Intro to Global Health Exam Midterm
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Economic Approach
Expansive view
Usually measured by GDP
• Gross Domestic Product (GDP) = value of
goods and services produced and
consumed in a country (shows size of
economic activity)
• GDP per capita = GDP divided by
population
• Size of economy relative to
population
• GDP growth rate = percent change
• Shows how much economy is
expanding
• Problems with economic growth/GDP as
Development
In simple terms:
Development = economic growth, usually in terms of GDPent as economic
growth but it does not account for income distribution, environmental sustainability, or social well-being.
Poverty Alleviation Approach
But what is poverty?
• Absolute poverty = having less than
amount needed to survive (meet basic
needs for food, water, shelter)
Currently, the World Bank sets at
$2.15/day
Relative poverty = not having enough
to fully participate in society
How poverty is measured in
developed/wealthy countriesPoverty is about MORE than a lack of money
In simple terms:
Development = alleviating poverty and ensuring economic growth
reaches the poor
Amartya Sen
Development as
creating conditions
that allow people to
thriveConditions include
resources to meet
basic needs,
individual self-
esteem and dignity,
freedom of choice,
national autonomy
In simple terms
Increase in individual freedom to lead lives they value, ability to make choices and act on them (capability)
Seers and Goulet
Development as
increase in
individual freedoms
or the ability to lead
lives they value
Ability to make
choices and act
on themLow income doesn’t
necessarily mean
low capabilities
In simple terms:
Creating conditions that allow people to thrive, including meeting
basic needs, individual self-esteem, freedom of choice, national
autonomy
SDGs
UN-led efforts to set concrete goals and
timelines for multidimensional
development in wealthy and poor
countries
Sustainable Development Goals
(SDGs) start in 2015 supposed to
be met by 2030, include views of
developing countries, tackles
causes of underdevelopment
In simple terms
17 global goals to address poverty, inequality, education, ill health,
and environmental degradation
Sid Israel
Development =
progress that
increases level
and quality of
life
Expand income
and
employment
without
damaging
environment
Create
conditions to
sustain
In simple terms:
Progress that increases quality of life, expands employment and income without hurting environment
Barder
Development =
process of
creating social
change that
allows people
to achieve their
human
potential
It is political
because it’s
about power –
who can do
what to whom
In simple terms:
Improvements in wellbeing and capacity of political, economic,
and social systems to sustain it
SOAS
Development = improvements in wellbeing and capacity of political,
economic, and social systems
to sustain that
wellbeing\
• Wellbeing is
more than
incomeIn simple terms:
Bring about social change that allows people to achieve their
potential
Right to Development
Development = constant improvement of the population’s well-being based on participation
and fair distribution of
benefitsEconomic, social, cultural, and political the process
In simple terms:
Constant improvement in population's wellbeing based on
participation and fair distribution of benefits
Similarities between Development Definitions
Well-being as more than income
Provision of basic services
Freedom of choice
Long-term change
Differences between Development Definitions
What is most important – income, wellbeing,
sustainability, rights, equality, power
What needs to change – social systems,
economy, everything
Individual vs. population
End goal or constant improvement
Venezuela
Petro state – very dependent on oil for economy
Government controls and little investment in other areas
When oil prices plummet, Venezuela screwed
Wealthiest to poorest country in S. America within 2 years
Very high inflation
Political problems – dictatorships
Maduro is a functional dictator
Political unrest
Globally isolated, except for Russia and China
•• All services deteriorate
Haiti
Food insecurity – more than 40% of population
5.2 million need help with food and shelter, getting
worse
Poor infrastructure
Vulnerable to natural disasters
Hurricanes, earthquakes
•• Political instability
President was assassinated in 2021, and there has been no election since
Rise in violence and gang activity
More than half of people live in poverty
Lack of services and access to services long-term
problems
History of foreign intervention and abuse
Somalia
Political instability – civil war
Terrorist groups – Al Shabaab
Economic instability due to political issues
Natural disasters due to climate change
Drought → food insecurity, 700,000 people nearly starving
Floods afterwards also problematic, displacement, spreads disease
Poor infrastructure
Sanitation, water, health
Yemen
Active civil war since 2011
Government vs. Houthi
Political instability
Religious and cultural differences
2 different countries until 1991→ unrest
Foreign interference
Less aid to Yemen after COVID
Humanitarian crisisHumanitarian crisis
3 out of 4 people need aid
4 million displaced
High malnutrition → long-term consequences
2.5 million kids out of school
Afghanistan
US and NATO withdrawal → Taliban in power
Western aid cut → humanitarian crisis
Hunger, poverty, economic stagnation, very little money for government, food insecurity
Opium economy banned by Taliban
Makes crisis worse
Serious gender inequality under TalibanSerious gender inequality under Taliban
Infrastructure deteriorates without aidInfrastructure deteriorates without aid
War for 20 years also problem
Graveyard of Empires – lots of wars due to foreign interference
Papua New Guinea
Some economic growth, but lots of mismanagement of economy
Lack of infrastructure – health, education, sanitation, water
Causes lots of problems
Wellbeing issues
40% of the population is in poverty
Very high maternal and child death rate
Not much investment in improving well-being – a lack of skilled workers, underfunded health system
High rates of diabetes, TB, malaria
Really low literacy rates, but gendered
Violence
Domestic violence towards women and children
Discrimination against folks with disabilities
Police violence, ethnic violence
Political instability – electoral corruption, ethnic divisions
Moldova
Government corruption
Massive embezzlement scandal → no money to fund government services
Poor infrastructure, limited investment → health and sanitation
issues
Landlocked country, relies on agriculture
Not very remunerative
Affected by the war in Ukraine and COVID
High inflation, everything harder
Small population and high rates of immigration → small
workforce
Demographic crisis
Breakaway region → political unrest
Worse with Ukraine war because it’s backed by Russia
Common themes amongst “less” developed countries
Conflict and violence
Political Instability
Climate Change and Disasters
Economic Instability
Social Underinvestment
Foreign Interference
Inequality
Disparities between groups, denial of equivalent
enjoyment of rights, and/or arbitrary discrepancies in worth,
status and dignity
Some definitions of development require
equality in countries
Explicit: Right to Development, SDGs
Implicit: SOAS, Sen
Inequality makes development harder
Undermines prospects for long-term economic growth by keeping some groups from improving
Makes society more unstable by increasing tension
May violate human rights to equal treatment
Wealth vs Income
Income: The money you earn from your job
Wealth: is acquired through property, stocks, bocks
Wealth is much more easily distributed than income
Why?
Discrimination; certain generations
It is usually expensive to use income to invest in wealth
Enlightenment
Move away from tradition to a society ruled by reason
Reason
logic based on empirical
(observable) phenomenonValued progress and change
Saw religion as stagnant tradition,
valued secularismBelieved in equality for some people
West is Best
The West seen as more modern compared
to the rest of the world
West was where reason/light held most sway
“the Rest” were dominated by
tradition/darkness
So the Rest should be more like the West → development and modernization = Westernization
Thought achievements and trajectory of the
West were universal
Ignored cultural specificity of values and
beliefsIgnored contributions of other societies
Science
Many development projects still involve
using Western science and technology to
improve the Rest
Developers assume that science and
technology work same everywhere
Colonialism
Civilizing Mission
The Rest” were inferior and
needed to progress, be more like
West
West as more civilized and
reasoned, had duty to “improve”
other places even if by force
Colonizer Benefits
All colonization projects focused on
extracting profit for ruling country
Usually through exporting minerals or
agricultural products
Negative Legacies
All relied on violent conquest and threat
of violence to maintain power
All increased tensions within colonized
societies by creating winners and losers
Western values, practices, technology still seen as better
Missionary
Focusing on European and American Christian
missionaries working between 1600s and 1900s
LOTS of denominations sent missionaries
– Reached very remote places, often before colonial
officialsMissionaries worked alongside or in advance of
colonialism
Service Delivery
Many missions also provided
services to people around themPart of convincing people of
power of ChristianityAlso part of desire to help others
and live religions ideals
Biomedicine = healing system
based on scientific knowledge
Westernization
Mission schools taught “Western” cultural
norms along with academics
Required children to wear Western clothes and
learn colonizer’s languageMost focused on Euro-American history and
culture, some also celebrated colonization
Missionary societies sent people from
colonies to other countries for
seminary
One of few ways for colonized to access
higher education
Self-Sacrifice
Truman doctrine
Point Four introduced a new vision
Help other countries acquire the knowledge and technology to
improve incomes, agriculture, manufacturing
First 3 points reaffirmed commitments to supporting the UN, the Marshall Plan and NATO (a military alliance with non-communist Europe)
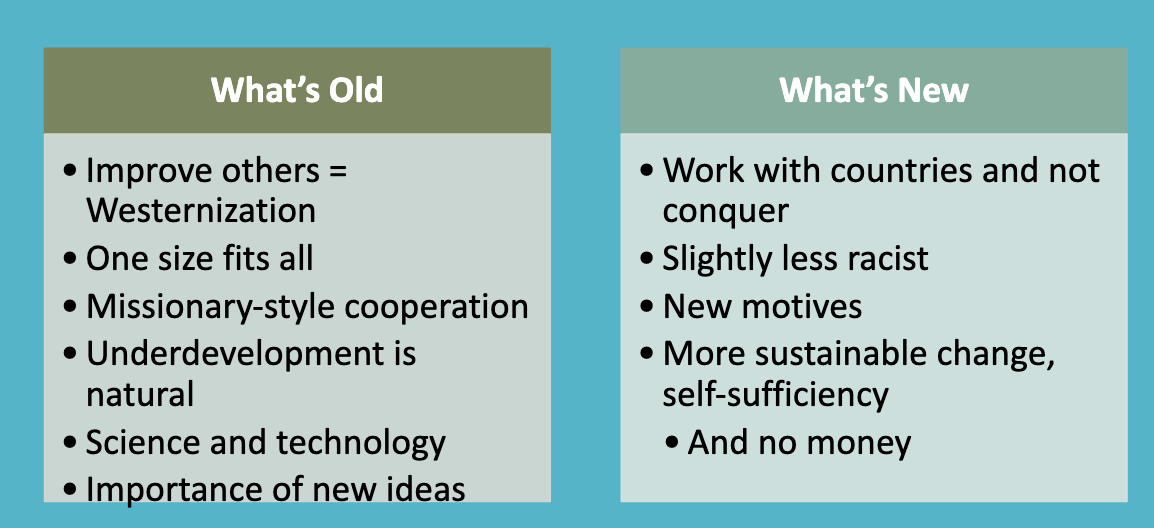
Underdevelopment
Countries that lack enough food, health, income, or
industry = underdeveloped, economically “backward”
Seen as natural state, not caused by colonialism or
Western economic growthLack of development is threat to peace
Development
Sharing technology and scientific knowledge from the
developed world to fix underdevelopment
No need to conquer and control countries to develop
them, can work collectively
Main aim of development = economic growth
does not acknowledge providing money
Marshall Plan
The plan to reconstruct Europe
Huge amount of resources and money
Major Development Institutions
United Nations
World Bank
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
United Nations
Help countries work together on a variety of things
Avoiding conflict
International laws
Human rights
Development
Sent groups of experts to advise
developing countries
Gave scholarships for technical training
to people from developing countries
Multilateral aid – aid funded by multiple
countries (member countries of UN)
Focuses on giving out loans
World Bank
Development
Created to help fund reconstruction in Europe
WB looking for new mission (Helping development countries )
Focuses on giving out loans
IMF
Stabilize the global economy
created to keep world economy stable after WWII
Both located in Washington, DC – new
center of global powerBoth get involved in development through
giving loans to developing countries (also
multilateral aid)
IMF looking to keep global economy
stable
National Development Agencies
Come along later
Government agencies that fund development projects in foreign countries
Composed of mostly western countries to help fund development
Bilateral aid – aid from one country to another
Overall idea of Major development Instit.
Nearly all development efforts until the 1980s were associated with the UN, WB, IMF or a national development agency in cooperation with developing country governments
Largely designing, implementing, and funding, development
(UN not so much with funding)
IMF and World Bank are considered sister
BOTH Focuses on giving out loans
Modernization
Developemnt = industrialization
All societies pass through five stages of growth based on what
happened in the WestMove from traditional agriculture to an industrialized consumer economy though technological advancement
Planned based on Western aid and help
Criticism of Mondernization Theory
Assumes everyone goes through same stages in same
order, but not true for all countriesDoesn’t fit experience of colonized countries – no longer traditional
Focused on economic growth, not population’s well-being
Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI)
To try to substitute domestic made goods for all imports (wanted to make their own stuff and not just buy it from the West
Government-supported expansion of manufacturing
Mostly done by former colonies wanting to be less dependent on “the West” for manufactured goods
Replace imported goods with locally made goods
Starts with easy to make goods like processed
food and clothing
Then durable consumer goods (appliances, cars)Then durable consumer goods (appliances, cars)
Large countries eventually made expensive, technologically complex goods like steel and airplanes
How do they pay for this though?
Domestic taxes
Private foreign investment
Technical assistance from the UN or Western
development agency
Exported- Oriented Industrialization
Government support of industrialization in certain industries
State or market discipline to ensure standards to keep
support met
Support policies change over time
Encouraged exports after industries established domestically
Industries became more internationally competitive so were
more likely to survive without support
Issues with EOI
Dependence on exports leaves countries
vulnerable to downturns in global markets
Asian Financial Crisis of 1997 slowed
economic growth and devalued currencies
across the region
Growth can’t last forever and sometimes
doesn’t pay to be economically prudent
Japan’s Lost Decade – growth slowed
dramatically from 1991-2001 because of drop
in property values and anti-inflation policies
Neoliberalism
Grow economy through competitive advantages and openness to
international markets