The Vascular system: Arterioles and Control of Arteriolar Smooth Muscle
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
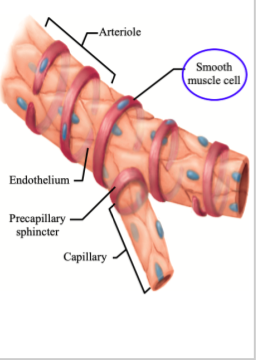
Arterioles function
in individual organs, determine relative blood flow to the organ at any given mean arterial pressure
All together are the major factor in determining mean arterial pressure (MAP)
causes drop in MAP as distance from heart increases
Circular smooth muscle
state of contraction can be regulated
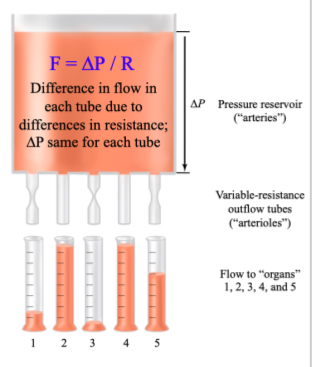
Arterioles and resistance to blood flow
Vasodilation
Vasoconstriction
High resistance vessels due to small size
altering arteriolar diameter alters resistance and flow
Vasodilation → relaxation of arteriole smooth muscle
increased blood flow to organs
Vasoconstriction → contraction of arteriolar smooth muscle
decreases blood flow to organs
Arterioles and resistance to blood flow
intrinsic or basal tone
Intrinsic or basal tone
Arteriole smooth muscle is partially contracted in the absence of external factors
Other factors can increase or decrease the state of contraction to cause vasoconstriction or vasodilation
Arterioles and resistance to blood flow
Extrinsic or intrinsic factors alter basal tone
Extrinsic → factors external to the organ or tissue; whole body needs (MAP); nerves and hormones can affect constriction of arterioles muscles
Intrinsic → local controls; organs and tissues alter their own arteriolar resistances independent of nerves or hormones, not whole body only certain organs and tissues
External controls of ANS
Sympathetic neurons
Parasympathetic neurons
Noncholinergic, nonadrenergic neurons
Sympathetic neurons
arterioles innervated by sympathetic postganglionic neurons
NE → vasoconstriction (a-adrenergic receptors)
Can be used to cause vasodilation
Sympathetic tone can be increased (vasoconstriction) or decreased (vasodilation)(in addition to vessel’s intrinsic/ basal tone)
To vasodilate: decrease rate of sympathetic activity to below the basal level
Regulating MAP
Parasympathetic neurons
little/no parasympathetic innervation of arterioles
Noncholinergic, nonadrenergic neurons
NO (nitric oxide) → vasodilation
Extrinsic controles: Hormones
epinephrine from adrenal medulla
Arteriolar smooth muscle may contain both adrenergic receptor subtypes (α/β)
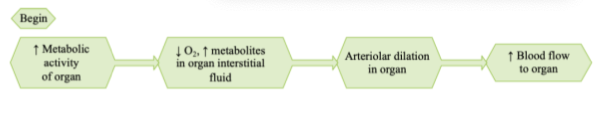
Local Controls: Active hyperemia
Arteriolar smooth muscle is sensitive to local chemical changes (e.g. O2, CO2, H+)
Local chemical changes are the result of changes in metabolic activity
Increased metabolic activity
results in vasodilation of arterioles and increased blood flow
no nerves or hormones involved
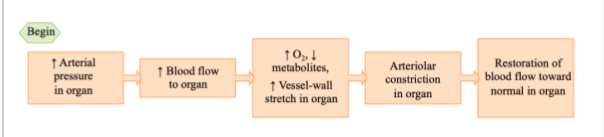
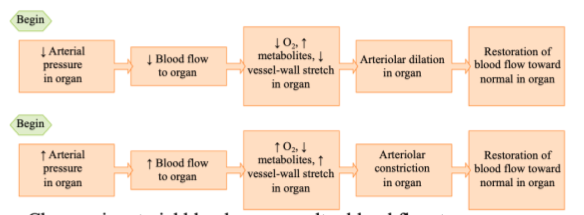
Local Controls: Flow Autoregulation
changes in arterial blood pressure alter blood flow to an organ
changes the concentration of local chemicals (e.g. O2, CO2, H+)
Arterioles change their resistance to maintain constant blood flow in the presence of a pressure change
Constant metabolic activity
No nerves or hormones involved
Local Controls: Flow Autoregulation
Flow autoregulation may also be mediated by the myogenic response
direct response of arteriolar smooth muscle to stretch