Final -- History of the Greek Polis
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
Attica
Almost all mentions of the polis in Greek literature come from what region?
Ethnos (common origin)
Polis (city)
Demos (deme) or phyle (tribe)
Rank the hierarchy of identifying groups to which an individual citizen belongs.
magistrates, council, assembly
What are the three main political institutions of a polis?
synoecism
creation of one political power by voluntarily uniting multiple municipalities
Battle of Chaeronea
What battle marks the end of the full autonomy of the Greek poleis?
Thebes & Athens
In the Battle of Chaeronea, Philip of Macedon defeats a coalition between what two Greek city-states?
Hegemonies like Athens, Sparta, and Thebes (the polis continued to exist, even with limited autonomy)
What aspect of Greek political power disappeared after the Battle of Chaeronea?
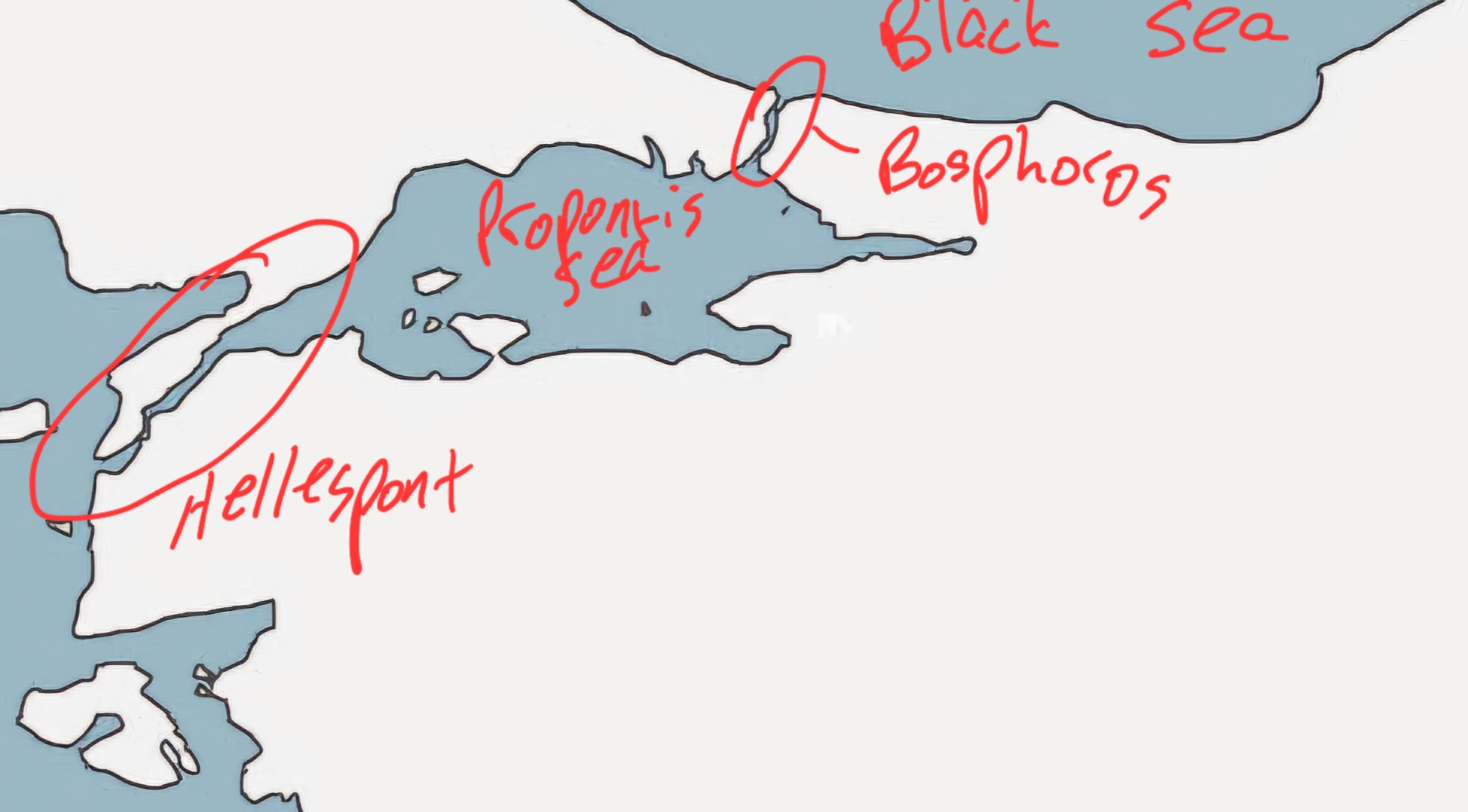
Label the Hellespont, the Bosphoros, the Propontis Sea, and the Black Sea.
Internal political and social problems (Partheniai in Sparta, famine in Thera)
Relative overpopulation of Greece; land shortage
Desire to control Mediterranean trade routes
List some “push and pull” factors which encouraged Greeks to colonize marginal/coastal areas.
8th-6th centuries BCE; Archaic period
When did the major wave of Greek colonization of coastal areas (like those of Thrace) occur? Give the centuries and the corresponding period.
local population fallen into a state of dependence
Where did the agricultural labor force for colonial farmland come from? (possibly)
Consolidation of the organizational model of the Greek metropolis
Common Greek identity enhanced by contact with outsiders
Strengthened relations with the Near East
Three major effects of Greek colonization
bought their own armor, horse, and lance
How did hoplites distinguish themselves from the rest of the population?
a man is not to be kosmos (chief city official) more than once per ten years
Law of Dreros (Archaic period)
aristocracy
Greek tyrants were typically from what social class?
Struggle for domination within the aristocracy
General dissatisfaction among the (rural) demos
Two preliminary conditions for tyranny
hoplite; aristocrats
Tyrants were meant to be seen as leaders of the __ class against the __
inciting popular emotion by misinformation or flattery
What does it mean to be a demagogue?
influential individuals
Ancient sources focus on the acts of __ rather than the general populace.
aristocratic
What form of government was the constitution of 7th century Athens?
Colonies are independent of their metropolis;
Settlers of a cleruchy retained city-state citizenship and political rights (dependence)
Colony vs. cleruchy
head of the army
polemarchos
Cylon attempts to establish a tyranny by occupying the Acropolis, but fails (630-600 BCE)
What is the first recorded historical event of Athens?
Draco
Which Athenian legislator instituted homicide laws forbidding personal retaliation in favor of public accusation, and established a court of 51 ephetai to determine if a murder was premeditated?
aidesis
term for the purification of the pollution caused by murder, performed by the relatives of the aggressor
political/agricultural crisis
Solon was elected by the Athenian people as a reconciler (diallaktes) and reformer following what kind of event?
leveraging a freedom as a guarantee of agricultural debt payment
(prior to Solon’s law, debtors would be sold into slavery to fellow Athenians AND abroad)
What policy did Solon completely abolish?
We don’t know
Was slavery as debt security an old Athenian law, or a recent practice established by greedy aristocrats in the late Archaic period?
cancellation of debts
abolishing use of personal freedom as debt security
retrieving Athenians who had been sold abroad
Solon’s policy of seisactheia
“due share”
Solon’s goal was not complete equality, but giving everyone their __
redistribute the land; cancel debts
Poor Athenians complained that Solon did NOT ___, while rich Athenians complained that Solon DID ___
land ownership; 4
Solon reorganized social classes based on what factor? How many classes were there?
richest
Under Solon’s new social classing system, the pentakosiomedimnoi were the __ Athenian citizens.
thetai
Under Solon’s new social classing system, who were the poorest (unpropertied) Athenian citizens, and also the majority?
only the pentakosiomedimnoi
Which of Solon’s social classes were eligible for archonship?
ALL four classes
Which of Solon’s social classes were considered politically equal in the Assembly?
pentakosmiomedimnoi, hippeis, jeugitai (ONLY EXCLUDED THETAI)
Which of Solon’s social classes comprised the hoplites?
demos
The heliaia was a new court system instituted by Solon that was presided over by the ___
right of any citizen to prosecute on behalf of a victim
What was special about Solon’s court system?
aristocratic factionalism
What societal condition after Solon ceded power allowed the tyrant Pisistratus to rise?
nine
number of annual archons in Athens
hoplites
Pisistratus exploited his popularity among which class to seize power during a struggle between two other aristocratic groups?
Pisistratus
Which Athenian leader was the first to impose an income tax?
Pisistratus
Which Athenian leader established naturalization processes?
Pisistratus
Which Athenian leader extended foreign policy to Salamis and the Hellespont?
festivals like the Dionysia
support for the arts
temples and shrines on the Acropolis
political center in the agora
urban infrastructure
How did Hippias and Hipparchos, the successors to the tyrant Pisistratus, create representative symbols of their rule?
Cleisthenes
Athenian leader who reorganized the city’s political structure by even multiples of 10
10
Number of Athenian tribes under Cleisthenes
10
Number of Athenian strategoi (military generals) under Cleisthenes
500; 50
How many citizens comprised the Council which set the agenda for the Athenian assembly? How many from each tribe?
by lot
How were Athenian citizens appointed to the Assembly?
Council of 500
Every Athenian citizen was elected to which political institution at least once in his life?
“mix up” the Athenians to promote political participation
creation of new military & economic units that escape the control of the aristocracy
Why did Cleisthenes establish the ten tribes of Athens?
Sparta
What city-state did Isagoras call on to aid him in ousting Cleisthenes from popular rule?
murder of Cylon’s partisans at the refuge of Athena
Why was the Alcmeonid family considered cursed?
not abolished, but power was divided among new positions
What happened to the old Athenian magistracies after Cleisthenes’ reforms?
the deme
Under Cleisthenes, personal identification by what sociopolitical grouping bestowed Athenian citizenship?
Cyrus the Great
Greek cities of Ionia passed to Persian control under which Persian leader?
Greek tyrants
Who did Cyrus appoint to rule Persian-controlled Greek cities?
Herodotus
From which writer do we get the majority of our information about the Persian Wars?
Aristagoras allied with the satrap Artaphernes to capture Naxos, but failed → fear for his life
Why does Aristagoras, tyrant of Miletus, call the Ionians to revolt against the Persians in 499 BCE?
equal rights to all citizens
What does it mean for ισονομια (isonomia) to be declared, as it was by Aristagoras at Miletus?
Ionian Revolt (499-494 BCE)
During what event do Greek cities expel their Persian-appointed tyrants?
Athens
Which city-state helps the Miletians during the Ionian Revolt by contributing twenty triremes?
entire Ionian fleet defeated
Miletus destroyed
satrapies reorganized by Mardonius and Artaphernes
What was the outcome of the naval Battle of Lade (494 BCE)?
Independent Greek city-states on the mainland kept Persian rule in Ionia unsteady
What was the main motivation of Persia to expand control into Greece?
Mardonius
What Persian commander led campaigns to retake Macedonia and Thrace after the Ionian Revolt?
(fleet was destroyed by a storm)
earth and water
What did the Persians ask Sparta for in 491 BCE, a request taken by the kings as an insult?
aristocracy
Among what Greek social class was there most sympathy for Persian rule?
Battle of Marathon
battle between ten thousand Athenians and Plataeans led by Militades against twenty thousand invading Persians led by Datis
Militiades
general who led the Athenians and Plataeans against the Persians at the Battle of Marathon
Sparta
Which city-state was conspicuously absent from the Battle of Marathon?
phalanx
What military development allowed the Athenians and Plataeans to achieve victory in the Battle of Marathon?
Battle of Marathon
(marathonomachoi = heroes of Marathon)
From which battle did a new cohort of Greek heroes arise in the esteem of the common people?
jeugitai (third class — small-scale farmers)
Which of Solon’s Athenian classes was elevated in esteem because of their participation in the Battle of Marathon?
cultural importance of Battle of Marathon
(epigram named him a marathonomachoi rather than a poet)
What is signified by Aeschylus’ tombstone not mentioning his success as a tragic poet?
success of phalanx at Battle of Marathon
What Athenian event caused an ego boost to the collective lower classes that contributed to the later ostracisms of any leader who failed them in battle?
fleet of ships
What is the “wooden wall” that would save Athens, according to the Pythia?
Themistocles
leader (successor to Miltiades) who turned Athens into a major naval power
thetai
Which of the Solonian classes acted as the sailors of the Athenian fleet?
Sparta
Which city-state led the first Panhellenic alliance against Persia?
Battle of Thermopylae
battle of 6,000 Spartan hoplites led by Leonidas against over 100,000 Persians
Ephialtes
name of the traitor who exposed the path of Thermopylae to the Persians
delay the Persians long enough for the Greek fleet to win the battle at Artemision
What was the strategic aim of the Spartan hoplites at the Battle of Thermopylae?
Battle of Salamis
In what battle was Athens abandoned by its people to be sacked by the Persians?
Battle of Plataea (479 BCE)
What battle signified the end of the defensive war with Persia?
Pausanias
Which Spartan general defeated Mardonius’ army in the Battle of Plataea?
end of the Persian Wars
“We the Greeks have common blood and speech, and the shrines of gods and sacrifices.”
This quote demonstrating common Greek identity followed what major historical event?
the fifty years between the end of the Persian Wars (479 BCE) and the start of the Peloponnesian War (431 BCE)
The pentekontaetia refers to…
Sparta’s delicate internal structure prevented them from traveling that far from the Peloponnese
Why did Sparta reject the Ionian Greek cities from the panhellenic alliance?
Sparta
Continued battles with Persia after Xerxes retreated to Asia implies aggressive action by the Aegean fleet, against the wishes of what city-state?
Athens built the long walls around Piraeus
Themistocles thwarts Sparta’s proposal to expel neutral states from the Delphic Amphictyony
Spartan war-leader Pausanias recalled from Byzantium after accusations of despotic behavior
Describe the events which caused political tensions between Athens and Sparta after the end of the Persian Wars.
Dorcis, commander to replace Pausanias, was rejected by the Aegean confederacy
What was the excuse for Sparta to officially pull out of the “war” against Persia (after Xerxes pulls back to Asia)?
Herodotus: accusations against Pausanias were a pretext for Athens to seize power
Thucydides: Ionians asked Athens for help against Pausanias, and Sparta entrusted the war to Athens as its ally
Aristotle: Athens “gained the supremacy of the sea against the will of the Lacedaemonians”
Diodorus: most of the Spartans wanted to challenge Athenian power, but the gerousia and the people were convinced to leave it be since Spartans couldn’t man their own fleet
Different historical perspectives on the accusations of despotism against Pausanias and Sparta’s ensuing withdrawal from the war
ships or money
Under the Delian League, Athenian treasurers collected tribute in what two forms?
occupation of Skyros & forced annexation of Karystos
After Athens successfully expelled Persia from the Aegean, what two actions first garnered the disapproval of their allies?
suppression of rebellions at Naxos and Thasos (allies were kept in the League under threat of being besieged by Athens)
pivotal moment in determining the nature of Athenian hegemony following the Persian Wars
first city to be “enslaved” by Athens
In the words of Thucydides, what was the particular significance of Athens’ suppression of Naxos?
helot revolt; Athens
Sparta promised to help Thasos against Athens by invading Attica (~460 BCE). What stopped them from doing so? Who did they turn to for help with this problem?
fear of revolutionary spirit of democracy
Why did Sparta reject Athens’ help with the helot revolt, just after asking for that help?