Muscle Physiology/Histology [COMPLETE]
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcard set created to help GAC students with ANAT exam 2 with Harbitz.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Name the 3 types of muscle.
Skeletal (striated, voluntary)
Cardiac (striated, involuntary)
Smooth (non-striated, involuntary)
What are three functions of the skeletal muscle?
Produce joint movement
Support soft tissues
Store nutrient reserves
Connective tissue in muscles.
Dense regular connective tissue proper — becomes tendon at the end of muscle.
Epimysium - surrounds outside of muscle (separates muscle from other structures)
Perimysium - surrounds fascicles (bundles of cells)
Endomysium - surrounds fibers
Organization of a skeletal muscle (from biggest to smallest)
Muscle — fascicles — fibers (cells) — myofibrils (multiple sarcomeres) — myofilaments (actin and myosin)
What are skeletal muscle fibers?
Very long cells, with hundreds of nuclei, and made through the fusion of myoblasts in utero
Muscle terminology - Fiber =
Cell
Muscle terminology - Sarcoplasm = ?
Cytoplasm
Muscle terminology - Sarcolemma = ?
Plasma membrane
Muscle terminology - Sarcoplasmic reticulum = ?
Ca++ storage organelle
What is a sarcomere? What is it made of?
Sarcomere is the smallest/basic functional unit of skeletal muscle. It is made up of 2 Z-discs and the actin and myosin filaments between them.
Muscle terminology - Myofilament = ?
Multiple sarcomeres connected end to end.
ATP production.
Muscle cells store enough ATP for a second contraction. After that, it must be made.
ATP can be recycled with the use of creatine phosphate.
ADP + creatine phosphate = ATP + creatine (enzyme used is creatine phosphokinase)
ATP + creatine = ADP + creatine phosphate
How long can last the production of ATP?
About 15 seconds.
Anaerobic glycolisis
Production of ATP from glucose without the use of oxygen.
Produces enough ATP to keep muscle functioning a little while longer.
Causes build up of lactic acid.
Aerobic metabolism.
Production of ATP from glucose, fat, or protein with the use of oxygen.
Uses the Kreb’s Cycle to produce a lot of ATP
Can sustain muscle fiber contraction for long periods of time
Slow twitch and fast twitch muscle fibers.
Slow Twitch fibers - have high aerobic capacity, slow contraction, less powerful than Ft fibers, small motor units.
Fast Twitch A fibers - medium aerobic capacity and high anaerobic capacity, fast contraction speed.
Fast Twitch B fibers - low aerobic capacity and high anaerobic capacity, fast contraction speed, and large motor units
Muscle hypertrophy.
Muscle growth from heavy training
Increases diameter of muscle fibers
Increases number of myofibrils (actin and myosin)
Increases mithochondria, glycogen reserves
Muscle atrophy
Lack of muscle activity. Reduces muscle size, tone, and power
Motor unit
Motor neuron and muscle fibers it innervates
What do small motor units control?
Fine motor control
What do large motor units control?
Strength
Length-tension relationship of skeletal muscles.
If a muscle and its fibers and sarcomeres are overly shortened at the beginning of contraction, less force (tension) can be produced.
If a muscle and its fibers and sarcomeres are overly stretched at the beginning of contraction, less force (tension) can be produced.
If a muscle and its fibers and sarcomeres are just the right length with some overlap of actin and myosin, but not too much, then the maximal amount of tension can be produced. “The Goldylocks zone”
What are the 3 phases of a muscle fiber twitch?
Latent phase
Contraction phase
Relaxation phase
What is the relationship between stimulus frequency and tension production?
Higher stimulus frequency = more tension production
What are the parts of a muscle?
Origin - fixed end
Belly - where all the fibers are (middle)
Insertion - movable end
What are the skeletal muscle shapes?
Parallel
Convergent
Circular
Pennate
Unipennate
Bipennate
Multipennate
** Bipennate produces more tension because there are more muscle fibers/unit area
Describe muscles and their actions.
Agonist (prime-mover) does the action. E.g., biceps brachii - flexes elbow
Synergist helps the prime mover to do the action (brachialis)
Antagonist is the muscle that opposes the action and must relax for action to occur (e.g, triceps brachii)
Fixator prevents movement at another joint (rotator cuff, deltoid, rhomboids)
Describe the types of muscle contraction.
Isometric - tension production without a change in length
Isotonic - tension production with a change in length
Concentric - shortening of the muscle
Eccentric - lengthening of the muscle
Define intrinsic muscles.
Intrinsic muscles are located within the structure or region they act on.
Define extrinsic muscles.
Extrinsic muscles are located outside the structure or region they act on.
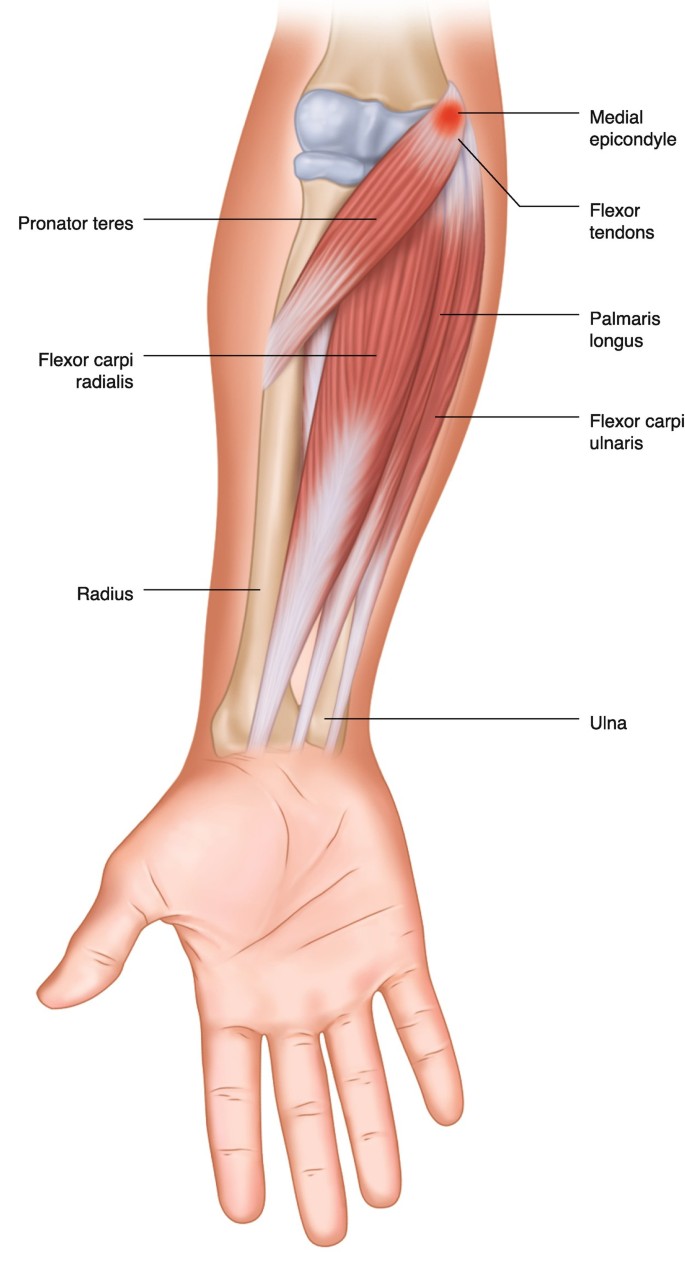
Common flexor and extensor origin for wrist and hand muscles.
Flexor - medial epicondyle of humerus
Extensor - lateral epicondyle of humerus
Anterior muscles acting on the hip.
Ilipsoas - primary hip flexor
Lateral thigh muscles
Tensor fasciae latae
Iliotibial band
Gerdy’s tubercle
Flexors of the knee
Hamstring muscles
biceps femoris
semitendinosis
semimembranosis
Extensors of the knee
Quadriceps muscles
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedius
Sartorius - “tailor’s muscle”
Crosses leg
Gracilis
Adductor muscle of hip
Define Pes Anserine.
A structure on the inner side of the knee where three tendons converge and attach to the Tibia.
It is the point of insertion of three muscles: Sartorius, Gracilis, and Semitendinosis.
Define Pes Anserine Bursitis.
Occurs when the bursa inside your knee joint becomes irritated and inflamed.
Compartments of the leg.
Anterior
Lateral
Deep posterior
Superficial posterior