Contact Lenses
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
For a GP wearing patient with moderate peripheral cornea desiccation (3-9) staining, what contact lens parameter adjustments can you make to minimize this?
Most common complication with RGP is peripheral corneal dessication (3-9 staining)
Often due to excessive edge lift of contact lenses
Result in areas of tear film disruption → areas of dryness and desiccation of the corneal epithelium
Decrease edge lift and increase the lid apposition to the peripheral cornea
Steepen the base curve and/or steepen the peripheral curves
Thinning the CL edge and lenticulating higher minus also helps
3-9 staining is purely fit related, so changing lens material won’t make a difference
If a patient is wearing a +5.00 D soft CL and does NCT, how would you expect the pressures to be affected?
NCT over plus SCL (greater than +3.00 D) → IOP overestimated
Due to increased center thickness & increased rigidity
NCT over minus SCL (greater than -6.00D) → IOP underestimated
The Dk/t value of a contact lens is referred to as what?
A. Oxygen permeability
B. Oxygen transmissibility
B. Oxygen transmissibility
Oxygen transmissibility is directly proportional to the oxygen permeability of a material (Dk) and inversely proportional to the avg thickness of a lens material (t).
Cl companies use a standard -3.00 CL rx to calculate this value
What type of toric GP lens design is this?
BC: 7.58 mm and 7.84 mm
CLP: -1.00D and -2.50
First step: Convert BC from mm to Diopters
BC 1 = 7.58 mm = 337.5/7.58 = 44.50 D
BC 2 = 7.84 mm = 337.5/7.84 = 43.00 D
Change in BC = 1.50 D
Second Step: Calculate Change in CLP
Change in CLP = 1.50 D
Differences in Changes
BC = CLP means SPE Bitoric
3/2 BC = CLP means Base Curve Toric
3/2 BC does not = CLP means CPE Bitoric
When fitting a scleral contact lens, how much clearance over the steepest area of the cornea is considered ideal?
100 - 300 microns
What is the power of the tear lens created by a GP? Round to the nearest 0.12 D
BC = 42.87 D
Placed on a cornea with a spherical curvature of 43.25 D
Tear Lens (TL) = Base Curve (BC) - Keratometry (K)
When the base curve is flatter than the k values, the tear lens will be a negative value
TL = 42.87 - 43.25 = -0.37 D
Increasing silicone content and decreasing water content has what effect on the oxygen transmissibility of soft contact lenses?
Oxygen transmissibility increases
But this combination increases chance of lipid deposition and increases the modulus of the material
More water content = less oxygen transmissibility
More silicone = more oxygen transmissibility
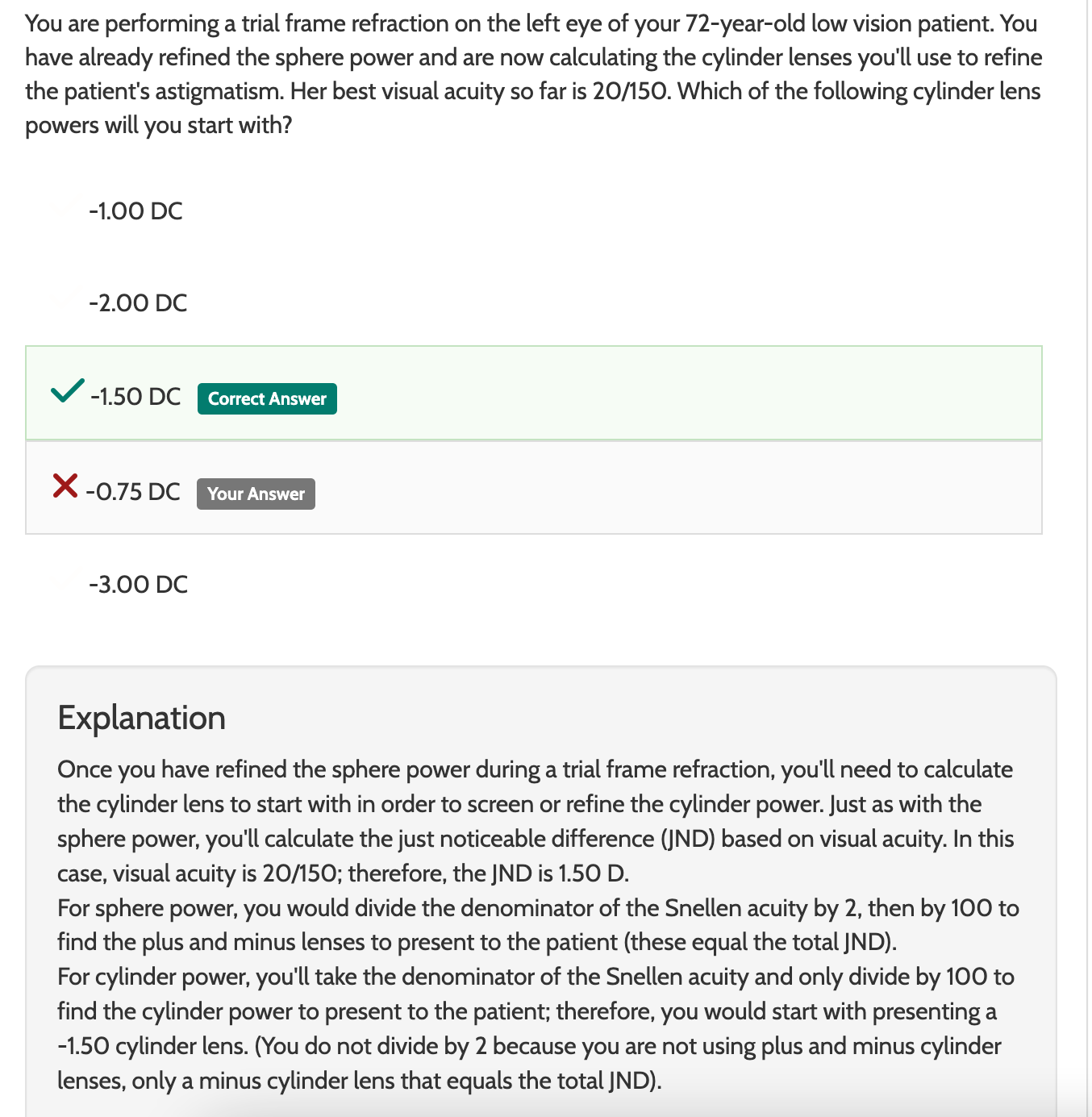
How do you calculate the SCw for a GP?
OAD = OZ + 2(SCw) + 2 (TCw)
In a minus SCL, does the periphery of the lens have a higher or lower Dk/t? What about a plus lens?
Minus
Lower Dk/t in the periphery
Minus lens is thickest in the periphery
Plus
Lower DK/t in the center
Plus lens is thickest in the center
What happens to the accommodative demand and convergence demand for a +10.00 going from spectacles to CLS? How about a -10.00?
Hyperopes (+10.00)
Less accommodative demand
More (+) power in contacts
More convergence demand
When hyperopes look at near targets, their eyes will converge and move inward (Imagine prisms with its bases facing each other)
They will be looking through BO prisms which moves the images inward and increases the convergence demand even more
Myopes (-10.00)
More accommodative demand
Minus spectacles reduce near accommodative demand due to vertex-distance effects.
Minus contacts do not.
Less convergence demand ??? ( To double check)
What parameter changes do you do to loosen a tightly fitting GP?
Flattening the base curve (most common)
Decrease optic zone
Decrease the overall diameter (OAD)
Widen the peripheral curve system
Flatten the peripheral curve system
What parameter changes do you do to tighten a loosing fitting GP?
Steepen the BC
Increase the OAD
Increase the optic zone
Steepen the peripheral curve system
Narrow the width of the peripheral curves
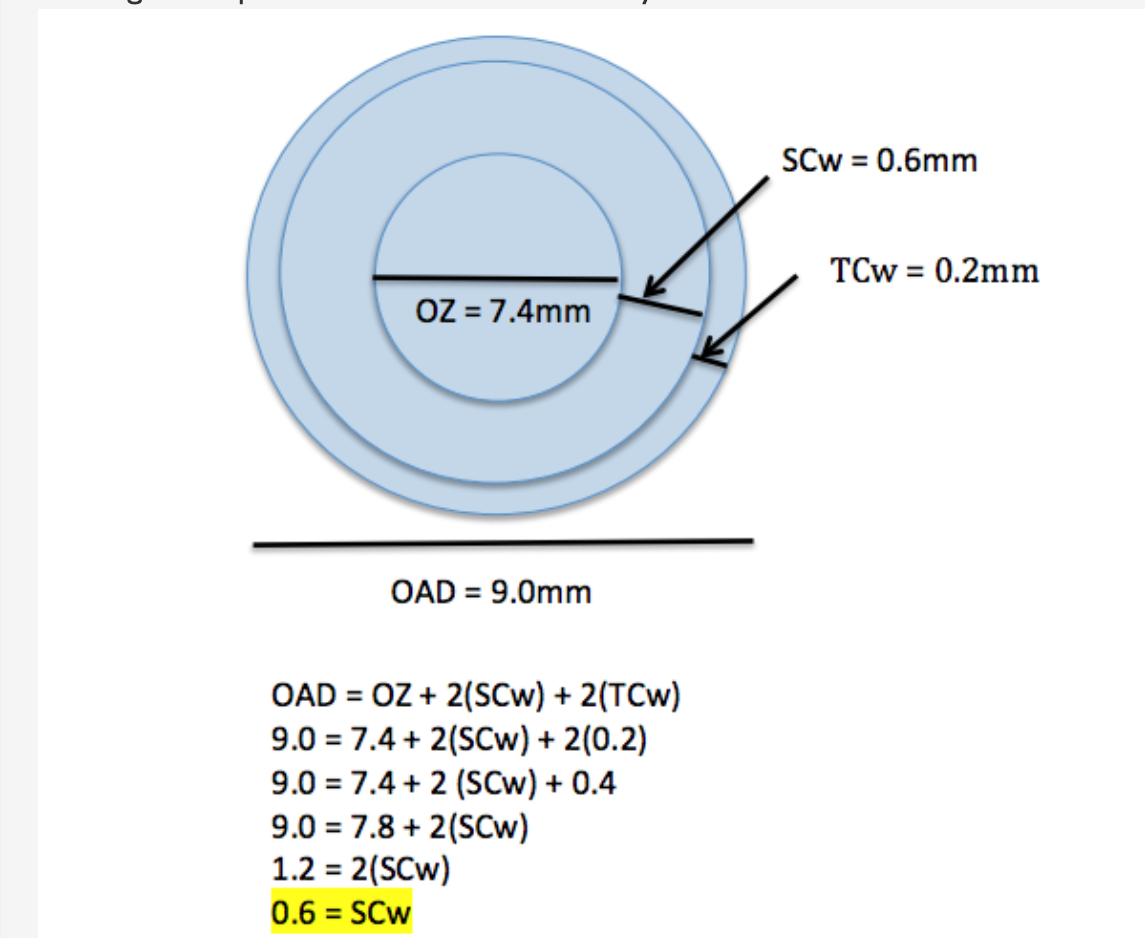
How to prescribe mononvision CL powers when given eye dominance, NaFl patternm and OR
If the fit is already alignment, you can simply add the OR onto the power. Don’t have to change the BC
If the fit is flat or steep, make that adjustment, SAM/FAP, and then add the near power
Dominant eye = distance
Non dominant eye = near
How overall diameter and BC affects the center thickness of an RGP
As the overall diameter of the CL increases, the center thickness of the contact increases
As the base curve of the CL becomes steeper, the center thickness should increase
Example of remember to vertex OR thats > 4.00D
Vertex formula: D/ 1-dD
Default d = 13 mm = 0.013 m
In addition to flattening the base curve, what alterations will help loosen a tightly fitting GP? What alterations would tighten a GP?
Loosen: (Notice you decrease and flatten everything except for peripheral curve system which you widen)
Flatten BC
Decrease the optic zone
Decrease OAD
Widen peripheral curve system
Flatten peripheral curve system
Tighten: (Notice you increase and steepen everything except the peripheral curve system)
Steepen BC
Increase optic zone
Increase OAD
Narrow peripheral curve system
Steepen peripheral curve system
Procedures for measuring certain aspects of the fitting relationship of soft contact lenses
Sag:
Have the patient move from primary gaze to superior gaze; measure the amount of the soft CL drops
Centration:
Have the patient look in primary gaze without blinking & measure the amt of decentration (if present)
MOB:
You know this
Lag:
Have patient move from primary gaze to lateral gaze; measure the amt the soft CL moves relative to the cornea
Push Up Test:
You know this
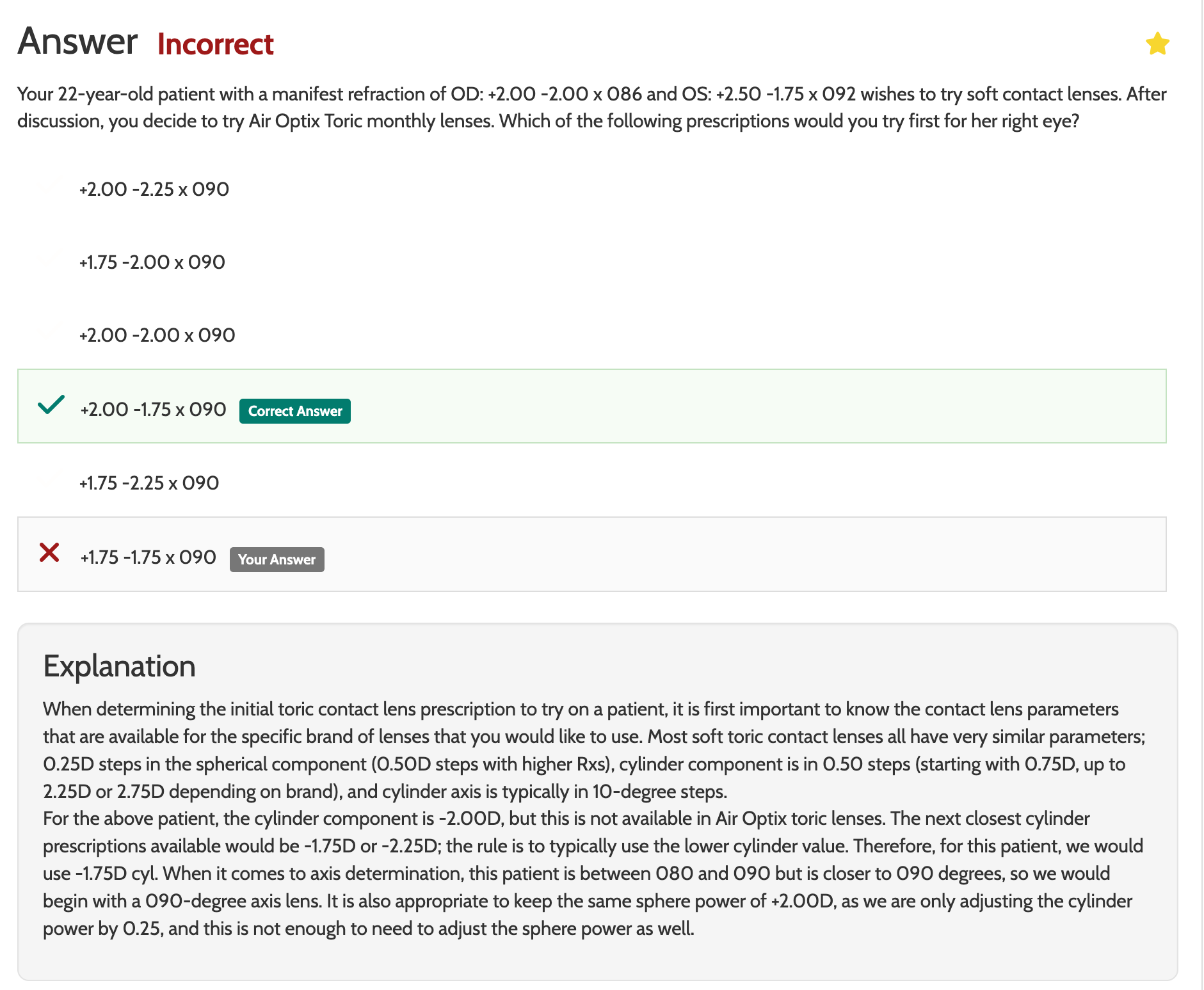
Know the contact lens parameters that are available
Spherical: 0.25 D steps or 0.50 steps with higher Rxs
Cylinder: 0.50 D steps (starting with 0.75 D)
In the example, -2.25 Cyl is available but -2.00 is not
0.4 mm OZD change round to 0.25D BC
What causes dimple veiling in an RGP and how can this be fixed?
Dimple veiling happens where there is excessive steepness
Result of poor tear exchange under the GP, leading to entrapment of bubbles of carbon dioxide under the central curvature of the lens
Flatten:
Treatment of choice is to decrease the diameter of the optic zone
Allows for better tear flow that may have been impeded by a tight mid-peripheral junction of the optic zone and the intermediate and peripheral curvatures of the contact lens

Trial framing a 72 year old low vision patient. You have already refined the sphere power and now calculating the cylinder lens you’ll use to refine the patient’s astigmatism. Her BCVA so far is 20/150. Which cylinder lens power do you start with?
-1.50 D (JND)
We don’t divide by 2 because we are not showing ± lenses rn, only a minus cylinder lens that equals total JND)
You do ± half when wanting to check cyl power and axis with a handheld JCC