CH 12: metabolism and bioenergetics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
overview of metabolism
-includes metabolism and anabolism
catabolism→ breakdown process, glucose → CO2 + H2O + ATP
-generates energy to be used in anabolism
oxidative
Anabolism→synthesis process, require energy, reductive
starchy foods are hydrolyzed by amylases
digestion:
carbs.→monosaccharides
proteins→amino acids
lipids→ free fatty acids/glycerols
bonds are covalent, need enzyme to break bonds
amylase is in the mouth, where digestion begins
-proteins are hydrolyzed by proteases
-Fatty acids are hydrolyzed by lipases:released from glycerol backbine, don’t travel well in blood due to hydrophobic character
for transport some fatty acids are linked to cholesterol
-cholesteryl stearate- fatty acids, lipids, cholesterol, proteins
-packed into lipoprotein or chylomicron→ travel through lymphatic system and be processed by liver → high density lipoporteins
-protein travel through blood
adipocytes hold triacylglycerols
-store excess lipids
-carbs used as main energy source
-excess energy/carbon→stored as lipids
lipids do not interact with H2O, not hydrated so takes up less weight
more energy when oxidize lipids
glycogen structure
-stored only in liver/muscle
-limit of storage for glycogen
-can store a lot glucose and stay stored
-in liver: regulate blood glucose
in muscle: only used for muscle
-only have 1 reducing end, can break off glucose for energy
glycogen breakdown
-occurs via phosphorolysis
-liver break down glycogen
-cleave glycosidic bond and add a phosphate
intermediates of glucose metabolism
glucose→ glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (in photosynthesis, precursor for glycerol) → pyruvate ( intermediate)→acetyl-coA (intermediate)
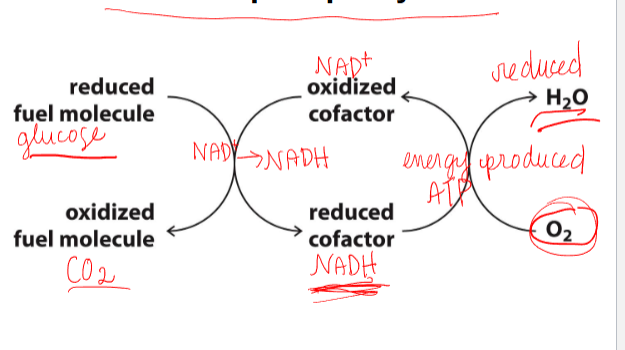
many metabolic pathways include redox reactions
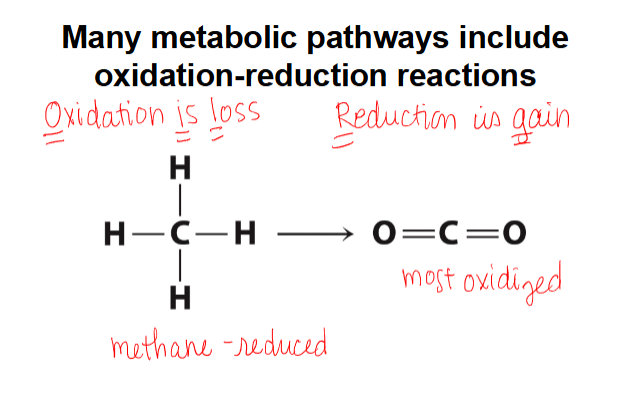
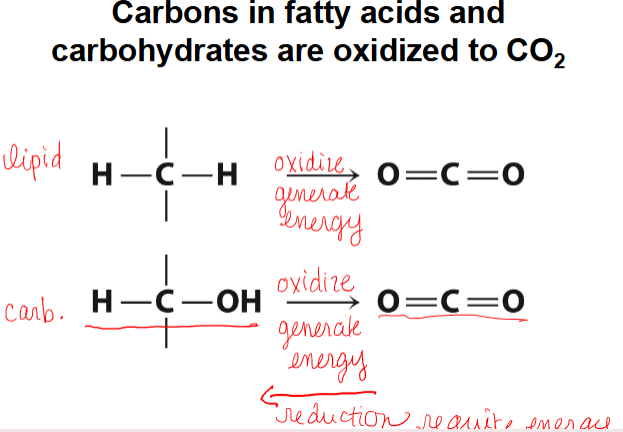
carbons in fatty acids and carbohydrates are oxidized to CO2
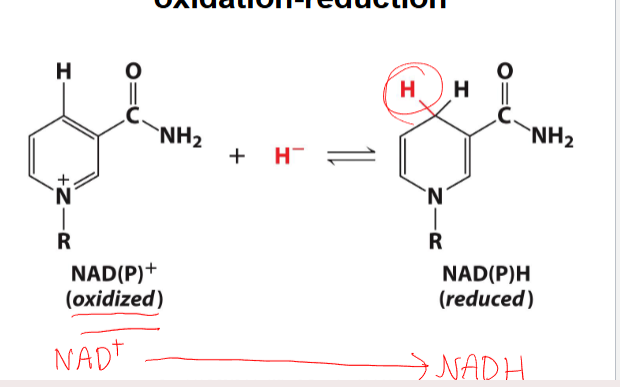
some cofactors undergo redox reactions
-has intermediate thats oxidized when NAD+ is reduced
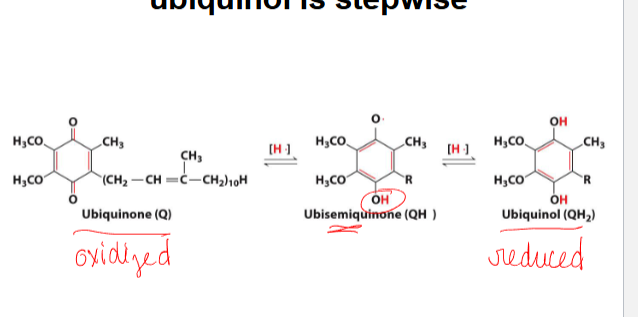
reduction of ubiquinone to ubiquinol is stepwise
-ubiquinone (q) is the oxidized form, and ubiquinol ( qh2) reduced form
cofactors are recylced through oxidative phosphorylation
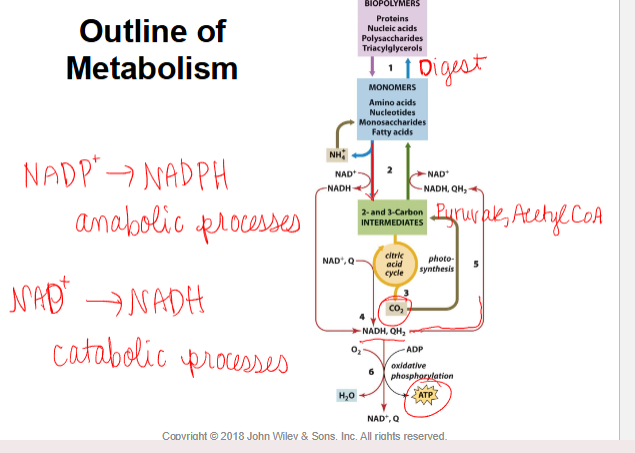
outline of metabolism
NADP+→NADPH - used in anabolism
NAD+→NADH- used in catabolism
things to know: humans do not synthesize some important molecules that are essential
-humans do not synthesize vitamins-need to consume vitamins for metabolic processes to work
complexity of metabolic pathways
all connected
highly/tightly regulated-energy efficient
not every cell involved in every pathway
unique metabolic repertoire
organisms may be metabolically interdependent
the free energy change depends on reactant concentrations
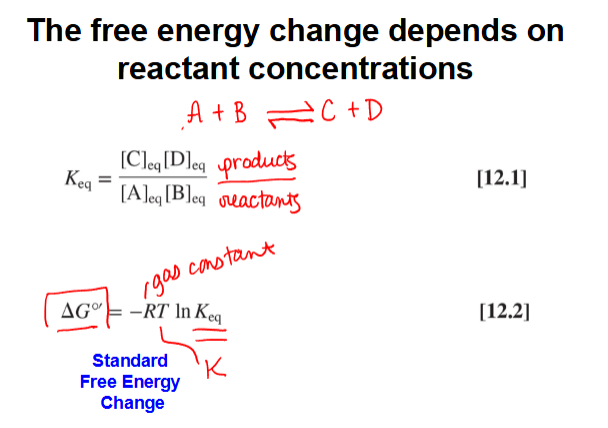
calculating actual free energy changes
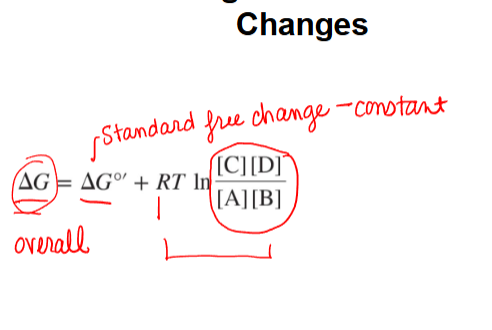
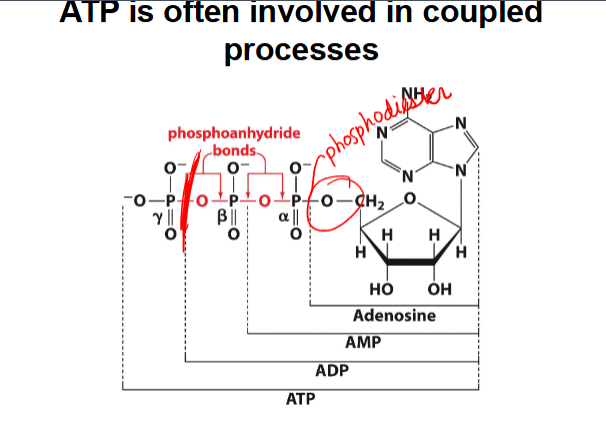
ATP is often involved in coupled processes
-couples an endergonic reaction with an exergonic reaction
-lot of protential to release energy in phosphoanhydride bond →couple with adding phosphate to glucose : unfavorable
favorable : ATP + H2O →ADP + Pi
unfavorable: glucose + Pi→ glucose-6-phosphate
-ATP hydrolysis provides energy for glucose phosphorylation
whats so special about ATP?
-anaerobic proceses to make product-generate energy as breakdown precursors
negative delta G prime → hydrolyze it
-releases a lot of energy-cleavage of phosphoanhydride bond to get energy from
-several different molecules can serve as energy currency within a cell, ex: phosphoenolpyruvate releases -61.p kj of energy
-thioester hydrolysis also releases a large amount of free energy-thioester bond, cleavage is energetically favorable and releases energy
-regulation occurs at steps with the largest free energy changes-tight regulation. if rxn is near equilibrium it could go forward or backward
-if the delta G is very negative, reaction can only go forward