LING 425, study of language
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
phonetics/phonology
possible speech sounds and sound combinations
morphology
word formation
syntax
sentence formation
semantics
word and sentence interpretation
pragmatics
language use in discourse
Displacement
ability to talk about events remote in space or time from the current situation of the speaker
Productivity
ability to express and understand an infinite number of new sentences
Traditional transmission
transmitted from one generation to the next
Arbitrariness
no dependence between speech sounds and the meanings they represent
Discreteness
set of discrete elements that clearly contrast with one another
Duality of Patterning
linguistic units exist at multiple levels (e.g., meaningless units – sounds – combine into meaningful units – morphemes and words)
Theoretical linguistics
studies competence
Psycholinguistics
studies performance
Consonants defined by
place of articulation
manner of articulation
voicing
Vowels defined by
tongue height
tongue position (front vs. back)
lip roundedness
lax vs. tense quality
sounds articulated using two lips
p,b,m
sounds articulated using bottom lip and top set of teeth
f,v
sounds articulated using the area behind your teeth (alveolar ridge)
t,d,s,z,n,l,r
sounds articulated the velum (the soft palate)
k,g
sounds articulated by completely stopping the air
p, b, t, d, k, g
sounds articulated by using the naval cavity
m, n
sounds articulated by blowing air through a small space (hissing sound)
s, z, f, v, th, sh, zh
phones
all speech sounds
phonemes
speech sounds that can contribute to the meaning
minimal pairs
words that differ in only one phoneme
free morphemes
can stand on their own
bound morphemes
must attach to other morphemes
-ed
past tense (participle)
-s
third person singular, past tense
-ing
progressive
-en
past participle
-s
plural
-’s
possessive
-er
comparative
-est
superlative
N à Adj
boy + ish
V à N
clear + ance
Adj à Adv
exact + ly
N à V
vaccin(e) + ate
Adj à N
tall + ness
V à Adj
read + able
regular inflections
•kid + -s = kids
•dash + -ed = dashed
irregular inflections
•children
•ran
S
à NP VP
NP
à (Det) (AP) N (PP)
VP
à V (NP) (PP) (Adv) (S)
PP
à P NP
AP
à Adj (PP)
N
à girl, boy, dog, cat, book, meat, ice-cream
V
à ate, broke, kissed, saw, thought, said
P
à on, under, in, with
Adj
à quiet, red, happy, wormy
Adv
à quickly, hard, yesterday
Det
à a, the
Recursion
Dumbledore is disappointed that Ron is happy that Harry hates Malfoy.
Structural Ambiguity
The wizard [cast a spell on [the child] [with the wand]].
Homonyms/homophones
different words pronounced the same
Polysemy
words with multiple related meanings
Information processing system
sensory stores
working memory
permanent (long-term) memory
episodic memory
memory of an event that happened when one was present
semantic memory
type of memory containing generalized knowledge of the world
procedural memory
type of memory containing information about how to do things
serial processing
when a group of processes takes place one at a time
parallel processing
when two or more processes take place at the same time
top-down processing
information at the higher levels may influence processing at the lower levels (often parallel)
bottom-up processing
proceeds from the lowest level to the highest level of processing (usually serial)
automatic processes
do not require extensive capacity of working memory
controlled processes
require substantial resources
methods of studying psycholinguistic questions
observation
judgement
experiment
Dempster (1981)
Significant differences between older and younger children on memory span test (test of short-term memory)
Case et al. (1982)
•No substantial increase in overall working memory capacity with development, at least from age six to adulthood
•Functional increase in storage due to greater efficiency of processing (automaticity), not increase in working memory size
Piaget (1952)
Children’s thinking processes are qualitatively different from those of adults
Diamond (1985)
Object permanence tasks in infants – problems stem from memory difficulties
Speech is rapid
•estimates vary between 120-180 wpm
•= 25-30 phonetic segments/second!
Speech is continuous
•no easily identifiable boundaries between words
•but we still segment the speech signal into discrete units of phonemes, words, …
articulatory phonetics
study of speech pronunciation
acoustic phonetics
study of speech perception
bilabial
two lips, /b/, /p/, /m/
labiodental
lower lip & upper set of teeth, /f/, /v/
interdental
tongue between the teeth, ‘the’, ‘through’
alveolar
ridge just behind the upper set of teeth, /n/, /t/, /d/, /s/, /z/...
(alveo-)palatal
‘shine’, ‘measure’, ‘champion’, ‘gym’
velar (back of the palate)
(/k/, /g/)
glottal
/h/, and glottal stop in ‘uh-uh’
uvular
German and French /r/
pharyngeal
Hebrew, Arabic
airflow stops
complete closure of airflow before release (/p/, /b/, /t/, /d/…)
airflow fricatives
turbulence (/s/, /z/, /f/, /v/, /h/…)
airflow affricates
stop + fricative (e.g., chime, cats)
airflow nasals
lowering the velum and letting air pass through the nose (/n/, /m/…)
airflow liquids
mild obstruction of airflow (/l/, /r/)
airflow glides
very slight obstruction of airflow (semi-vowel) (‘yellow’, ‘wet’)
Auditory level of perception
frequency, intensity and temporal properties of the signal
Phonetic level of perception
identifying individual speech sounds (phones) from acoustic cues
Phonological level of perception
identifying phonemes (meaningful sounds)
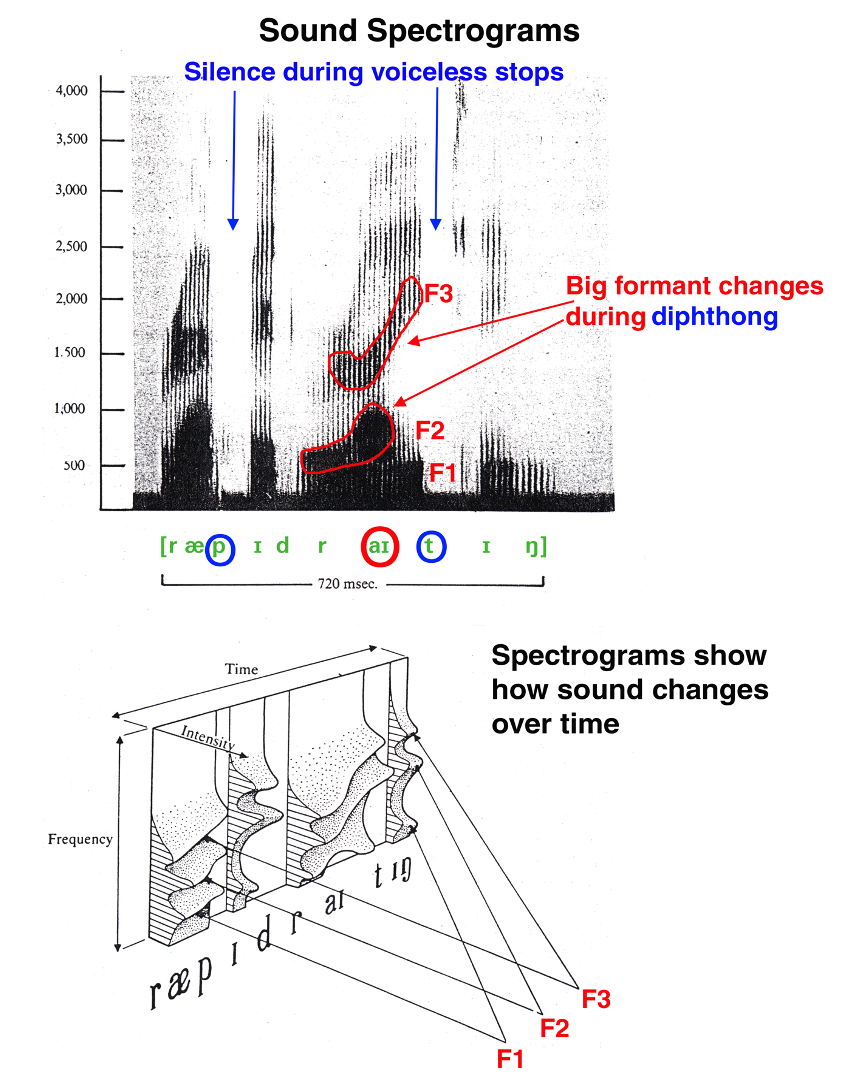
sound spectrograms
•vertical axis: frequency of speech sound
•horizontal axis: time
•dark band (formant): intensity at specific frequency levels
4 stages in speech perception
auditory
phonetic
phonological
lexical, semantic, syntactic
Top-Down Processing
using semantic and syntactic information to decode individual words in fluent speech
Bottom-Up Processing
using acoustic information to encode the speech signal
Bottom-up cues
•VOT
•place & manner of articulation
•speech rate