18. Marketing, society, sustainability and ethics
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Framing
Trying to change the way we show things to convince customers of something
Commodity fetishism
Society is overly dominated by consumption due to capitalism
Sustainable marketing (3 E’s)
Ecological
Marketing should not negatively impact the environment
Equitable
Marketing should not promote unethical practices
Economic
Marketing should encourage long-term economic development

Material recovery
Materials going from the end consumer back to the company
Collaborative consumption
Sharing economy: No ownership, but able to lease something
Ex. Uber, Airbnb…
They don’t own the car or building, but they make an app to share, swap or rent possessions
Relies on Peer-to-peer network (P2P)
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
= A company’s commitment to act ethically and responsibly towards society, the environment, and its stakeholders
Environmental responsibility
Social responsibility—Encourage diversity, support local companies…
Economic responsibility
Ethical responsibility—Be fair, eliminate forms of corruption…
Stakeholder marketing
Create value for any stakeholder (not just shareholders)
Reduce negative impact & generate positive outcomes

Ethics
= The branch of knowledge that deals with moral principles
Deontological
Importance of rules
Ensure customer satisfaction via finished offering + ensure honesty in how the offering was produced & marketed
Teleological
Focus on consequences of actions
Managerial egoism
Focus on maximizing shareholder value
Utilitarianism
The greatest good for the greatest number of people
Maximizing benefits for the largest possible population
Virtue ethics
Honesty, bravery, generosity…
Good character
Ethical decision-making process
Individual factors
Knowledge—Awareness of the ethics of the activities
Values—Norms about rights and wrongs
Attitudes—Feelings toward certain behavior
Intentions—What people are planning to do
Ethical issue or dilemma
Significant others
Differential association—Learn behavior by observing those around us
Role set configuration—Behave in a specific position
Opportunity
Be ethical
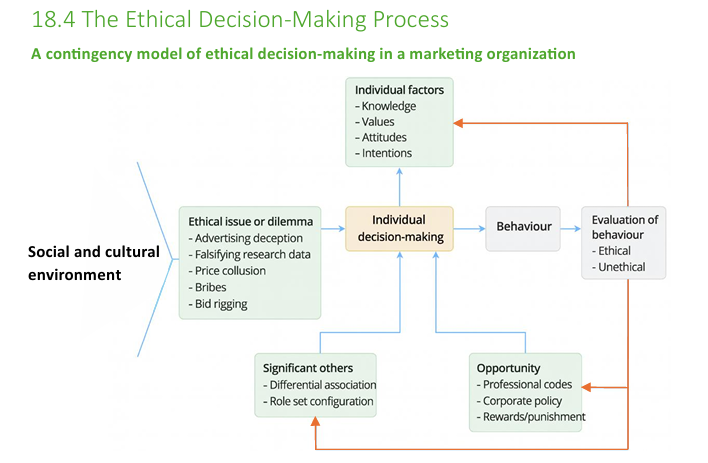
Ethical issues or dilemmas
Advertising deception
Intentionally deceiving the clients through fake advertising
Product in ad ≠ Product in-store
Falsifying research data
Changing and misreporting data or results
Price collusion
When competing companies conspire to fix/raise/stabilize prices instead of competing fairly
Leads to unfairness, prices will be way higher
Free competition → Leads to the best prices for customers, more innovation…
Bribes
Offering something of value in return for people’s behavior to your advantage
Bid rigging
Agreeing in advance who will win a bid
Use of shock appeals
Create controversy
Capture attention → More likely to be remembered
Evoke emotions
Ex. Anti-smoking campaigns, anti-drunk-driving ads, DV awareness…
Product labeling
Greenwashing
Promoting products as sustainable or ethical, but they’re false claims
Health misrepresentation
Health claims on the packaging, but the other ingredients are not healthy
Ex: “Low in fat”, but doesn’t mention it’s high in sugar