Biochem Lect 22: Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Hemoglobin location/function/structure
blood
O2 transport
tetrameric (2 alpha chains, 2 beta chains)
Myoglobin location/function/structure
muscle
O2 storage
monomeric
Both Hb and Mb contain ____ and have ___ alpha helices
heme protein, 8
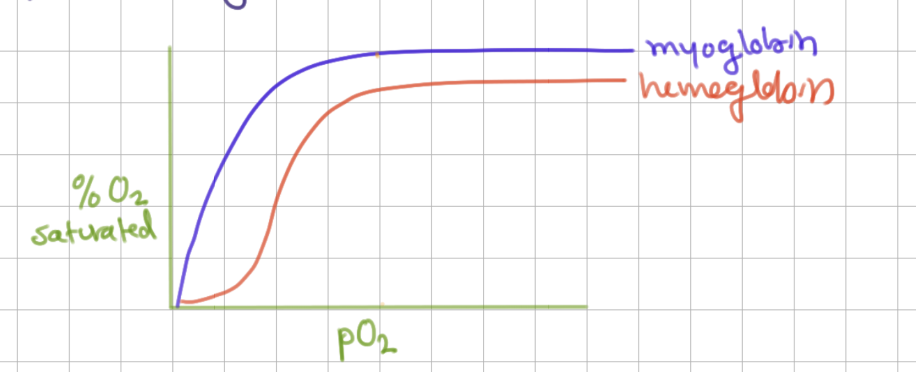
Mb binding curve shape
hyperbolic (binds 1 thing)
like MM
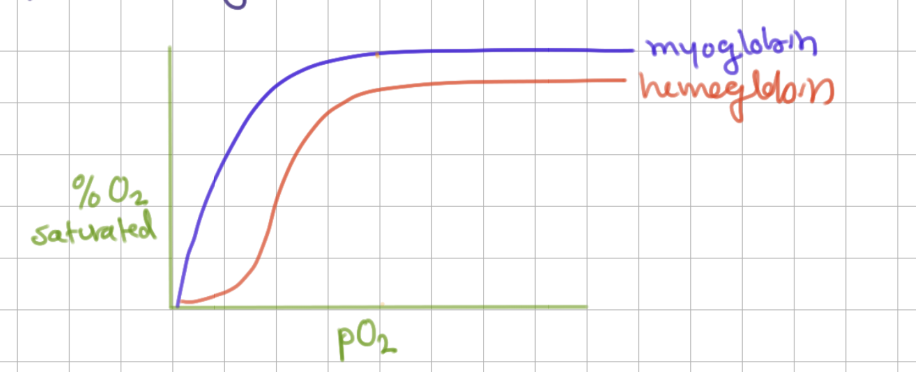
Hb binding cure shape
sigmoid (cooperativity)
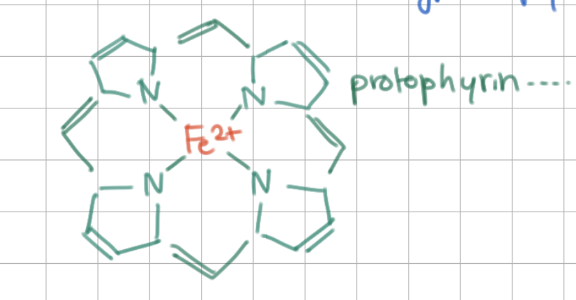
Heme structure contains _____ and ____ at center
protoporphyrin IX ring (4 pyroles), Fe2+
Heme structure binds to _____ above and _____ below
His F8 (8th residue on F helix), O2
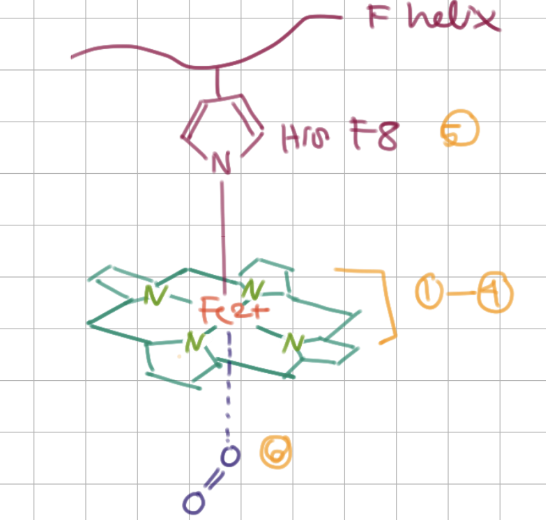
In total, Fe2+ is bound to 5/6 things:
3 Ns from ring, N from histidine, O2
O2 binding causes Fe2+ to be drawn closer to/further from the ring
closer to
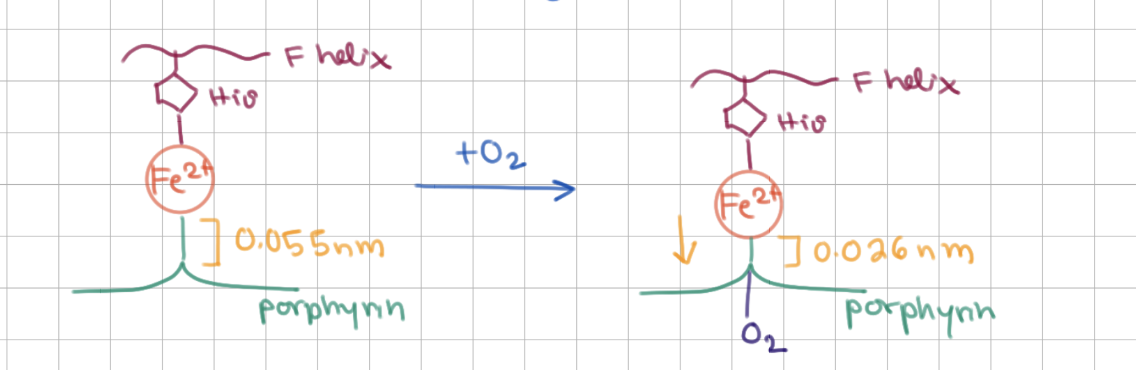
O2 binding has a bigger effect on Mb or Hb?
Hb (causes major conformational change)
ferrous ion
Fe2+
ferric ion
Fe3+
a myoglobin with a ferrous ion is called…
metmyoglobin (does not bind O2)
Hb is a ____, and some/all part of it are touching
ɑβ dimer (2 alpha 2 beta parts), some
How many oxygens (n) can be bound to Hb? How many usually are?
n = 4 → maximum = perfect cooperativity
n = 2.8 → average
n = 1 → no cooperativity

What is T state?
deoxy-Hb
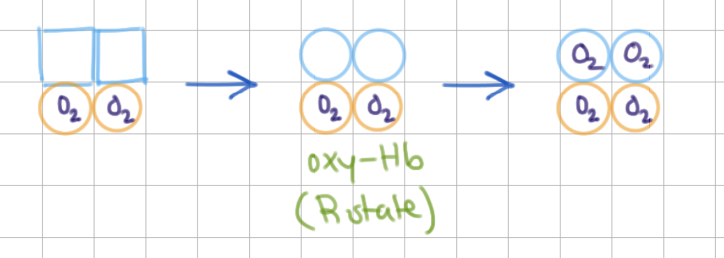
What is R state?
oxy-Hb
Does T or R state have salt bridges and how many?
T state, 8 (broken when transition to R state)
Hb cooperativity has both MWC and KNF features. Define each.
MWC = all or none (all subunits in same conformation)
KNF = sequential model (one changes neighbor, etc.)
ɑ/β cannot bind until all ɑ/β are bound.
β,ɑ
What happens when 1 O2 binds? Which model is this?
binds to 1st ɑ, neighboring subunit relaxes
-
KNF (sequential)
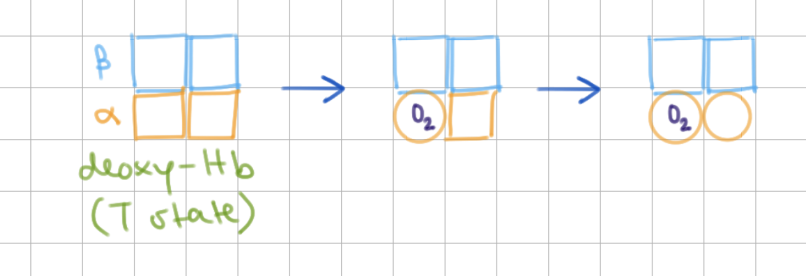
What happens when 2 O2 binds? Which model is this?
binds to 2nd ɑ, entire molecule relaxes
-
MWC (all or nothing)
Mb/Hb has higher affinity for O2 at all pressures.
Mb (due to non-cooperativity)

Why is cooperative binding helpful for Hb function? (lungs vs capillaries)
pick up/drop O2 as needed
lungs have high pO2 → Hb fills with O2
capillaries have low pO2 → Hb drops O2

pH effect on O2 binding
high H+ = low pH → makes Hb tense → decrease O2 affinity
-
aka H+ bad
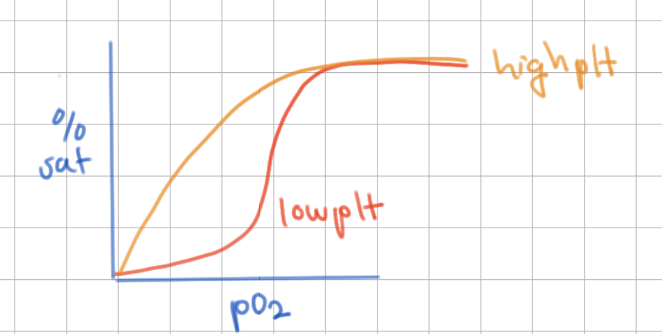
CO2 effect on O2 disocciation in tissues
high CO2 → shifts to make more H+ → decrease O2 binding → O2 dropped into tissues

CO2 effect on O2 disocciation in lungs
low CO2 → shifts to make less H+ → increase O2 binding → O2 taken into Hb
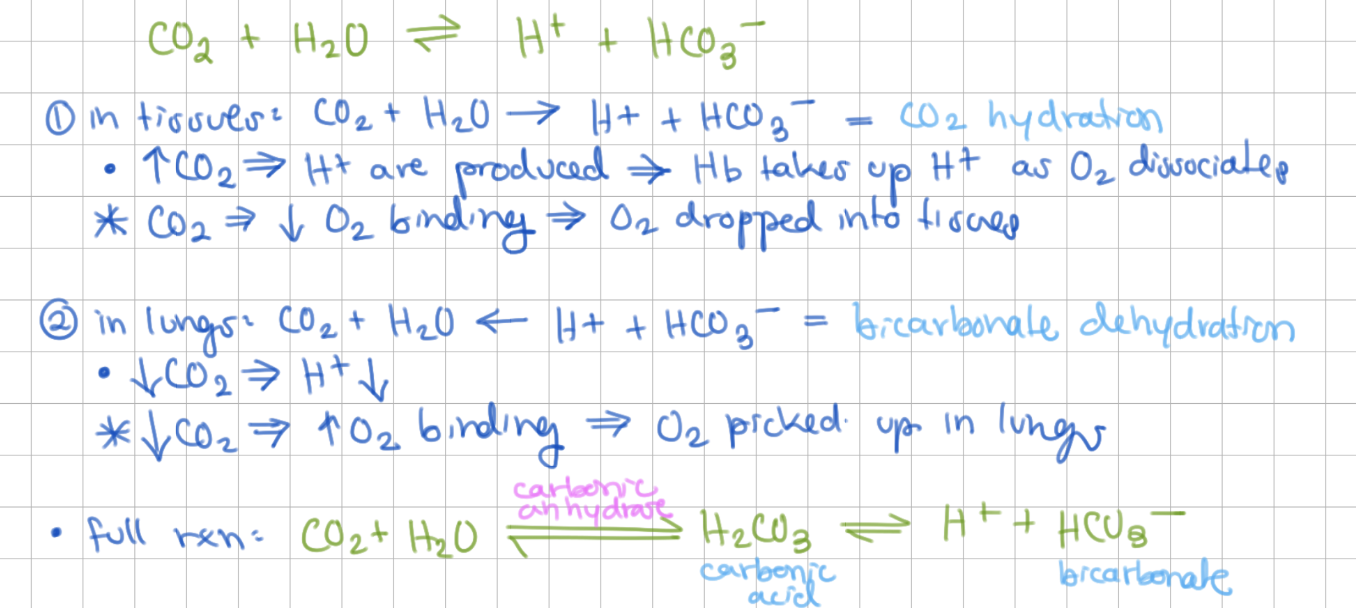
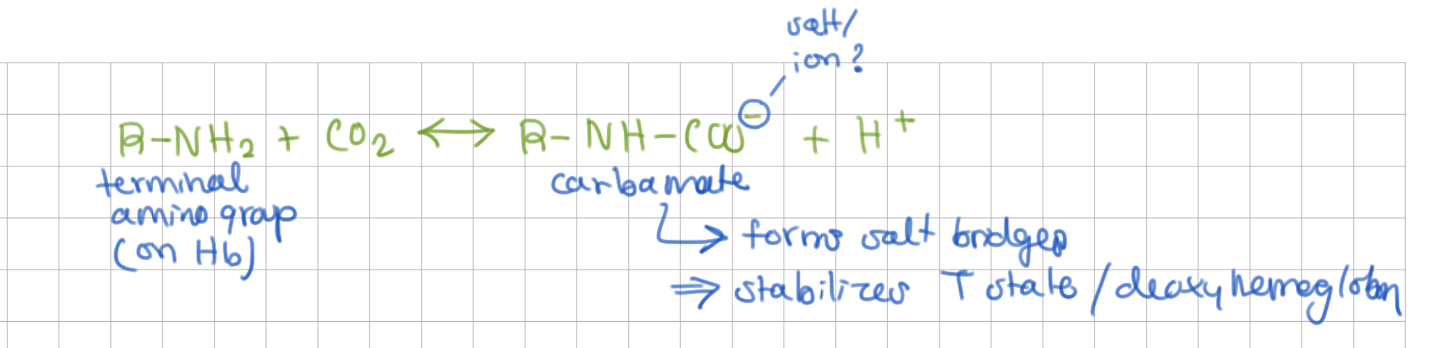
CO2 also favors O2 release from Hb by stabilizing deoxy-Hb → reacts with _____ to form _____
terminal amino groups, carbamate group (negative charged, forms salt bridges)
2,3 BPG activates/inhibits Hb
inhibits (causes sigmoid bonding)
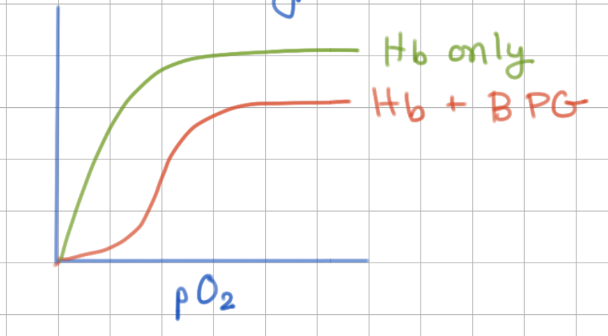
2,3 BPG binds at same/different site as O2
different (allosteric)
Fetal Hb has higher/lower affinity for O2 compared to Adult Hb
higher

Fetal Hb has __ chains instead of __ chains
ɣ,β
ɣ chains have __ amino aicd instead of His
Ser
What is the functional difference between ɣ and β?
Serine is more negative than His → 2,3BPG binds less tightly (less inhibited) → fetal Hb has higher affinity for O2