B1.2 Proteins
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
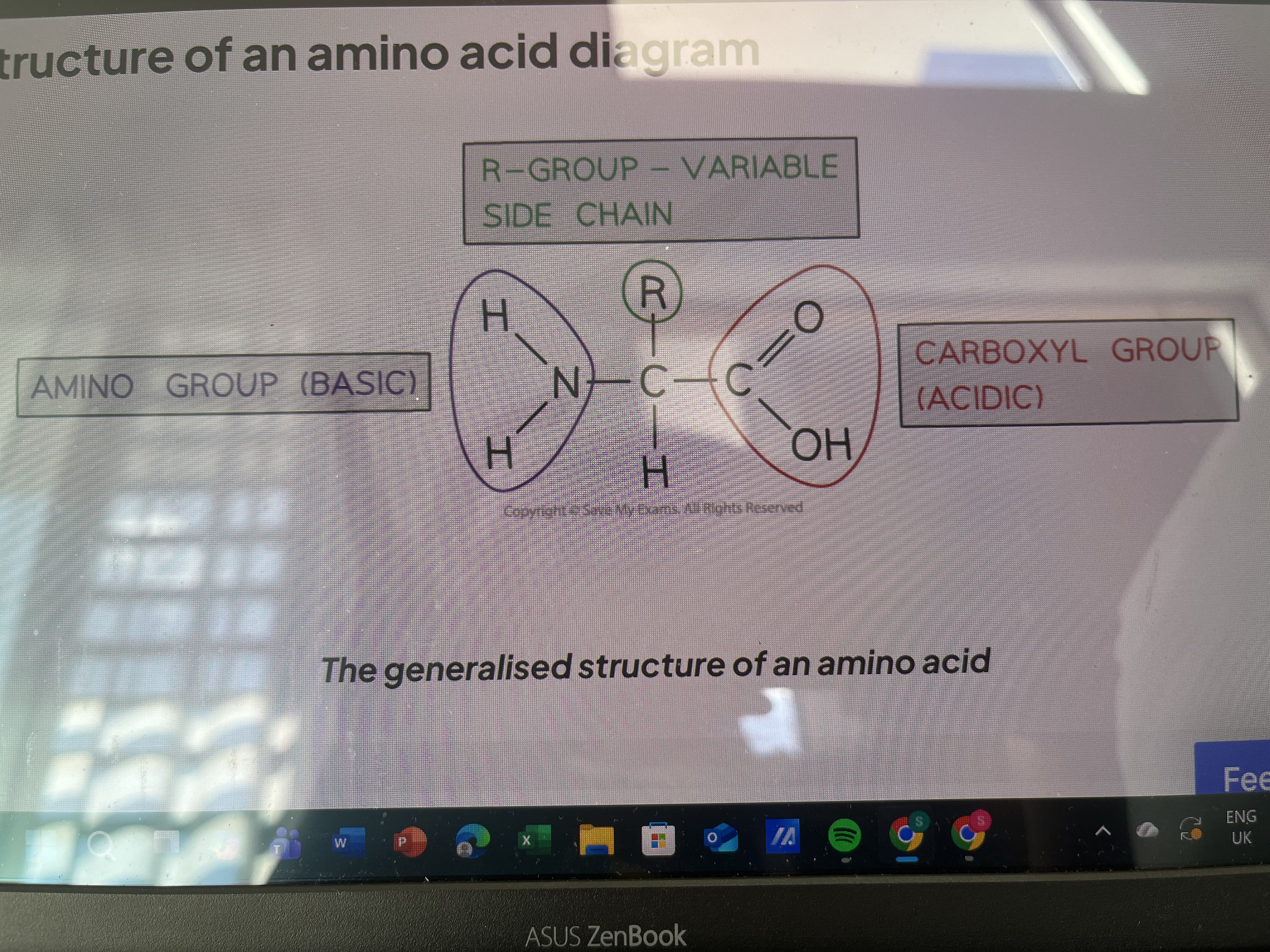
Structure of amino acid
Amino grp, R-grp, carboxyl grp
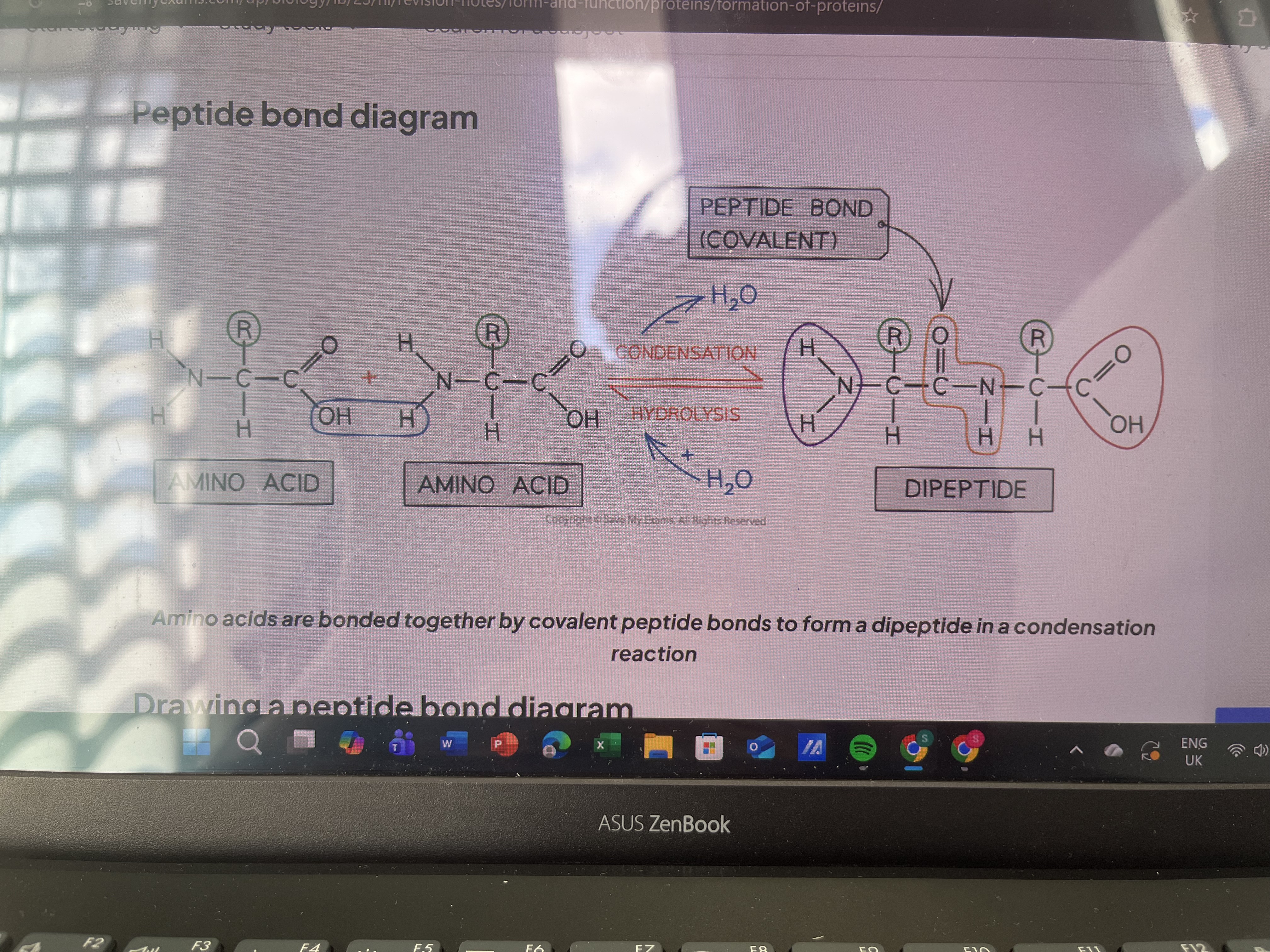
Peptide bond formation
What are non-essential amino acids
Amino acids that can be synthesized by our cells(11 amino acids)
What are essential amino acids
Amino acids that cannot be synthesized and are obtained from food(9 amino acids)
Why do vegans have to pay attention to their diets
Meat contains all 9 essential amino acids→vegan diet needs to be well balanced and ensured all essential amino acids
How many naturally occurring amino acids are there
20
Examples of polypeptides
Rubisco- enzyme catalyzing CO2 fixation from atmosphere during photosynthesis
Insulin(produced in pancreas)- absorbs glucose from blood
Immunoglobulin- antibodies(Y-shape)
Rhodopsin- pigment in retina of eye
Collagen- fibrous protein
Spider silk-spiders use it to suspend themselves
Haemoglobin
Keratin
Histones
What is denaturation
Irreversible change of protein conformation(bonds between R groups break easily)
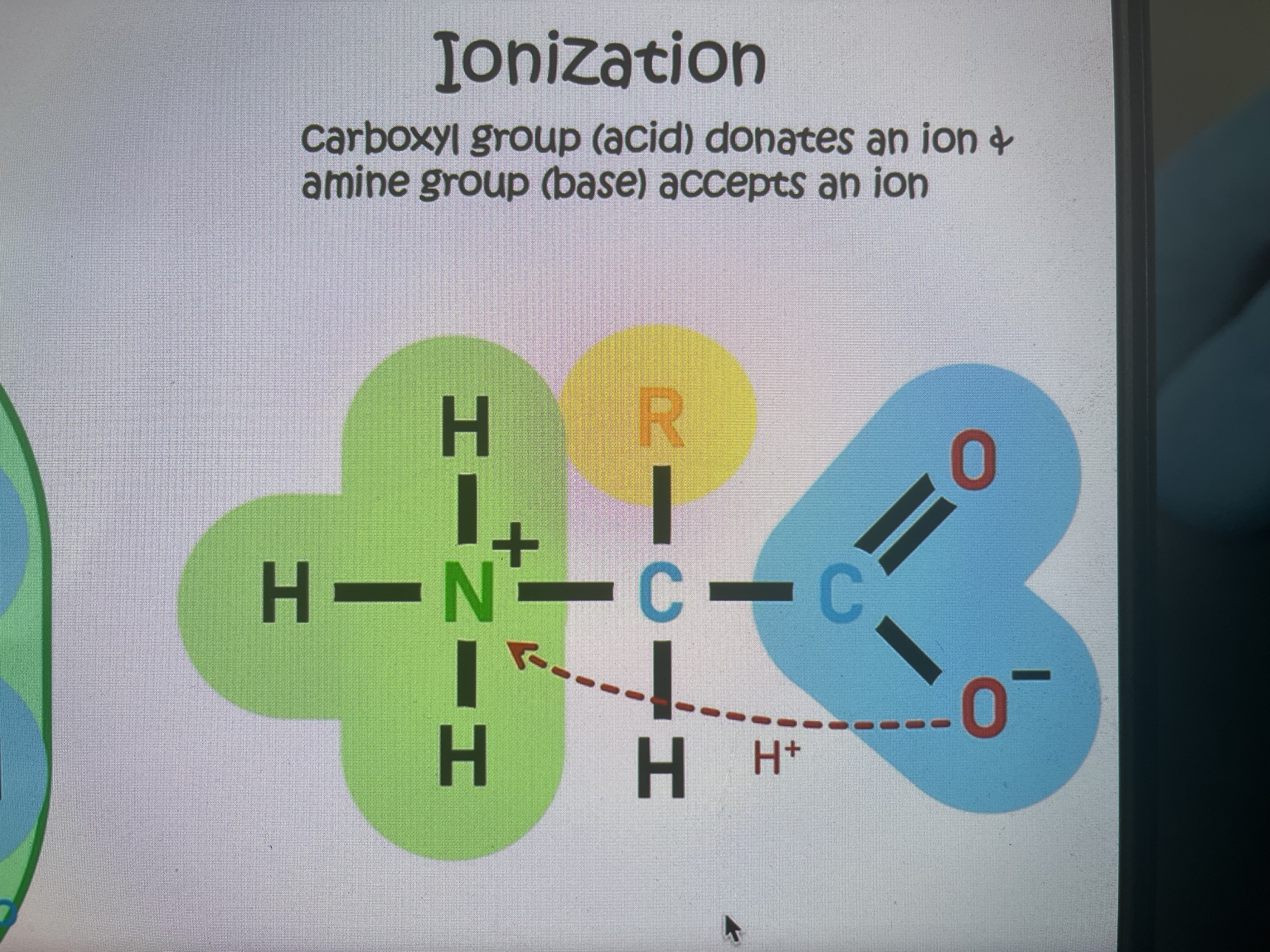
Ionized amino acid structure
Types of R-groups
(Hydrophobic)Non-polar: neutral charge(hydrocarbon)
(Hydrophilic)Polar: forms polar cov bond(partial charge)
Polar ionised: can form +ve(basic) or -ve (acidic)charge
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids(the DNA determines this)
The precise position of each amino acid determines 3D shape of protein
The same sequence always gives rise to same 3D shape→proteins have precise, predictable and repeatable structures
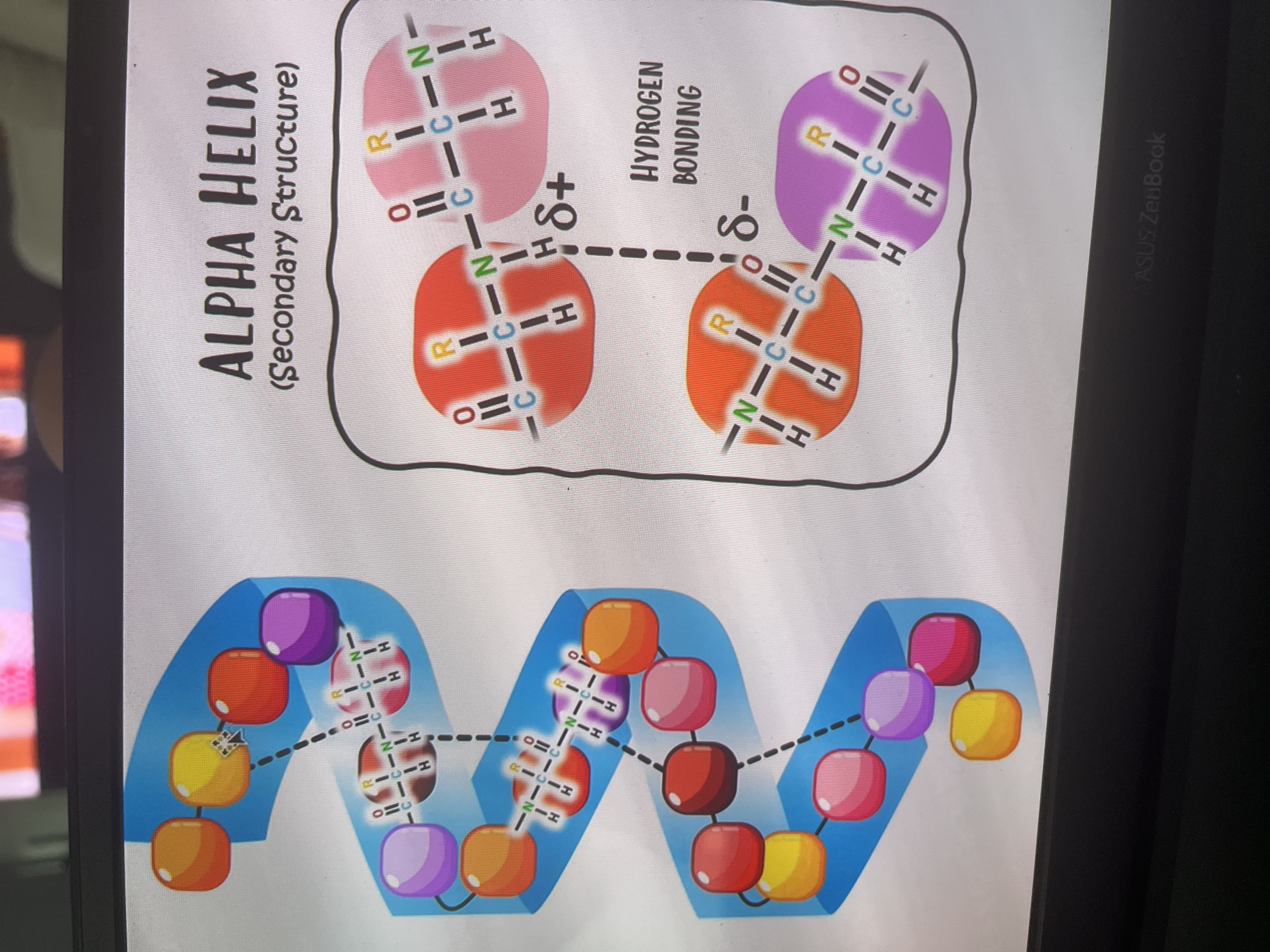
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
Forms due to pleating and coiling of amino acid chain
Held tg by weak H-bonds(betw non adjacent amino acids→N-H and C- -O))
Forms alpha helix and beta pleated sheets
What is the tertiary structure?
Complex 3D shape into which secondary structure folds(gives protein specific shape)
Folding occurs due to interactions betw R groups
Bonding involved in tertiary structures of protein
H-bond: betw polar R-groups(different from location of H-bonds in secondary structure)
Disulfide linkage(S-S): cov bonds betw cysteine amino acids
Hydrophobic interactions: betw non-polar R groups and water→fold intro interior of polypeptide to avoid h2o
Ionic bond: betw ionised R-grps(carboxyl grp can become -ve while amino grp becomes +ve through ionic bonding)
Solubility of proteins(with polar and non polar amino acids)
Forms globular structure:
Hydrophilic amino acids on the outside(interacting with water)
Hydrophobic amino acids clustered in the centre
Where are polar amino acids proteins found
Surface of membranes→interacts with water
Interior pores within membrane→creates hydrophilic channels for polar molecules to pass in n out of cell
On outside of enzymes so enzymes r soluble
Where r non-polar amino acids found
In regions of proteins that don’t interact with aqueous solutions
Integral proteins have regions with hydrophobic amino acids, helping them embed in membranes
What is the quartenary structure of a protein
Multiple polypeptide chains(subunits) functioning tg as one protein
Difference between conjugated and non-conjugated protein
Conjugated- contains non-protein components(prosthetic grps)
eg: Haemoglobin(4 subunits with prosthetic haem grp each that contains iron ion)
Non-conjugated- contains only amino acids
eg: insulin(2 polypeptide subunits joined by disulfide bridges) and collagen(fibrous protein, consists of 3 subunits tg in helix shape)
NOS: Cryogenic electron microscopy
Cryo-EM: involves rapid freezing of protein solutions, exposing them to many electrons to produce image(can be used to recreate 3D shape of proteins)
NOS: crystallography
Until recently, proteins had to be crystallized to reconstruct and visualise them with X-ray crystallography. Had issues such as:
Time consuming, works on single pitied protein only
Some proteins don’t crystallize
Structure visualised out of cellular environment, removing contextual info
Globular proteins
Spherical(non polar inside, polar outside)
Soluble therefore easily transported
Eg: insulin: consists of 2 polypeptide chains(polypeptide A has 21 aa residues, B has 30) held tg by 3 disulfide bridges
Fibrous protein
Long strands of polypeptide chains, has cross linkages due to H-bonds
Little or no tertiary structure
Large number of hydrophobic R-grps therefore insoluble
Contains highly repetitive sequence along with insoluble property→makes it strong n suitable for structure
Other than polarity, what other chemical property of amino acids vary due to charge?
Solubility(non-polar r neutral, polar r charged)