Chemistry Chapter 1 "The particulate nature of matter"
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Book: https://dl.ibdocs.re/IB%20BOOKS/Group%204%20-%20Sciences/Chemistry/CAMBRIDGE/Chemistry%20-%20Steve%20Owen%20-%20Third%20Edition%20-%20Cambridge%202023.pdf
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Element
Pure and chemical substance that consists of only one type of atoms and can’t be broken down into a simpler substance
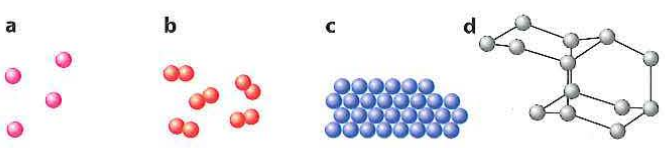
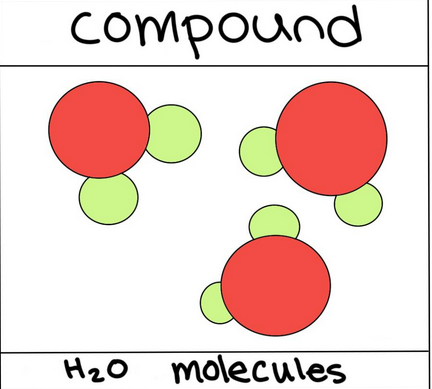
Compound
Pure substance formed when 2 or more elements bond chemically
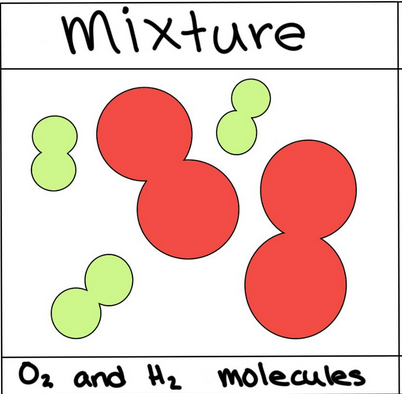
Mixture
Physical combinations of two or more substanced (elements or compounds) that are not chemically bonded
Homogeneous mixtures
Mixture that possess the same composition (phase) throughout the mixture
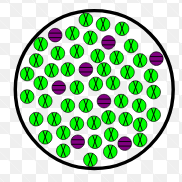
Heterogeneous mixture
Mixture that does not possess the same composition (phase) throughout the mixture
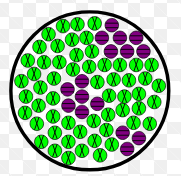
Examples of homogeneous mixtures
Rain, wine, steel, air, etc
Examples of heterogeneous mixtures
Salad, blood, cereal, ice in water
Chemical properties
How a substance behaves in a chemical reaction
Physical properties
All the other properties that a substance possesses besides chemically (Melting point, Odor, Color, Density)
Filtration
Separate insoluble liquid from solid or gas
Evaporation (Chemical process)
Remove solvent from the solution to leave the solute
Distillation
Separate solvent from solute
Solvation
Separate a mixture of two or more substances due to differences in solubility
Recrystallisation
Purify solids which contain relatively small amounts of impurities
The three (common) states of matter
Solid, Liquid, Gas

Typical traits of solids
Fixed volume, fixed shape, particles close together, regular arrangement, particles vibrate in fixed positions, strongest forces between particles

Typical traits of liquids
Fixed volume, no fixed shape, particles further apart, random arrangement, particles move around, weaker forces between particles

Typical traits of gases
No fixed volume, no fixed shape, particles far apart, random arrangement, particles move around in all directions, weakest forces between particles

0 degrees celcius in K
273.15 k
Absolute zero
0 k = -273.15 degrees celcius (lowest temperature possible)
Deposition
Gas to solid
Sublimation
Solid to Gas
Freezing
Liquid to Solid
Condensation
Gas to liquid
Melting
Solid to liquid
Evaporation
Liquid to Gas
Substances are solids if their temperature…
…below their melting point
Substances are liquids if their temperature…
…between their melting and boiling point
Substances are gases if their temperature is..
…above their boiling point
(s) (state symbol)
Solid
(g) (state symbol)
Gas
(l) (state symbol)
Liquid
(aq) (state symbol)
Aqueous (Dissolved in water)