Anatomy & Physiology Quiz #3
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Define articulation
mobile and immobile articulators brought into contact to shape the sounds of speech
the undifferentiated buzz produced by vocal folds is shaped into phonemes in the oral cavity
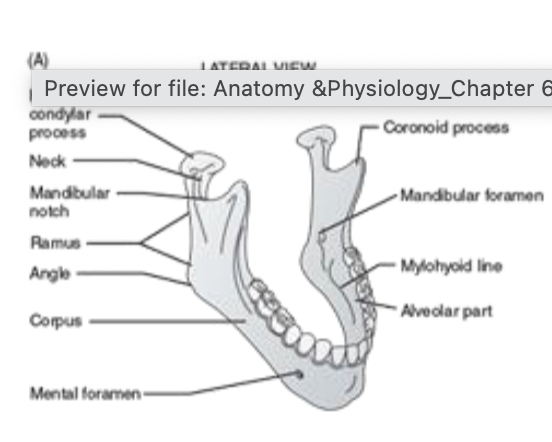
Mandible
lower jaw
sensory innervation for the teeth and gums
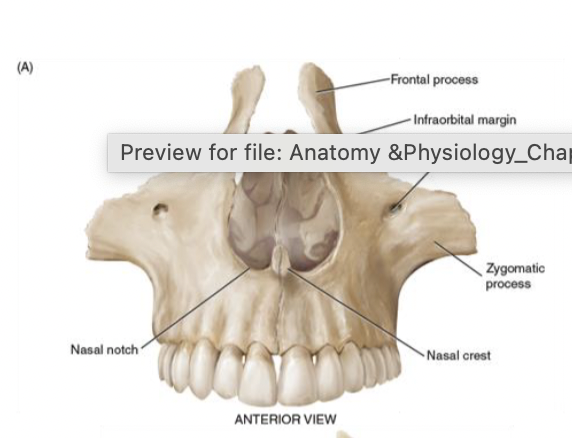
maxillae
compromise the upper jaw
involved in clefting of the lip and hard palate
make up most of the roof of the mouth
support for the eye ball
nasal bone
small
superior nasal surface

nasal conchae
small scroll-like bones on lateral surface of nasal cavity

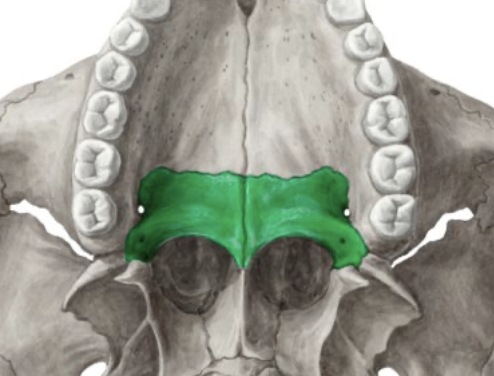
palatine bones
provide posterior ¼ of hard palate
horizontal plate
perpendicular plate: makes up posterior wall of nasal cavity
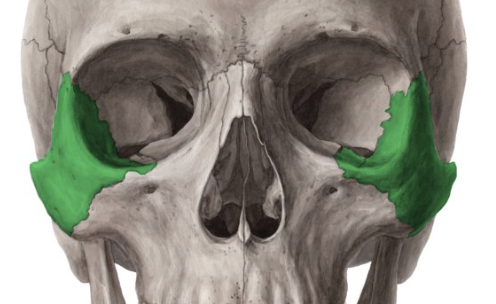
zygomatic bones
forms the cheekbones
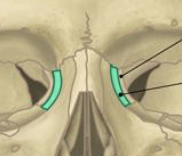
lacrimal bones
almost completely hidden
small portion of the lateral nasal wall
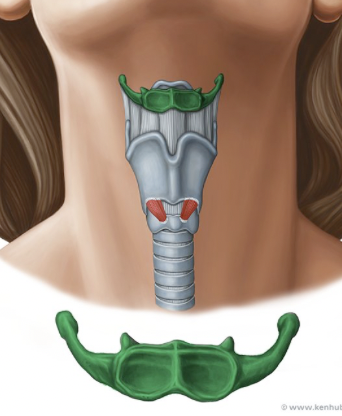
hyoid bone
demonstrates interconnection of the phonatory and articulatory systems
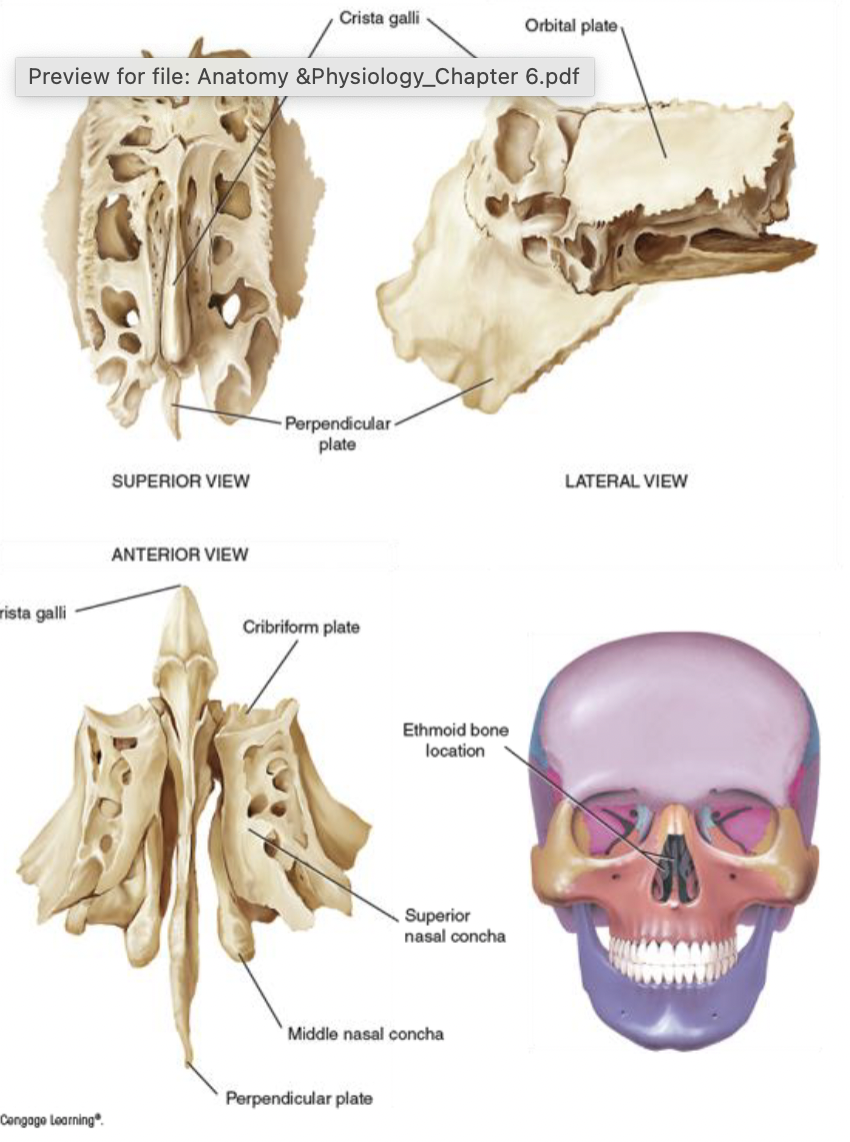
ethmoid bone
the core of the skull and face
complex, delicate structure
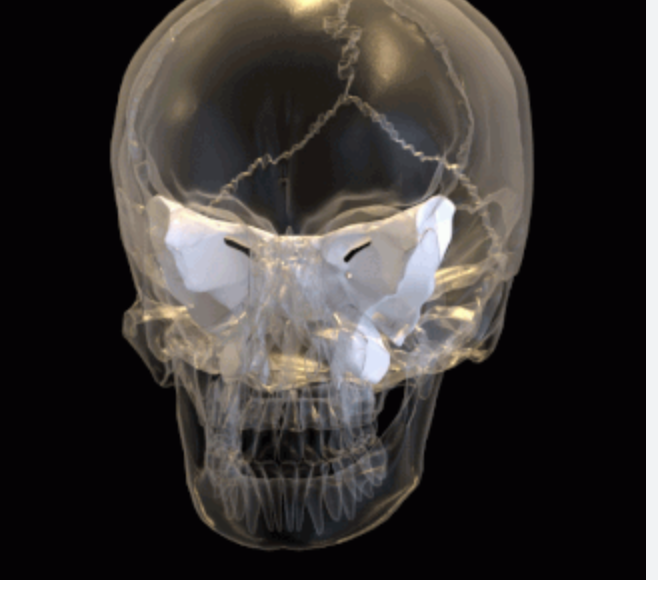
sphenoid bone
located within the brain case
lesser and greater wings
Frontal bone
makes up bony forehead
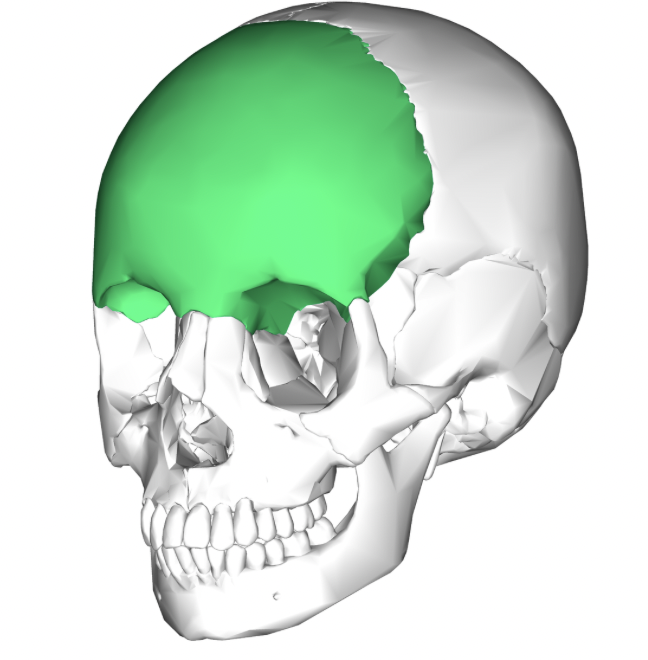
Parietal bone
paired bones form middle portion of the brain case
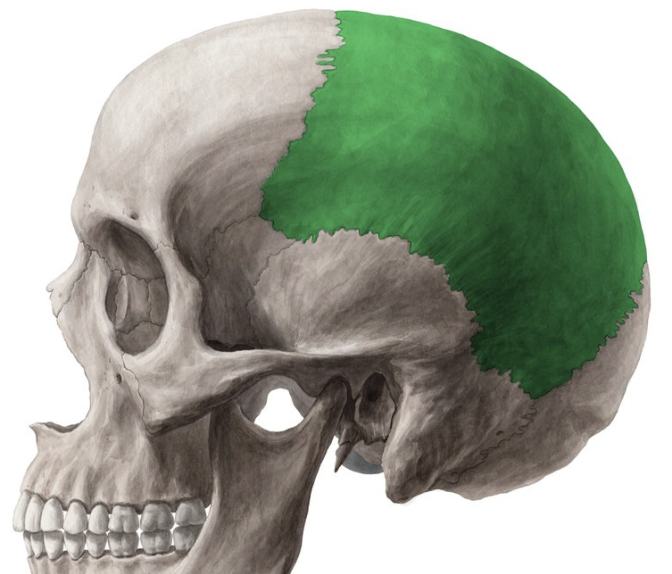
occipital bone
posterior braincase
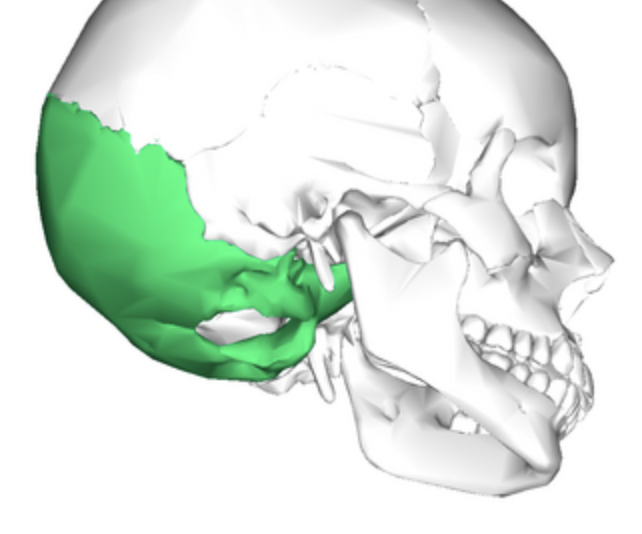
temporal bone
lateral skull
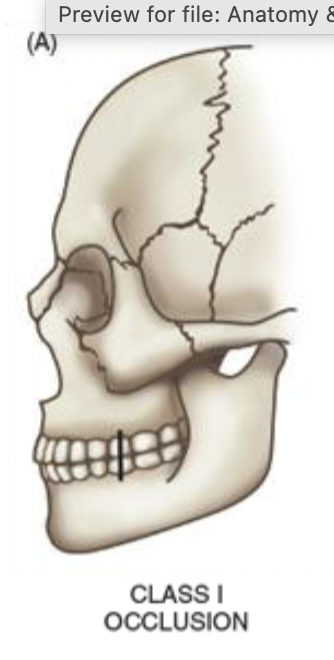
Dental Occlusion
process of bringing upper and lower teeth into alignment
Class I Occlusion
normal orientation of mandible and maxillae - few millimeters of overbite
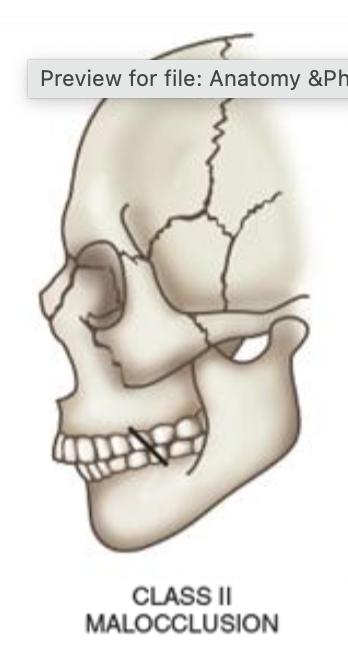
Class II Malocclusion
relatively retracted mandible
may be product of relative micrognathia (undersized jaw)
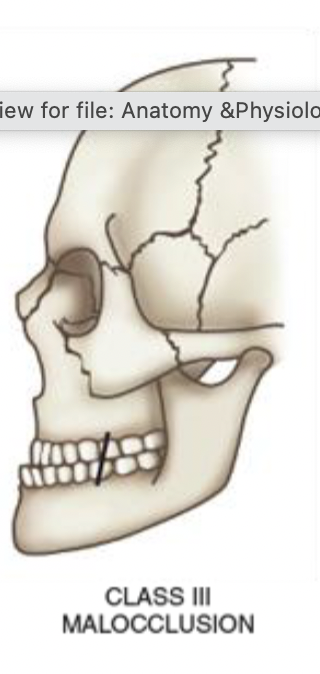
Class III Malocclusion
relatively protruded mandible
Cavities of the Vocal Tract
source filter theory depends upon cavities to shape acoustic output
Oral cavity
most significant of the cavities
undergoes most change during speech act
strongly involved in articulation
shaped by movements of tongue and mandible
Oral Cavity: Hard palate
hard roof of the mouth
Oral Cavity: Velum
soft palate - soft roof of mouth - movable muscle that separates oral and nasal cavities
Oral Cavity: Uvula
terminus of soft palate
Oral Cavity: Anterior and posterior faucial pillars
sides of the velum
Oral Cavity: Palatine tonsils
between faucial pillars
Buccal cavity
plays a role in oral resonance and high level consonant production
lies lateral to oral cavity between teeth and cheeks
Pharyngeal cavity (pharynx)
shaped altered by pharyngeal constrictor muscles, laryngeal elevation, and depression
Types of pharyngeal cavities: oropharynx
posterior to fauces, above is velum
Types of pharyngeal cavities: laryngopharynx (hypoharynx)
anterior epiglottis, inferior esophagus
Types of pharyngeal cavities: nasopharynx
above the soft palate, contains Eustachian tube - aerates the middle ear
Types of pharyngeal cavities: Velopharyngeal port
opening between oropharynx and nasopharynx
Nasal cavities
warms and humidifies air to protect the lungs
fine nasal hairs prevent particles from entering lower respiratory tract
What are the three significant structures for speech?
lips, tongue, and velum
Lip movement:
muscles of the face
Tongue movement:
muscles of tongue, mandible, and hyoid
Velum movement:
muscles of oral and nasal regions
Lip muscles: obicularis oris
encircle mouth opening
Lip muscles: Risorius
retracts corner of mouth
Lip muscles: Buccinator
deep to risourius, retracts corner of mouth, involved in mastication
Lip muscles: Zygomatic major
elevate and retract angle of the mouth, smiling
Lip muscles: mentalis muscle
elevates and wrinkles chin, pulls lower lip outpout
Lip muscles: Platysma
depresses mandible
Muscles of tongue: mastication and deglutition
extrinsinc muscles - move tongue in desired direction
intrinsic muscles - fine control of articulatory gestures
Regions of Tongue: dorsum
superior surface
Regions of Tongue: tip/ apex
most anterior portion
Regions of Tongue: base
resides in oropharynx
Regions of Tongue: Root
pharyngeal portion
Intrinsic Lingual muscles: superior longitudinal
elevate tongue tip
Intrinsic Lingual muscles: inferior longitudinal
pulls tongue tip down
Intrinsic Lingual muscles: transverse muscle
narrows tongue
Intrinsic Lingual muscles: vertical muscles
flatten tongue
Extrinsic Lingual muscles: genioglossus
prime tongue mover
Extrinsic Lingual muscles: hyoglossus
pulls sides of tongue down
Extrinsic Lingual muscles: styloglossus
draw tongue back and up
Extrinsic Lingual muscles: chondroglossus
tongue depressor (part of hyoglossus)
Extrinsic Lingual muscles: palatoglossus
evades back of tongue, makes up anterior faucial arch
Mandibular elevators: masseter
elevates mandible
Mandibular elevators: temporalis
elevates mandible and draws it back if protruded
Mandibular elevators: medial pterygoid
elevates mandible
Mandibular:
muscle of protrusion
Lateral pterygoid
protrudes mandible - grinding action
Mandibular depressors: digastricus
anterior and posterior - depresses mandible
Mandibular depressors: mylohyoid
depresses mandible if hyoid fixed
Mandibular depressors: geniohyoid
depresses mandible if hyoid fixed
Velum muscles: soft palate (velum)
combination of muscle, nerves, tissues, and blood supply covered by mucous muscle
Muscles of the Velum:
depressed for nasal sounds “m,n,ng”
elevate structure to completely separate oral and nasal areas: during most speaking time and when swallowing
Velar Elevators: levator veli palatini
makes up bulk of soft palate; primary elevator of the soft palate
Velar Elevators: musculus uvulae
muscle embodies in uvula which makes up medial and posterior portion of soft palate - shortens the soft palate
Eustachian tube dilator - tensor veli palatini
opens auditory tube to permit aeration of the middle ear cavity
Velar Depressors: