located
on either side of the uterus, close to the open ends of the fallopian tubes in the pelvis
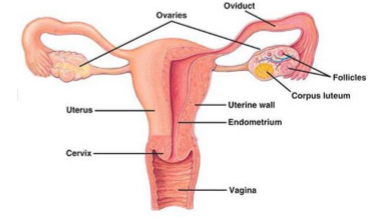
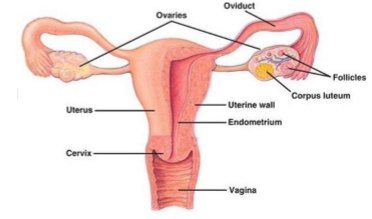
what is the structure of each ovary
cortex containing primordial follicles embedded in supportive tissue
how many primordial follicles are present at puberty
approximately 200,000
what is a primordial follicle composed of
an ovum (oocyte) surrounded by a single layer of epithelial granulosa cells
how many follicles mature during a woman’s reproductive life
approx 450
what happens to remaining follicles
they undergo spontaneous degeneration (atresia)
what happens to follicles at menopause
only a few primordial follicles remain in the ovaries
how many stages of follicle development are there
3
what is the final mature ovarian follicle called
the Graafian follicle
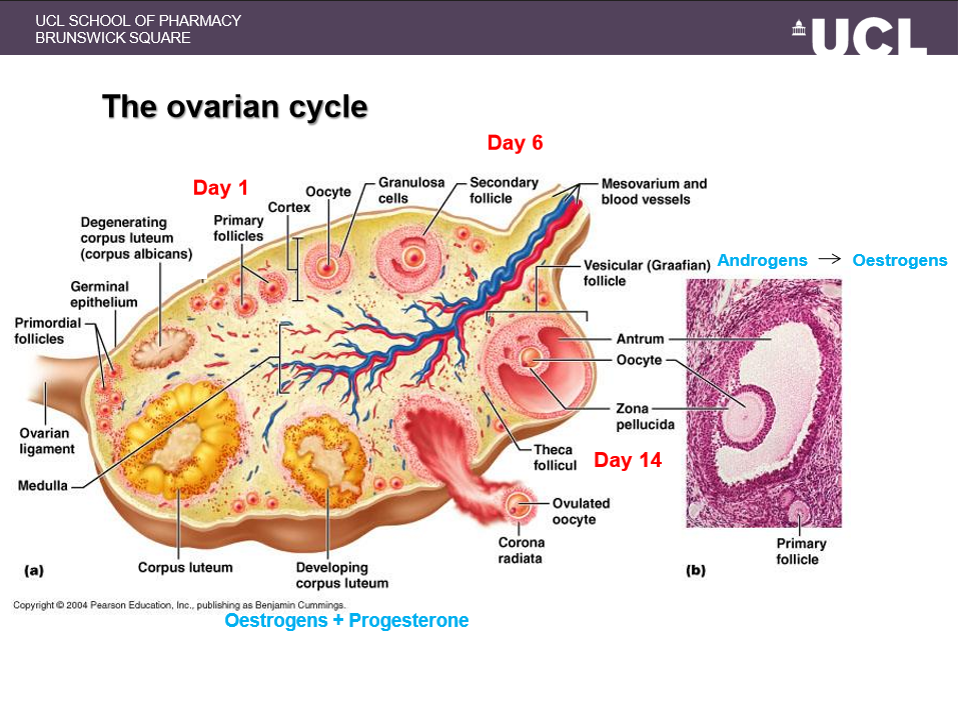
what happens at day 1 of the menstrual cycle
the follicular phase begins; FSH stimulates ~10–20 primordial follicles to develop into secondary follicles
what happens around day 6 of the cycle
1 follicle usually becomes dominant and continues to mature
what happens mid cycle around day 14
ovulation occurs — the Graafian follicle ruptures and releases the oocyte
where does the oocyte go after ovulation
into the abdominal cavity and then into one of the fallopian tubes
how long does the ovum take to pass down the fallopian tube
approximately 3–4 days
what happens if fertilisation occurs
cell division begins before implantation in the uterus
describe primary (primordial) follicle
an immature oocyte surrounded by a single follicular cell layer
describe secondary follicle
the oocyte enlarges; granulosa cells multiply under FSH influence, and a fluid-filled antrum appears
describe the Graafian follicle
Large antrum
Outer layer of thecal cells
LH stimulates thecal cells to produce androgens
Androgens are converted to oestrogens by granulosa cells (FSH + LH)
what forms the corpus luteum
granulosa and theca cells of the collapsed follicle after ovulation
how long does the corpus luteum persist if pregnancy does not occur
approximately 10 days
what hormones does the corpus luteum secrete
oestrogen and progesterone
what happens to the corpus luteum if fertilisation occurs
it survives and secretes hormones for 2–3 months until the placenta takes over