(BIO 386) Lec 11 - Lakes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Significance of lakes
Part of network of water connecting terrestrial environment and the sea
Can be thought of as large pools in the stream
Foci of processing because of long retention time
Locations of endemism
Lakes make up…
52% of the population
Societal roles of lakes
Resources
Drinking water
Food resources
Recreation
Hydrography
Water Storage
Flood control
Climate
Source of moisture
Landscape heat capacity
Lake chemistry reflects…
chemistry of sources waters
Degree of alteration of lake chemistry depends on
Biological activity (productivity)
Residences time
Three sources of water
1) Precipitation (rain, snow)
very dilute
usually acidic
affected by aerosols (sea spray, dust)
2) Overland flow (Rivers/streams, runoff)
Dissolved composition
Reflects geological material in watershed
Presence of wetlands in watershed
Depends on flow path to stream
Particle Loads
Amount depends on flow of stream and parent material
Position in river continuum may affect type of particles
3) Groundwater
Very few particles
High in dissolved substances
Products of slower weathering - depends on time
Depends on materials encountered along flow path
Closed Basin lakes
Lake with no outlet
Water evaporates, minerals stay behind
some lakes drainage lakes → closed lakes
response to climate change recorded in sediments
Types of closed basin lakes
1) Soda lakes - bicarbonates (minerals from weathering)
2) Saline lakes - chloride (minerals from precipitation)
Lake classification
Water color, reflects:
abundances of photosynthetic
inputs or organic matter from watershed
Physical structure - density stratification
Temperature change with depth
Effects of solutes on density
Seasonality of density
Wavelengths of sunlight are…
absorbed differently by pure water
Red light and UV are absorbed the most
Blue penetrates the furthest and is most commonly scattered back to eye, why clear water appears blue
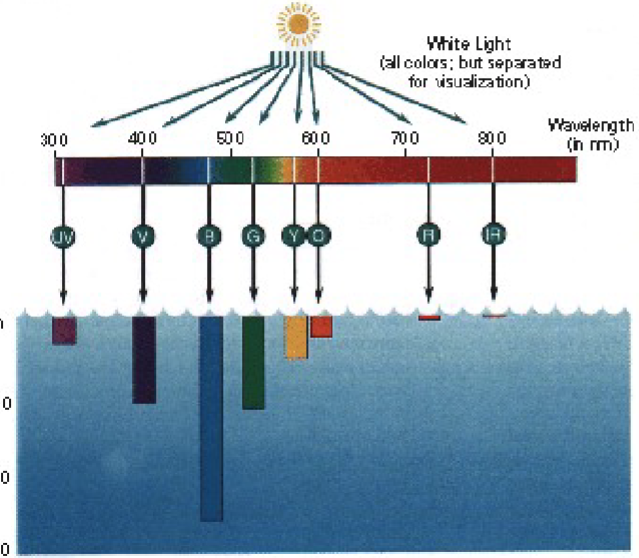
What is CDOM?
Colored dissolved organic matter
absorbs blue, reflects in yellow, green and red
looks brown
Algal biomass affects…
water clarity
Water always absorbs same light, but algae vary in abundance
transparency measures algal biomass
Water clarity lake types
Dystrophic (Brownness)
(Goes from blue to most green)
Oligotrophic
Mesotrophic
Eutrophic
Implications of light for lake structure
Light radiation absorbed by water, DOM or particles
This energy heats water
Heating occurs most in surface water
Water becomes lighter than deep water
The difference affects chemistry and biology
Temp and light declines exponentially with depth. This is stable stratification because…
warmer water is less dense than colder water
The effect of wind on lakes
Acts against buoyancy forces resulting from density differences related to temp.
Physical structure of deeper lakes
In deeper lakes, wing can only mix the surface to a certain depth. Erosion of the boundary is slowed by stronger buoyancy forces and the growing inertia of the surface mixed layer.
Resulting temperature zonation is…
Reversed in the summer and winter
Three layers of deeper lakes
1) Epilimnion
Warm, low-density, surface waters
2) Thermocline
Zone of rapid temperature change
3) Hypolimnion
Cold, high-density, deep water
Deep water and thermocline are isolated from atmosphere
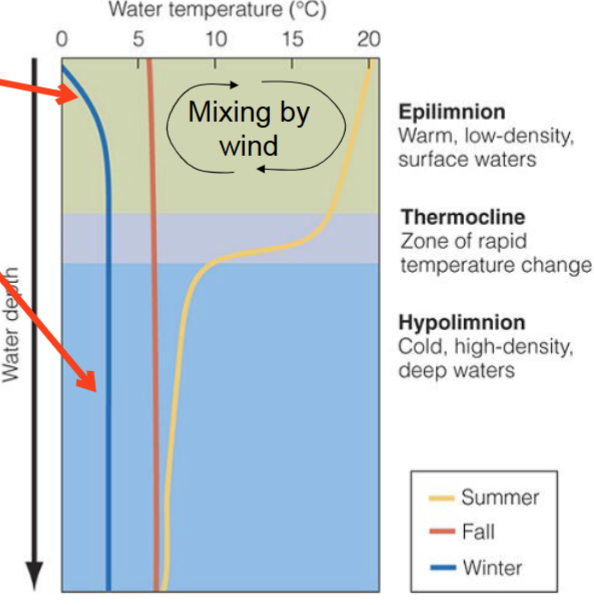
Density gradient prevents…
mixing of deep water with surface water
Primary producers
1) Macrophytes
Submerged in aquatic vegetation
In freshwater, usually higher plants
Much less structural tissue than on land
2) Phytoplankton
Free floating
Microscopic single celled plants
Can form colonies
Cyanobacteria (Phytoplankton)
Many fix N2
Can float due to gas vesicles
Can be toxic in freshwater
Methods for measuring production
Bottle incubations
Whole lake studies
Euphotic zone
Zone where light is great enough to support some photosynthesis
Compensation depth
The depth at where compensation light level is reached, where NPP = 0
Critical mixing depth
The mixing depth where NPP over a day = 0
Short term limitations of primary production
What the current plankton community needs now
Assessed by growth in bottles after nutrient addition
Long term limitations of primary production
What determines total ecosystem biomass
Ecosystem processes can alter nutrients in response to additions
Algal communities can change, altering needs
Assessed by
Accumulation of biomass in whole ecosystem experiments
comparisons between lakes
CO2 limiting ONLY short term
CO2 is removed by photosynthesis replenished
1) Carbonate buffer system - increases pH
2) Carbon concentrating mechanisms (CCMs)
3) Diffusion from atmosphere - decreases pH
Sources of nutrients to lakes
Dust - mineral particulate P
Riverine inputs
Mostly particulate P
Dissolved P where pollutants are important
Agricultural P
Sewage P - detergents
Groundwater - mostly dissolved phosphate
Animal Vectors
Can be important in lakes
Oceans are too large
Short term N is often…
Limiting
System adjusts N pools based on available P
Denitrification can remove excess nitrate
N-fixation can be limited by MO, light, and other factors
70% of aquatic algae are eaten by…
herbivores
Export affects O2 depletion in deep waters
organic matter fuels respiration by bacteria
can lead to fish kills
O2 sensitive species especially at risk
Also cold-loving species must stay deep where O2 is low
Ecosystem heterotrophy
Where ecosystem respiration exceeds ecosystem NPP in most lakes