functional anatomy exam #1
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
systems oriented
-International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) - unified language for health and health-related states
-Occupational Therapy Practice Framework (OTPF) - consistent language/concepts to help define role of OT in internal and external audiences
-Standardized language/system for describing health-related states
-Larger contexts can be recognized (e.g., clients who have activity limitations as well as those at risk for them)
-Recognizes a variety of contexts for intervention
-Can enhance universal design for delivery and knowledge (e.g., theoretical models and frames of reference)
conceptual foundations
•ICF ß à OTPF
•ICF
-Demographic Information
-Impairments of Body Functions
-Impairments of Body Structures
-Activity Limitations and Participation Restriction
-Environmental Factors
-Health Information
-ICF Checklist
occupations
meaningful activities
contexts
environmental and personal factors
performance patterns
habits, routines, roles, and rituals
performance skills
motor, process, social interaction
client factors
values/beliefs/spirituality, body structures, body functions
holistic and client centered
-Biopsychosocial Model
-Medical Model - cure/prevent diseases
-Social Model - daily life participation
-Medical and Social models link together
therapist-client collaboration
•Team-approach to solving occupational performance problems
•Identify client priorities throughout OT process
-Assessment
-Intervention
-Education
-Goals
occupation based
•goal is improved functional performance that is meaningful
9 principles of occupation
-Therapeutic agent of change
-Facilitate transfer of skills to contexts
-Motivate change
-Promote self-exploration and identification of values and interests
-Start with current capacity of client
-Promote opportunities to practice skills
-Support most appropriate intervention approach
-Use of feedback to grade performance
-Successful experiences are necessary to achieve goals
evidence based
-Science-driven profession
-Evidence-based Practice - best available evidence to guide decisions and reasoning
factors influencing ot
-Client factors
-Values, beliefs, spirituality
-Body functions
-Body structures
-Performance skills
-Motor, process, social interaction skills
-Performance patterns
-Habits, routines, roles, and rituals
-Context
-Environmental and personal factors
-Activity demands
occupational therapy process
-Evaluation
-Intervention
-Measure of Outcomes
evaluation
-Occupational Profile - AOTA Example
-Analysis of Occupational Performance
-Intervention Plan Development
-Type of Intervention
-Determine Outcome Measures
interventions guided by ...
•occupation-based models and frames of reference - both inform holistic treatment
OTPF INTERVENTION TYPES
-Occupations and Activities
-Interventions to Support Occupations
-Education and Training
-Advocacy
-Group Interventions
-Virtual Interventions
intervention approaches
•Create/Promote - health promotion
•Establish/Restore - remediation, restoration
•Maintain
•Modify - compensation, adaptation
•Prevent - disability prevention
biomechanical approach
-Remediation/Restoration approach
-Change underlying body structures affected by injury, repetitive use, disease, etc.
For...
•Strengthening
•ROM
•Endurance
•Edema
rehabilitation approach
-Compensation and adaptation
-Change task
-Alter method for task completion
-Change task objects
-Change context
-Education
are they biomechanical or rehabilitation?
-establish/restore
-maintain
-modify
-prevent
-establish/restore: biomechanical
-maintain: both
-modify: rehabilitation
-prevent: biomechanical
outcomes
•measurable and should reflect treatment goals
outcome measures
-Valid, reliable, sensitive
-Consistent with targeted outcomes
-Congruent with client goals
-Able to predict actual and future outcomes
-Example - Nine-Hole Peg Test
What are some aspects of movement OT's should consider?
•Types of movement
-AROM vs. AAROM vs. PROM
•Motion terminology
-Flexion, extension, rotation, elevation, etc.
•Normal movement
-How can you tell?
•Abnormal movement
-How can you tell? Why can this be problematic?
types of performance skills
-Positioning the body (e.g., stabilize, aligns)
-Obtaining and holding objects (e.g., reaches, grips)
-Moving self and objects (e.g., coordinates, lifts)
-Sustaining performance (e.g., endures, paces)
types of client factors
-Sensory Functions (e.g., proprioceptive, vestibular functions)
-Neuromusculoskeletal and movement-related functions (e.g., joints, bones, muscle, movement functions)
-Body structures related to movement
formal/standardized movement analysis
-Range of Motion
*Goniometry
-Strength
*MMT, dynamometer, pinch meter
-Posture
*Posture grids
-Sit and stand positioning
range of motion
-goniometry
-measurement in degrees
-passive and active
strength testing
•Manual Muscle Testing (MMT)
-0-5 scale
•Dynamometer
-Grip strength
-Measurement: Typically pounds
•Pinch Meter
-Pinch Strength
-Measurement: Typically pounds
kinesiology
-The study and science of movement
-Includes study of forces
-Includes active and passive body structures
-anatomy and mechanics
what does it take for a human to move?
-Spinal reflexes
-Sensory input (afferent tracts)
-Perceptual processes
-Motor efferent tracts
-Tonic patterned responses (trunk, limbs, head)
-Balance and motor planning
-Movement coordination
-Motor unit recruitment
-Muscle elasticity and contractile abilities
-Joint structure and stabilization
-Motivation
-Cognition
anatomy
active and passive body structures
mechanics
forces and motion
statics
-Objects not in motion
-Objects in motion at constant speed
-Equilibrium
-Sum of forces acting on a body equals zero
external forces acting on the body
-Gravity
-Air
-Water
-Friction
-Other people
-Objects
internal forces acting on the body
-Ligaments
-Bones
-Tendons
-Fascia
-Skin
-Muscle
dynamics
movement
-kinematics and kinetics
kinematics
-Amount and direction of movement, speed, acceleration, joint angles
-Think "movement"
-NO FORCE
-example: ROM and speed
kinetics
-Forces in or on the body
-Stability or mobility
-Think "movement and force"
-example: strength and friction
law of inertia (newtons first law)
-Body at rest or in motion remains at rest or in motion until a changing force is applied
newtons 2nd law
-Acceleration is proportional to magnitude of acting force and inversely proportional to mass of object
newtons 3rd law
-"For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction"
-Equal and opposite forces between objects/bodies acting on each other
what happens when forces change an object
-Deformation
-Temporary or permanent
types of forces
-linear
-shear
torsion
-bending
what are the different force systems
-Parallel Force System (co-planar)
*Same plane, different lines of action
-Linear Force System
*Forces occur along same line of action
*Coracobrachialis
-Concurrent Force System
*Forces meet at one point
*Pectoralis Major
resolution of forces
-Used to determine the combined effect of force
-Different vectors of force influence the overall vector of force
-Horizontal and vertical vectors
friction
-Resistance force
-May provide stability
-May impede movement
factor limiting movement is
coefficient of friction (represents magnitide of friction)
equation for frictional force
frictional force= (coefficient of friction) x (normal force)
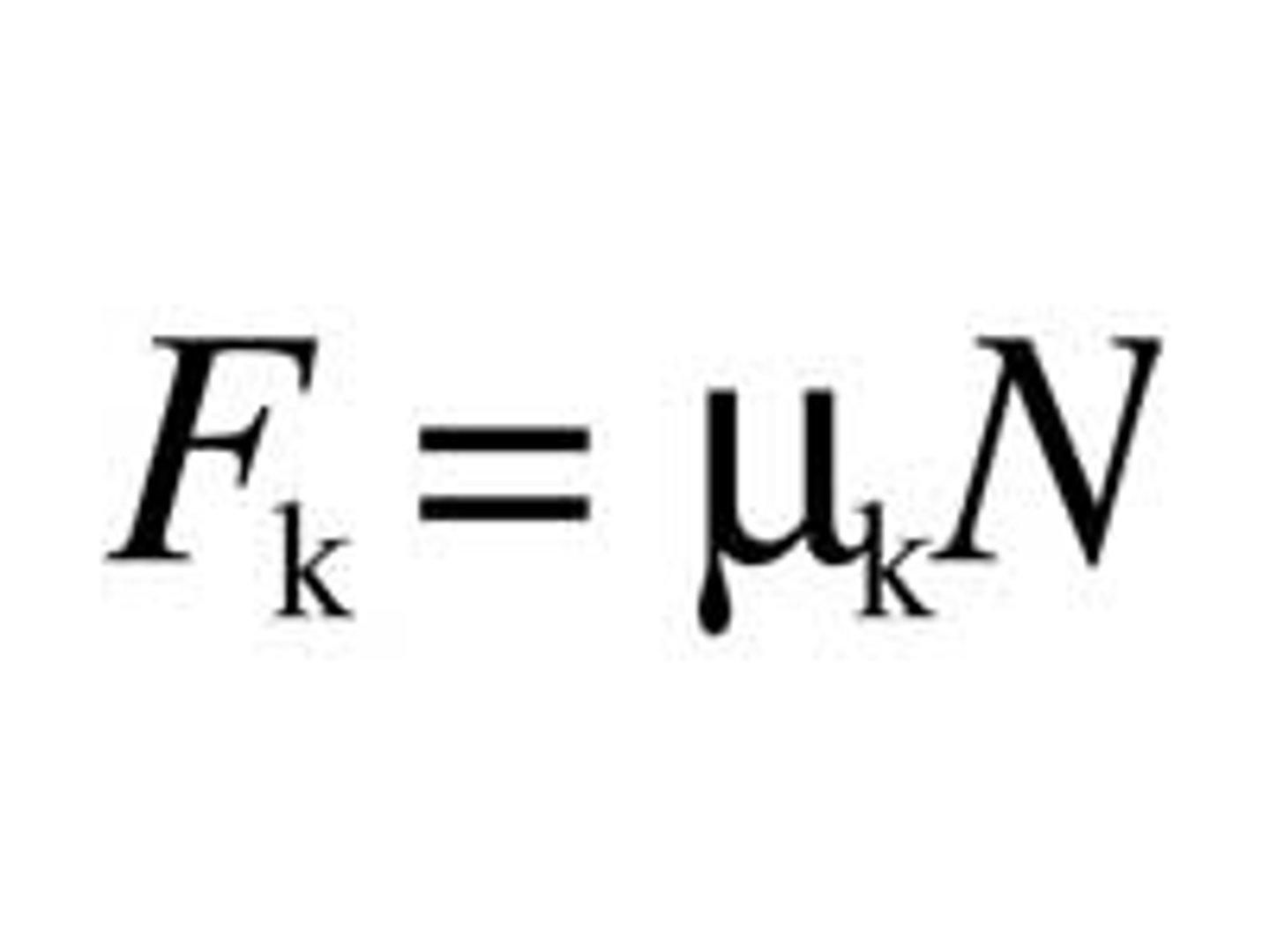
linear and translatory movement
•All parts of object move the same distance, and in the same direction
angular movement
•Movement that occurs around an axis or pivot point
•Segments of the object move various distances, but the same angle and same direction concurrently
•Arm Swing Example
•Parallel force system
force couple
force couple
-2 or more muscles contracting, different linear directions
-Example: upper trapezius, lower trapezius, serratus anterior à scapula rotation
lever
-an object that rotates around an axis when force is applied
levers balance when ...
-Force x Moment Arm = Resistance x Moment Arm
-F x FA = R x RA
types of levers
-first class
-second class
-third class
first class levers
-Forces on opposite sides of each other with axis in the middle
second class levers
-Resistance in the middle, with force and axis on either side
third class
-Effort force in the middle, with resistance and axis on either side
what is the most common lever in the human body
third class lever
torque
-Turning force
-Moment arm
-Perpendicular distance between fulcrum and line of action of force
the higher the torque = the ___ it is to lift
easier
further away from the axis = higher moment arm = _____ force
Lower
equation for torque
force x moment arm
line of force
point at which force is being opened to it; contact point where force is being applied
where the effort is
wheel and axle
-Force application to the wheel causes rotation around the axis
-Radius of the circle is the moment arm
-Example: Scapular rotation
mechanical advantage
-Ability to counteract resistance by applying a force
-Balance
equation for mechanical advantage
-MA = (Force x Moment Arm) / (Resistance x Moment Arm)
-MA = FA / RA
-Good/efficient MA = greater than 1
-Poor/inefficient MA = less than 1
why do second class levers have a significant mechanical advantage?
because effort has a high torque, it tends to always be higher than resistant force
why do third class levers have a minimal mechanical advantage
effort has a lower toque than resistant
what is the advantage of third class levers in the human body
we can reach in different motions and speed; makes us more functional
linear momentum equation
mass x velocity
angular momentum equation
-Mass x Distance from fulcrum x Velocity
-A change in one factor affects momentum greater than linear momentum
pulleys
-Can change the direction of the force
-Can increase mechanical advantage by increasing the moment arm
-Example: Peroneus longus muscle and ankle motion
osteokinematics
•Movement of the bones; angular changes at the joints
•Visible movement
•Planes and axes of movement
-Sagittal Plane
-Frontal/Coronal Plane
-Transverse/Horizontal Plane
arthrokinematics
•Motion of articular surfaces
•Cannot necessarily be visually observed
•Motions
-Rolling
-Knee extension
-Sliding
-Humeral head on glenoid fossa during abduction
-Spinning
-Pronation/Supination (radial head against humeral capitulum)
accessory motion
-Accompanies active motion
-Necessary for motion to occur
-Not voluntarily isolated
-Example:
-Scapular and clavicle movement as humerus is flexed or abducted
synarthrosis
-Immovable (example: skull)
amphiarthrosis
slightly moveable
-intervertebral disk
diarthrosis
freely moveable (elbow/shoulder)
-Uniaxial
*1 axis, 1 degree of freedom
-Biaxial
*2 axes, 2 degrees of freedom
*Condyloid/ellipsoid joint
*Saddle joints
-Triaxial/Multiaxial
*All axes, all movements
closed-pack position
-Maximum surface contact between bones
loose packed positon
joint surfaces do not fit together perfectly
open kinematic chains
-Distal end of chain is open and freely moveable
closed kinematic chains
-Distal end is fixed (or may be on a separate external surface/object)
stability
-Dependent on center of gravity and base of support
center of gravity
-Point where entire weight of body is concentrated
maintaining balance
-CNS function, musculoskeletal function, vision, vestibular function, proprioception, tactile input, visuo-spatial perception, muscle tone, muscular strength and endurance, joint flexibility
when convex surface moves on concave surface, convex surface move in ____ direction as bone segemtn
opposite
when concave surface moves on convex surface, concave surface moves in ____ direction as bone segment
same
kinematic chains
successive segments involving multiple joints
influencing factors of range of motion
-Client factors
-Psychological factors
-Environmental factors
-Skeletal factors
-Methodological and measurement factors
assessment of ROM
-occupational profile
-observation and palpation
-screening and assessment (standardized and non-standardized)
possible contributers to limitations of ROM
-Destruction of bone or cartilage
-Bone Fx
-Foreign body in joint
-Tearing or displacement of intracapsular structures
-Adhesions or scar tissues
-Muscle atrophy or hypertrophy
-Pain
-Psychological factors
-Edema
-Neurological impairment
end feel
•the feel when slight pressure is applied at end PROM of a joint's movement
-soft (soft tissue)
-firm (muscular stretch, capsular, and ligamentous stretch)
-hard (bone against bone)
-empty (pain)
precautions
-May be able to complete, but with caution, care, and following guidelines
contraindications
-not indicated
-do not complete
-not safe to do it
ROM precautions
-Infected/inflamed joints
-Pain medications/muscle relaxants
-Marked osteoporosis
-Hypermobile joints
-Subluxed joints
-Hemophiliacs
-Regions of hematomas
-Bony ankylosis
ROM contraindications
-Dislocations
-Unhealed fracture
-Myositis ossificans
-Immediately following surgery:
-Tendons
-Ligaments
-Muscles
-Joint capsules
-Skin
functional ROM
•Adequate ROM to complete a task
•Can vary between people and tasks
•Documentation: WFL
•Examples:
-Shoulder flexion: 115
-Forearm supination: 15
-Wrist extension: 25
normative ROM
•The typical value
•Documentation: WNL
•Examples:
-Shoulder flexion: 0-180
-Forearm supination: 0-90
-Wrist extension: 0-70
factors influencing strength
-Client factors
-Psychological/psychosocial factors
-Environmental factors
-Muscle factors - healthy and muscle pathologies
-Methodological factors
-Measurement factors