Lipoproteins (cholesterol)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What enzyme hydrolyzes triglycerides in the small intestine?
Pancreatic lipase (requires colipase)
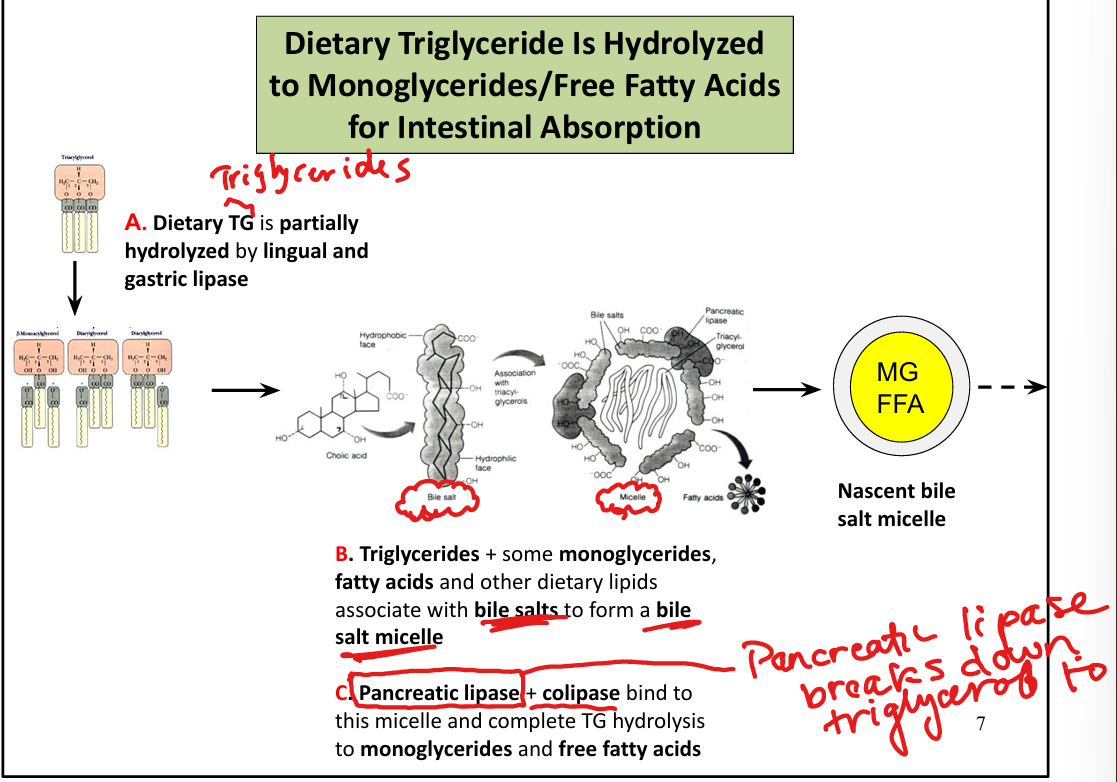

What are the products of triglyceride digestion?
Monoglycerides and free fatty acids
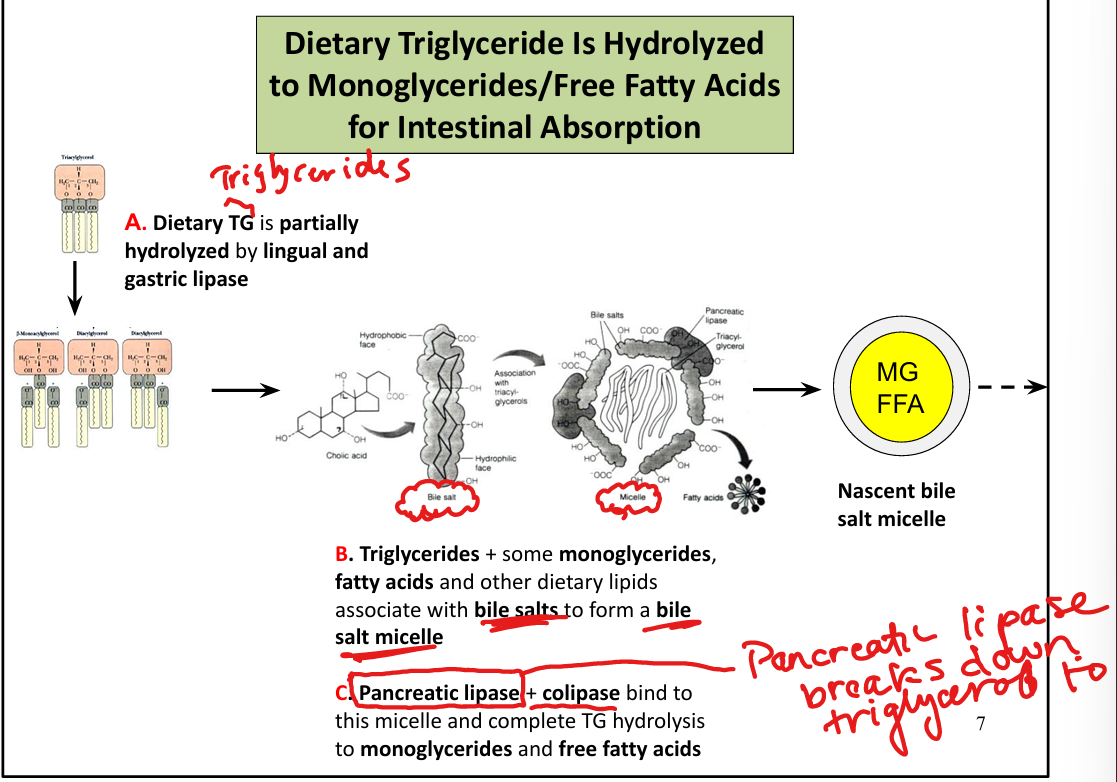

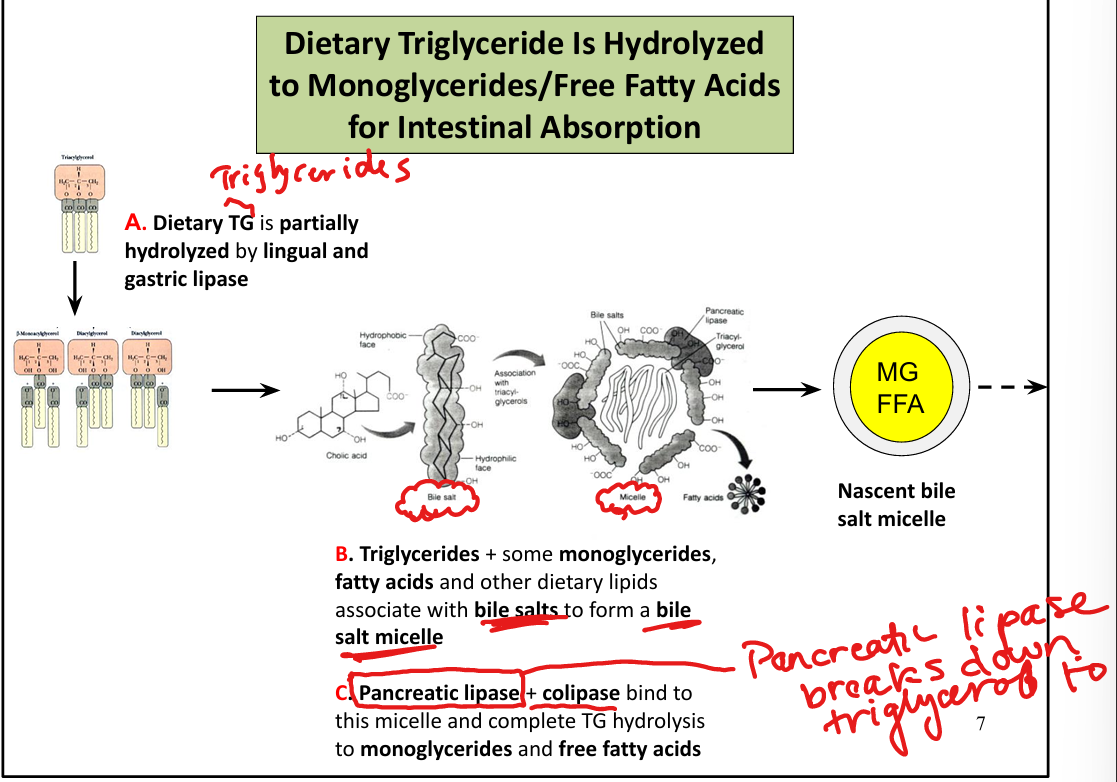
How are lipids absorbed into enterocytes?
As micelles formed by bile salts

What happens to lipids inside enterocytes?
Re-esterified into triglycerides and packaged into chylomicrons
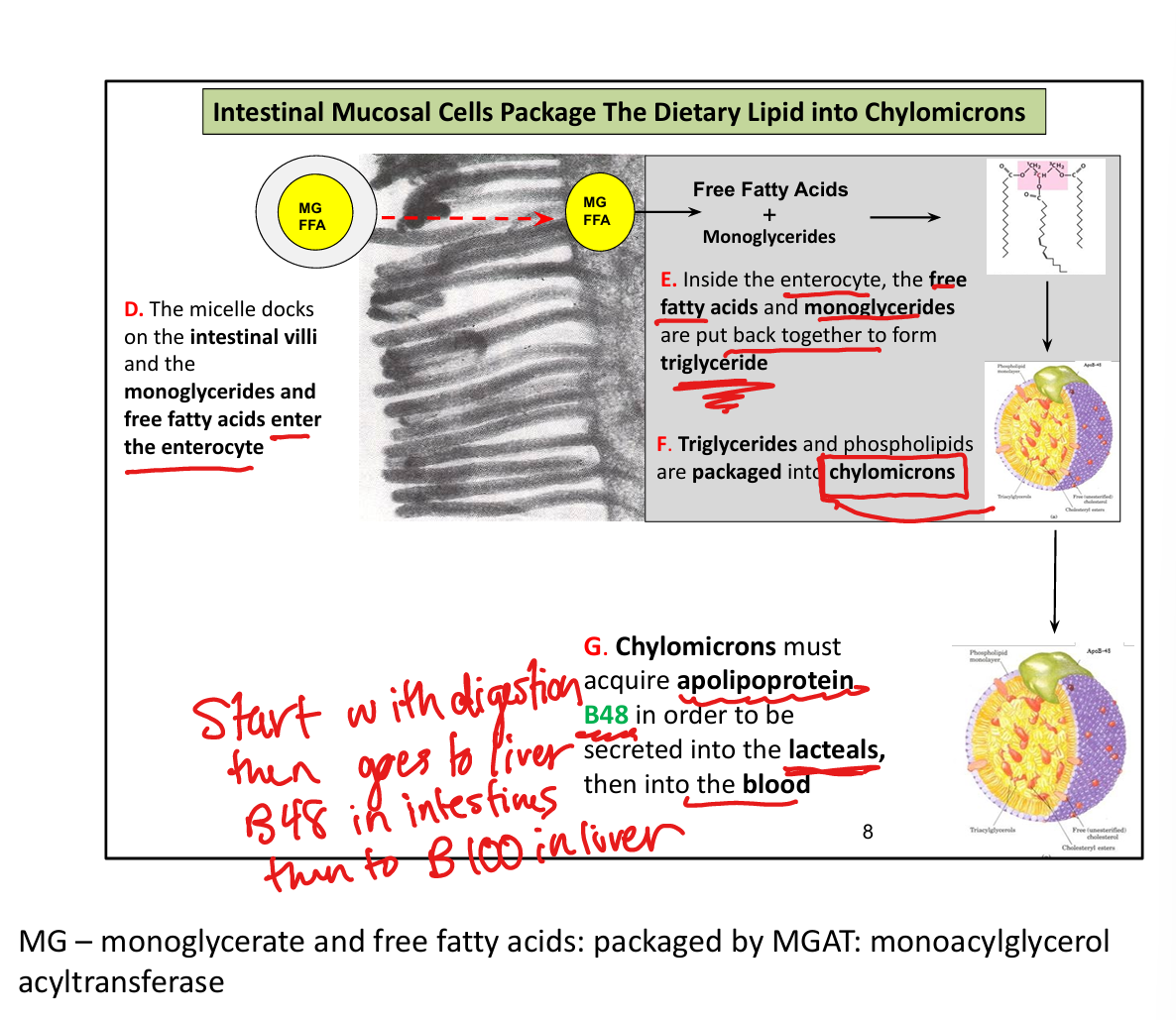

What apolipoprotein is required for chylomicron assembly?
ApoB-48
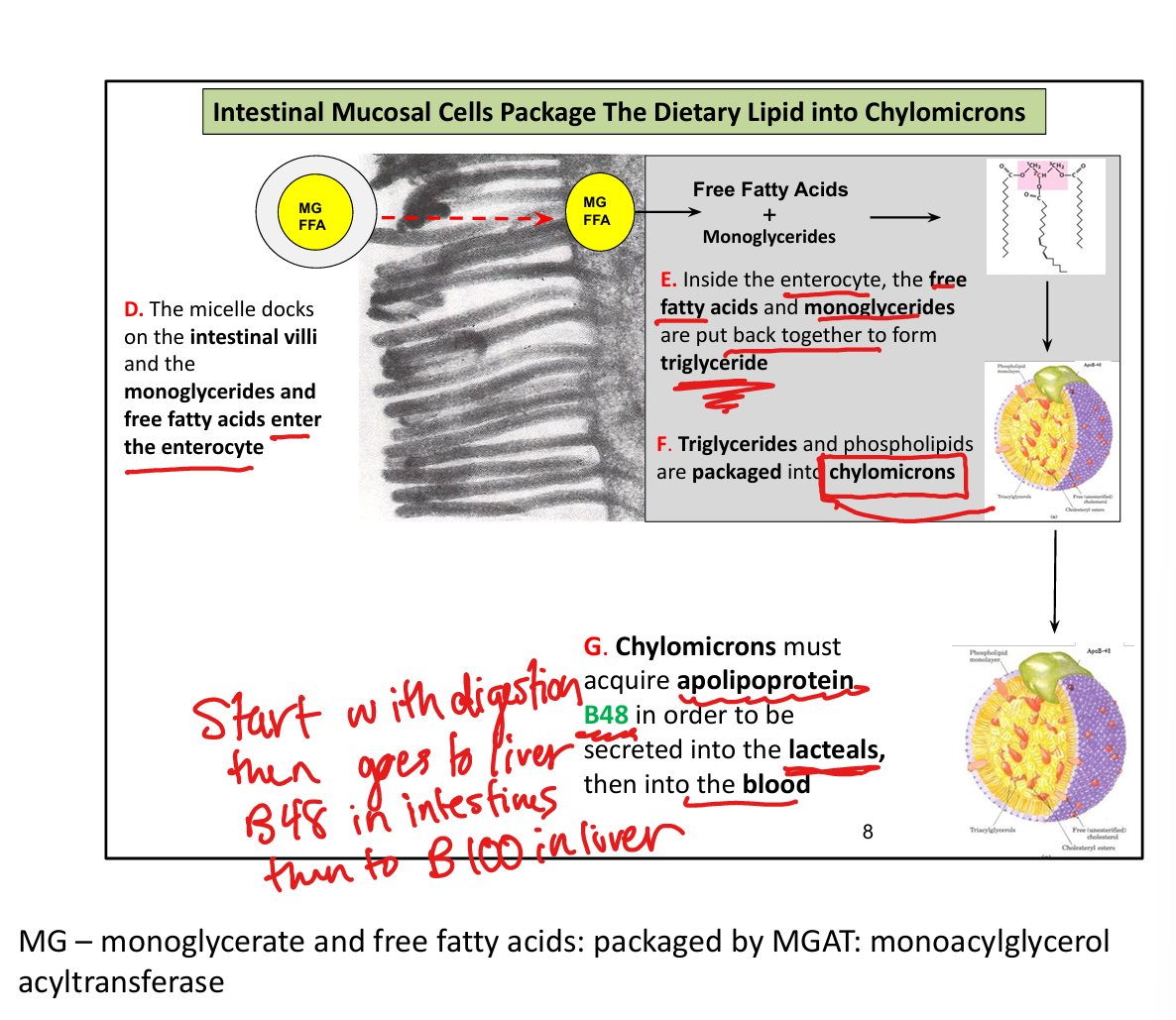

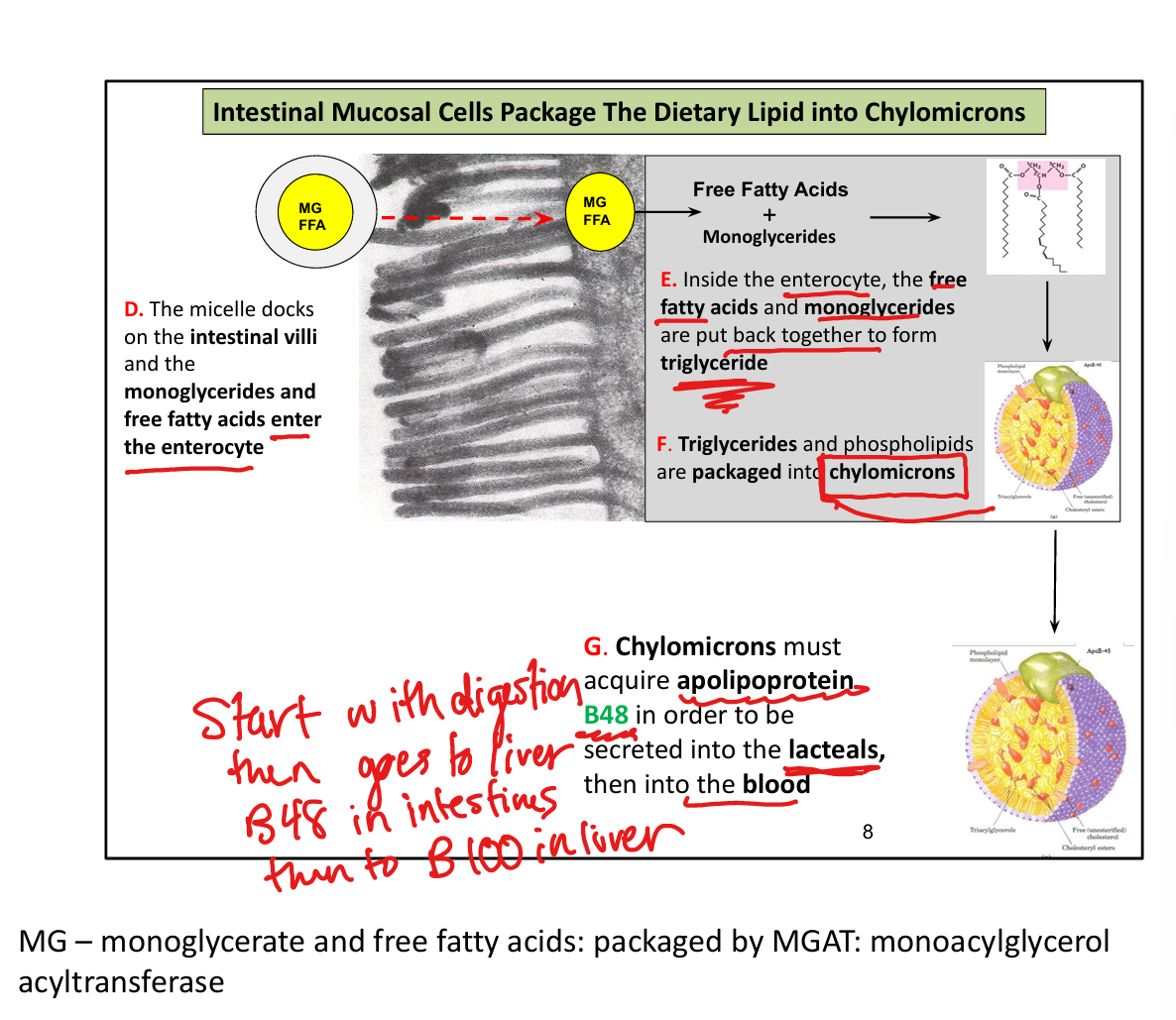
Where are chylomicrons secreted?
Into lacteals → lymph → bloodstream

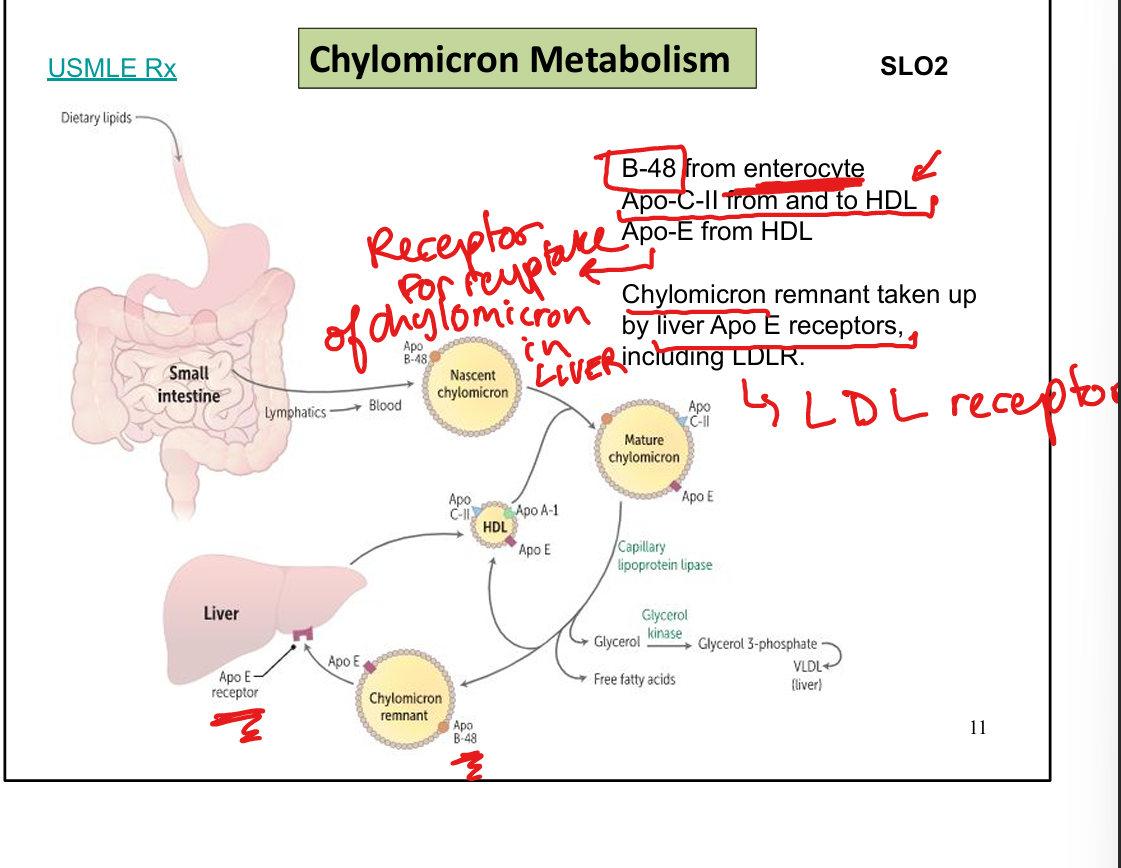
What apolipoproteins do chylomicrons acquire in circulation?
ApoC-II and ApoE (from HDL)

What enzyme activates lipoprotein lipase?
ApoC-II
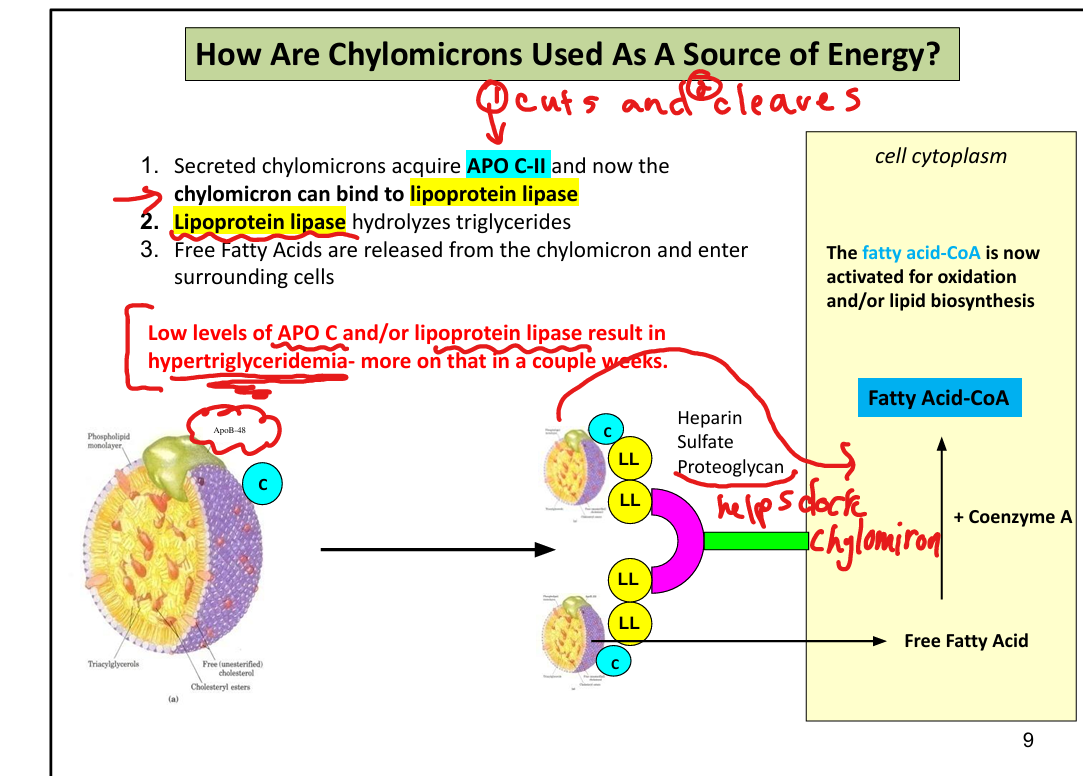

What does lipoprotein lipase do?
Hydrolyzes triglycerides in chylomicrons → free fatty acids
What is the function of chylomicrons?
Transport dietary triglycerides from intestine to peripheral tissues
What is the function of VLDL?
Transport endogenous triglycerides from liver to peripheral tissues
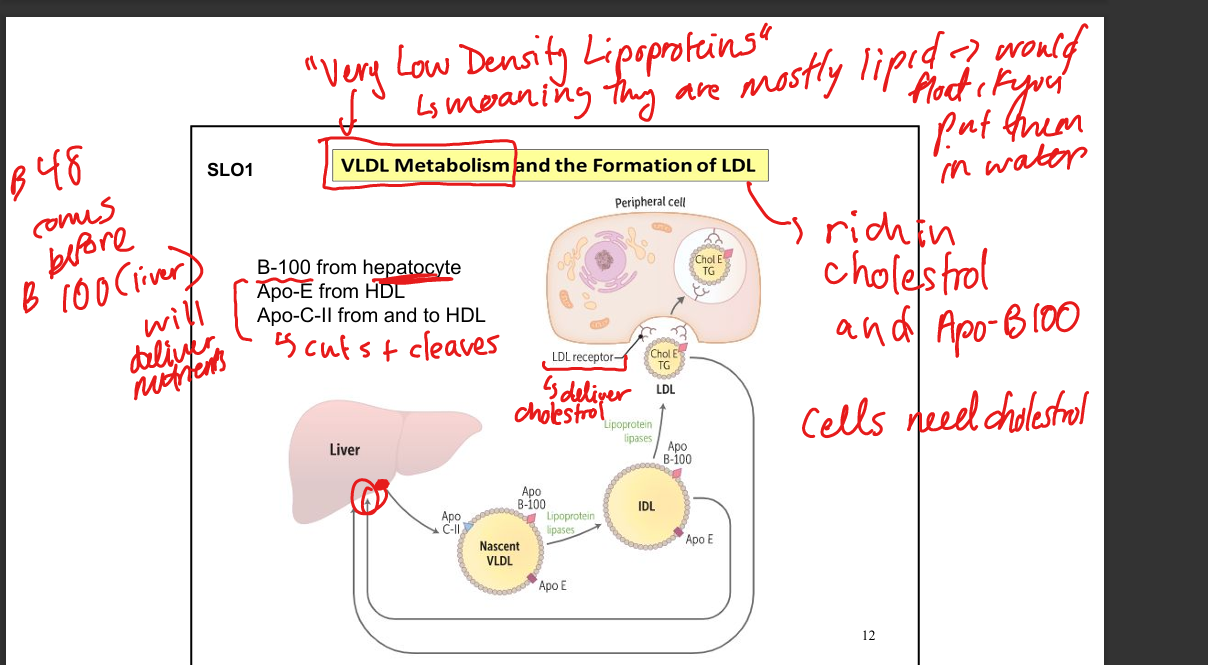

What is the function of LDL?
Deliver cholesterol to peripheral tissues via LDL receptors
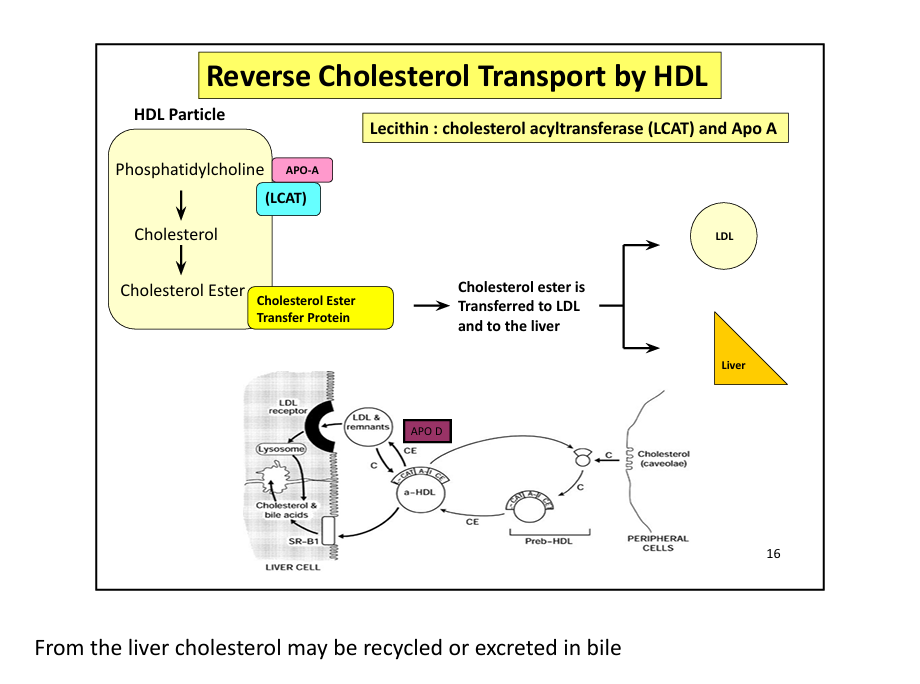
What is the function of HDL?
Reverse cholesterol transport: collects cholesterol from tissues → liver

What apolipoprotein is unique to chylomicrons?
ApoB-48
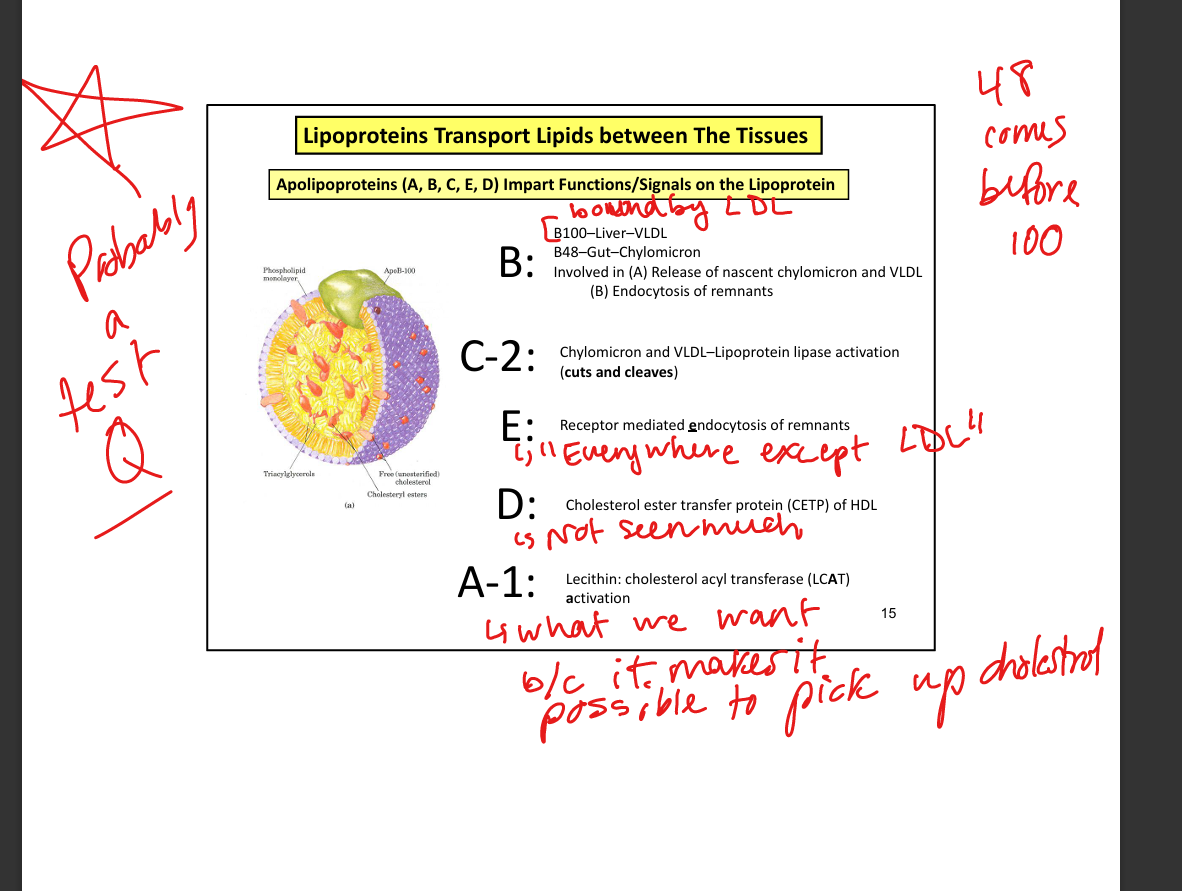

What apolipoprotein is unique to VLDL, IDL, and LDL?
ApoB-100
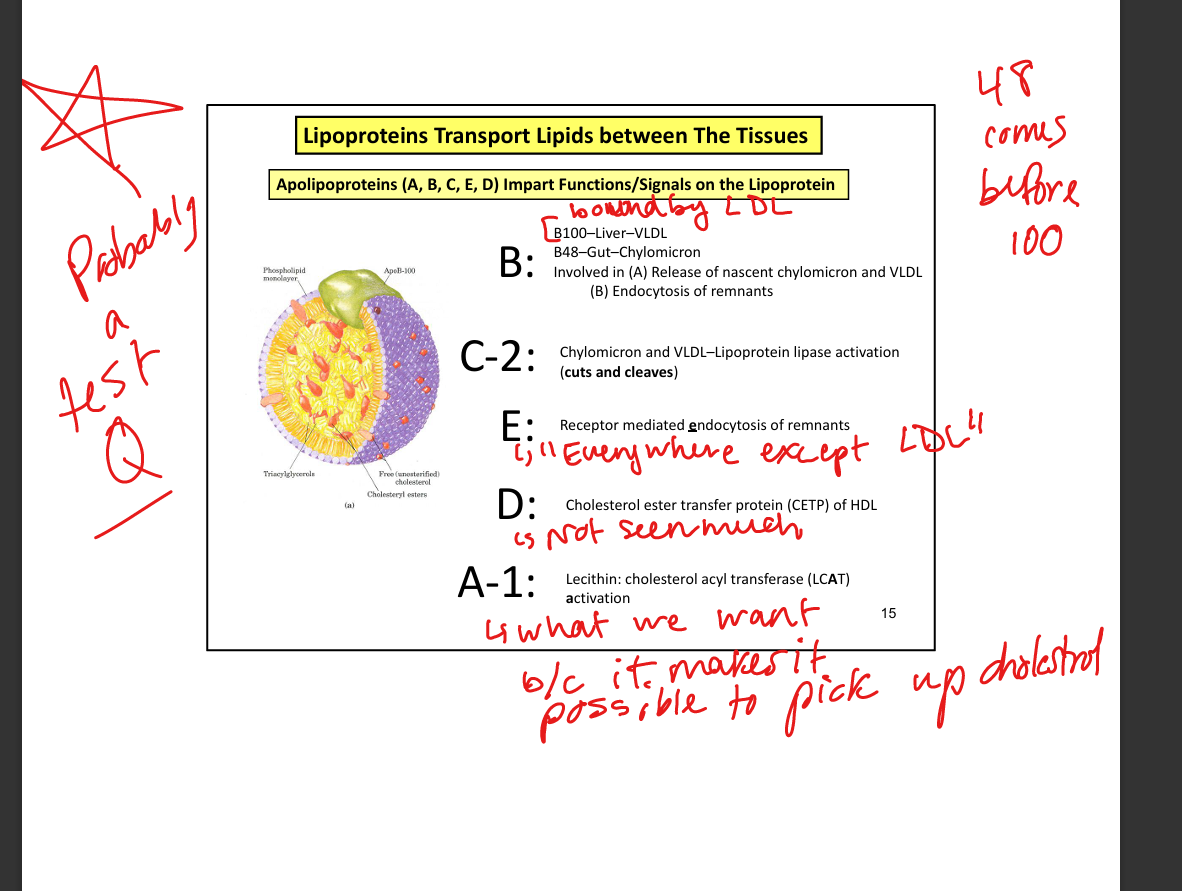

What apolipoprotein activates lipoprotein lipase?
ApoC-II
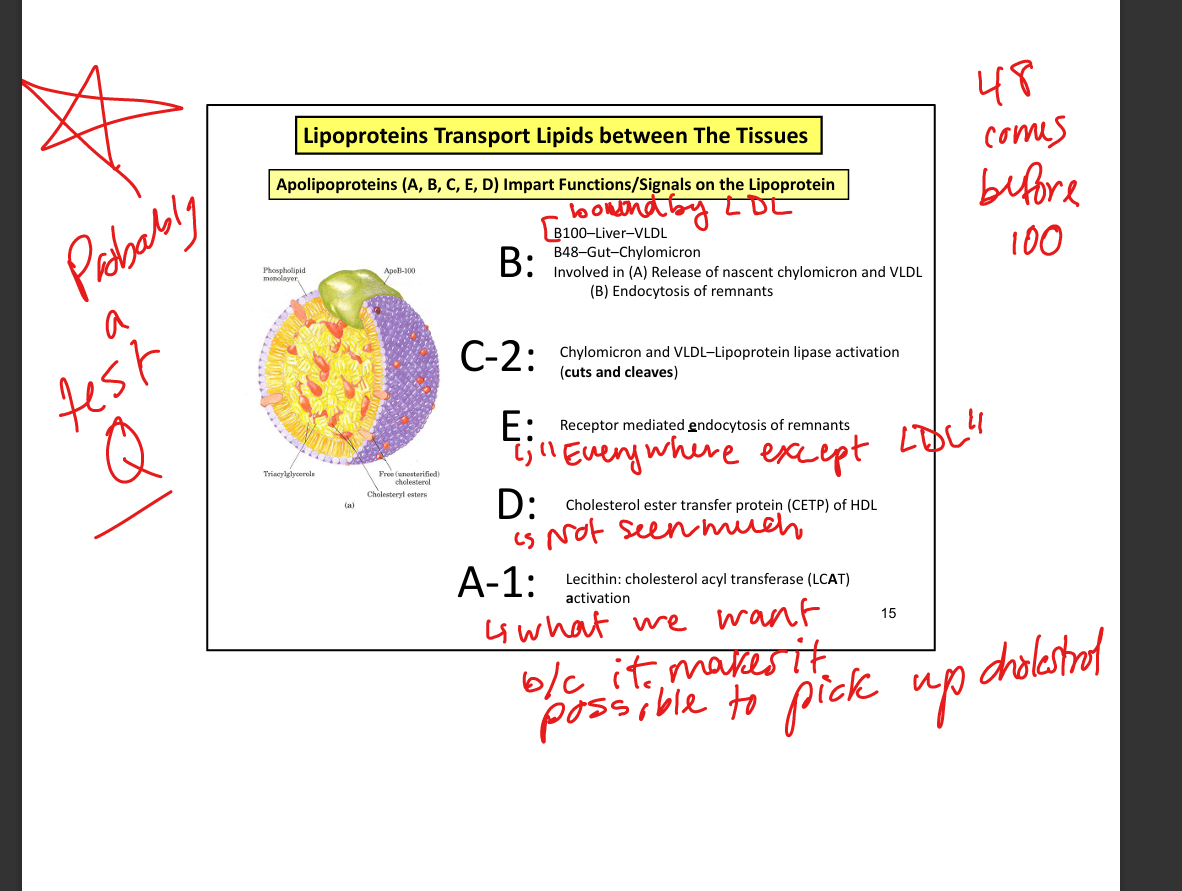

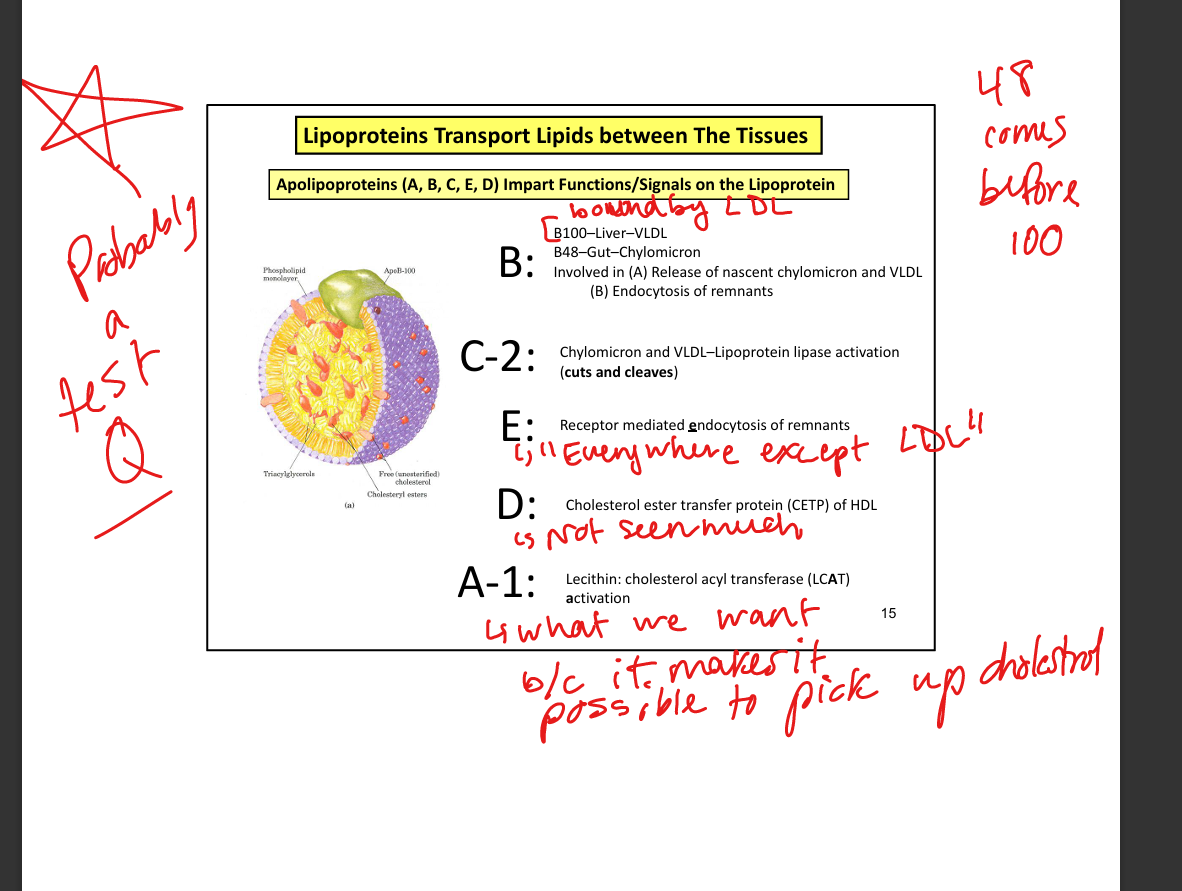
What apolipoprotein mediates remnant uptake by liver?
ApoE

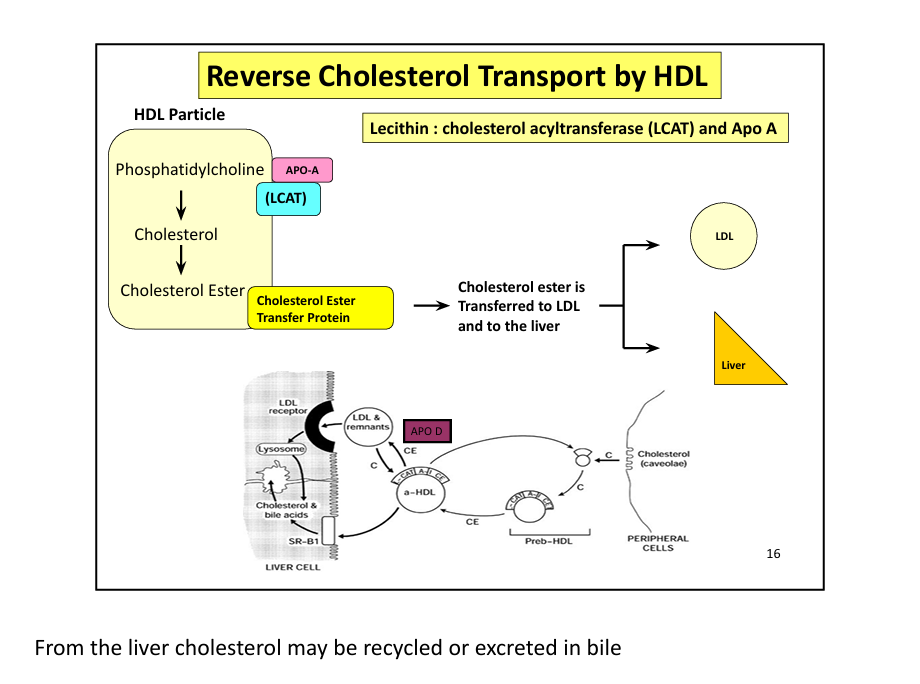
What enzyme esterifies cholesterol in HDL? (the LCAT esterifies me =the MCAT terrifies me)
LCAT (lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase)
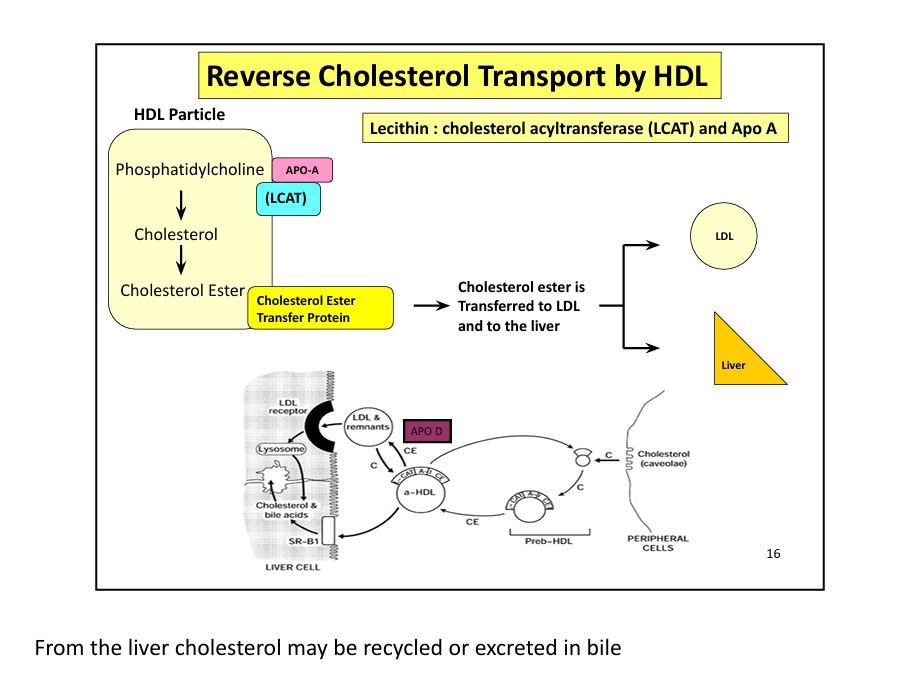

What protein transfers cholesterol esters between lipoproteins?
CETP (cholesterol ester transfer protein)

What is the precursor for cholesterol synthesis?
Acetyl-CoA
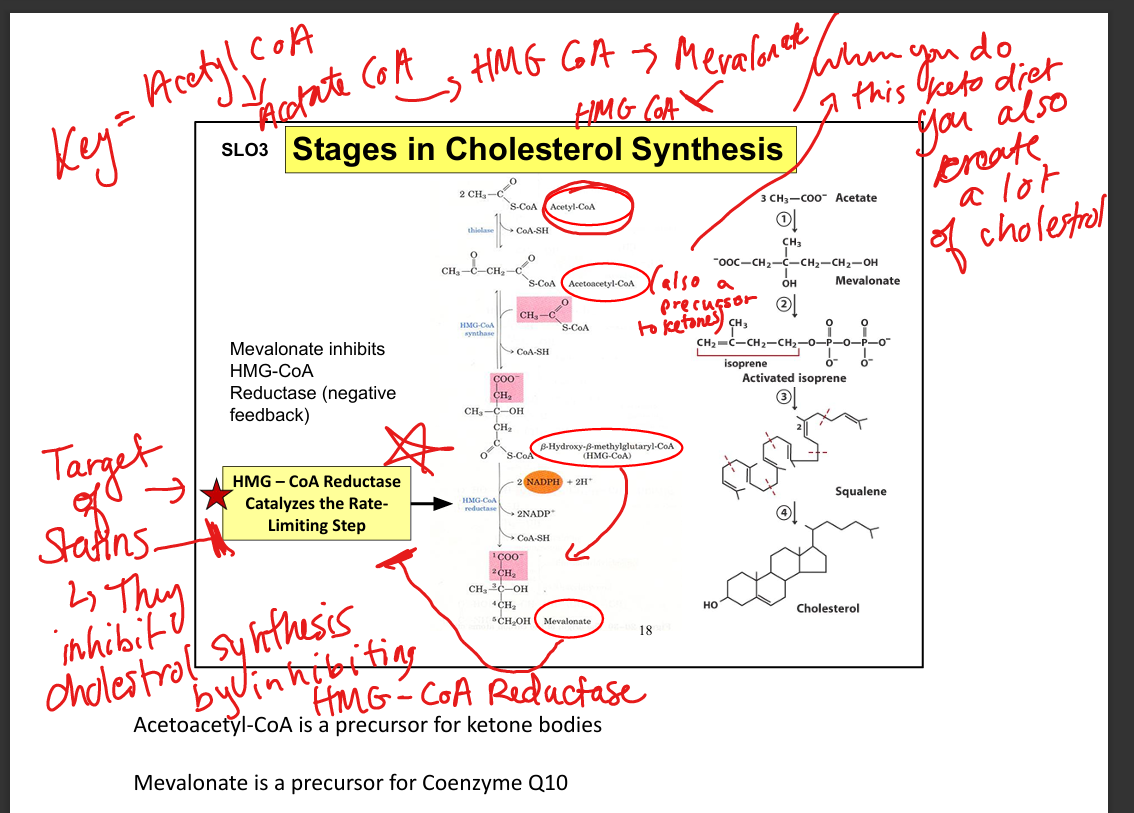

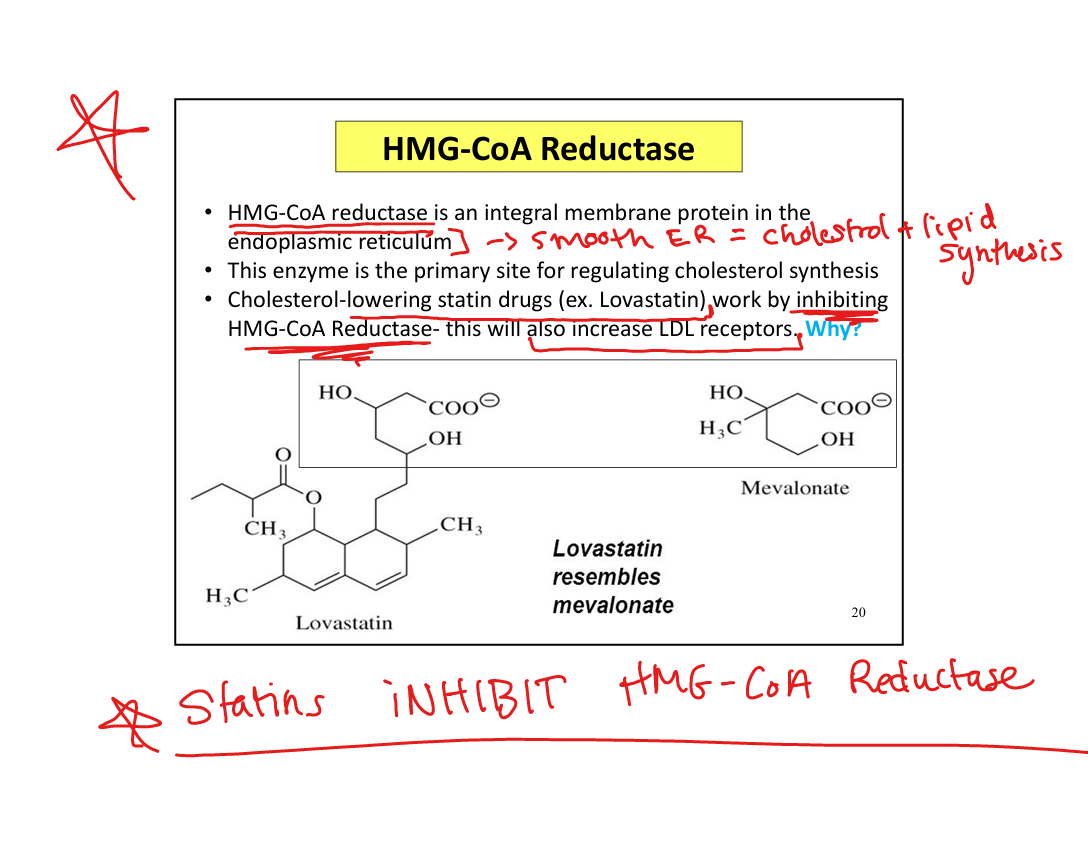
What is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis?
HMG-CoA reductase
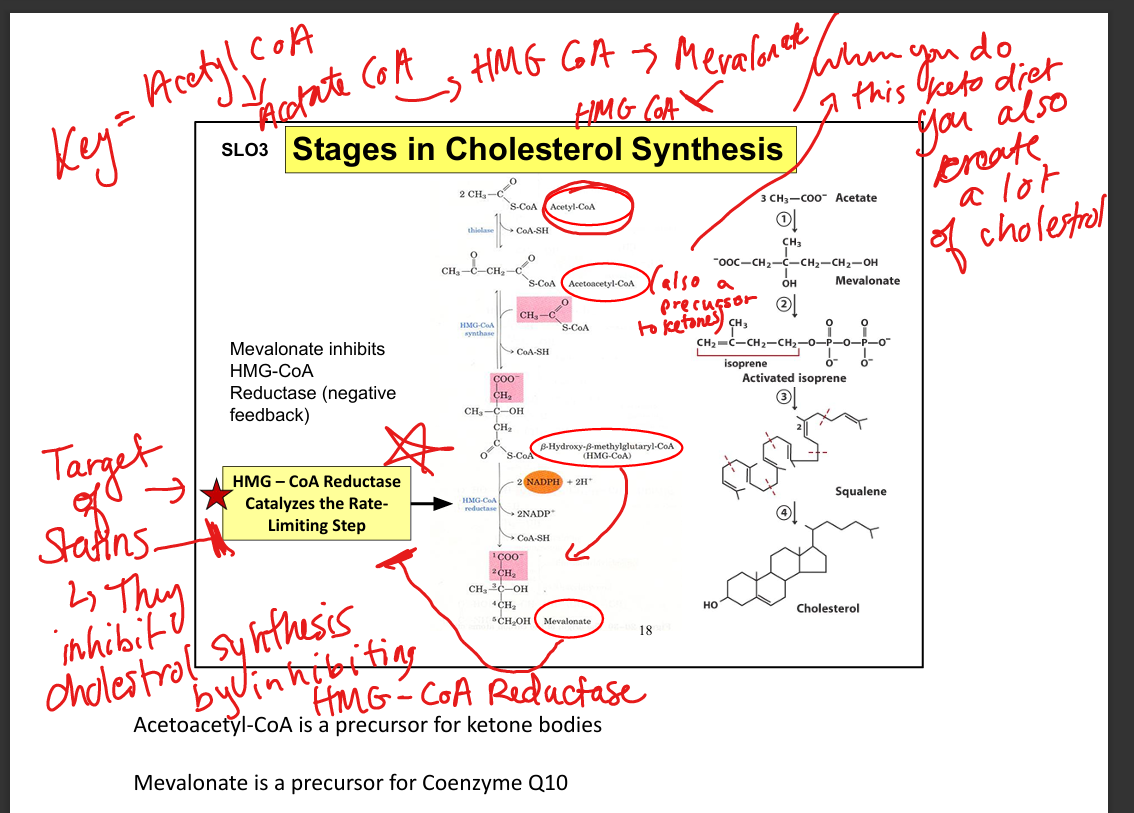

Where is HMG-CoA reductase located?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (makes sense bc lipid+cholestrol formation)
What is the product of HMG-CoA reductase?
Mevalonate
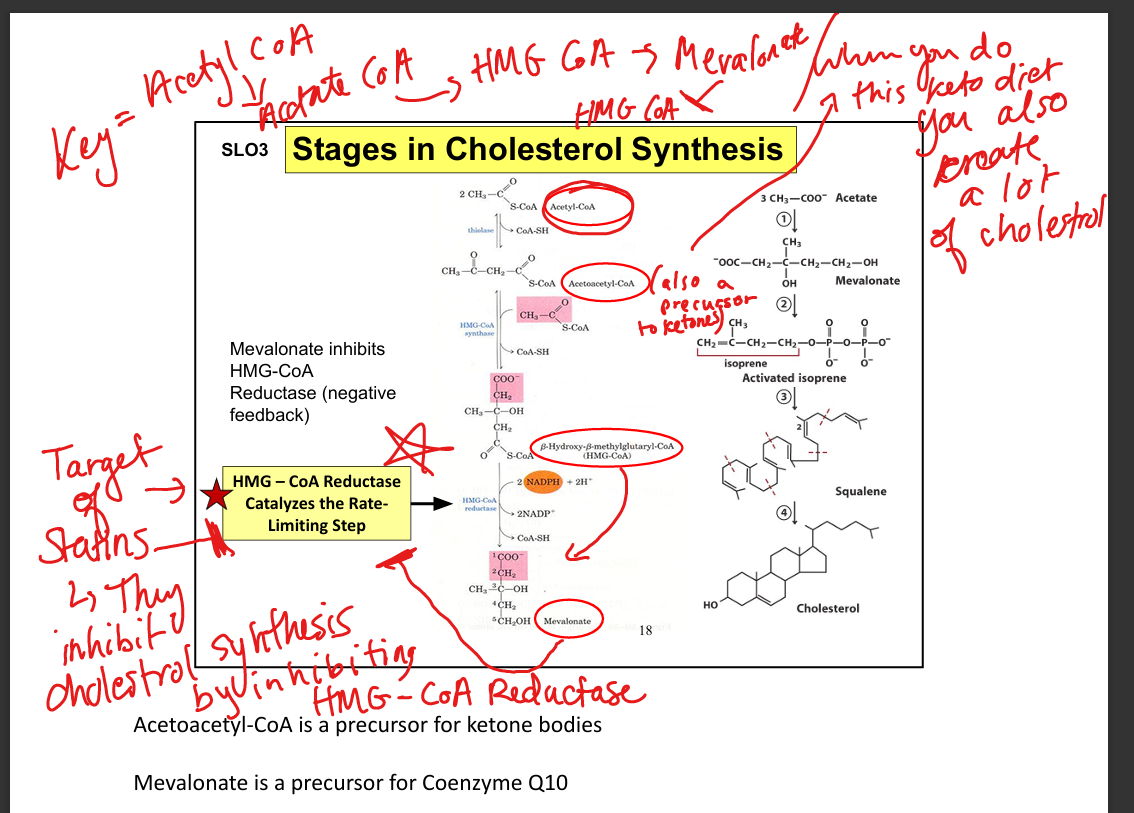

What is the mechanism of statins?
Competitive inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase
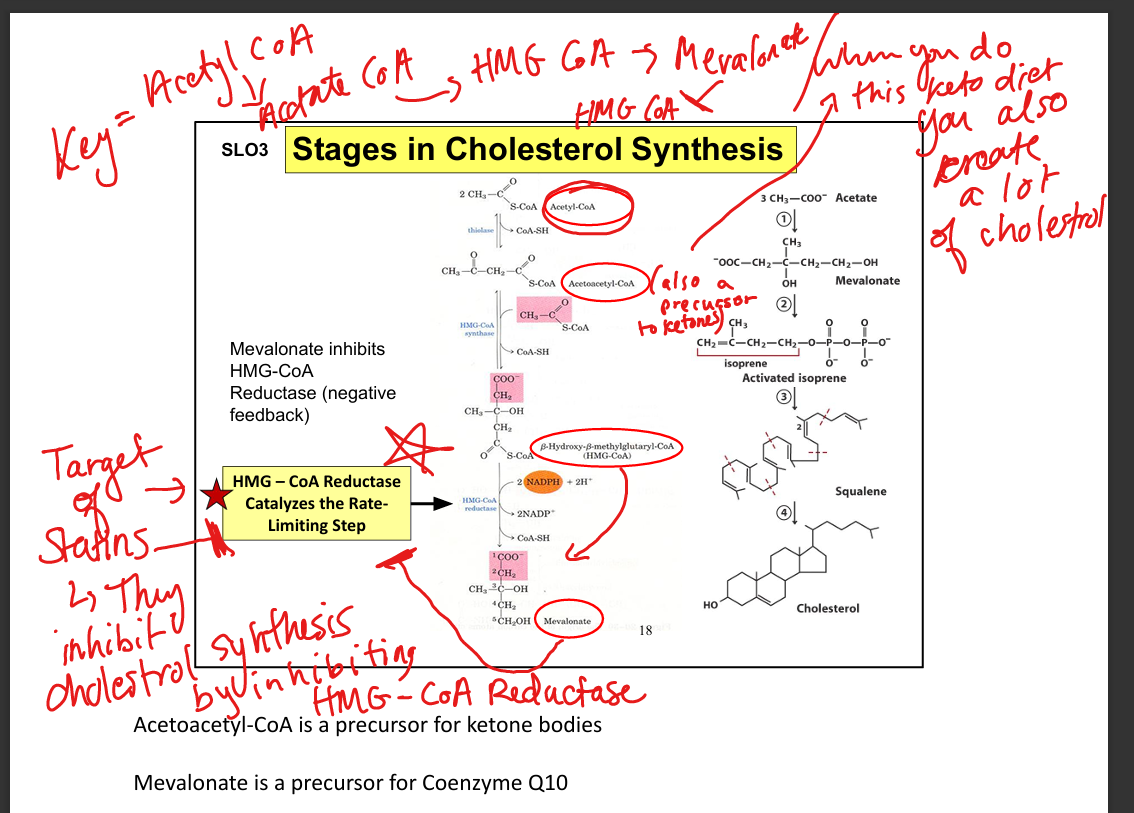

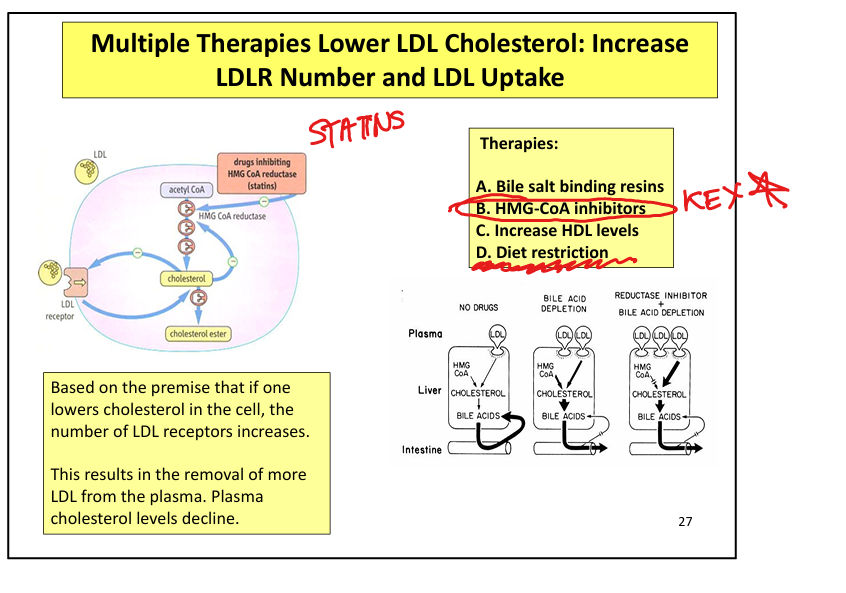
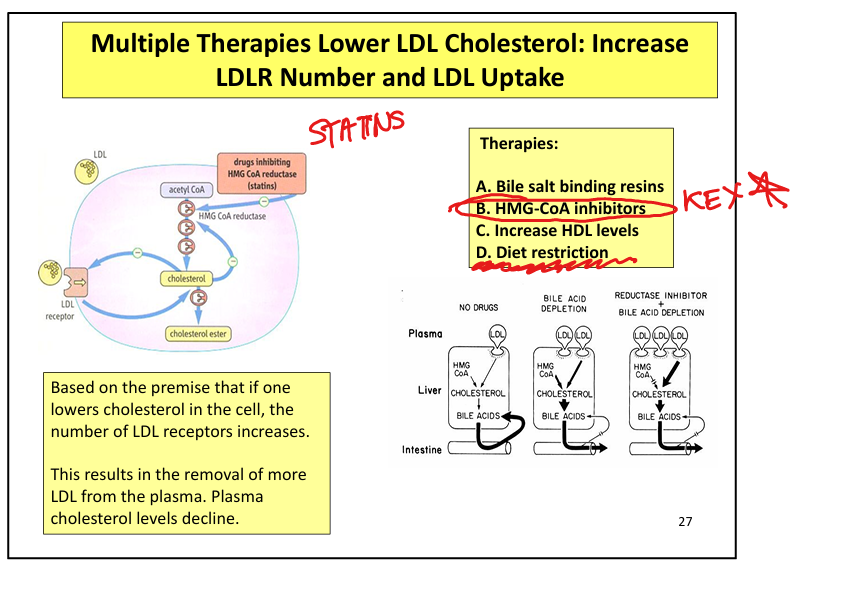
How do statins lower plasma LDL?
↓ intracellular cholesterol → ↑ LDL receptor expression → ↑ LDL clearance

What other molecule is derived from mevalonate?
Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone)
Why might statins cause muscle side effects?
↓ CoQ10 → impaired mitochondrial function (ETC)→ myopathy(muscle weakness)
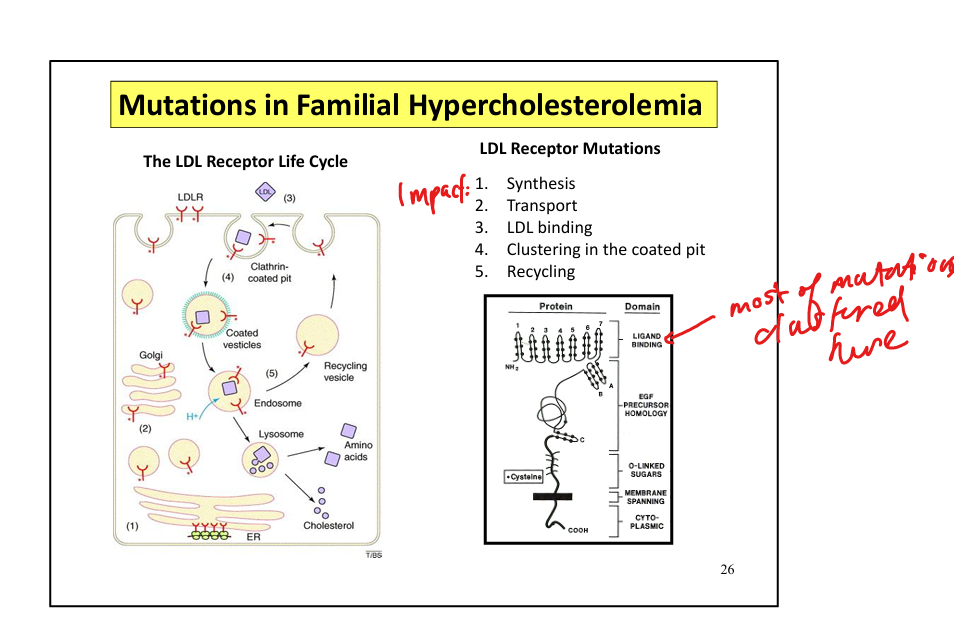
What causes familial hypercholesterolemia (FH)?
Mutations in the LDL receptor gene

What is the inheritance pattern of FH?
Autosomal dominant
What is the effect of LDL receptor deficiency?
↓ LDL clearance → ↑ plasma LDL cholesterol

What physical signs are seen in homozygous FH?
Tendon xanthomas, early-onset atherosclerosis
Why are statins less effective in homozygous FH?
Minimal or absent LDL receptor function
What therapies increase LDL receptor expression?
Statins, bile acid sequestrants

What is the role of LDL receptors?
Mediate endocytosis of LDL particles into cells
What happens to LDL after receptor-mediated endocytosis?
Delivered to lysosomes → cholesterol released