Lecture 5 -- Spinal Cord and Segments
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are the functions of the spinal cord related to sensory and motor signals?
Pass signals from sensory receptors to the brain and from the brain to different parts of the body.
Give one example of a local reflex coordinated by the spinal cord.
Patellar Reflex
Does the spinal cord extend the entire length of the vertebral column?
The spinal cord doesn't extend the entire length of the vertebral column, finishing in the lumbar region in animals like dogs and cats.
What do the thickened regions (intumescences) of the spinal cord correlate to?
Forelimb and hindlimb function.
Where do the denticulate ligament originate and insert to? What is the role of the denticulate ligament?
Extension of pia mater that anchor the spinal cord to the dura mater
→ To stabilize the spinal cord within the vertebral canal.
Describe the external anatomy components: Intumescences, Conus Medullaris, and Cauda Equina.
Intumescences = Enlargements associated with the forelimb (= Cervical intumescence C6-T2) and hindlimb (Lumbosacral intumescence L4 -S3 in dogs/ L4-S5 in ruminants and horses)
Conus medullaris = Terminal end of the spinal cord
Cauda equina is the 'tail of horse' comprised of spinal nerves.
What are the 'horns' of the grey matter?
Dorsal, lateral, and ventral horns.
What are the regions of the white matter?
Fasciculi, funiculi.
What type of information feeds into the dorsal horn of the grey matter?
Sensory information input.
What type of information originates from the ventral horn of the grey matter?
Motor information output.
In what spinal cord segments is the lateral horn present?
Thoracolumbar segments → Contain cell bodies of sympathetic nervous system and interneurons
Describe the development of the spinal cord.
Step 1: In the early embryo, there are marginal layer on the outside; mantlel layer in the middle and ependymal layer on the inside, surrounding the neural canal
Step 2: As the embryo develops, the mantle layer separates out into an alar plates dorsally and basal plate ventrally
Step 3: Those plate then coalesce and join together → Mantle layer in the middle forms grey matter + marginal layer (outer) forms white matter → Neural canal shrinks down to form central canal
In spinal cord development, what do the mantle and marginal layers become?
Mantle Layer forms grey matter, Marginal layer forms white matter.
What are the components of a spinal cord segment?
Dorsal root/ramus and ventral root/ramus.
Describe the distribution of spinal cord segments.
At the level of C3 - T2, the spinal cord segments get shorter and shorter + The spinal nerves come out laterally at almost 90 degree
BUT as it move down wards, the spinal cord segment get longer and longer, the spinal nerves also get longer and emerge more caudally
At the end of the thoracic region, the spinal nerves come out at 90 degrees
At the lumbar region, spinal cord gets shorter and shorter and end at lumbar region → The remaining nerve continue travel down and leave their foramina of their respective spinal level = Cauda equina
How does the location of the spinal nerve relate to its corresponding vertebrae?
Spinal nerve exits in foramina cranial to the corresponding vertebrae up to C8. Caudal to C8, spinal nerve exits caudal to corresponding vertebrae.
How does the cauda equina form?
The vertebral column grows faster than the spinal cord in the foetal period, pulling the nerves with it, forming the cauda equina.
Define Conus Medullaris
Natural tapering of the spinal cord caudal to lumbosacral intumescence.
Define filum terminale
Fine filament of neural tissue (glial and ependymal cells)
→ Attached to the vertebrae caudally, holding the cord in position
Where do the vertebrae terminate in different species?
Canine: L6/ L7
Feline: L7
Bovine: S1
Equine: S2
What area does the Cervical (C1-C5) spinal cord segment serve?
Neck
What area does the Cervical intumescence (C6-T2) spinal cord segment serve?
Thoracic Limb
What area does the Thoracolumbar (T3-L3) spinal cord segment serve?
Thorax and abdomen
What area does the Lumbosacral intumescence (L4-S3) spinal cord segment serve?
Pelvic cavity, pelvic limb and perineum
What area does the Caudal (Cd1-Cd5) spinal cord segment serve?
Tail
What are intumescences?
Subtle enlargements of the spinal cord related to the thoracic and pelvic limbs.
What are the Brachial plexus and Lumbosacral plexus?
Brachial plexus (C5-T2)
Lumbosacral plexus (L4 -S3)
What is a dermatome?
Sensory area over the skin
Why white mater is white?
white matter consists of axon. These axons are surrounded by fatty substance = Myelin → Acts as electrical insulation
What are the ascending tract and descending track responsible for?
Ascending track: Sensory neuron, from skin and musculoskeletal system to cerebral cortex
Descending track: Motor nerve tracts from cerebral cortex to skeletal muscles
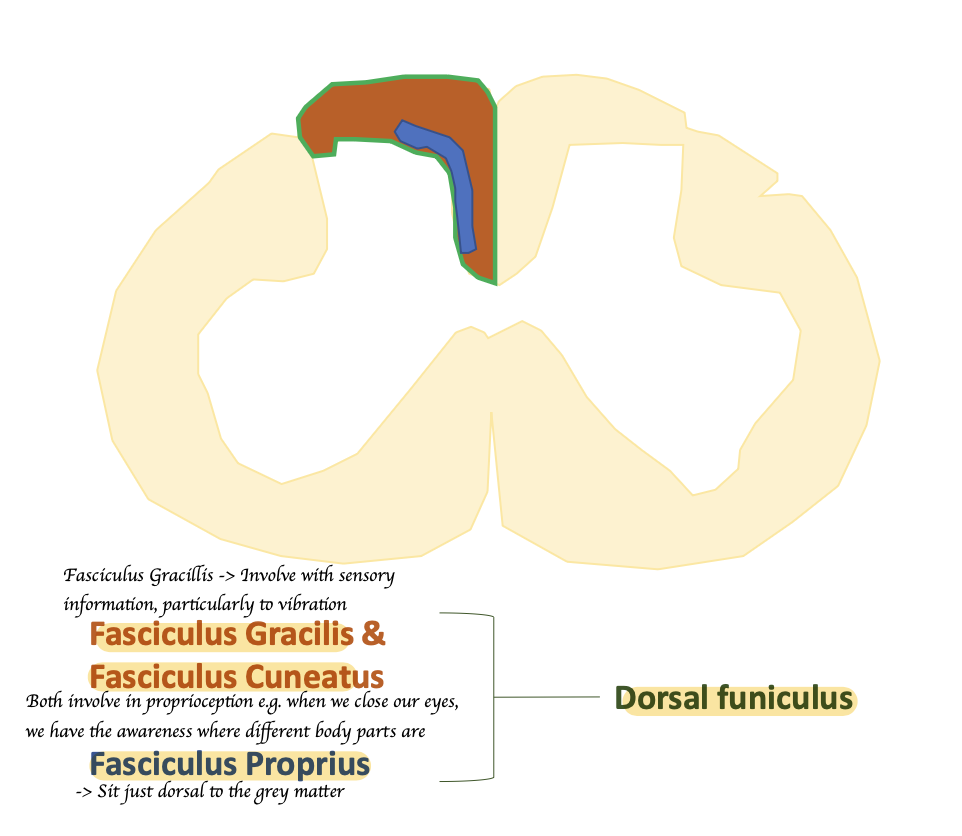
What is funiculus?
Funiculi = A region containing difference bundles of nerve fibres/ axons
→ Dorsal funiculus: Sensory tracts
→ Lateral funiculus: Sensory tracts + Rest mixed sensory and motor
→ Ventral funiculus: Mixed sensory and motor tract
What is fasciculus?
A bundle of the same anatomical nerve fibres that make a tract
= A funiculus contains multiple fascicle
What are included in the dorsal funiculus?
Fasciculus Gracilis + Fascicullus Cuneatus + Fasciculus Proprius