Cell Structure - Elul
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Euchromatin vs. Heterochromatin Location in the nucleolus
Euchromatin - located more centrally in the nucleus
Heterochromatin - located more on the periphery
What is a Histone?
A group of 8 sub-units comprised of 4 different types of proteins, H2A-H2B, H3-H4.
DNA wraps around it to form a nucleosome
Chromatin
Contains DNA of the cell
Nucleosomes packed together (add scaffolding proteins and you can eventually get to chromosome structure)
Two types of chromatin
Euchromatin - loosely packed chromatin, transcriptionally active
Heterochromatin - highly condensed chromatin, transcriptionally inactive
Nucleus
Largest organelle of the cell, contains the genetic material (DNA) of the cell. Responsible for RNA synthesis in the nucleoplasm.
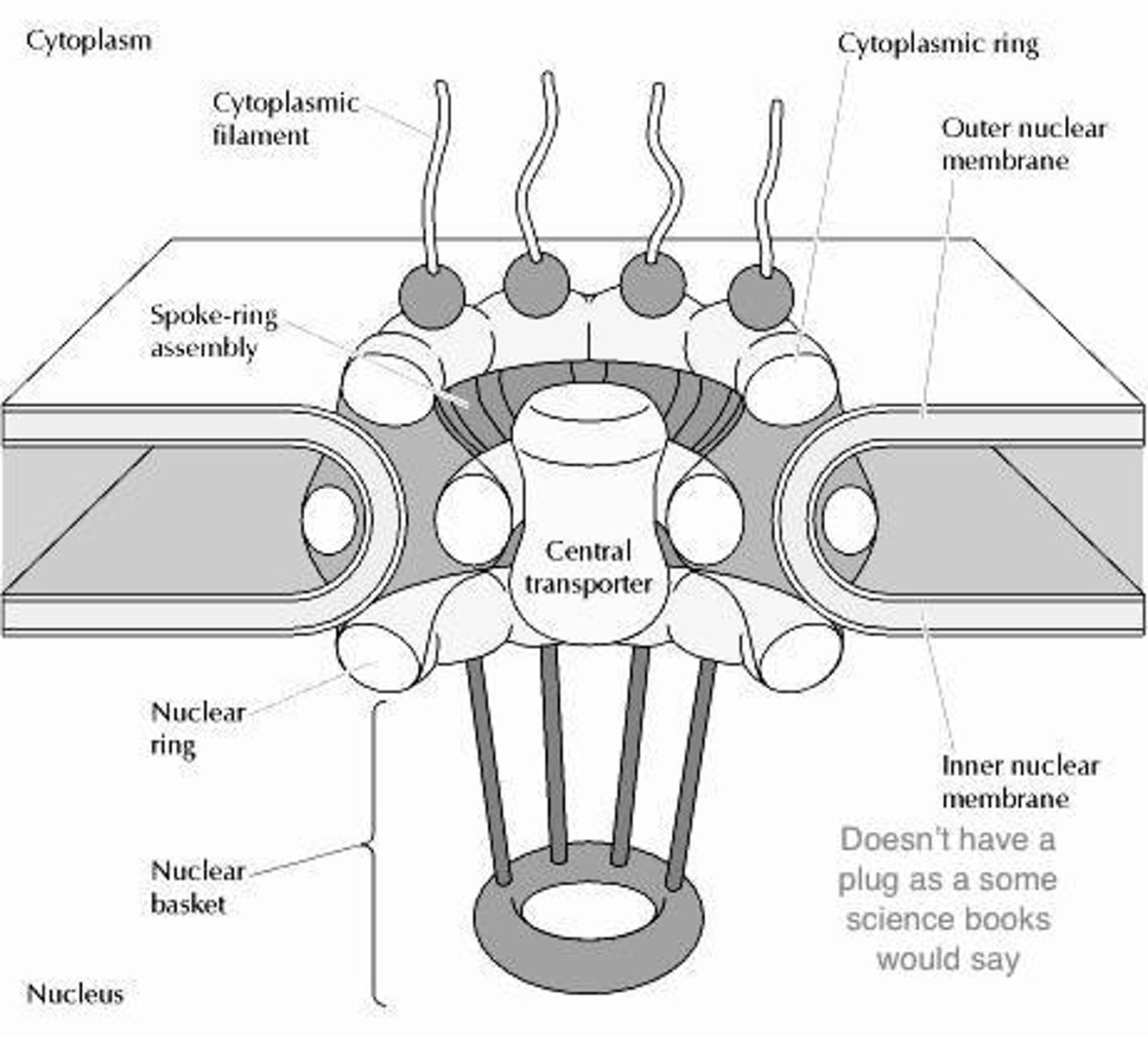
Nuclear Envelope
Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, nuclear pores throughout the membrane
Nuclear pore Function and structure
Pore that allows ribosomes and RNA to move to/from the cytoplasm
Need proteins importin and exportin to facilitate movement
**requires energy
Cytoplasmic Filament
Cytoplasmic ring
Nuclear Ring
Nuclear Basket
Nucleolus
Located within the nucleus (dark spots), site of ribosome/rRNA synthesis
**good histology marker ->shows which cells are actively synthesizing proteins
Nucleoli
Shown in neurons
Indicates high protein synthesis
Importin vs Exportin
-Work with the nuclear pore to facilitate movement.
-Exportins transport molecules from the nucleus to the cytoplasm(Ex. RNA).
-Importins transport molecules form the cytoplasm to the nucleus(Ex. Proteins)
Ribosome
-Composed of a large and small subunit, assembled in the nucleolus and then released into the cytoplasm -> then large and small sub-units come together
-Synthesize proteins from MRNA in the cytosol
Polyribosome (Polysome)
Many (2 or more) ribosomes translating the same strand of mRNA
If a protein is destined to be secreted or is a transmembrane protein the ribosome will associate with the...
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
**these proteins have a signal recognition particle (SRP) that is recognized ->bound to SRP Receptor
Exocytosis
Contents from a cell is released into the environment via vesicle
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Can be found throughout the cell but is in higher density around the nucleus.
Works with ribosomes (free and bound) in order to synthesize proteins to be secreted or intermembrane. Appears to be studded because of all of the ribosomes associated with the membrane
**if protein is to be;
-secreted -> Its secreted into the ER lumen
-transmembrane-> its inserted into the ER membrane
**RER->extensive system of interconnected tubules, cisternae and vesicles
Clinical Correlation: Cystic Fibrosis
Protein mutation causes mis-folding of a transmembrane chloride channel -> degraded before it makes in to the cell -> causes symptoms (salty sweat, dehydrated mucus)
Golgi Apparatus
-Located in-between the golgi and the plasma membrane.
-Modifies, sorts, and facilitates export of proteins synthesized in the Rough ER.
-Three levels of cisternae (Cis, Med, Trans)
-Transitional compartment ERGIC
-Proteins move through the organelle via vesicles (vesicle mediated transport)
Vesicles
Small circular membrane bound structure that can contain extracellular proteins
What are the protein coats(Names and when used)
-Mechanically facilitate budding
-COPII - ER to I
-COPI - within the golgi
-Clathrin - Trans-golgi -> Plasma membrane (regulated secretion, dock at the plasma membrane then fuse when signaled)
**uncoated vesicles from the trans-golgi (non-regulated secretion, have other final destinations)
Vesicle movement (In terms of membrane order, and which protein coat is used in-between)
ER->COPII->ERGIC->COPI->Cis-golgi->COPI->Med-golgi->COPI->Trans-golgi->Clathrin(Regulated)->Plasma Membrane
Endocytosis
A cell ingests macromolecules, matter, and other substances from the extracellular environment.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
ligand binds to a receptor, initiated endocytosis. The clathrin coat starts to assemble beneath the budding vesicle (intracellularly). Once the vesicle forms the vesicle loses the protein coat and then fuses with the Early Endosome
**vesicle has increased ligand concentration relative to the cell
Early Endosome
Located near the PM. (CURL) Compartment for Uncoupling Receptors and Ligands (ph 6) -> once uncoupled, receptor returns to pm in small vesicles. The Ligands are sent to the Late Endosome
Late Endosome
Located near the golgi complex. Contains ONLY material to be digested (so only ligands are sent here)
Lysosome
Cellular waste bin (pH of 5), digests and hydrolyzes molecules that were taken in by the cell, this is where ligands are completely digested into small diffusible molecules -> then transferred to cytosol to be used by the cell to exported.
**Contains many acid hydrolyses
Tay-Sachs Disease
Lysosomal disorder where lysosomes cannot digest proteins -> Undigested proteins begin to accumulate in the lysosome causing cells to swell ->cannot function properly
**diagnosed by red macula in retina
Mitochondria
Generates energy (ATP) and reactive oxygen, on the inner-membrane the ETC generates H+ and pumps it into the inter-membrane space, then H+ moves back into the matrix (down its concentration gradient) and this drives the production of ATP (by ATP Synthase)
Outer membrane contains porins with allow a passage was for most macromolecules
Inner membrane impermeable to many things ->cardiolipin (4 FA tails) -> facilitate H+ gradient
**more cristae->higher surface area->more ATP production
**mitochondria has its own DNA
Cytoskeleton
Systems of tubules and filaments that define shape, motility and cellular organization.
**Microtubules, Intermediate Filaments, Actin (localized differently)
Microtubules
Structural support. Located near nucleus.
Radiate out of the centrosome (microtubule organizing center), grow from pericentriolar fuzz to cell periphery.
13 protofilaments (Alpha/beta dimers) around lumen
+/- end (grows from + end)
**centrosome contains centrioles
**dynein and kinesin travel on microtubules
Actin
Cell motility. Located at cell periphery. 2 filaments that wrap around each other. +/- end, (+ end ATP bound (growing end), - end ADP and it is unstable (shrinking end))
Made up of g-actin
**can Interact with myosin(muscle myosin to generate movement)
Intermediate Filaments (+ major classes)
Mechanical Support to plasma membrane.
Ex. Keratin - Epithelial cells
Desmin - Muscle Fibers
Vimentin - Fibroblasts, Endothelial cells
Neurofilaments - Neurons
Nuclear lamins - Nuclear Envelope