5 Cells: The Living Units II
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the main job of a cell when it divides?
To ensure that each of the two new cells receives a full, perfect copy of genetic material.
What can mistakes during DNA copying lead to?
Unhealthy or non-functional cells.
What are chromosomes made of?
DNA, the hereditary material.
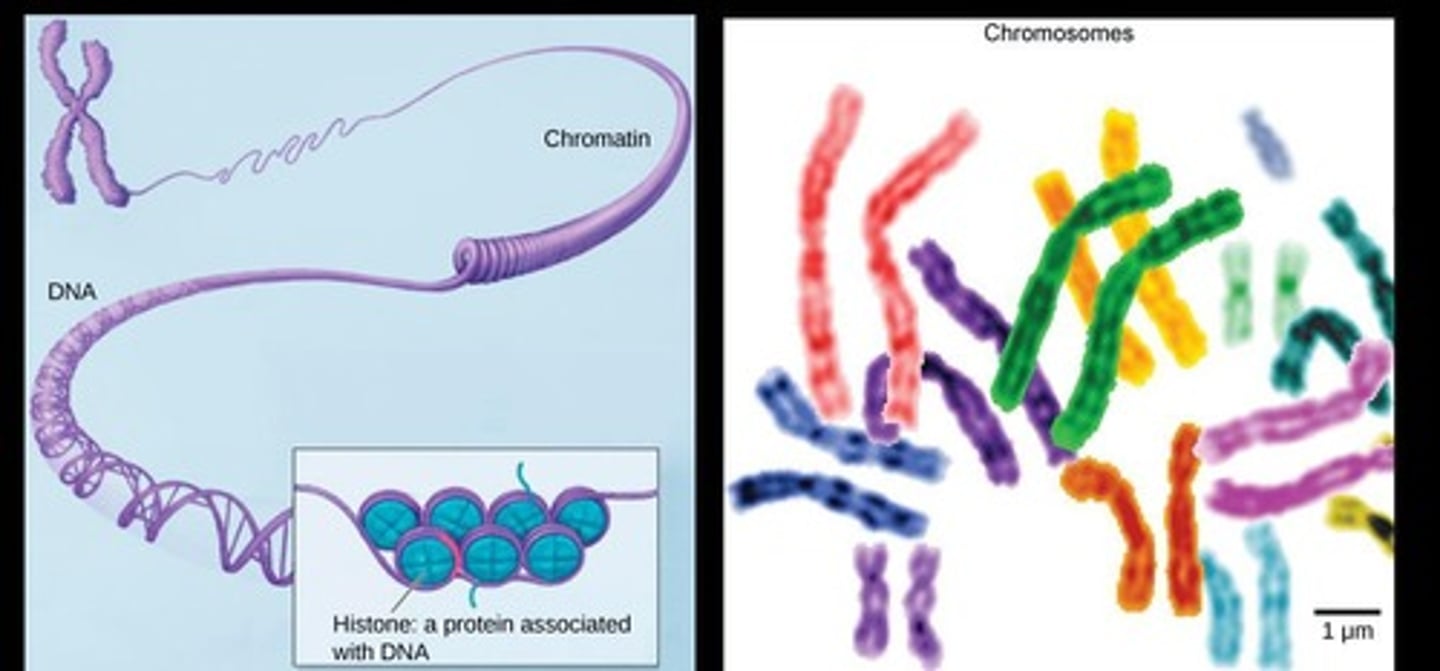
When are chromosomes visible?
Only when the cell is preparing to divide.
What is chromatin?
An unwound, jumbled bunch of threads that consist of DNA and proteins during the growth and maintenance phases.
What are the components of chromatin?
30% DNA, 60% histone proteins, and 10% RNA.
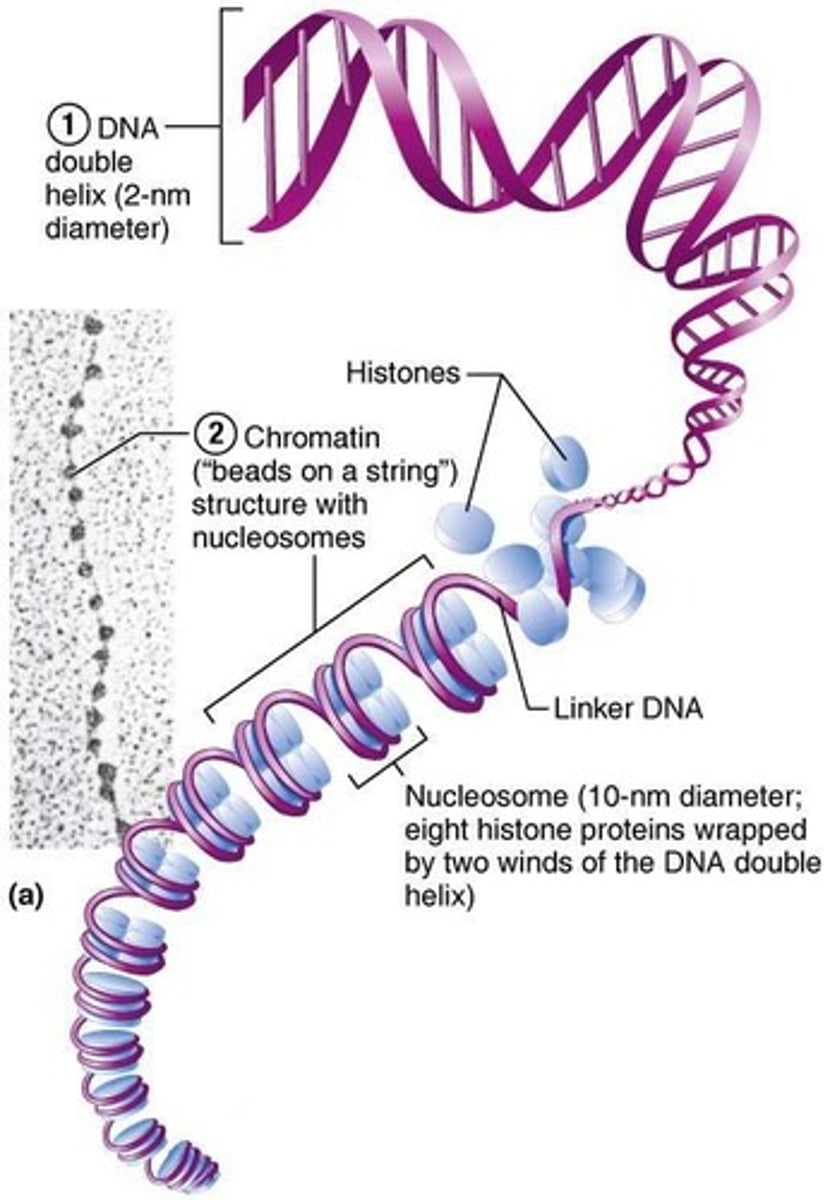
What is the fundamental unit of chromatin?
Nucleosomes, which consist of tightly packed clusters of 8 histones connected by DNA.
What is the purpose of histones in chromatin?
To keep the DNA compact and regulate its activity.
What happens to chromatin when a cell prepares to divide?
It coils and condenses to form chromosomes.
What is the cell cycle?
A series of changes a cell undergoes from formation until it reproduces.
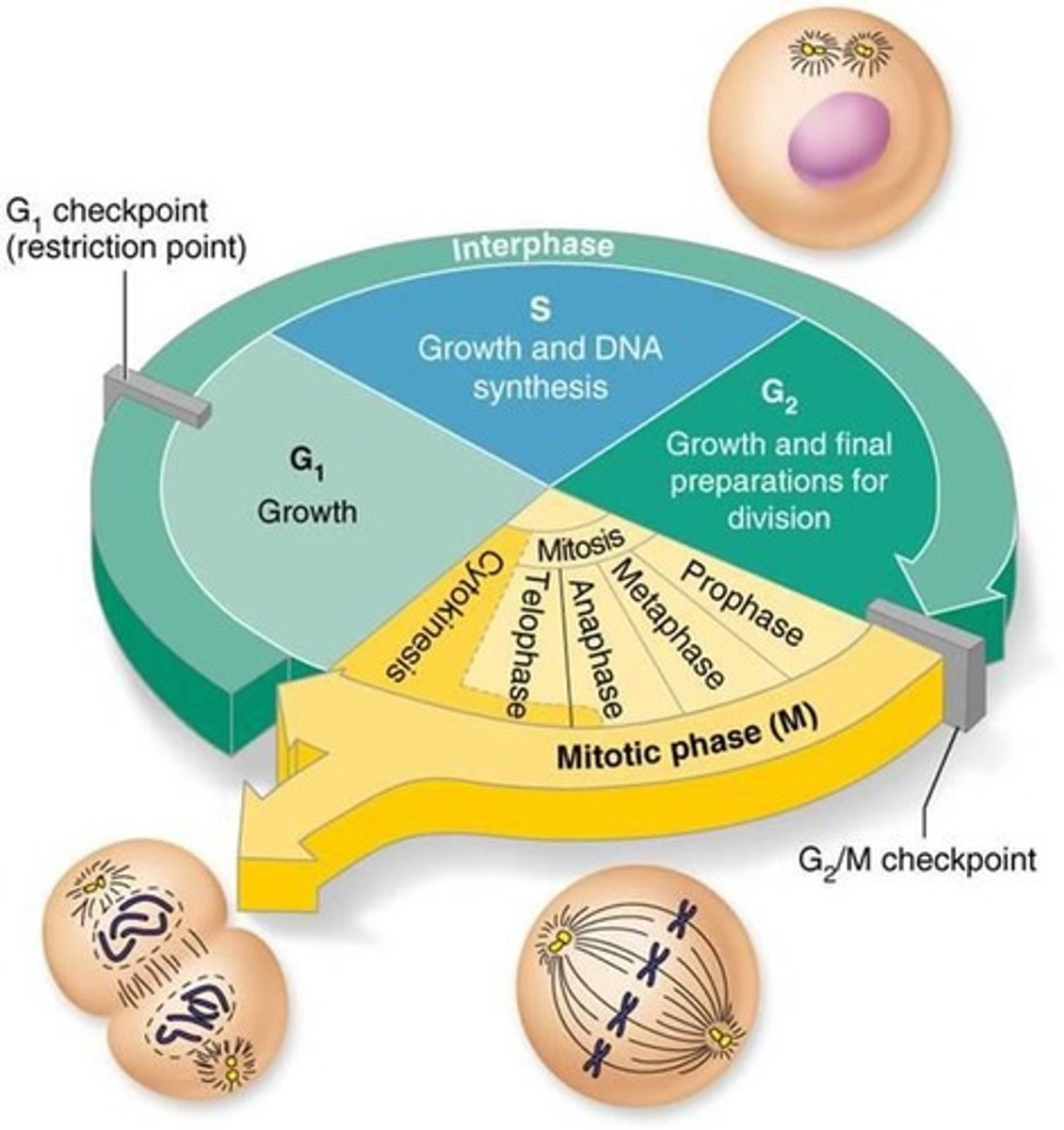
What are the two major periods of the cell cycle?
Interphase and the mitotic phase (cell division).
What occurs during interphase?
The cell grows, carries out routine activities, and prepares for division.
What are the three subphases of interphase?
G1 (gap 1), S (synthetic), and G2 (gap 2).
What occurs during the S phase of interphase?
DNA replication.
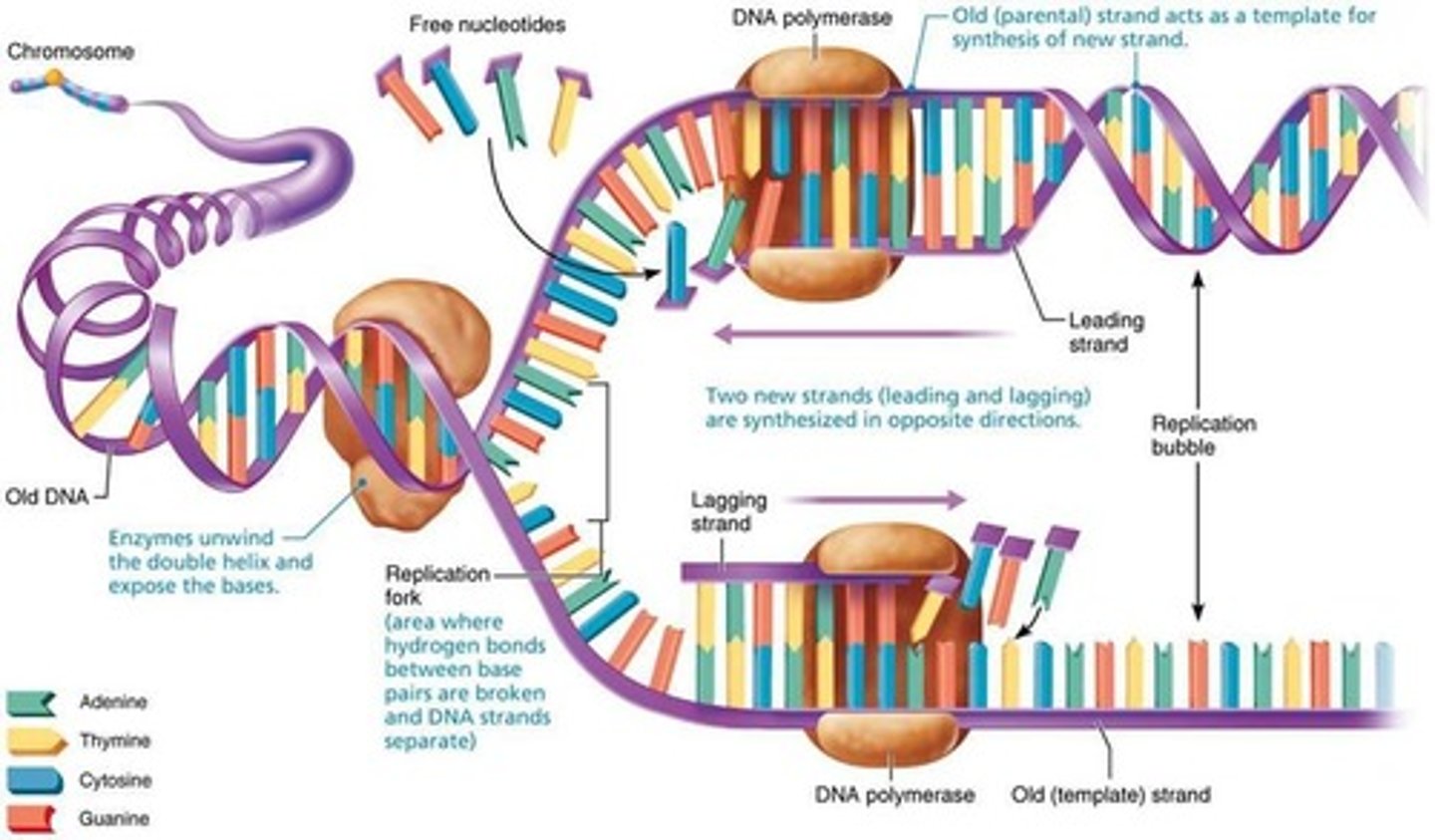
What is semiconservative replication?
A process where each new double-stranded DNA consists of one old strand and one new strand.
What are the two distinct events in the mitotic phase?
Mitosis and cytokinesis.
What is mitosis?
The division of the nucleus, distributing duplicated DNA to new daughter cells.
What are the four stages of mitosis?
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
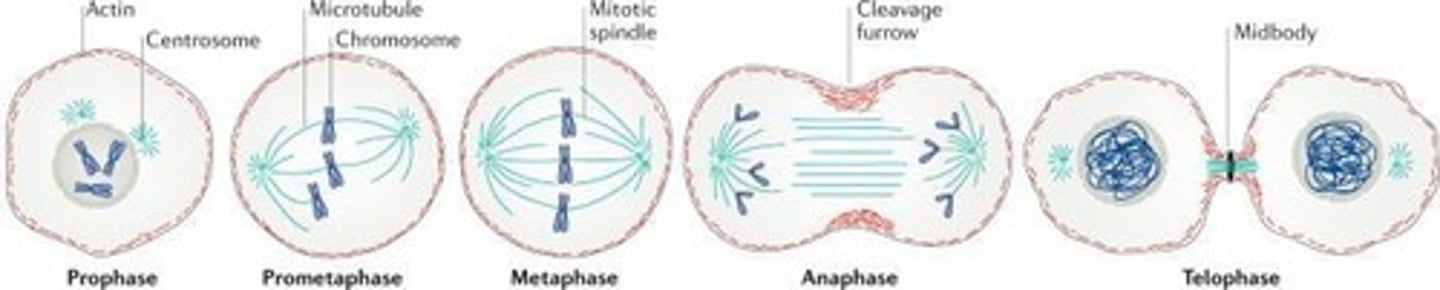
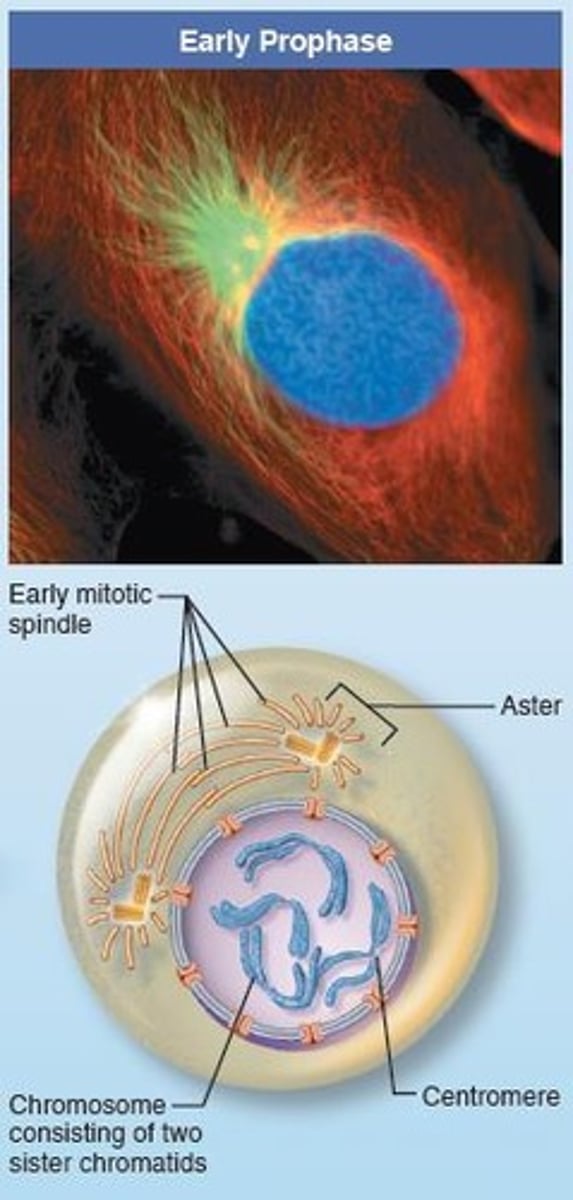
What happens during prophase?
Chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and microtubules begin to form the mitotic spindle.
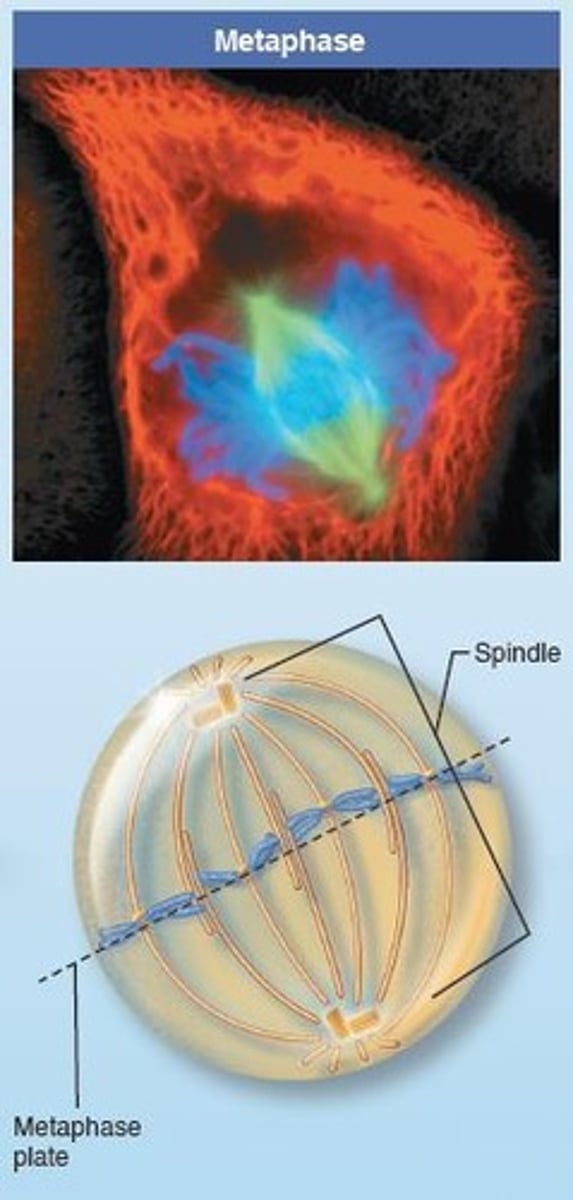
What is the metaphase plate?
The imaginary plane where centromeres of chromosomes align at the cell's equator during metaphase.
What occurs during anaphase?
Centromeres split, and sister chromatids are pulled toward opposite poles of the cell.

What happens during telophase?
Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin, new nuclear membranes form, and nucleoli reappear.
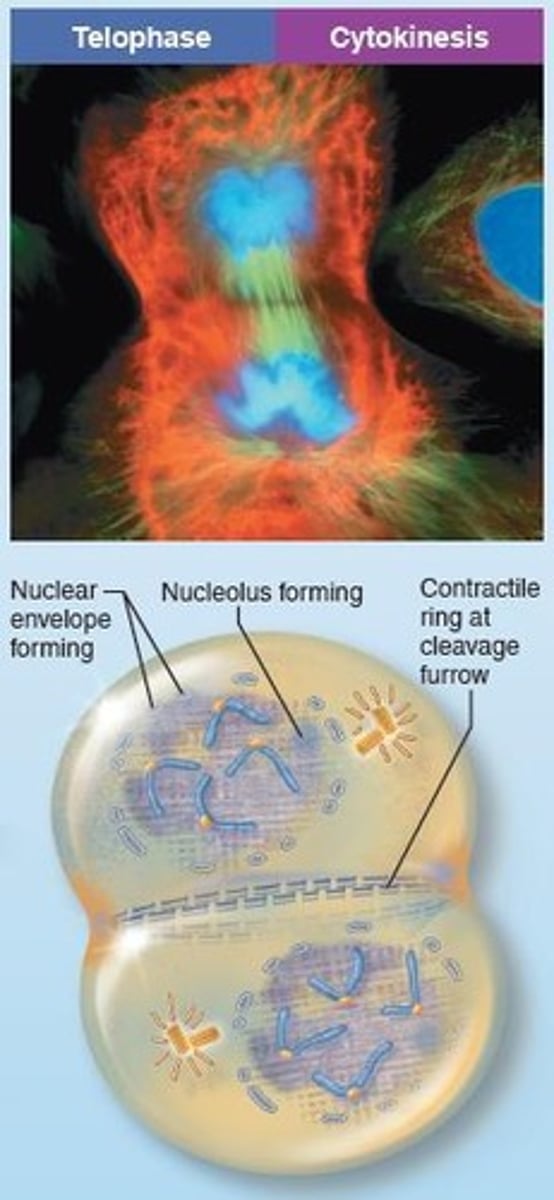
What is cytokinesis?
The actual division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two identical daughter cells.
What is the significance of DNA in cells?
It is the master blueprint for all protein synthesis, determining the chemical and physical nature of cells.
What is a gene?
A segment of DNA that carries instructions for creating one polypeptide chain (therefore protein).
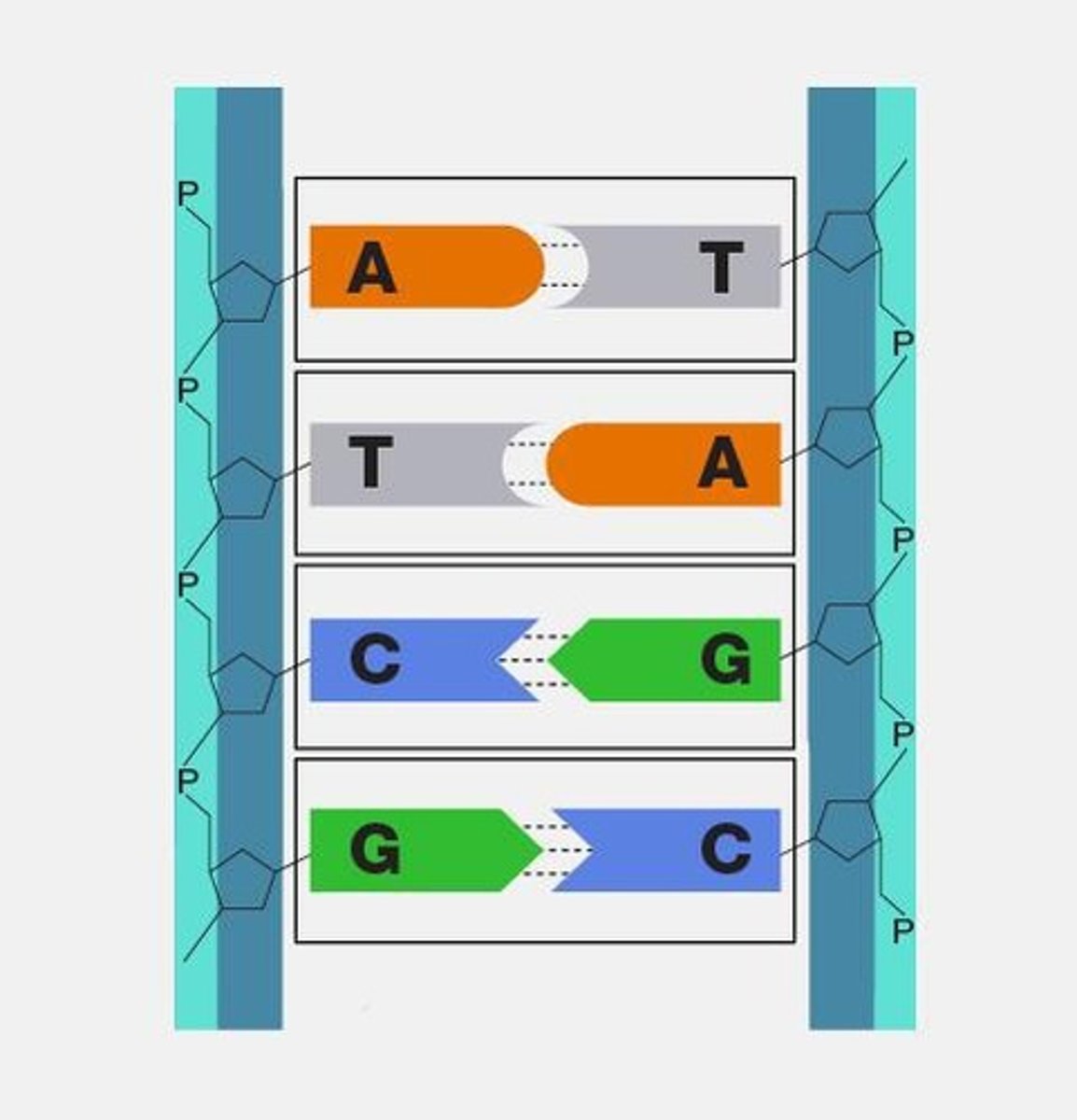
What accounts for the variation in possibilities of proteins?
The variation in the arrangement of nucleotide bases (A, T, C, G).