L4 - Heterogeneity and Probability Models
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
This week is about heterogeneity. Give three ways in which people can differ.

What is the result of heterogeneity for brands and strategies?


services
We have two types of heterogeneity, namely …
observed and unobserved
Give two examples of observed heterogeneity.
Household size
Income
Give two examples of observed heterogeneity.
heavy vs. light user
Coca Cola vs. Pepsi
price sensitive vs. not price sensitive

What has changed over the years leading to a new approach?
We now have detailed data on customer (purchase) behavior


What is the goal of basic clustering?


What are these observations?

There are two broad classes of algorithms for basic clustering. What are those?

What is the best known example of a non-parametric method for basic clustering?
k-means
What are the advantages of the k-means algorithm for basic clustering?
Simple, no distributional assumptions needed
Relatively fast
What are the disadvantages of the k-means algorithm for basic clustering?

Parametric methods alleviate some of the disadvantages (of course they have their own...). Which parametric method for clustering do we discuss in his course?
Mixture models
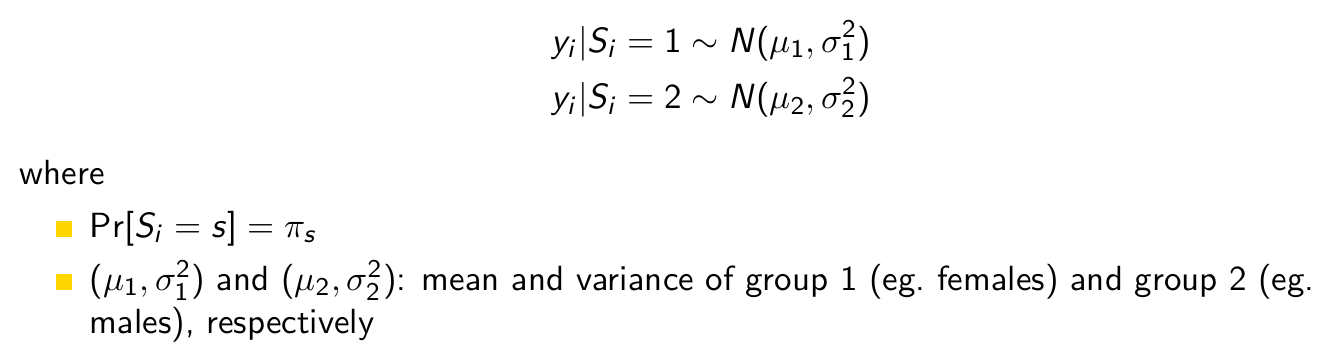
Consider this mixture model. What is he probability that a person is a male given his height?
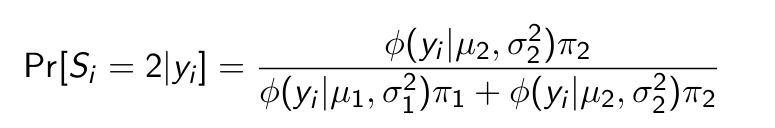
How do we estimate the mixture model?
EM (Expectation Maximization) algorithm. Not ML because the likelihood function is difficult (to maximize)
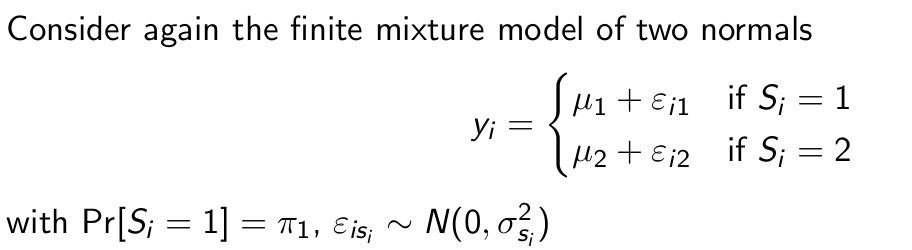
What is the likelihood function here?
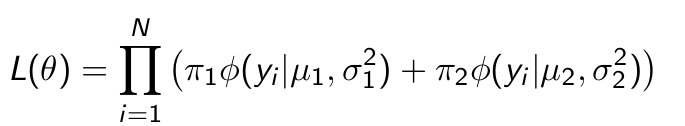
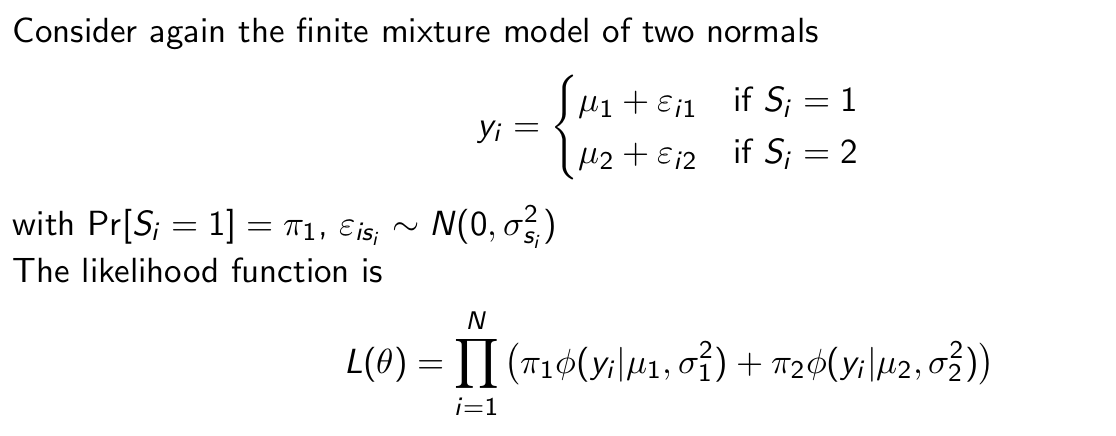
What is the idea of the EM Algorithm? What does this mean for the likelihood function?
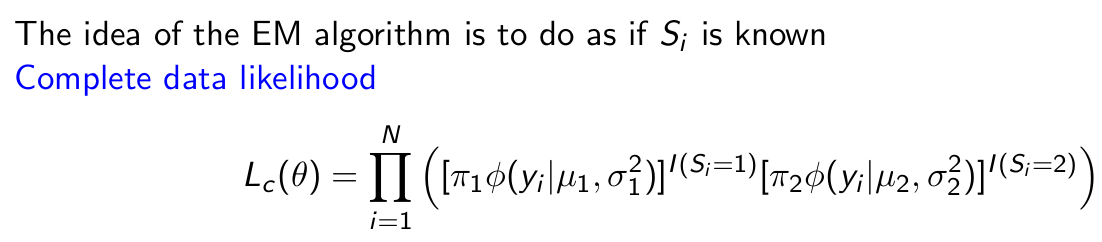
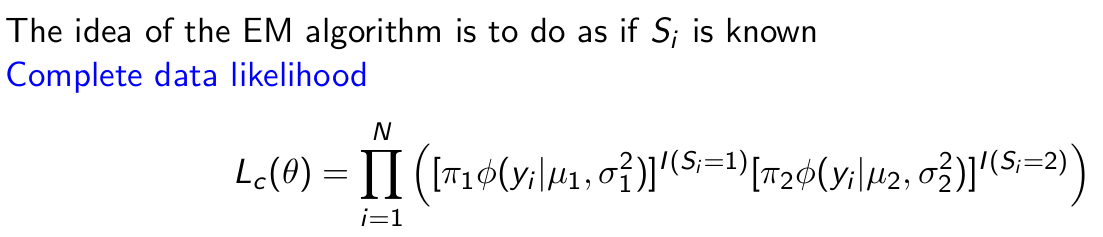
Give the log complete data likelihood.
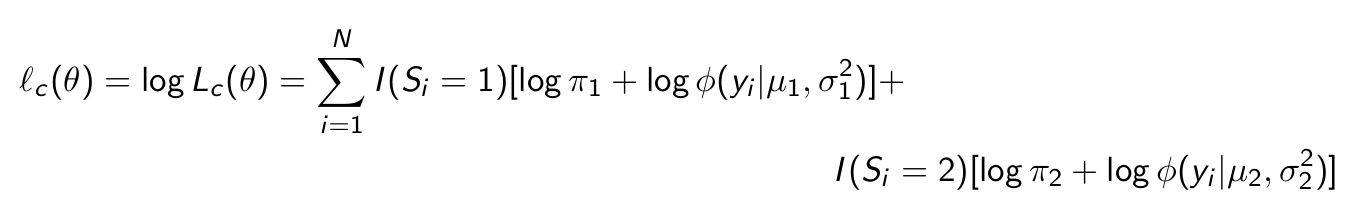
The EM algorithm consists of two steps. What is the first step?
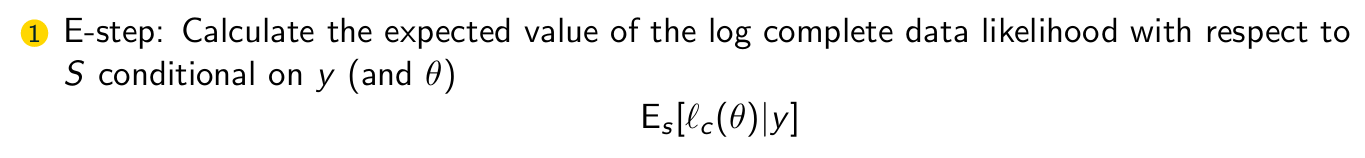
The EM algorithm consists of two steps. What is the second step?

So what is the idea of the EM algorithm and what is the algorithm?
The idea of the EM algorithm is to do as if the states are known.

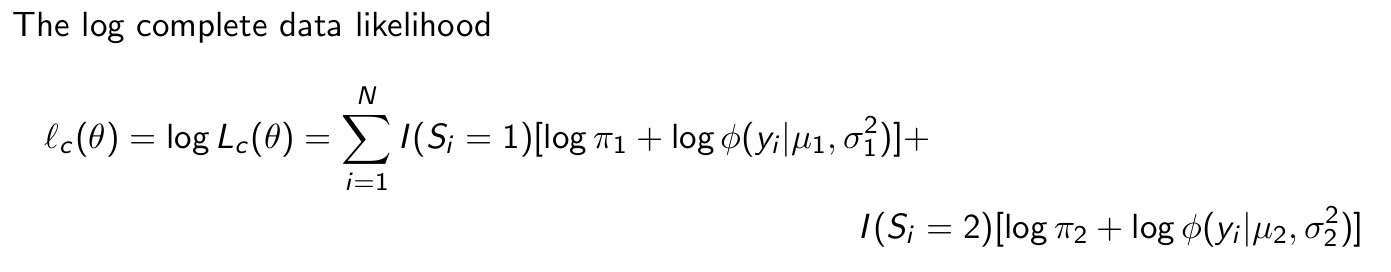
What is the expected complete data likelihood for the general case of k states?
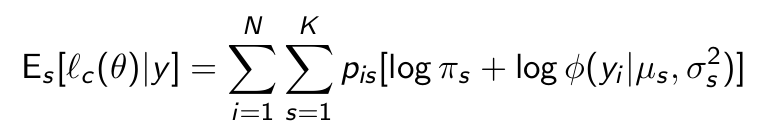
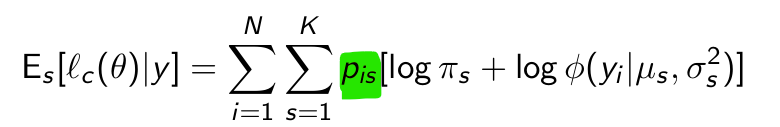
What is this thing?
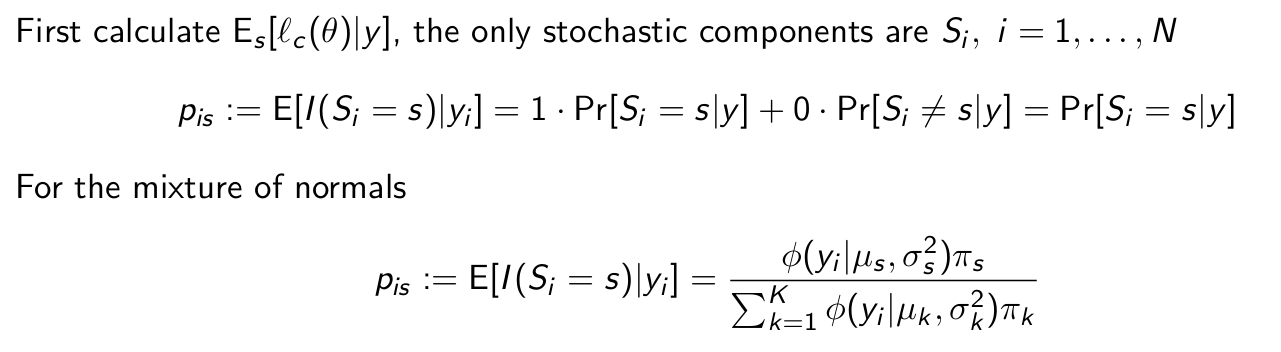
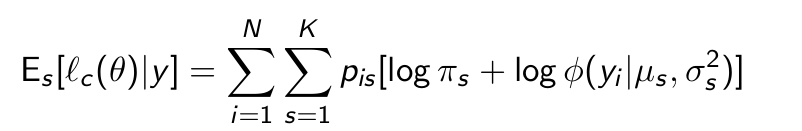
What is smart to do next?
Divide it into two parts because this makes the M-step easier as each part can be considered separately (if parameters do not appear in multiple segments) and no products appear anymore.
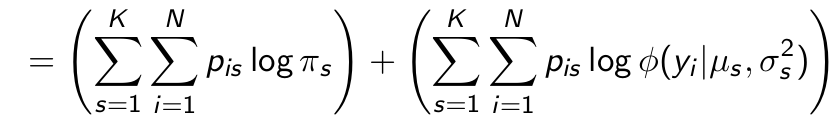
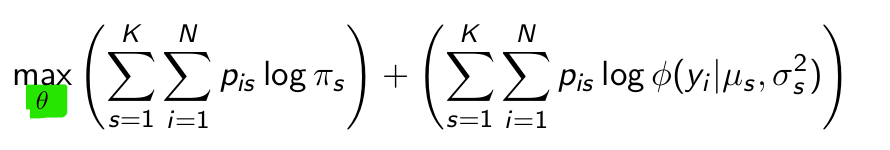
Which parameters are in this theta?
πs, μs, σs2
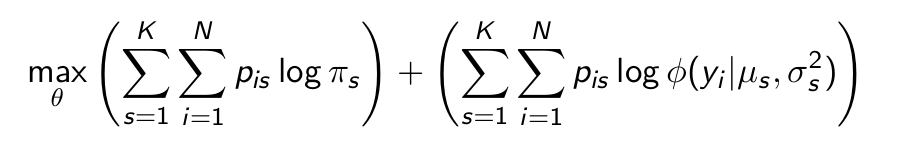
Which result does maximizing the first half give us?
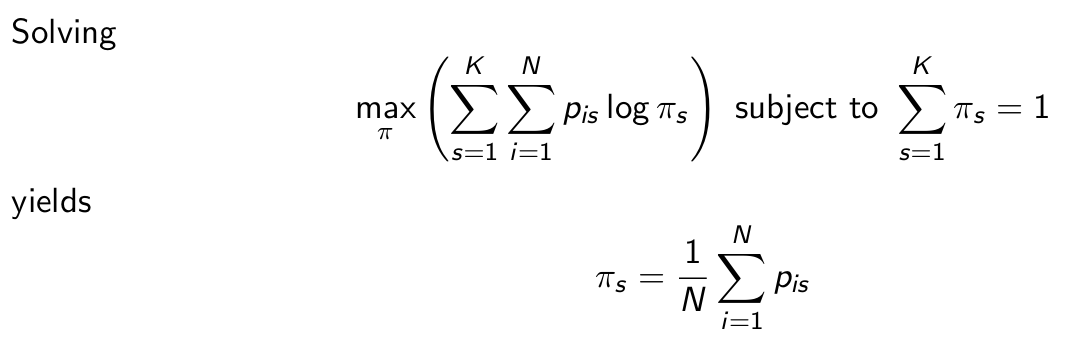
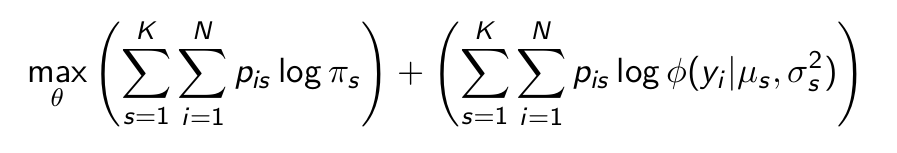
Which result does maximizing the second half give us?
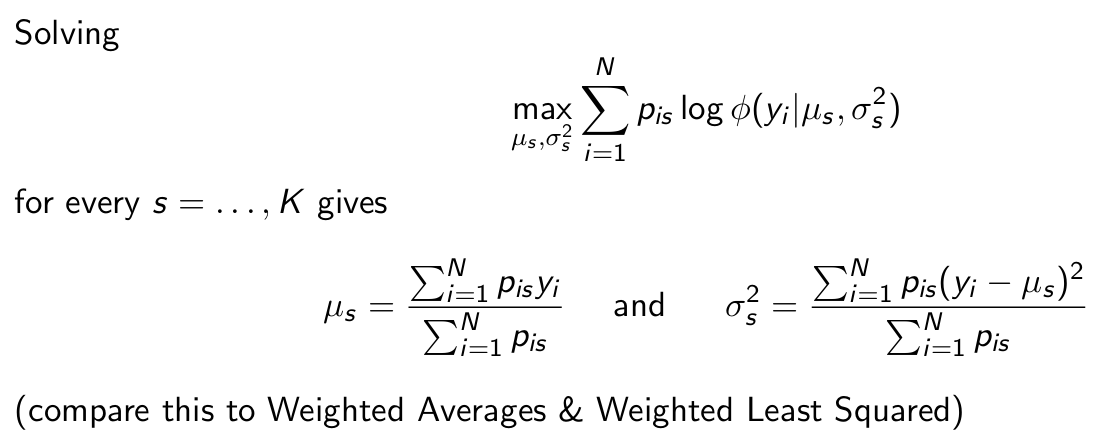
So the EM Algorithm is only two steps?
No. After the M-step, use the updated parameters to do the E-step again. Iterate until convergence.
What can you say about convergence of EM?
EM usually converges quickly to the neighborhood of a maximum of the likelihood function, but final convergence can be slow
Why should we use multiple starting values when using EM?
To avoid the risk of finding only a local maximum
What is the easiest way to obtain standard erros when using the EM algorithm?
use second order derivative of (standard) likelihood function
We can extnd the EM algorithm to mulivariate normal distributions. What changes in hat case?
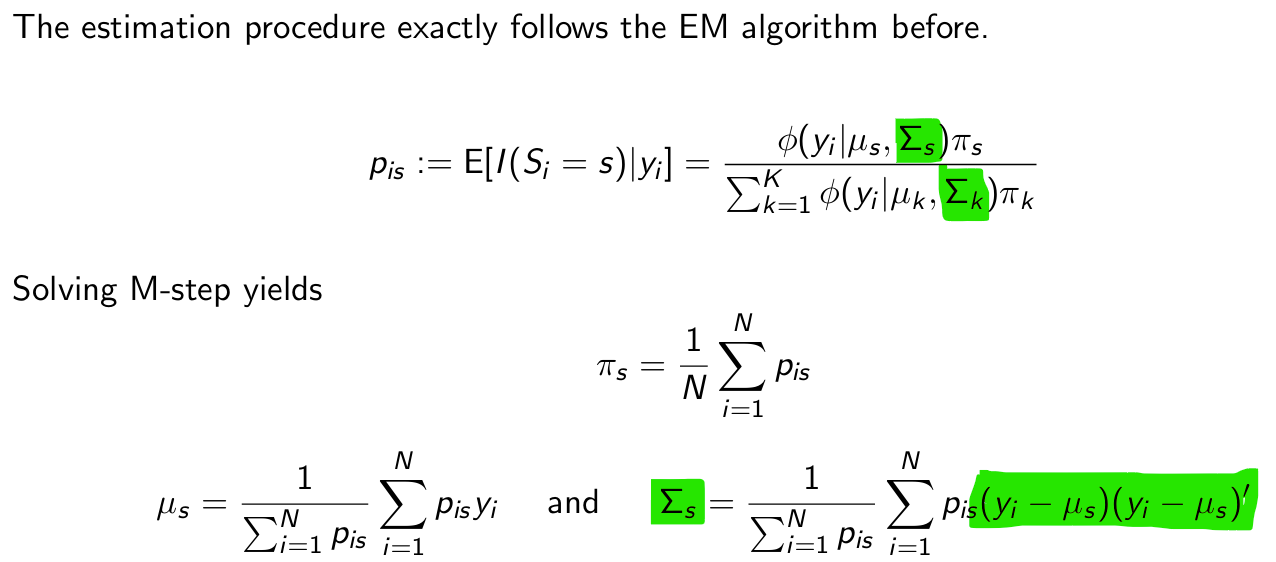
What is cool about multivariate mixture of normals in terms of prediction?
We can predict y1 given y2
What is the first thing we do to predict y1 given y2?
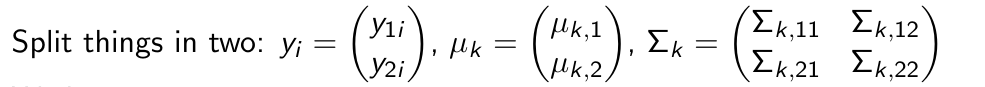
After splitting everything in two, what is the next thing we do to predict y1 given y2?
We construct
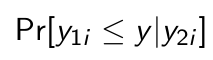
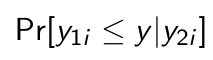
How do we rewrite this thing in order to predict y1 given y2?
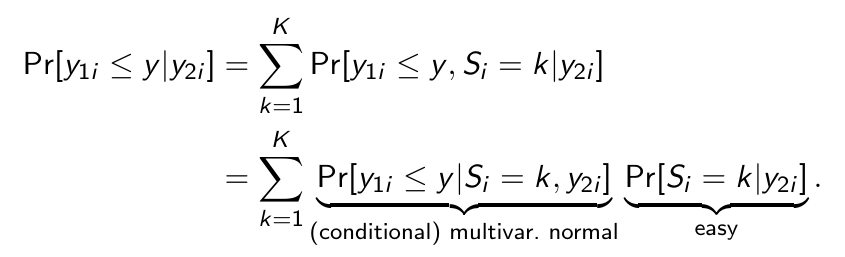

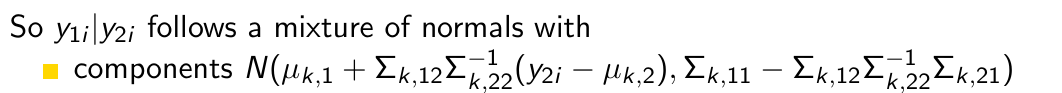
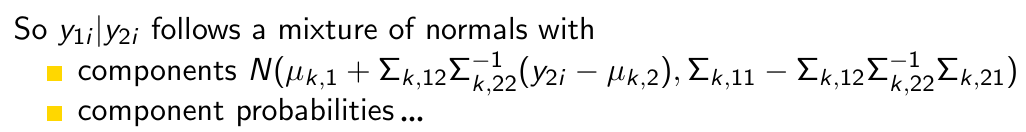
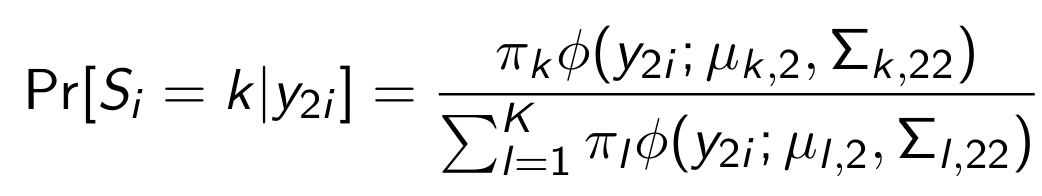
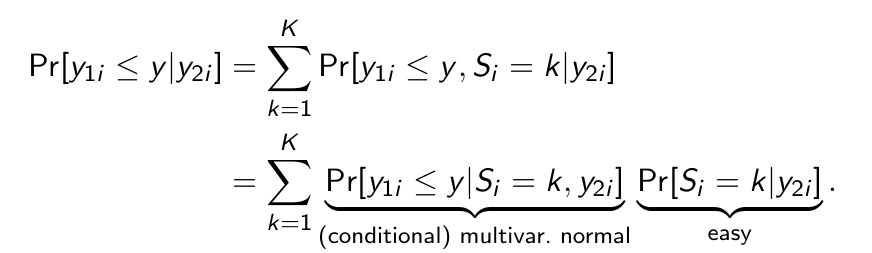
Okay but what is now the first step to turn this into an actual prediction?
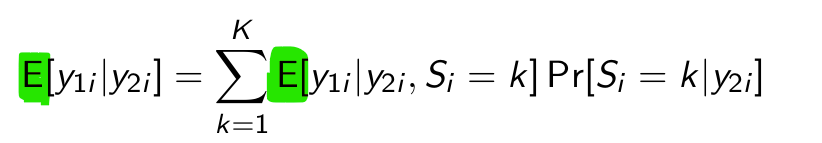
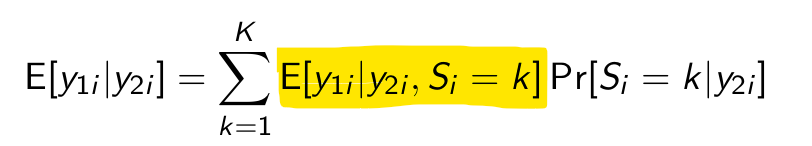
What can we substitute for this?
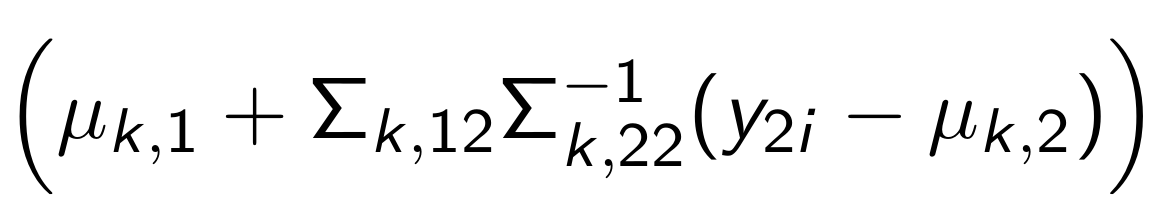
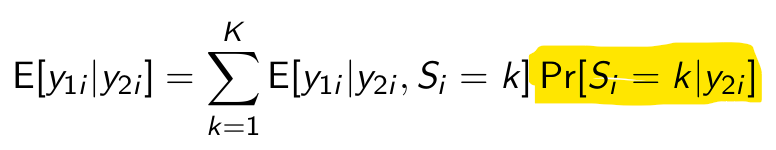
What can we substitute for this?
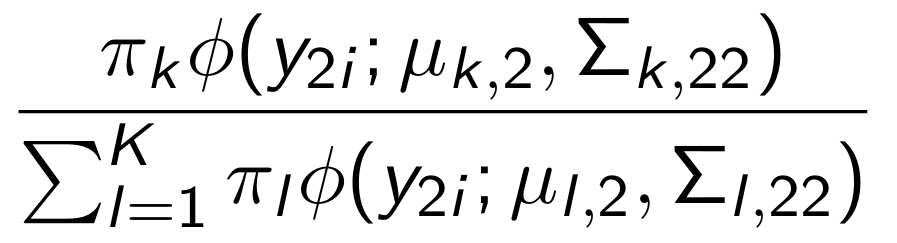
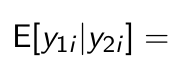
Now give the complete rewriting yourself
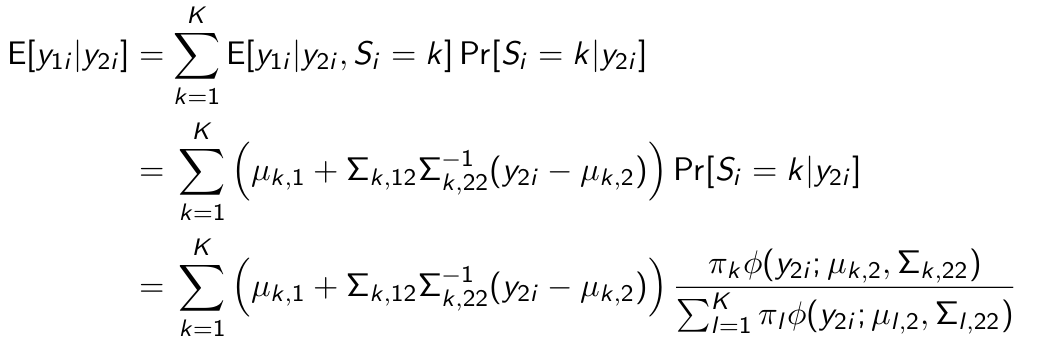
What are the advantages of clustering using mixtures?

What are the disadvantages of clustering using mixtures?

What are the challenges we face when clustering using mixtures?

Name some ways in which we can generalize the mixture model. In what context is this especially powerful?

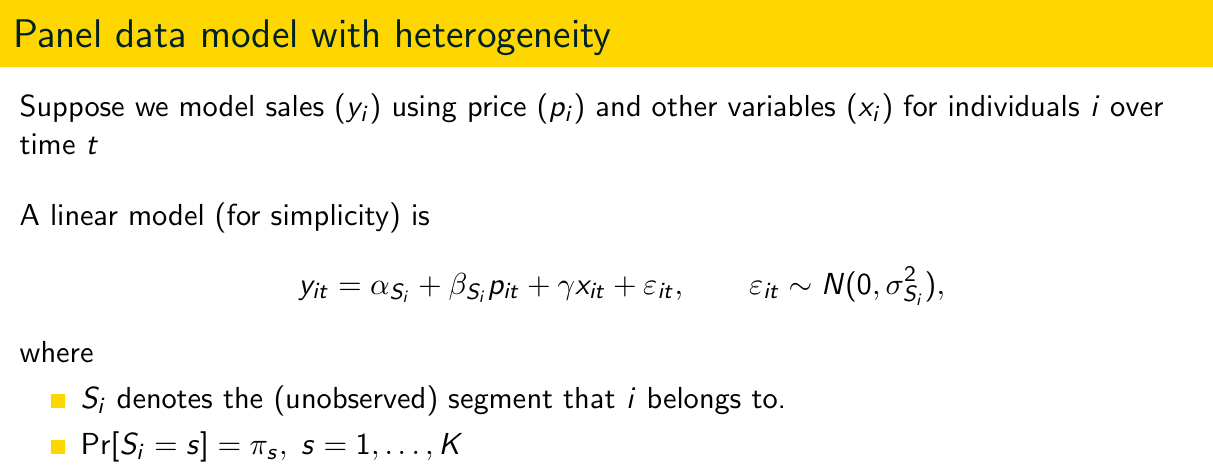
What is this model called?
Latent class model
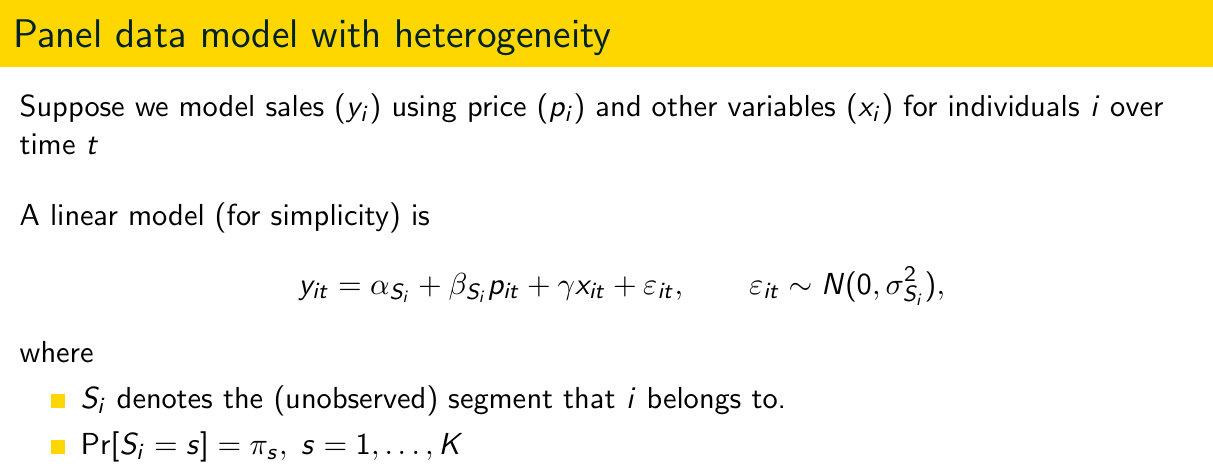
Can people switch segments? And according to which process?
NO People stay in the same segment over time!
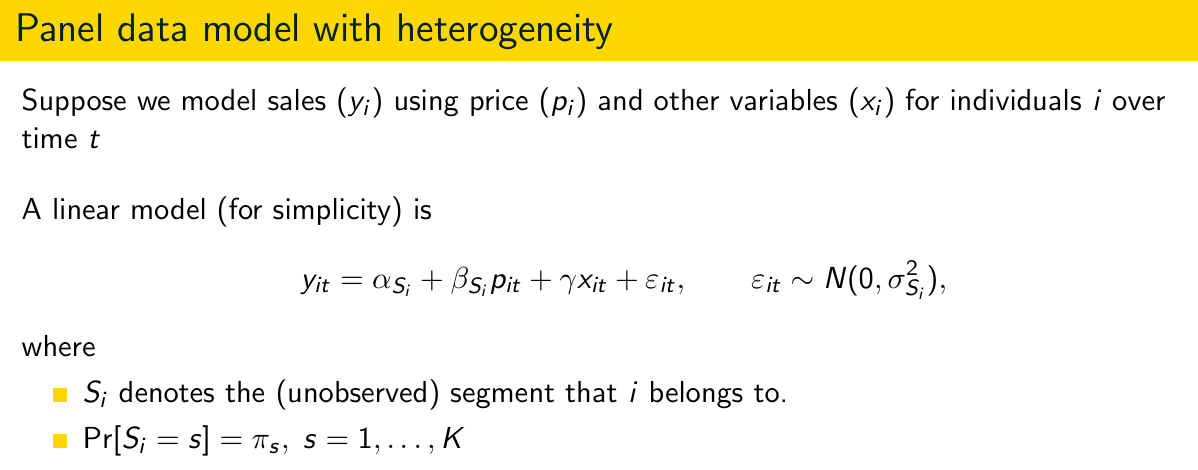
What do you notice when looking at the parameters?
Not all parameters are (or have to be) segment specific.
How do we estimate a latent class model?
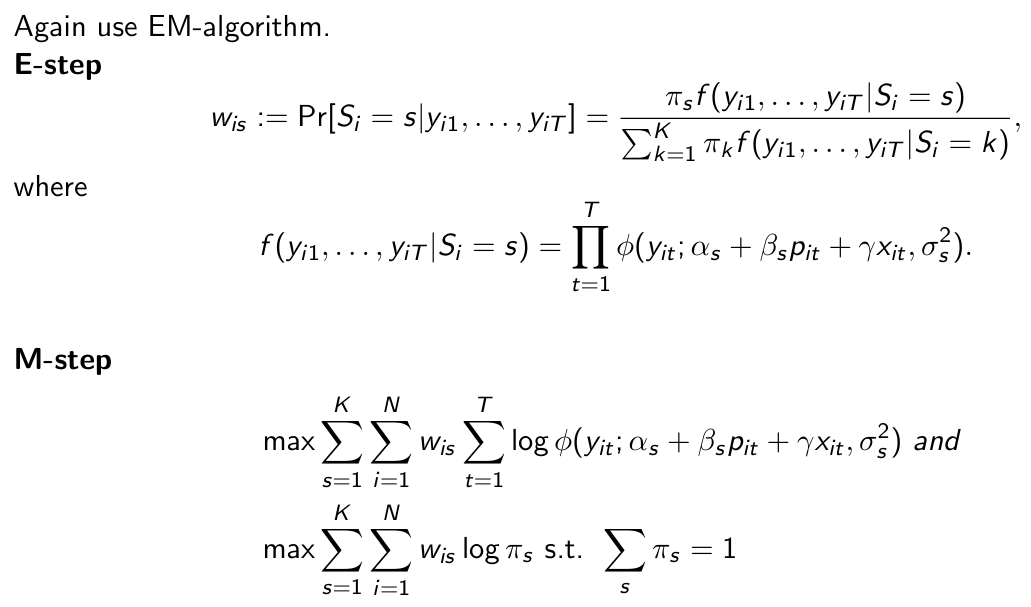
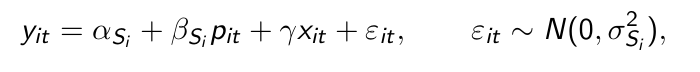
Why cannot we split the maximization over the segments anymore?
due to γ
Explain what we mean by learning in this course.

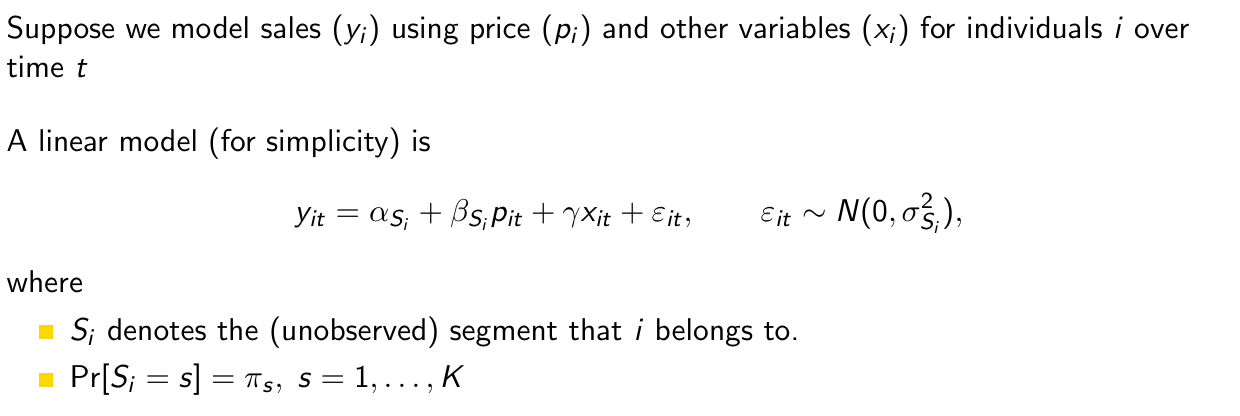
If no observed decisions are available something weird happens in this model. What is it and how could we solve it?


How?
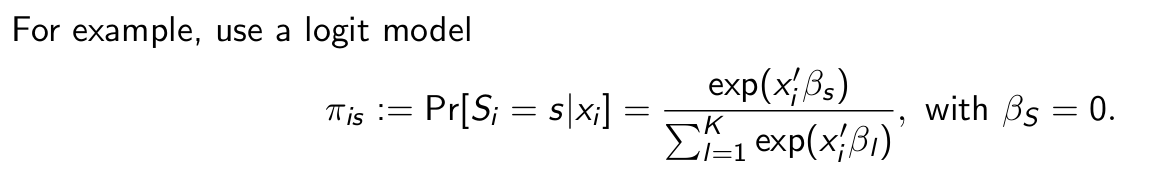
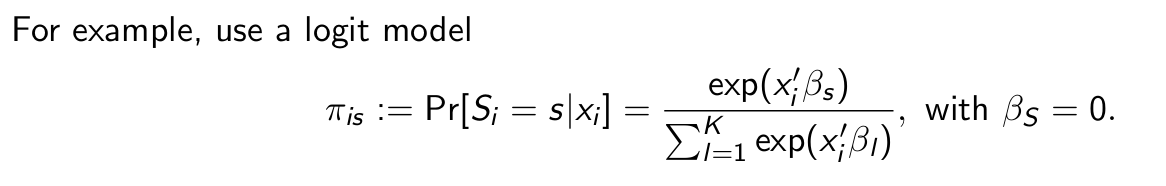
Can we still learn by observing behaviour?


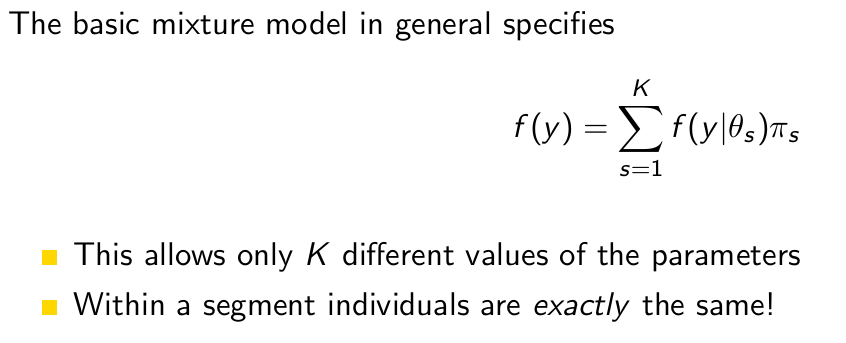
So how many different values of the parameters does this allow?

How can we generalize this to a continuous distribution?
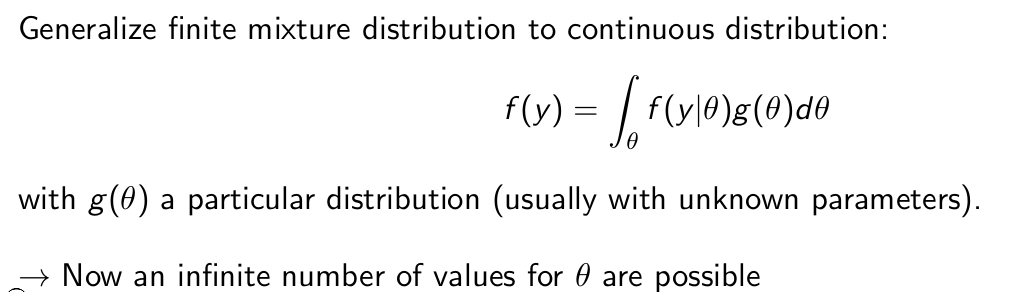
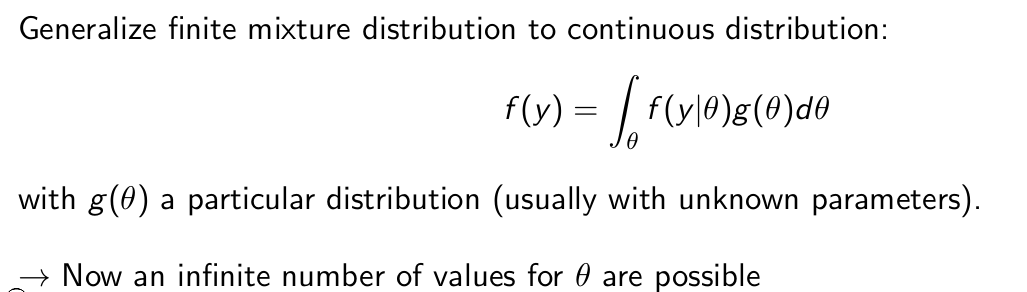
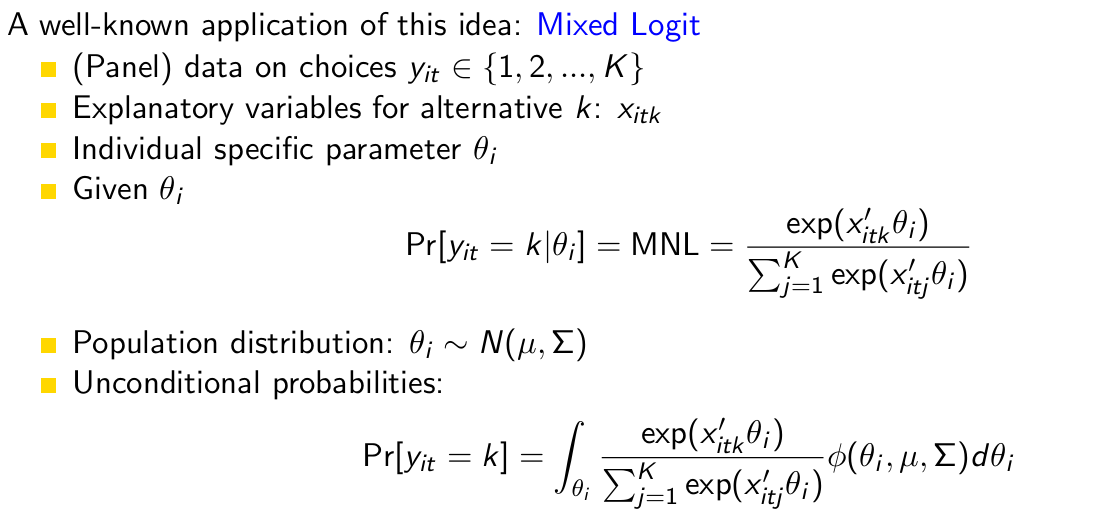
What is a well-known application of this idea?
Mixed logit
Explain the mixed logit model in detail.
What are advantages of the mixed logit model?


Express this in terms of the distribution of the data conditional on theta and the distribution of theta.
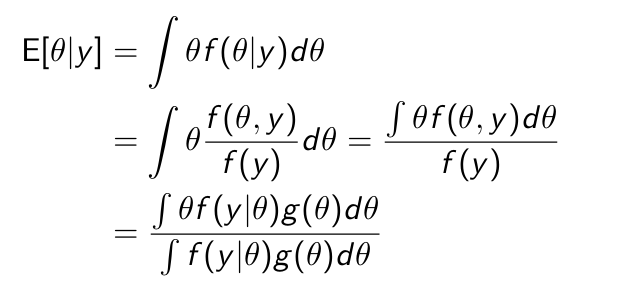
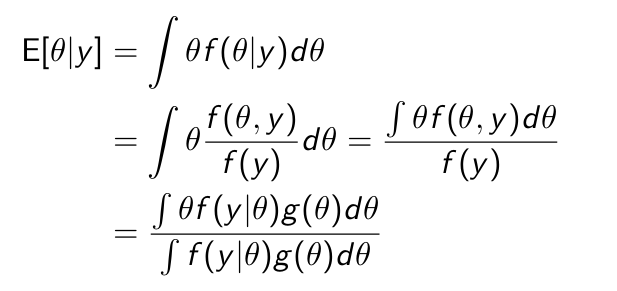
Can we give this expectation now?
This expression only contains known (estimated) density functions. However calculating this is not easy (neither is estimation).

Should we use continuous or discrete heterogeneity if we are interested in segmentation?
Discrete
Should we use continuous or discrete heterogeneity if we are interested in forecasting?
The forecasting performance between the two is comparable
Should we use discrete or continuous heterogeneity if we do not want to assume a particular distribution?
If you do not want to assume a particular distribution, use the latent class approach with many classes (the mixture approximates the true distribution as number of mixtures increases)
A combination of discrete and continuous heterogeneity is also possible. Give an example of when it would make sense to use his.
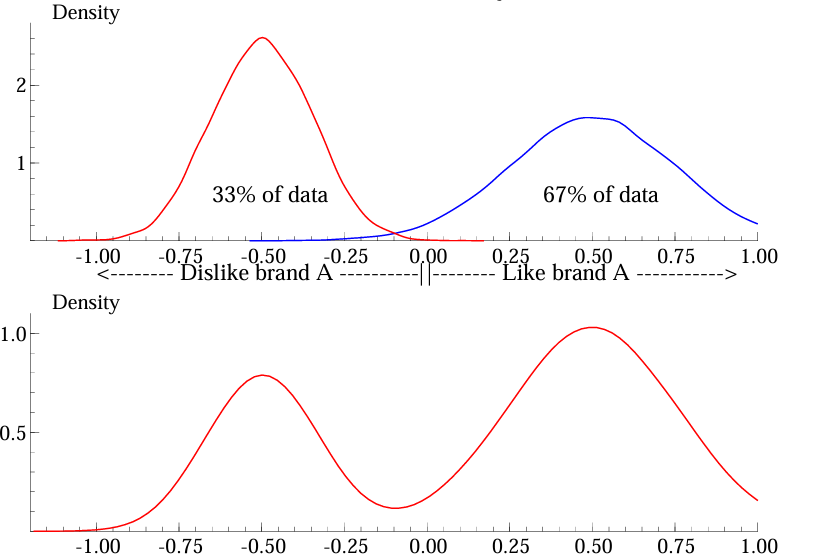
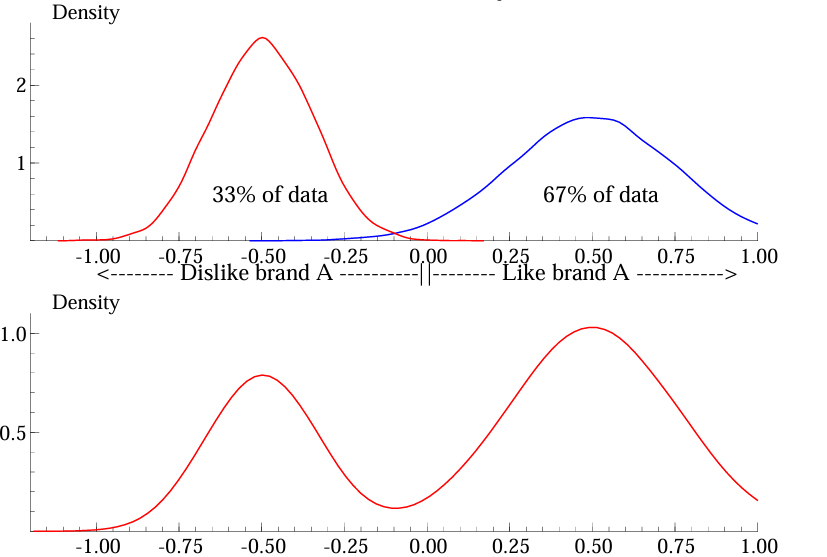
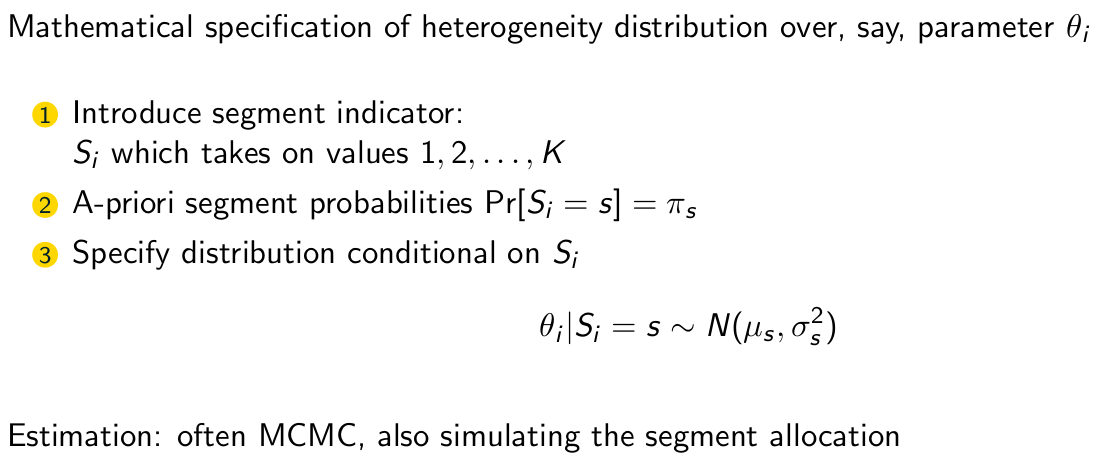
Give the mathematical specification for the segments and parameters. Also tell which estimation method is used.
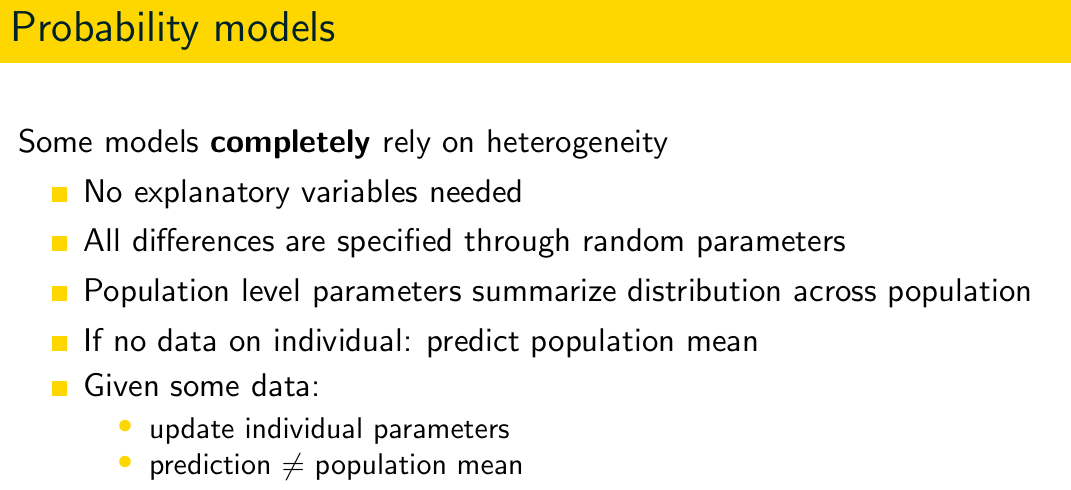
Some models completely rely on heterogeneity. What are those models called?
Probability models

Fill in the gaps
Give three examples of probability models.


What are the two questions that we want to answer?

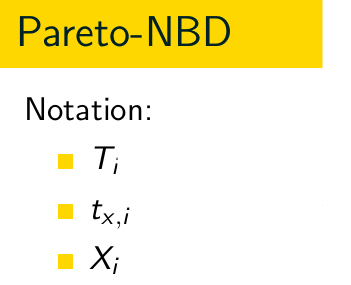
What do these symbols denote?

How is the (unobserved) defection time denoted in the BTYD model and what is its distribution?
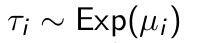
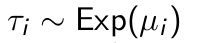
What are the expected value and variance of the (unobserved) defection time?
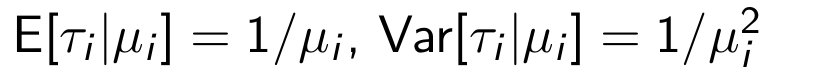
How are while alive purchases distributed in the BTYD model?

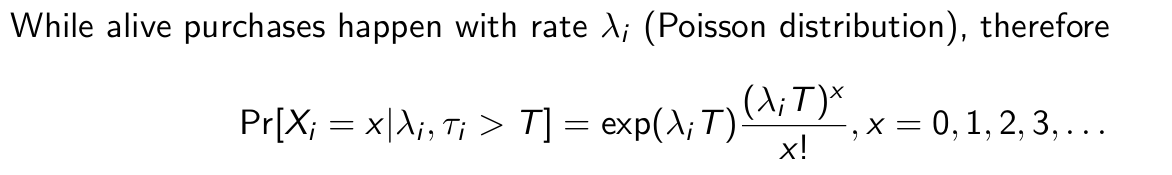

What can we say about these?
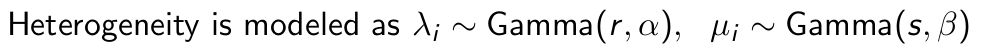
So what is the distribution of the number of purchases given alive?
Negative Binomial Distribution
So what is the distribution of time until defection?
Pareto distribution
How can we do inference in the Pareto-NBD?

What if we ignore unobserved heterogeneity?

In a choice model: ignoring heterogeneity leads to overestimation of …
state dependence
What is state dependence and what is the difference with loyal?

Loyalty and state dependence give very similar choice patterns, ignoring one leads to …
overestimation of the other.

