OpenStax Biology 2e: Chapter 23 - Protists
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
cytoplasmic streaming
movement of cytoplasm into an extended pseudopod such that the entire cell is transported to the site of the pseudopod
mixotroph
organism that can obtain nutrition by autotrophic or heterotrophic means, usually facultatively
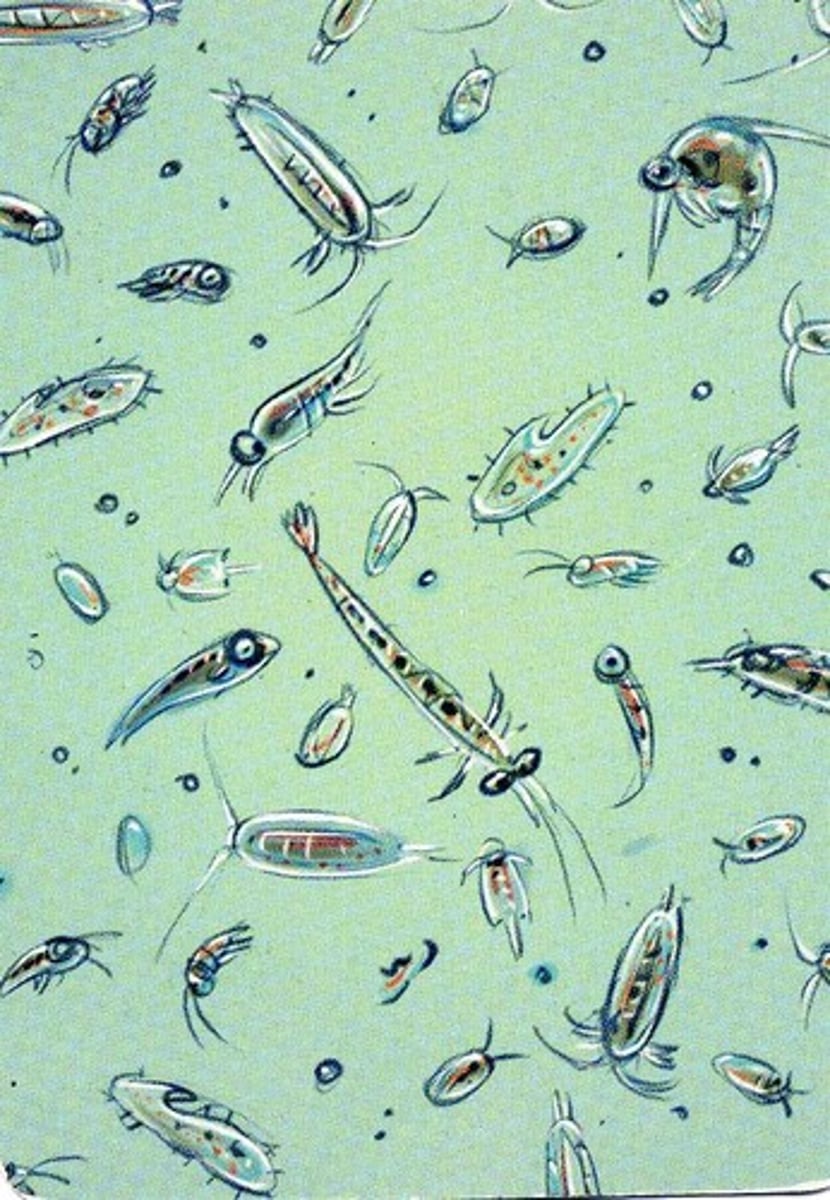
phytoplankton
diverse group of mostly microscopic photosynthetic organisms that drift in marine and freshwater systems and serve as a food source for larger aquatic organisms
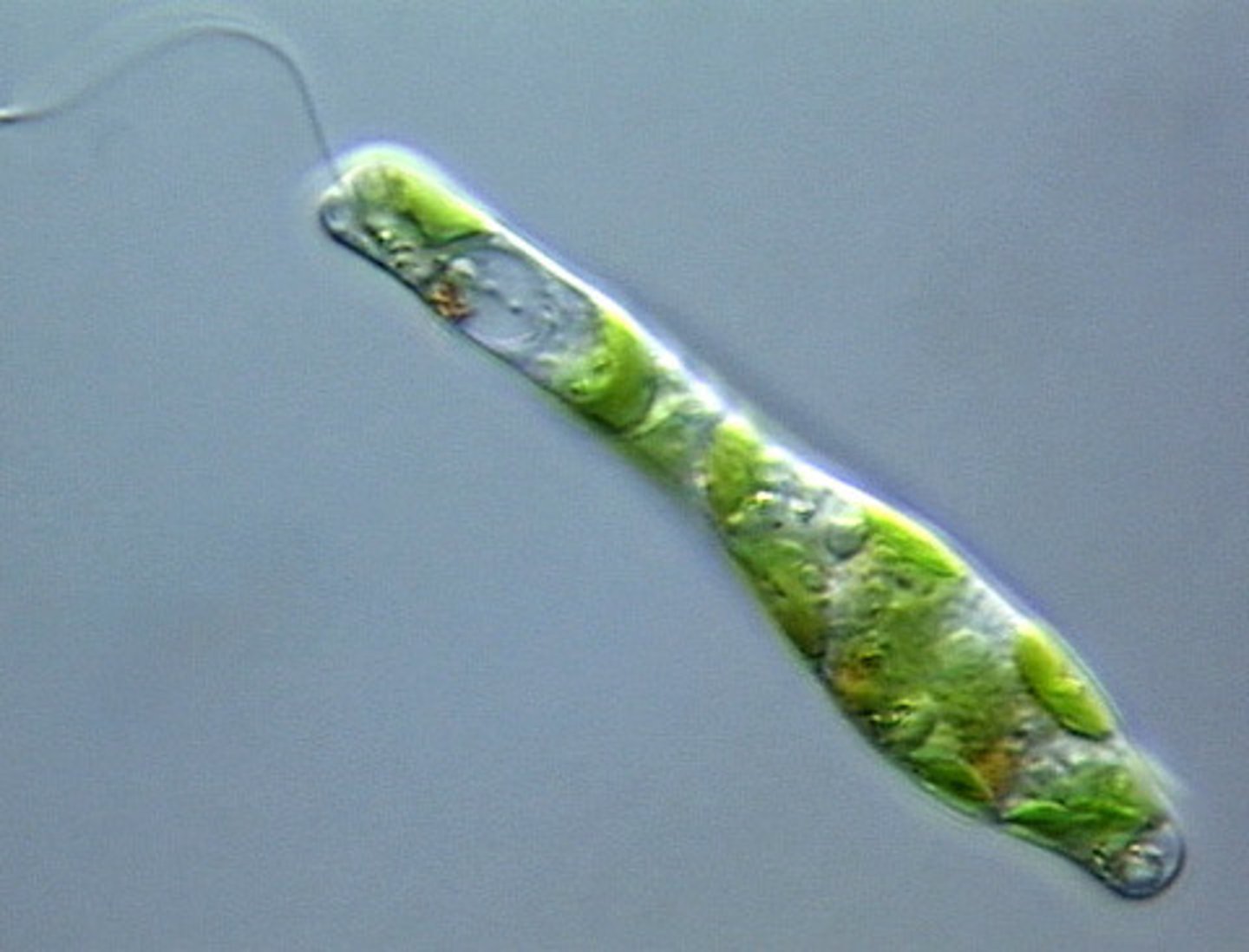
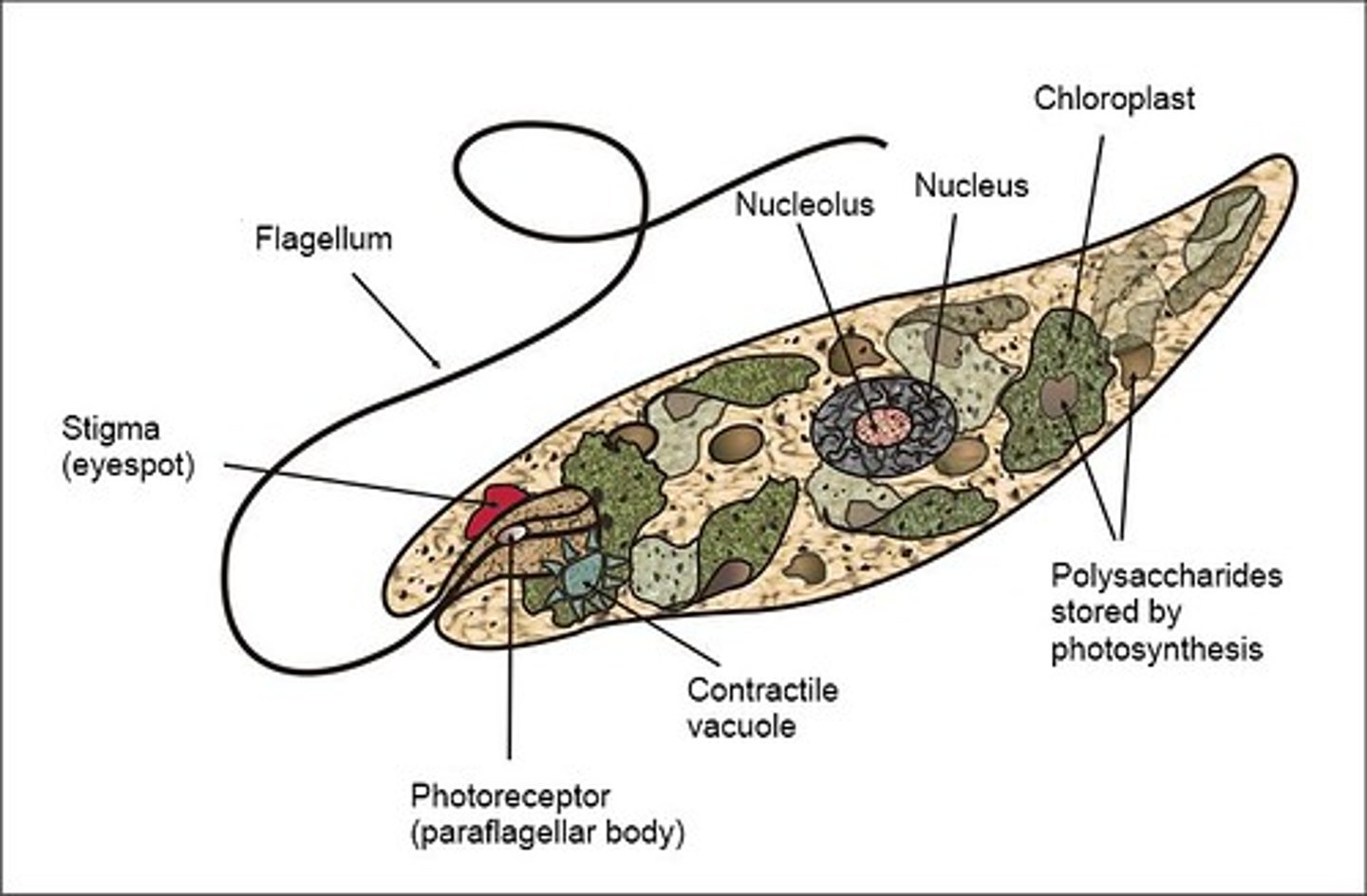
Euglena
Unicellular organism; moves using its flagella; asexual reproduction; have chloroplasts to absorb sunlight
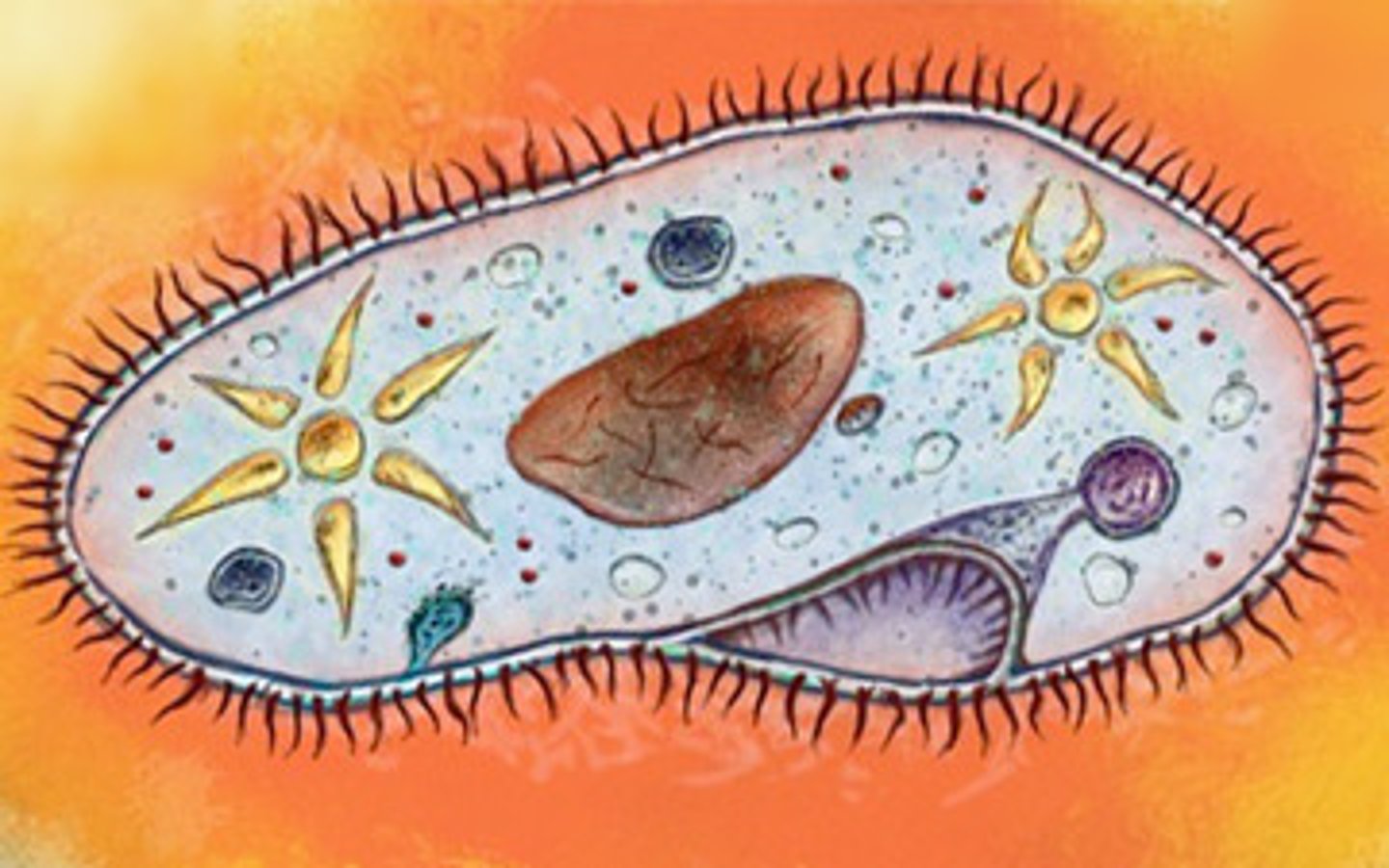
Paramecium
A ciliated (it propels itself via cilia) protist that lives in fresh water and eats other tiny organisms for food.
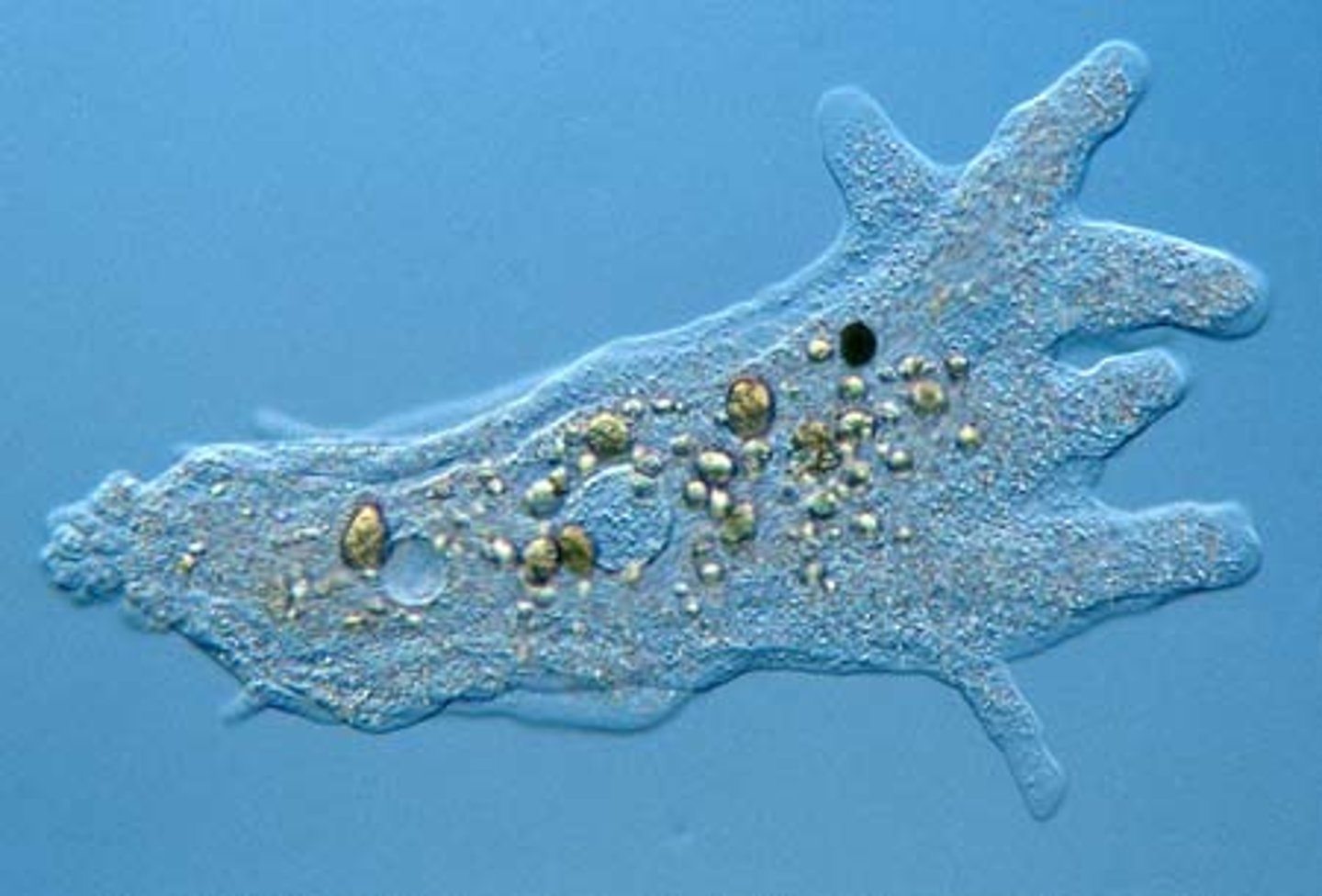
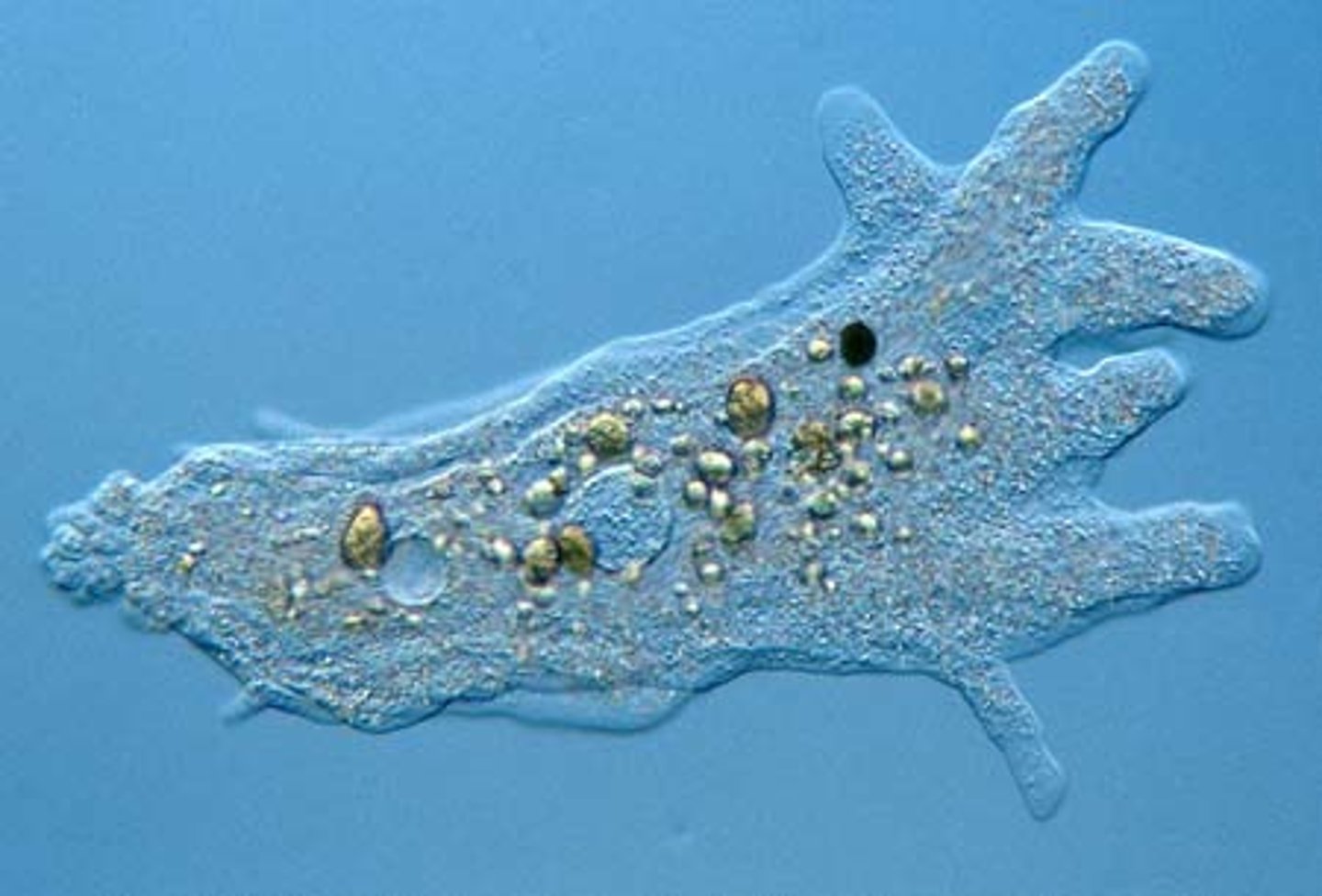
Amoeba
A type of protist characterized by great flexibility and the presence of pseudopodia.
Eukarya
domain consisting of all organisms that have a nucleus; includes protists, plants, fungi, and animals
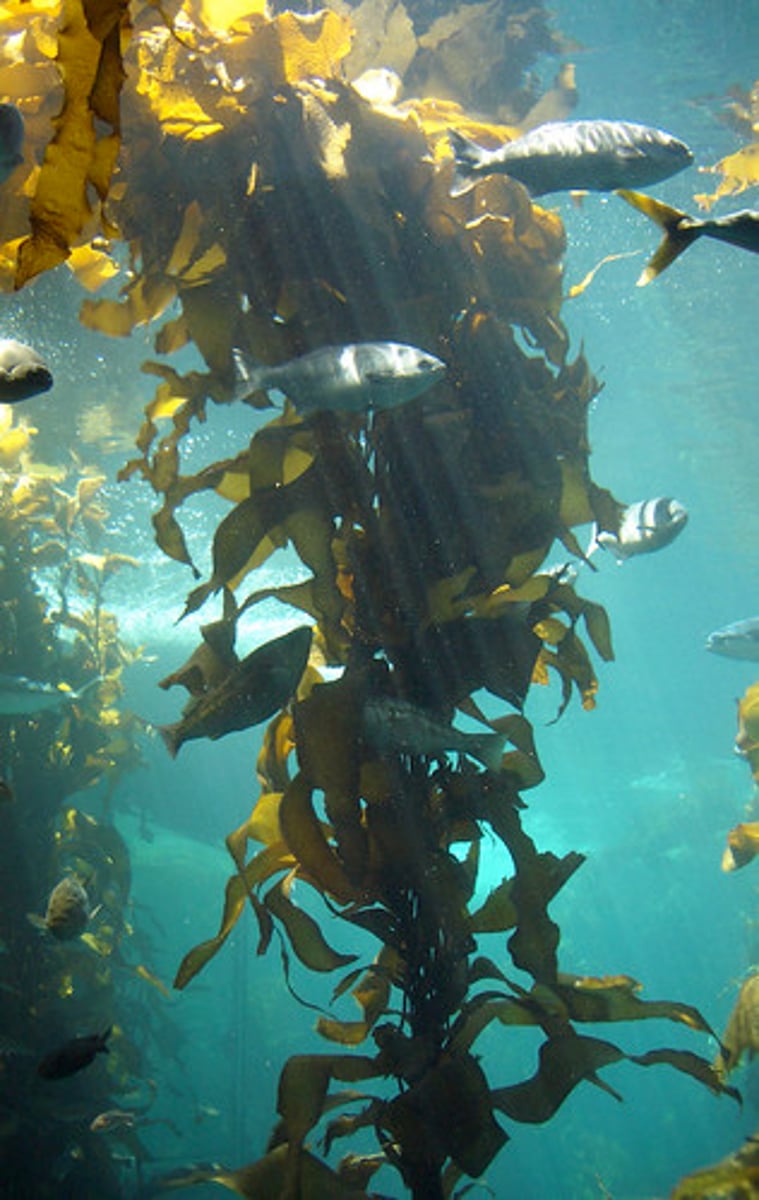
Algae
plantlike protists that produce food through photosynthesis using light energy and carbon dioxide

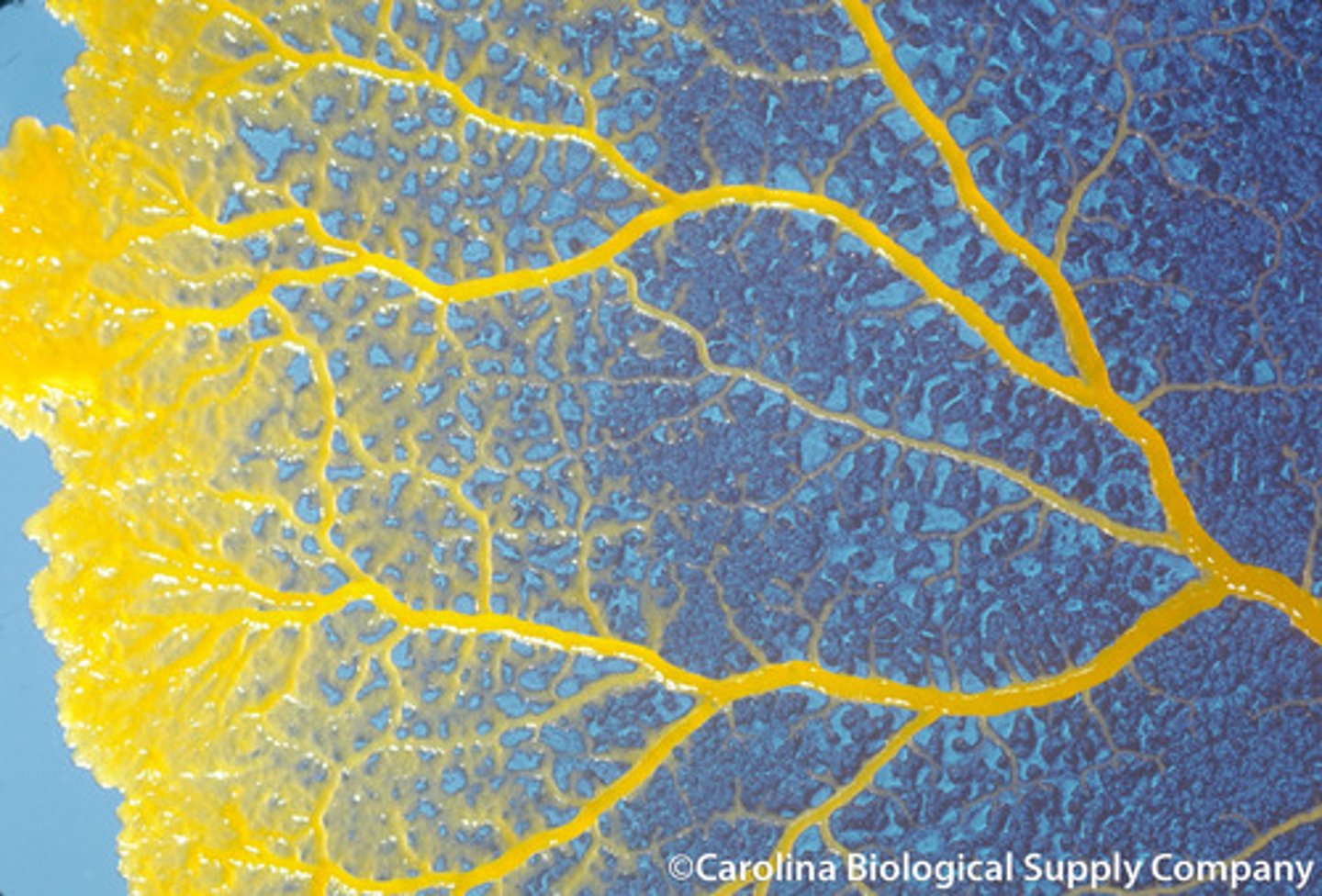
slime molds
Funguslike protists that play key roles in recycling organic material
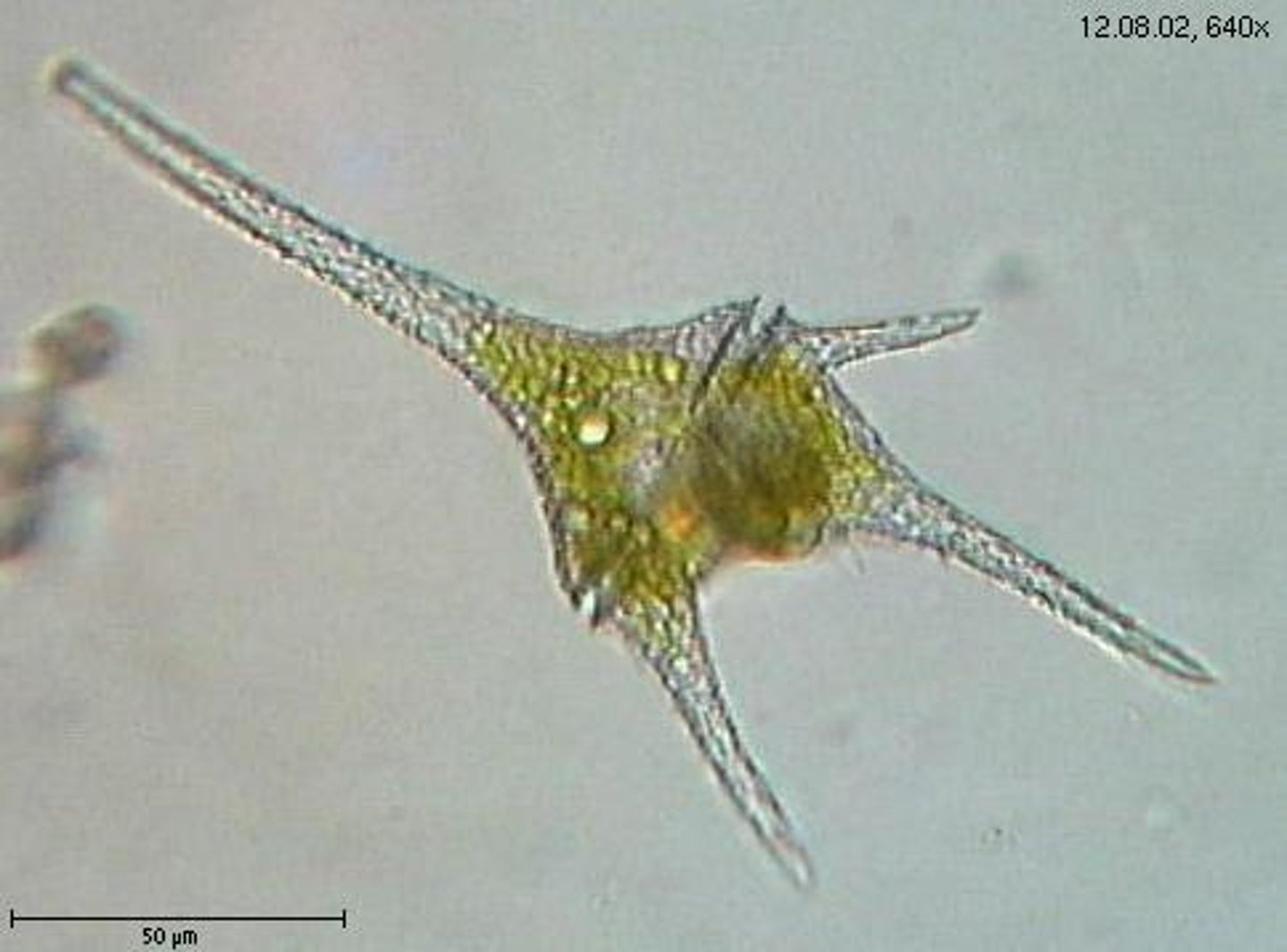
Dinoflagellates
Group of protists that form "blooms", can be toxic. make up phytoplankton and can be bioluminescent. They generally have two flagella, half are heterotrophic and the other half are photosynthetic, many species are luminescent

Plankton
Tiny organisms that float in the water
Eukaryote
A single or multicellular organism with cells that contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Protist
A eukaryotic organism that cannot be classified as an animal, plant, or fungus.
Cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility.
Pseudopod
A "false foot" or temporary bulge of cytoplasm used for feeding and movement in some protozoans.
Amoebozoans
A member of a clade of protists that includes amoebas and slime molds and is characterized by lobe-shaped pseudopodia.
Rhizaria
the eukaryotic supergroup that predominantly contains organisms that move by amoeboid movement and produce shells
Cilliates
Protozoans named for their hair- like structures called cilia, which provide movement for the protist and sweep food into its mouth
Stamenopiles
a diverse group of protists including water molds, diatoms, golden algae, brown algae
Euglenazoans
unicellular flagellates with flexible outer covering, an ocular eyespot and unique mitochondria