BSC2086L E.11 Digestive System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Last updated 2:29 AM on 4/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
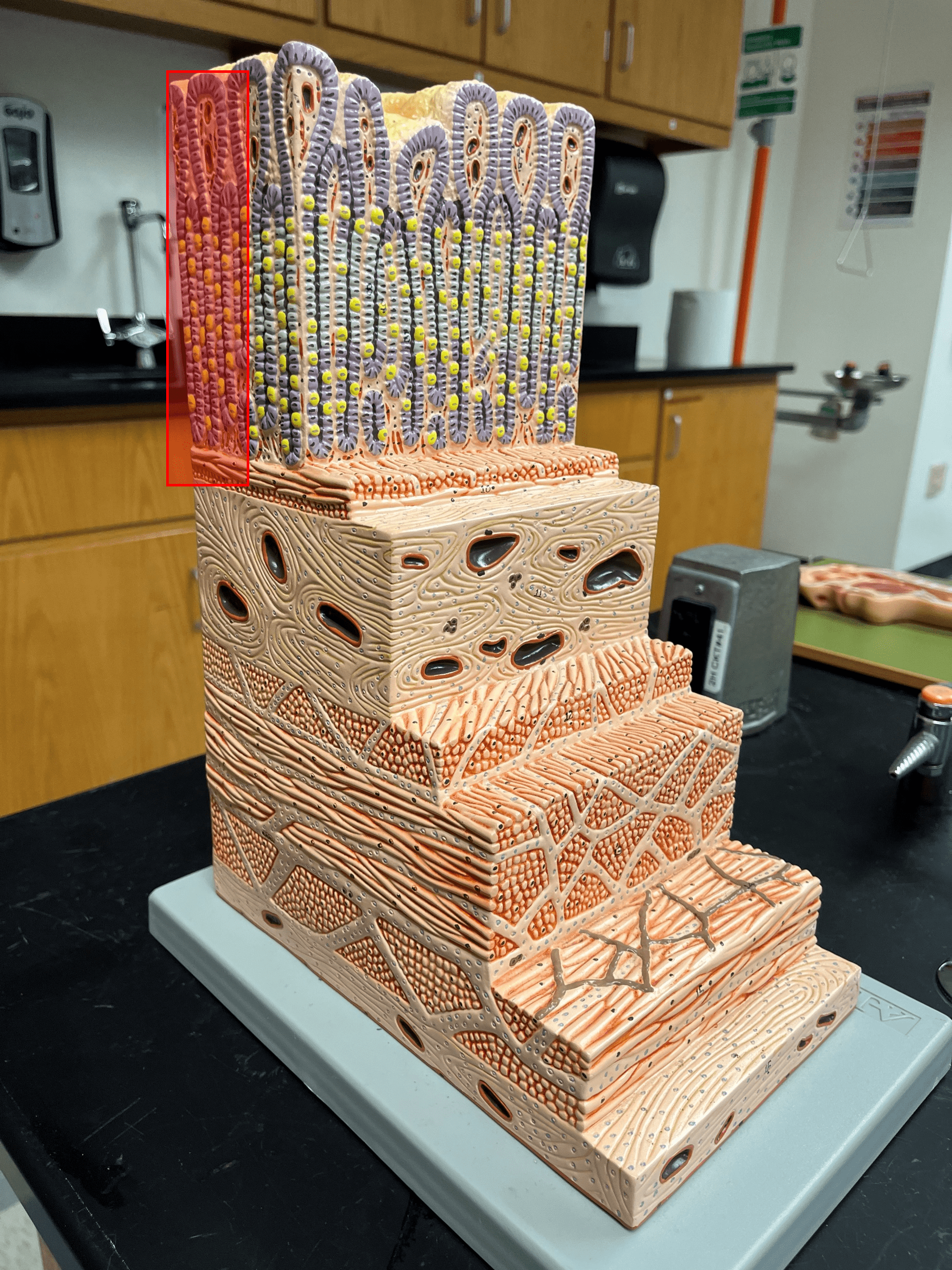
New cards
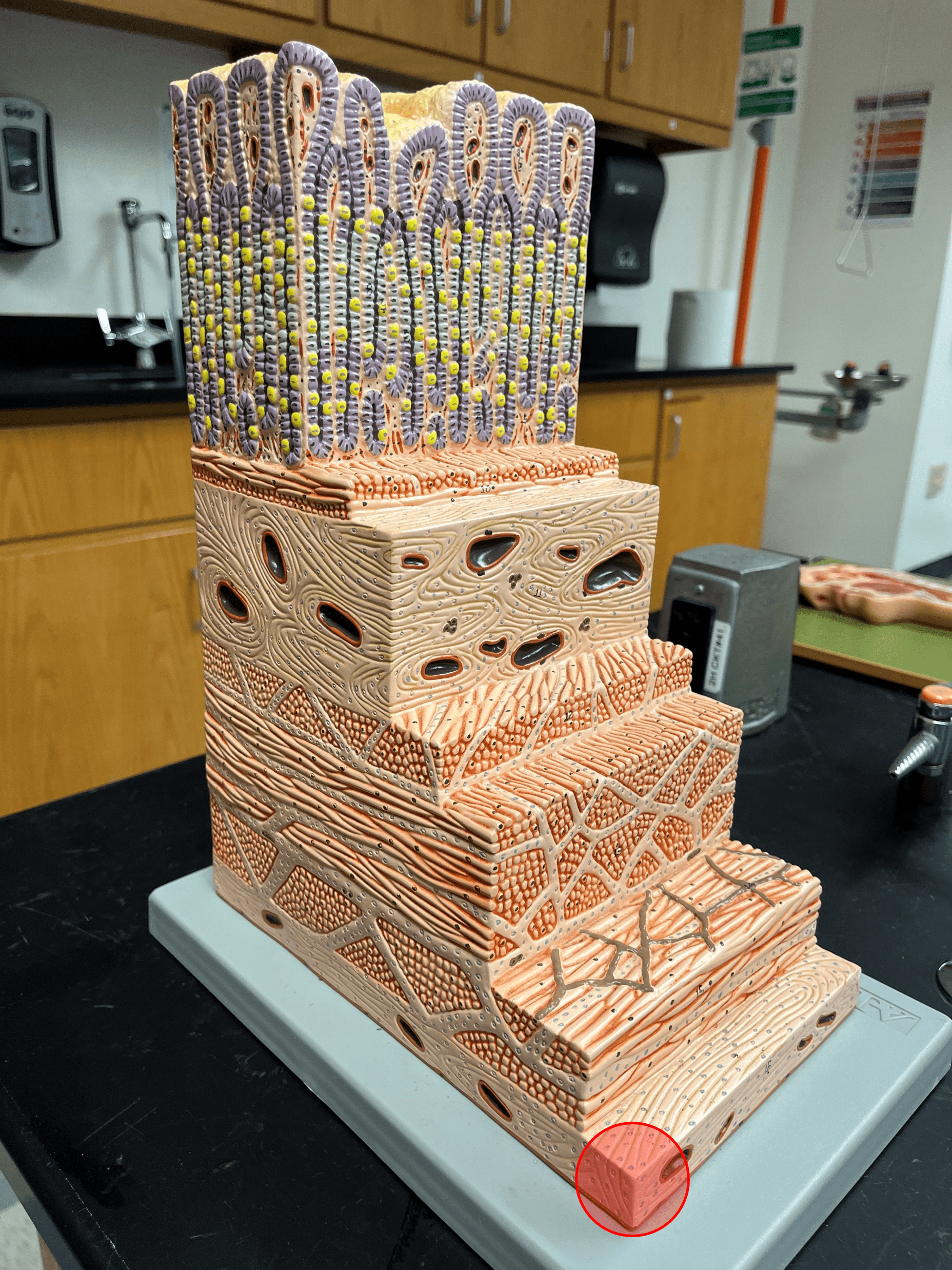
mucosa
• The deepest layer of the gastrointestinal tract.
• Superficial to the submucosa.
• Composed of a lining epithelium, the lamina propria, and the muscularis mucosae.
• Superficial to the submucosa.
• Composed of a lining epithelium, the lamina propria, and the muscularis mucosae.

2
New cards
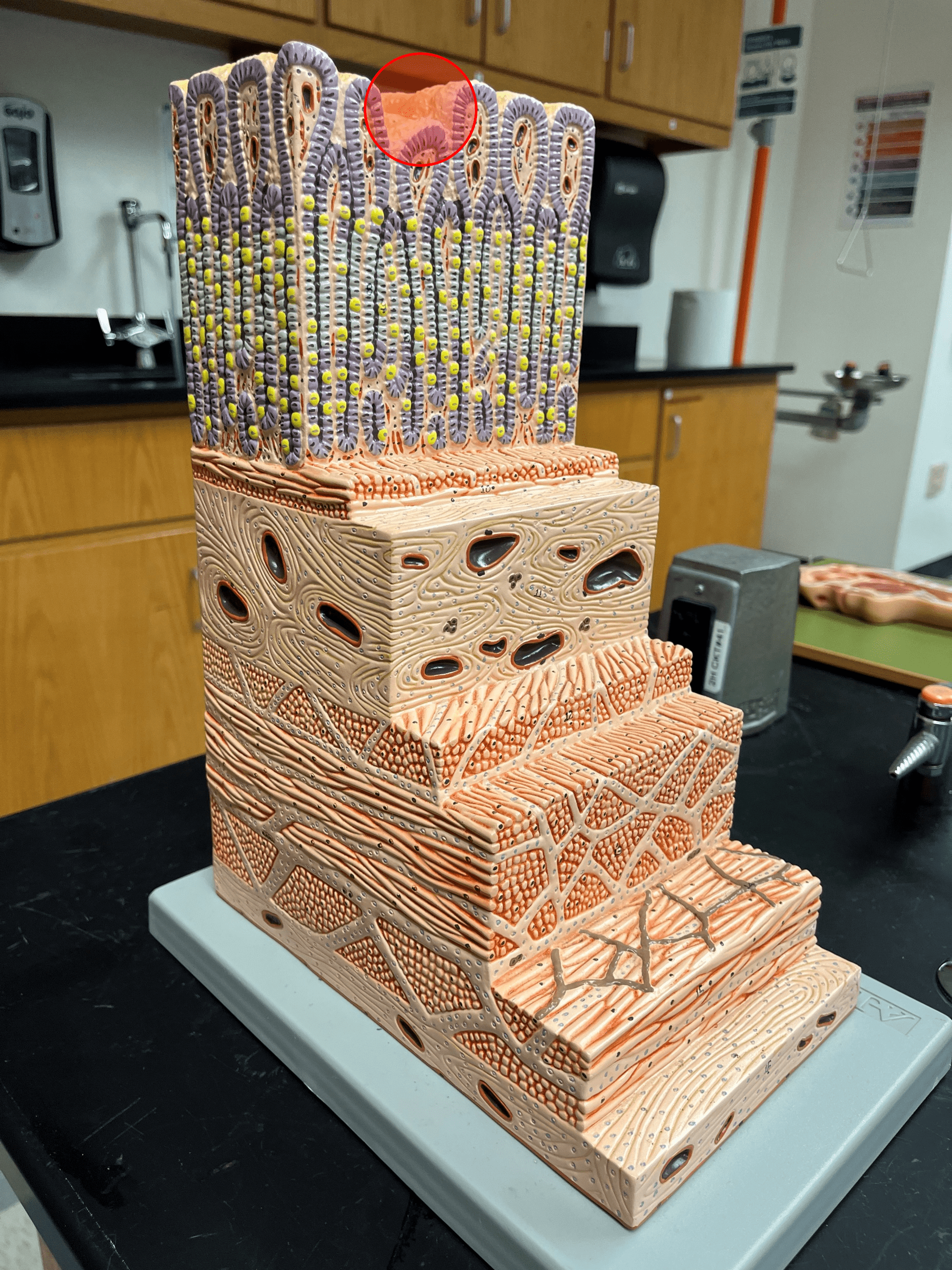
lining epithelium
• The deepest layer of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract.
• Kept moist by the secretion of mucus.
• Kept moist by the secretion of mucus.
3
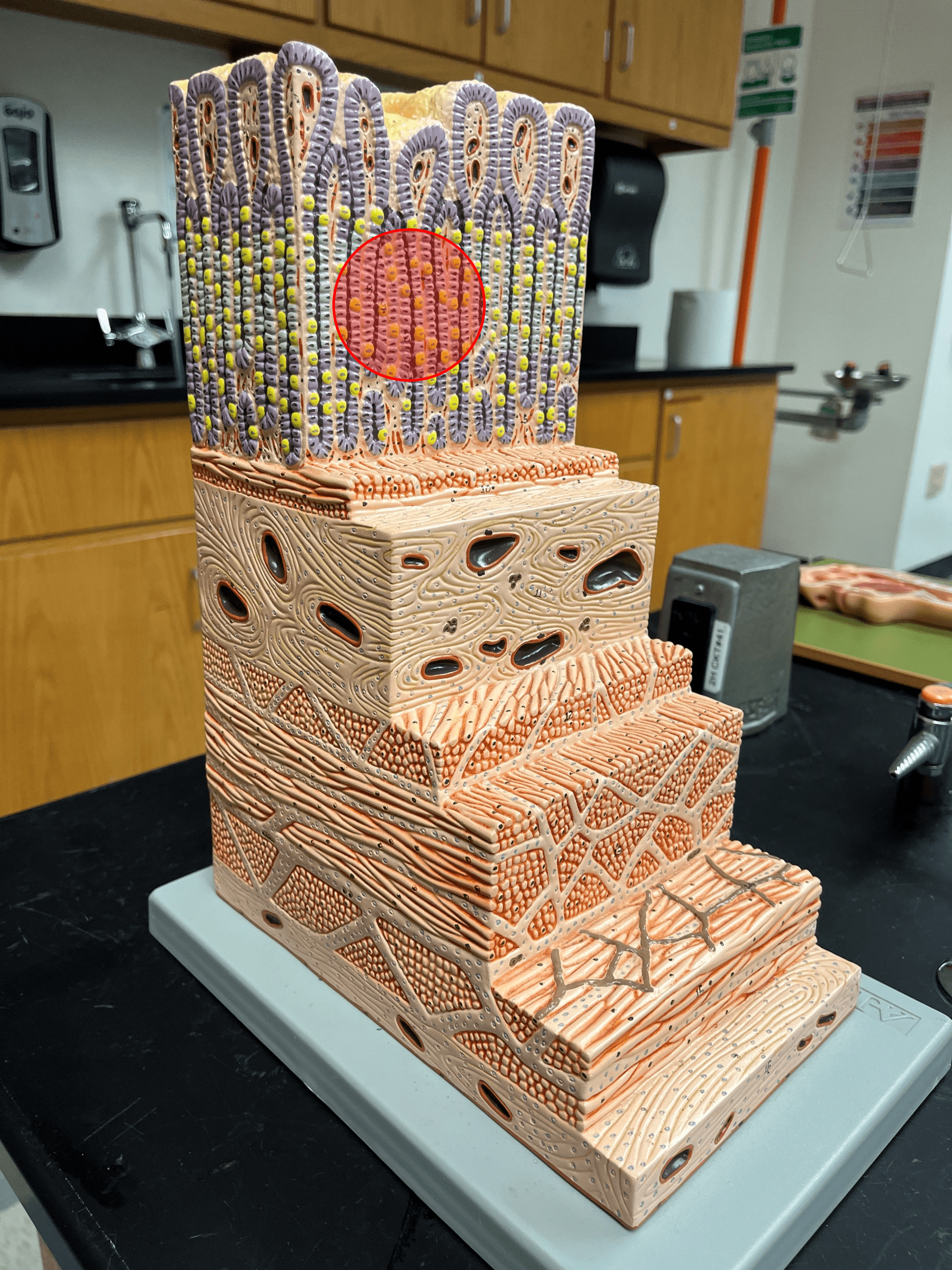
New cards
lamina propria
• The middle layer of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract.
• The connective tissue layer of the mucosa.
• The connective tissue layer of the mucosa.
4
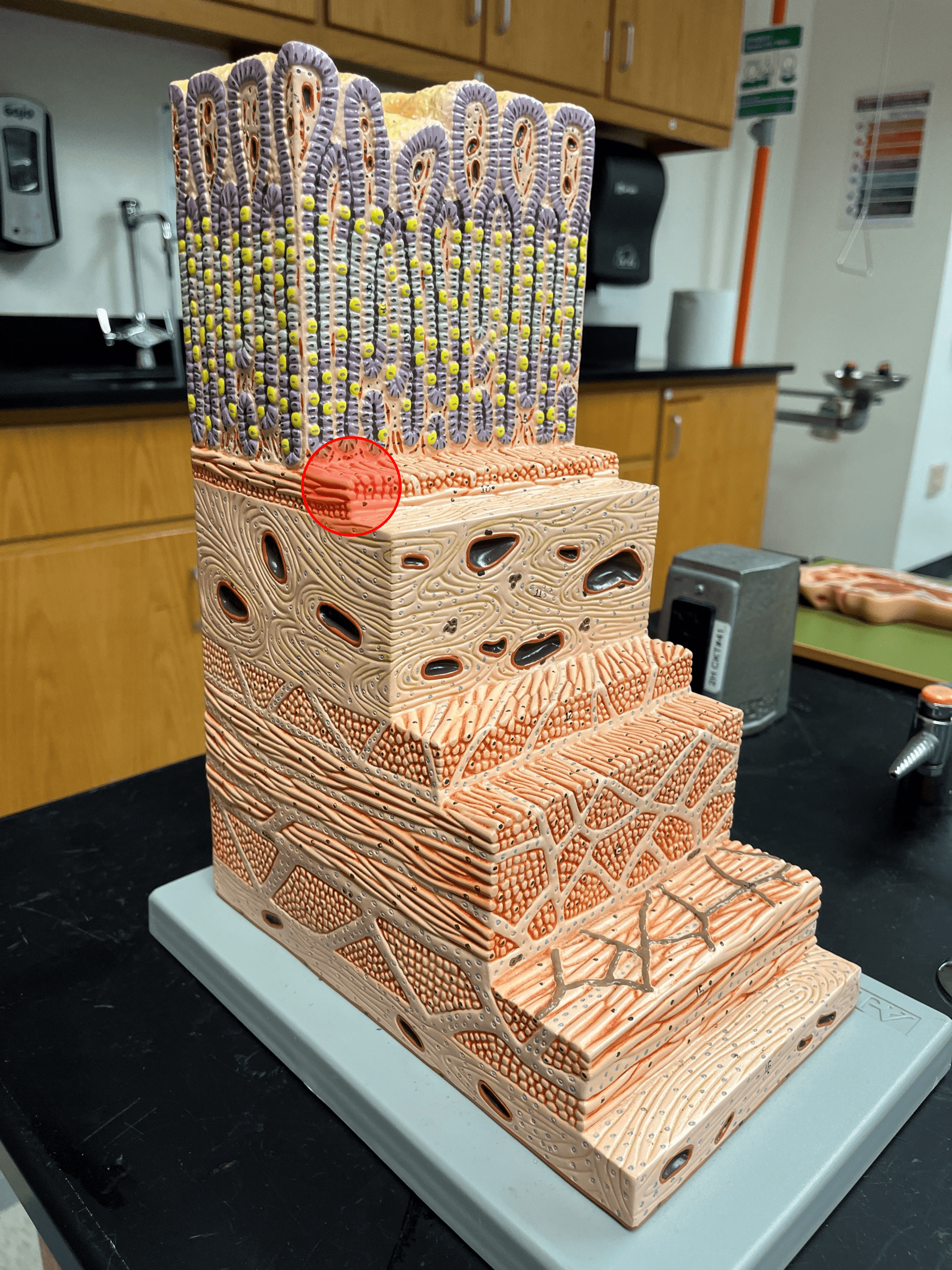
New cards
muscularis mucosae
• The most superficial layer of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract.
• The thin layer of smooth muscle.
• The thin layer of smooth muscle.
5
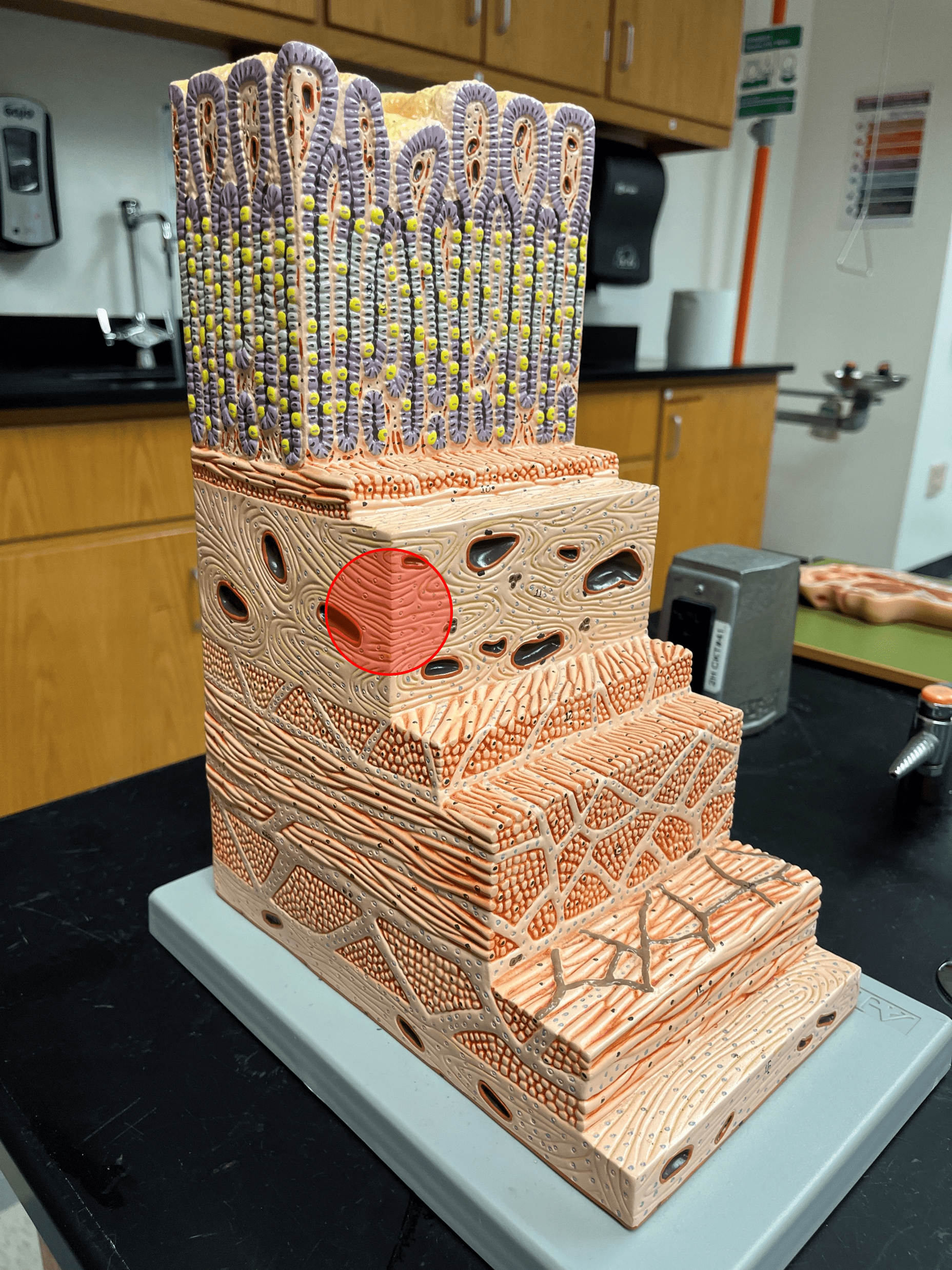
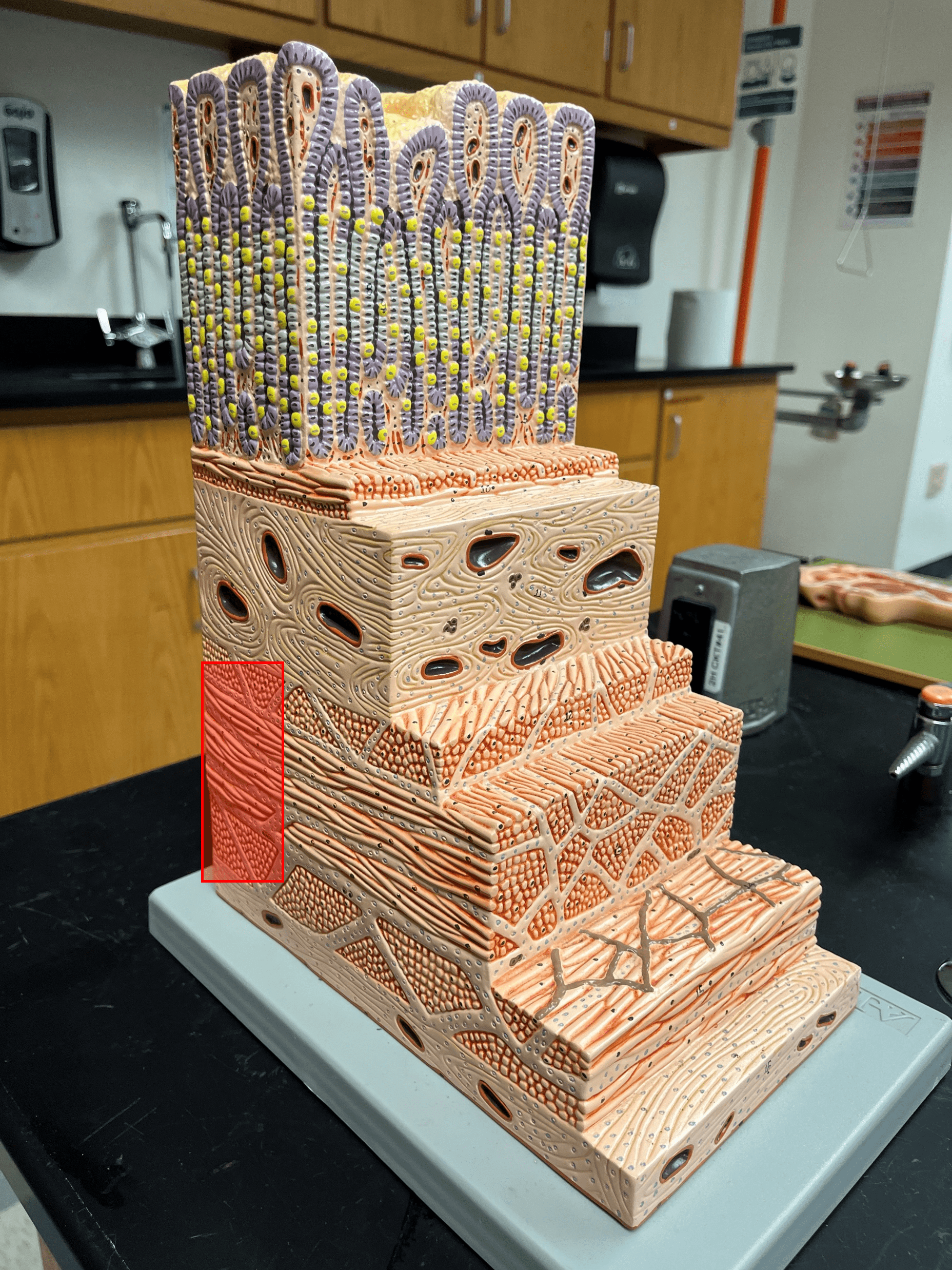
New cards
submucosa
• The second deepest layer of the gastrointestinal tract.
• Composed of loose connective tissue.
• Superficial to the mucosa.
• Deep to the muscularis externa.
• Composed of loose connective tissue.
• Superficial to the mucosa.
• Deep to the muscularis externa.
6
New cards
muscularis externa
• The secondmost superficial layer of the gastrointestinal tract.
• Composed of oblique (stomach only), circular, and longitudinal layers of smooth muscle.
• Superficial to the submucosa.
• Deep to the serosa.
• Composed of oblique (stomach only), circular, and longitudinal layers of smooth muscle.
• Superficial to the submucosa.
• Deep to the serosa.

7
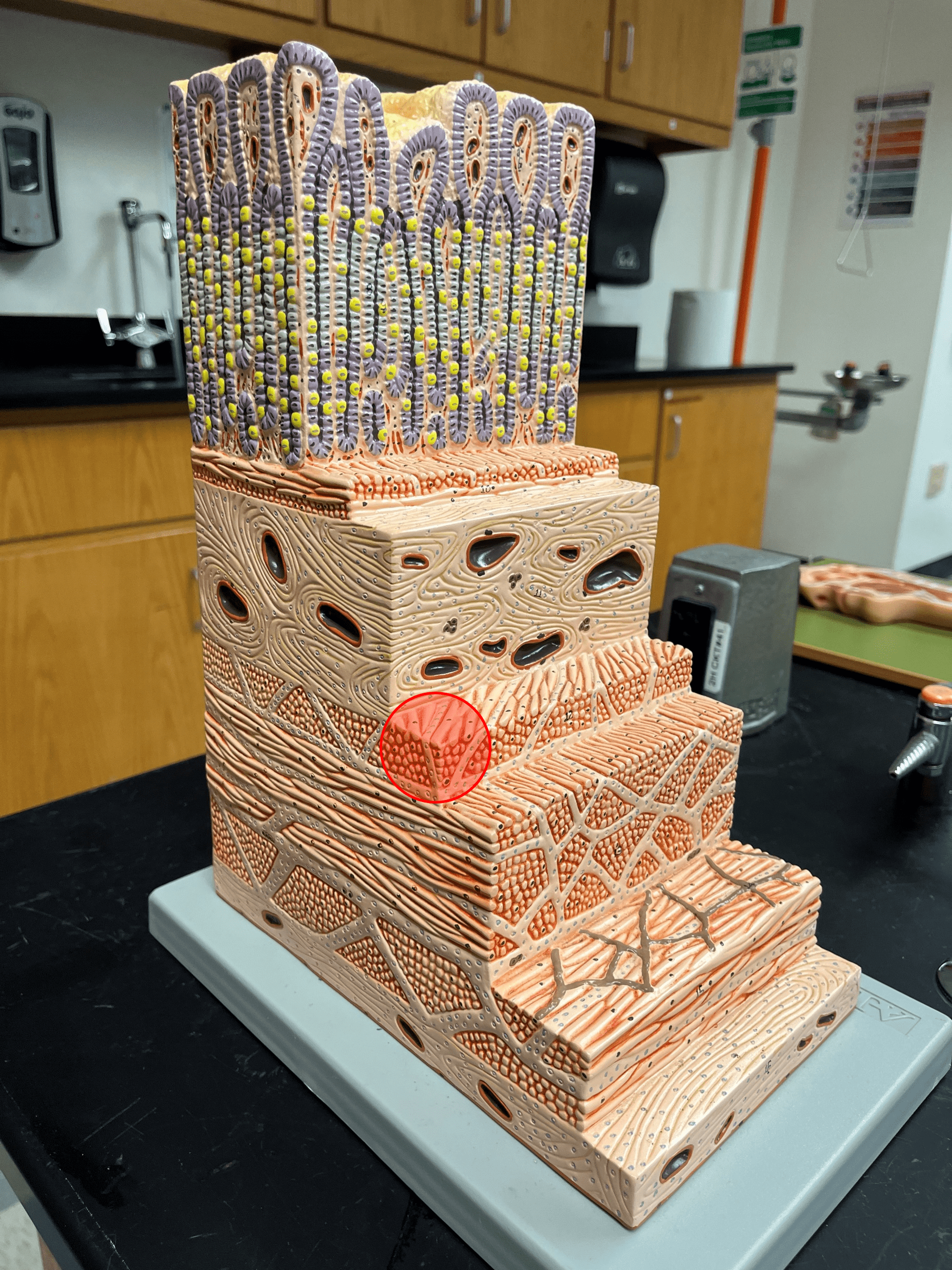
New cards
oblique layer of muscularis
The deepest layer of the muscularis externa of the stomach.
8
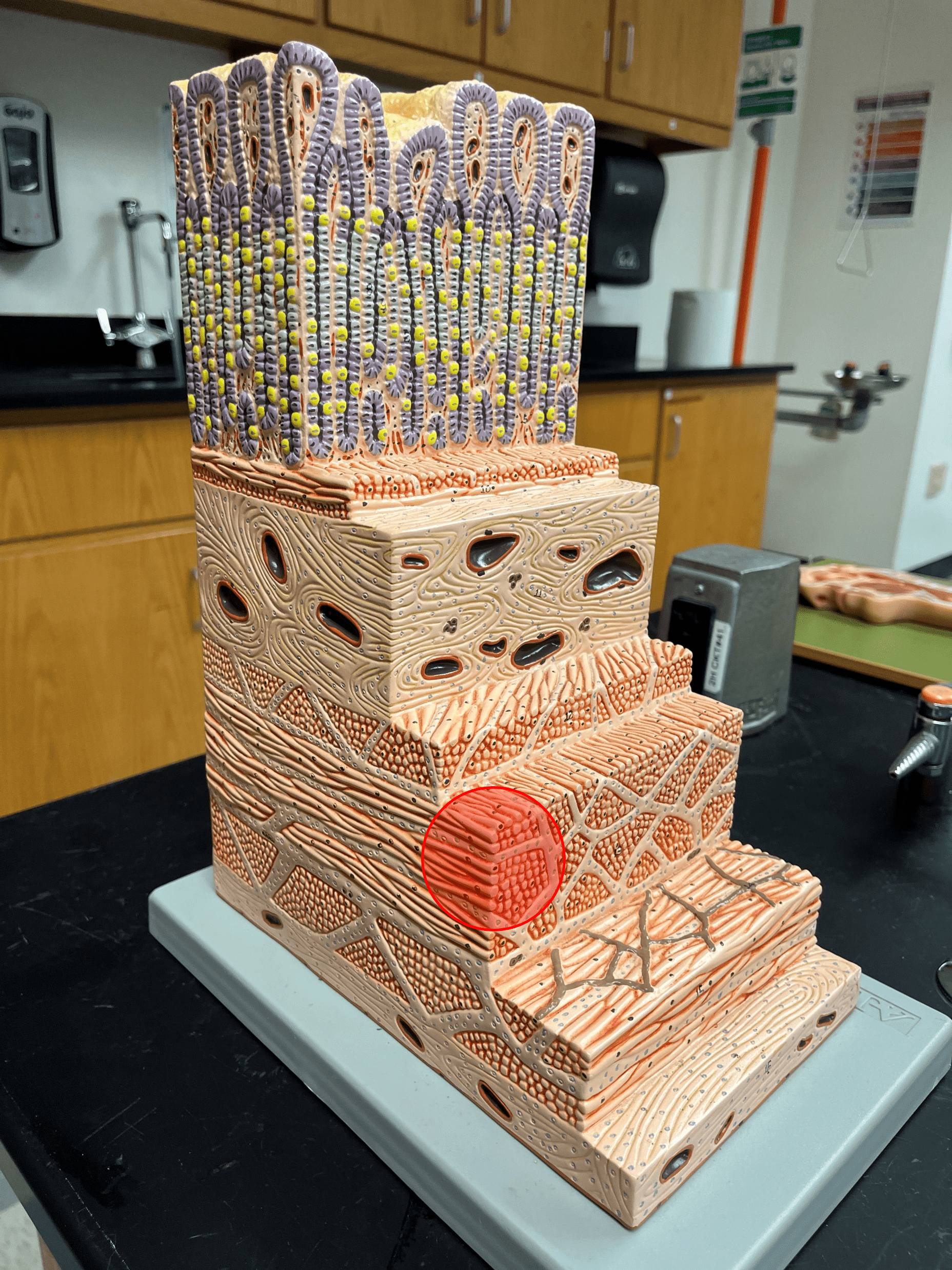
New cards
circular layer of muscularis
• The deepest layer of the muscularis externa of the gastrointestinal tract.
• The middle layer of the muscularis externa of the stomach.
• The middle layer of the muscularis externa of the stomach.
9
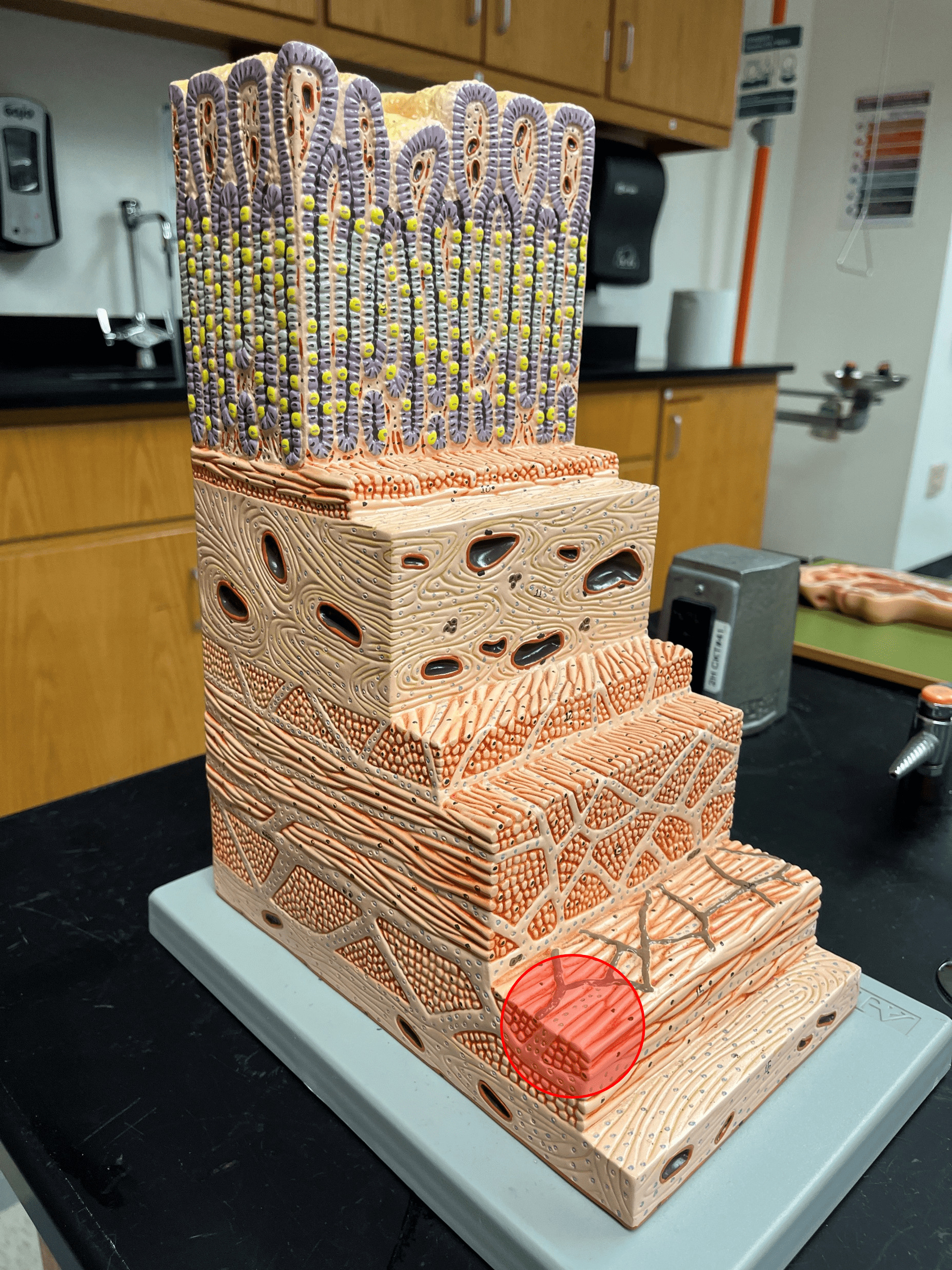
New cards
longitudinal layer of muscularis
The most superficial layer of the muscularis externa of the gastrointestinal tract.
10
New cards
serosa
• The most superficial layer of the gastrointestinal tract.
• Composed of a layer of epithelium and a layer of connective tissue.
• Also known as the visceral peritoneum.
• Composed of a layer of epithelium and a layer of connective tissue.
• Also known as the visceral peritoneum.
11
New cards
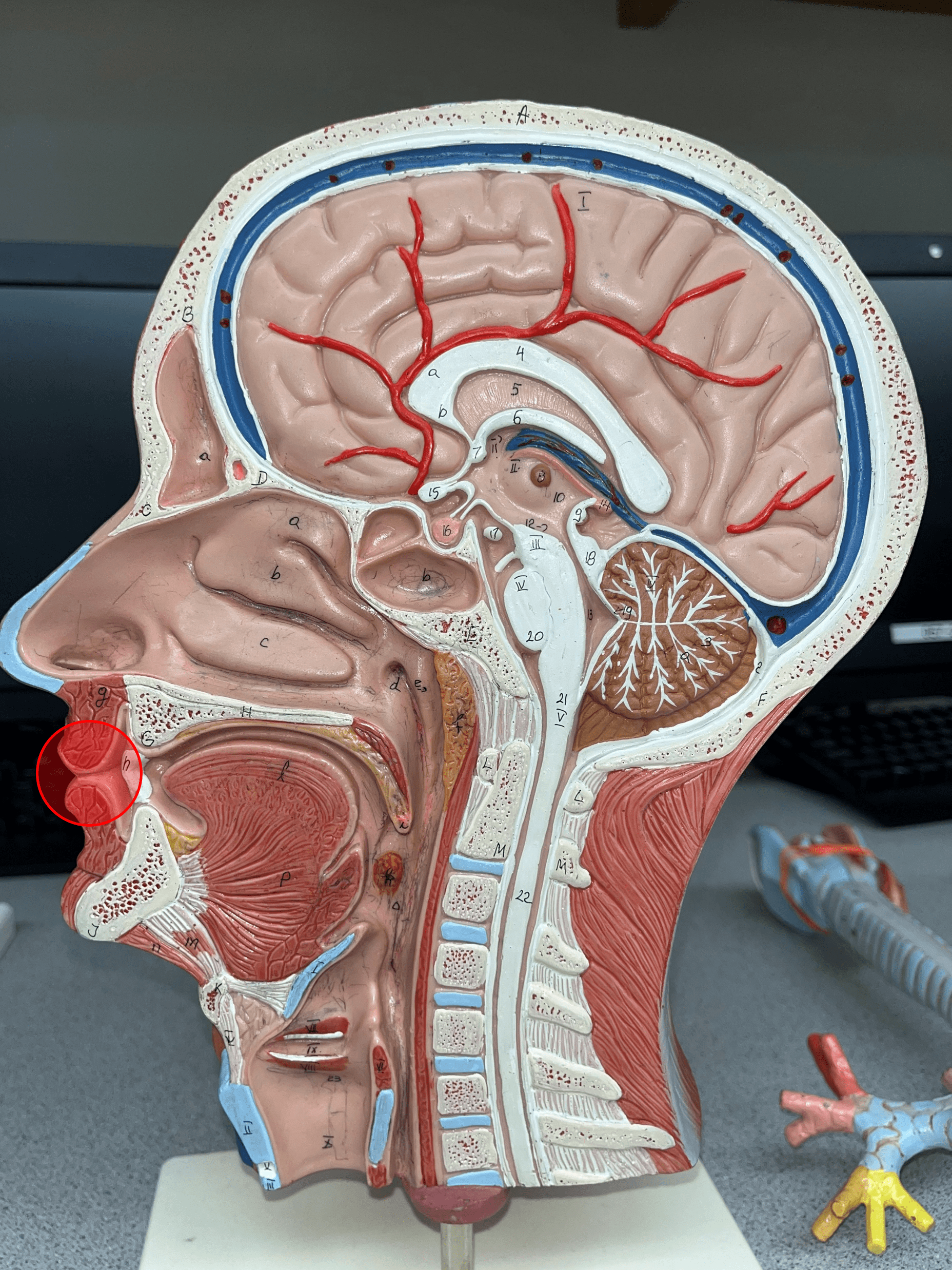
lip
One of the anterior borders of the opening of the mouth.
12
New cards
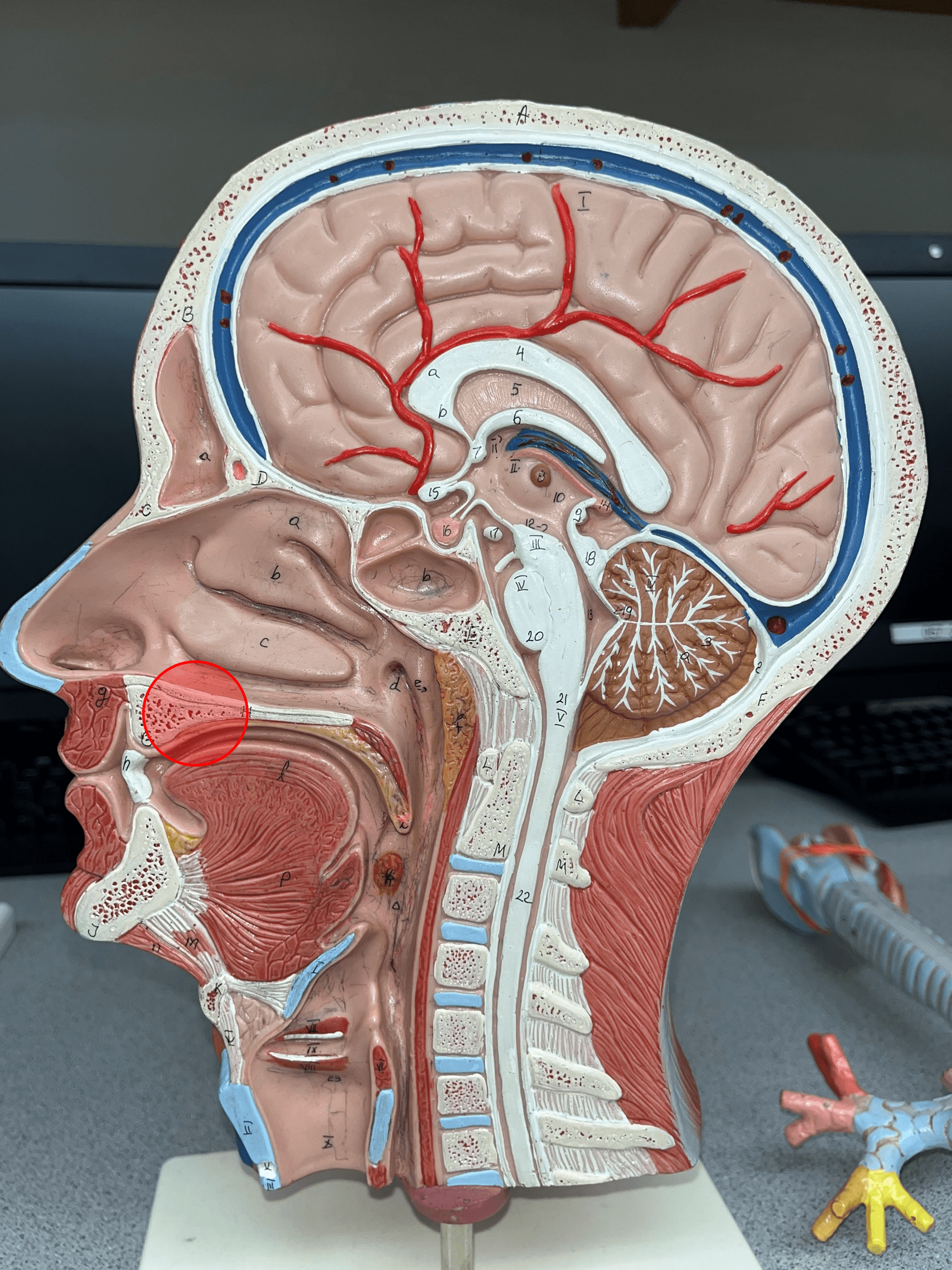
hard palate
Forms the anterior part of the roof of the mouth.
13
New cards
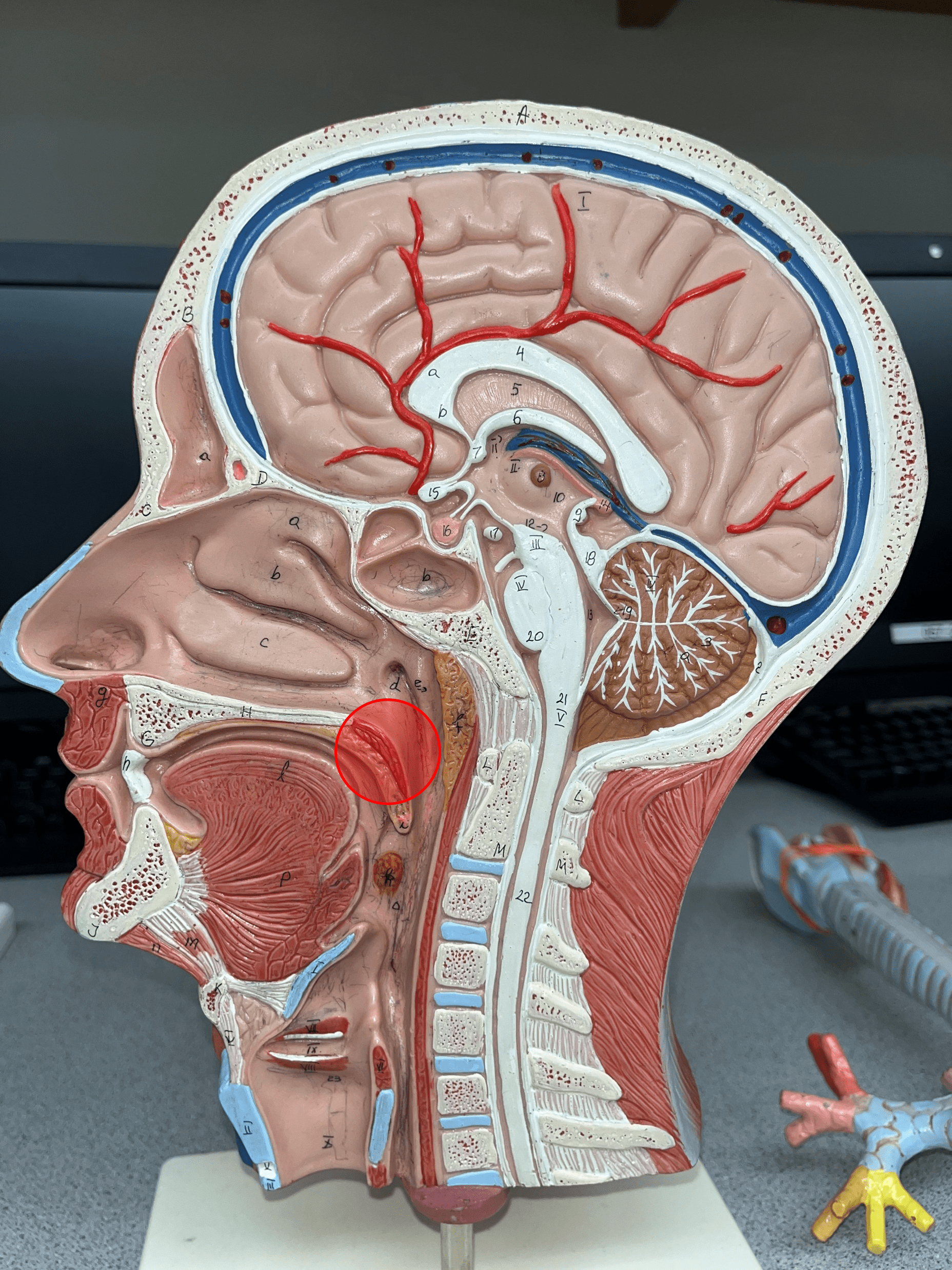
soft palate
Forms the posterior part of the roof of the mouth.
14
New cards
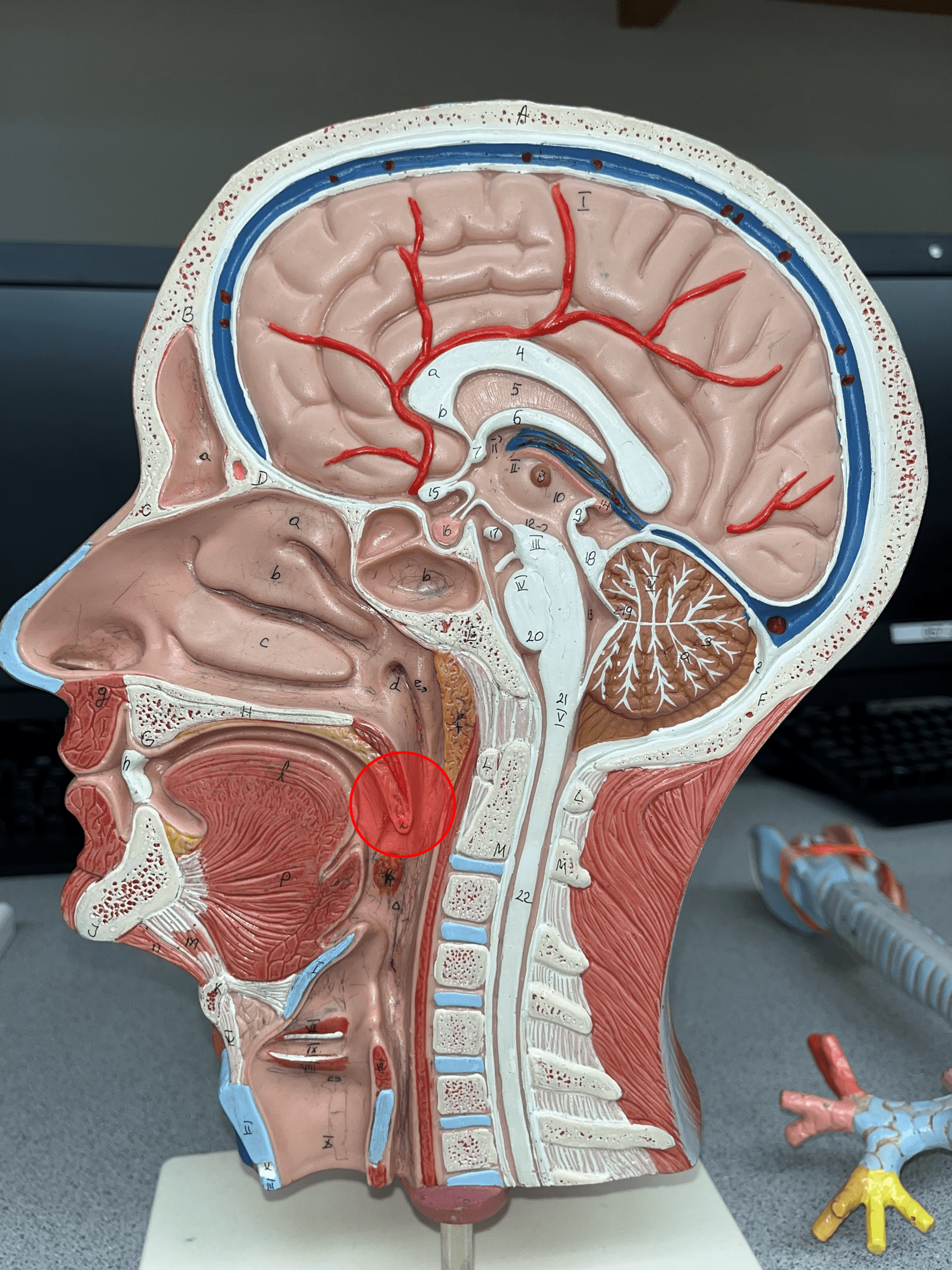
uvula
• An extension of the soft palate hanging downwards.
• Visible at the back of the mouth.
• Visible at the back of the mouth.
15
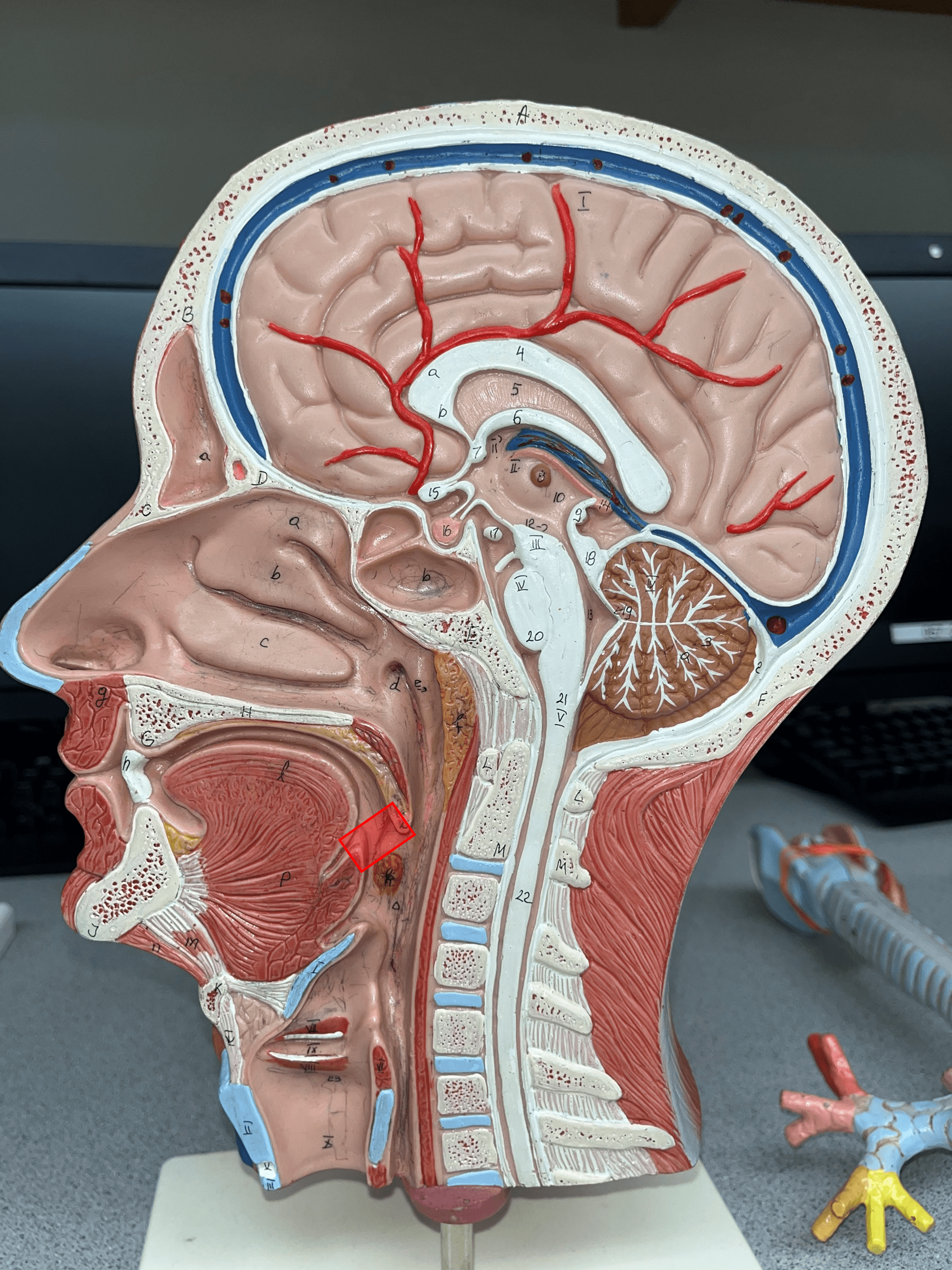
New cards
fauces
The opening of the mouth into the oropharynx.
16
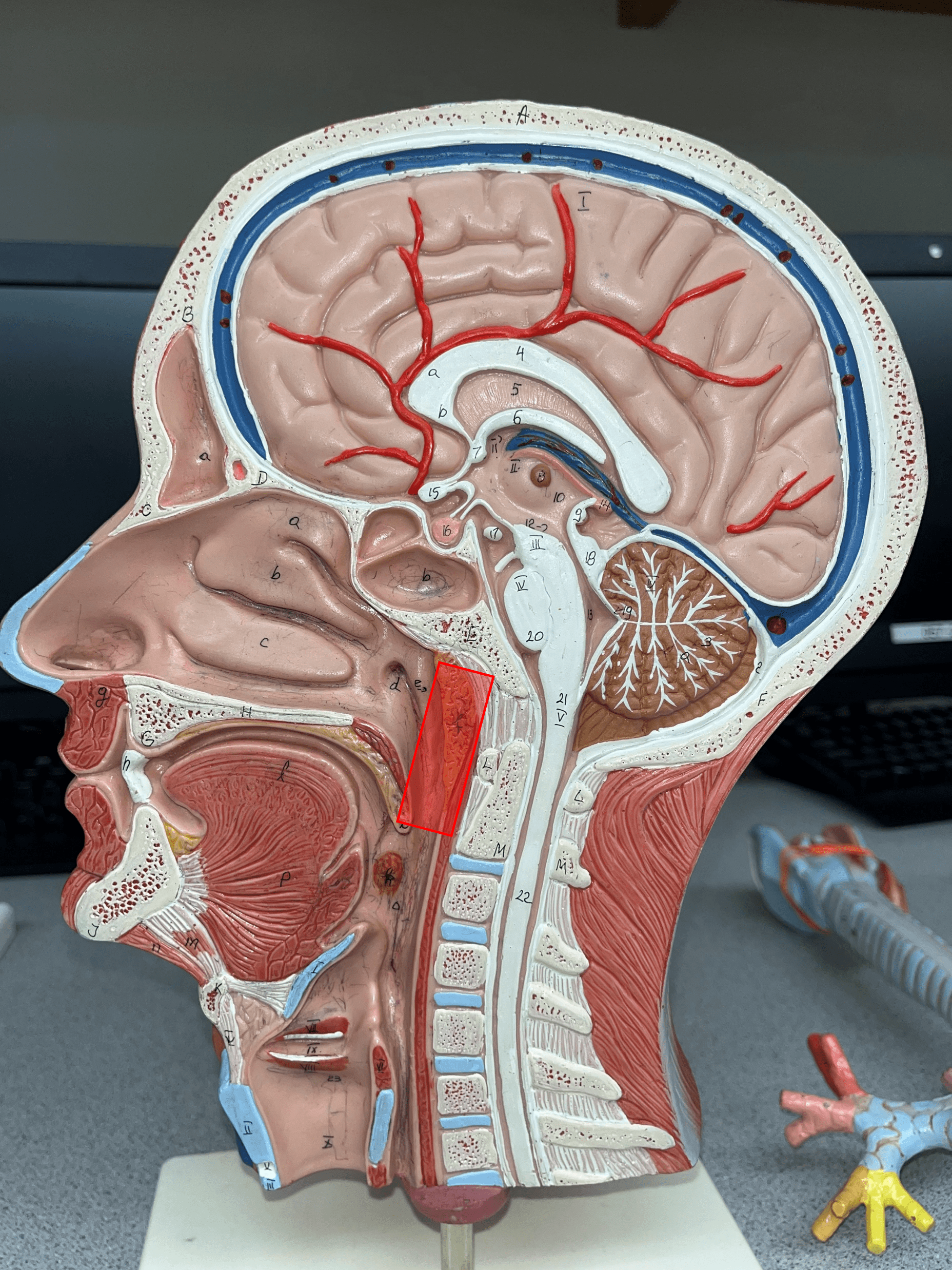
New cards
nasopharynx
• The superior segment of the pharynx.
• Above the level of the soft palate.
• Receives air from the nose by the internal nares.
• Above the level of the soft palate.
• Receives air from the nose by the internal nares.
17
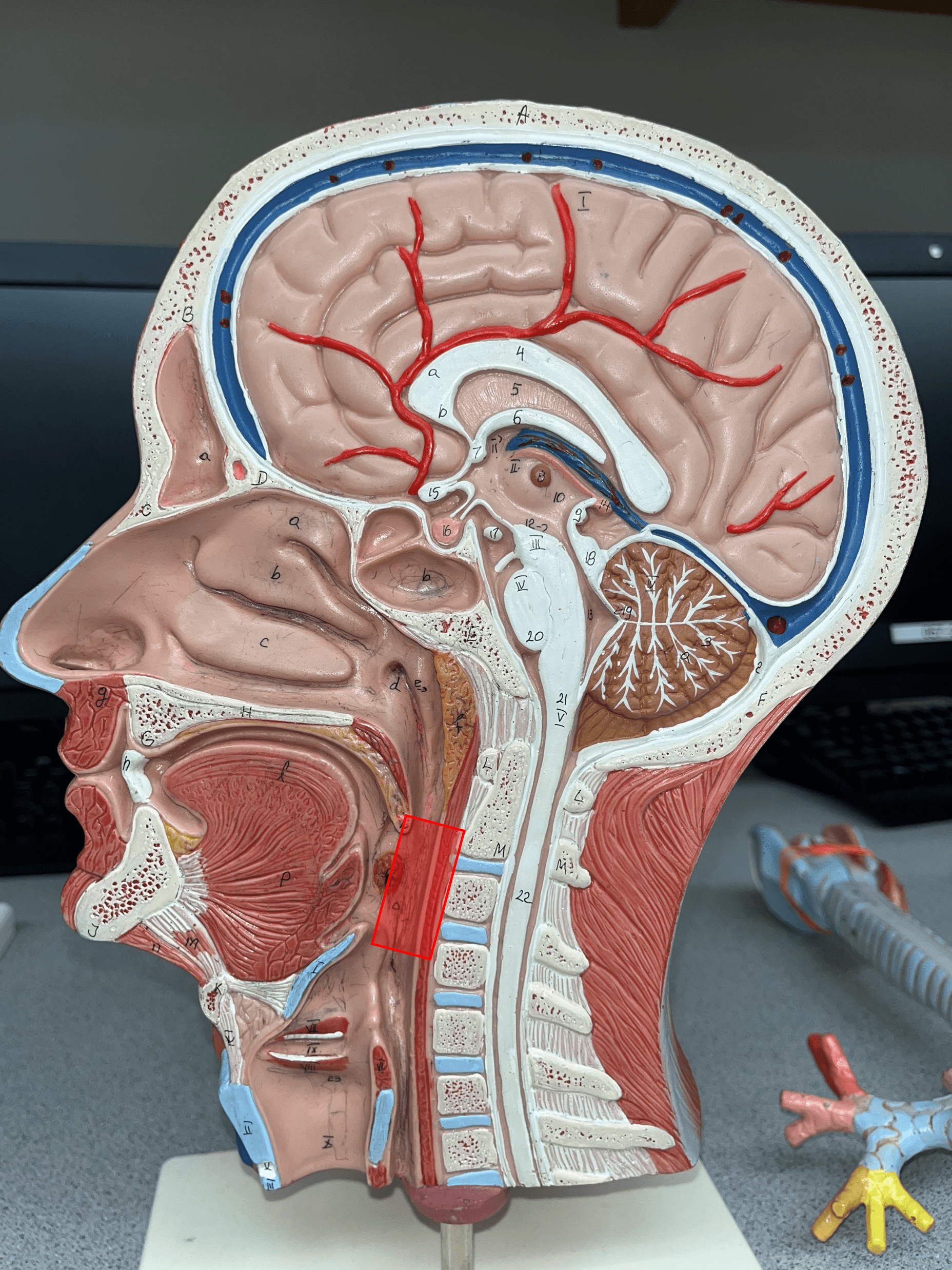
New cards
oropharynx
• The middle segment of the pharynx.
• Below the level of the soft palate and above the level of the hyoid bone.
• Receives food from the oral cavity.
• Below the level of the soft palate and above the level of the hyoid bone.
• Receives food from the oral cavity.
18
New cards
laryngopharynx
• The inferior segment of the pharynx.
• Below the level of the hyoid bone.
• Extends downward to meet the larynx.
• Below the level of the hyoid bone.
• Extends downward to meet the larynx.
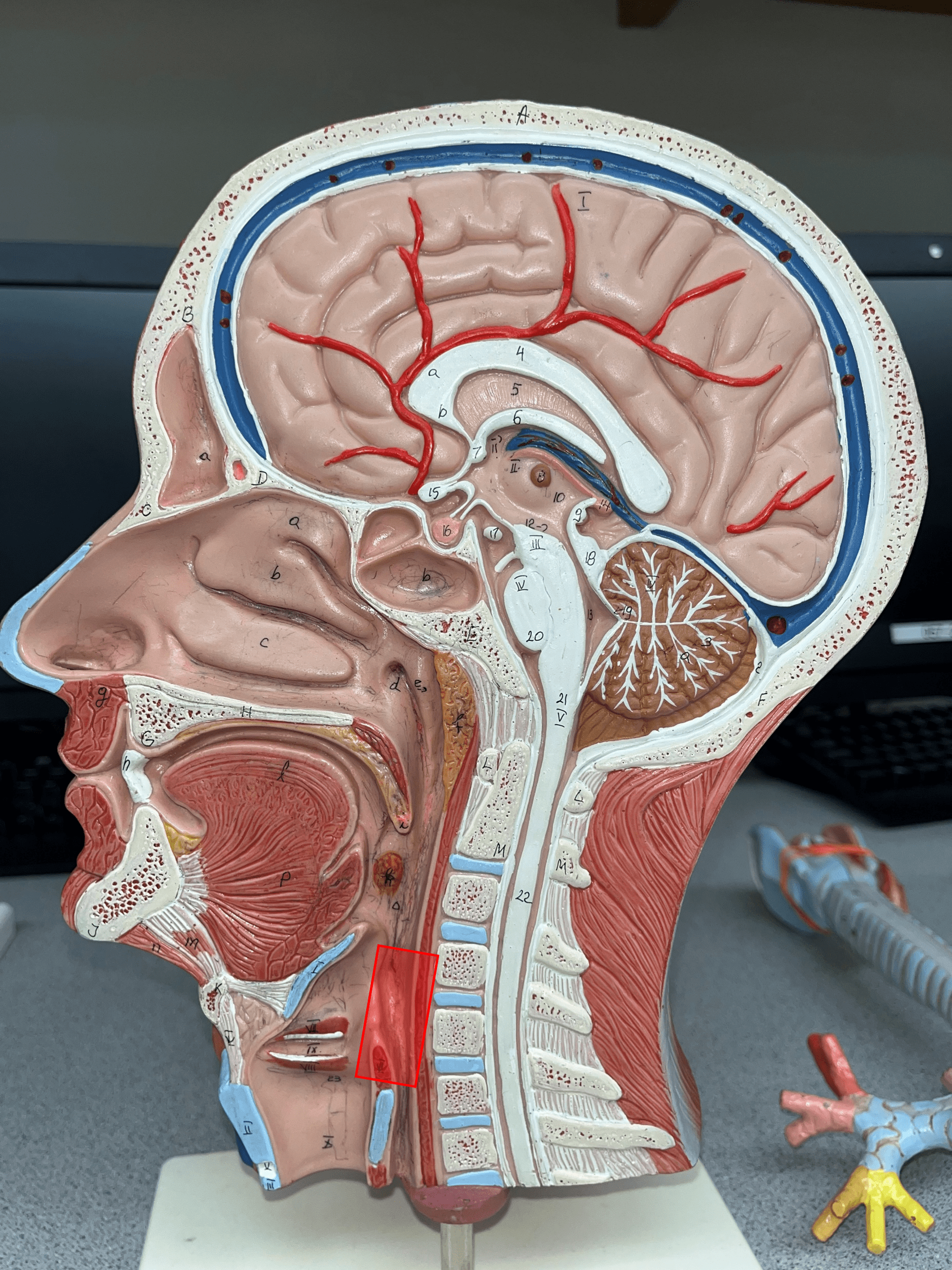
19
New cards
esophagus
• A muscular and slippery tube that stretches open to accommodate swallowed food.
• Propels food by peristalsis.
• Propels food by peristalsis.
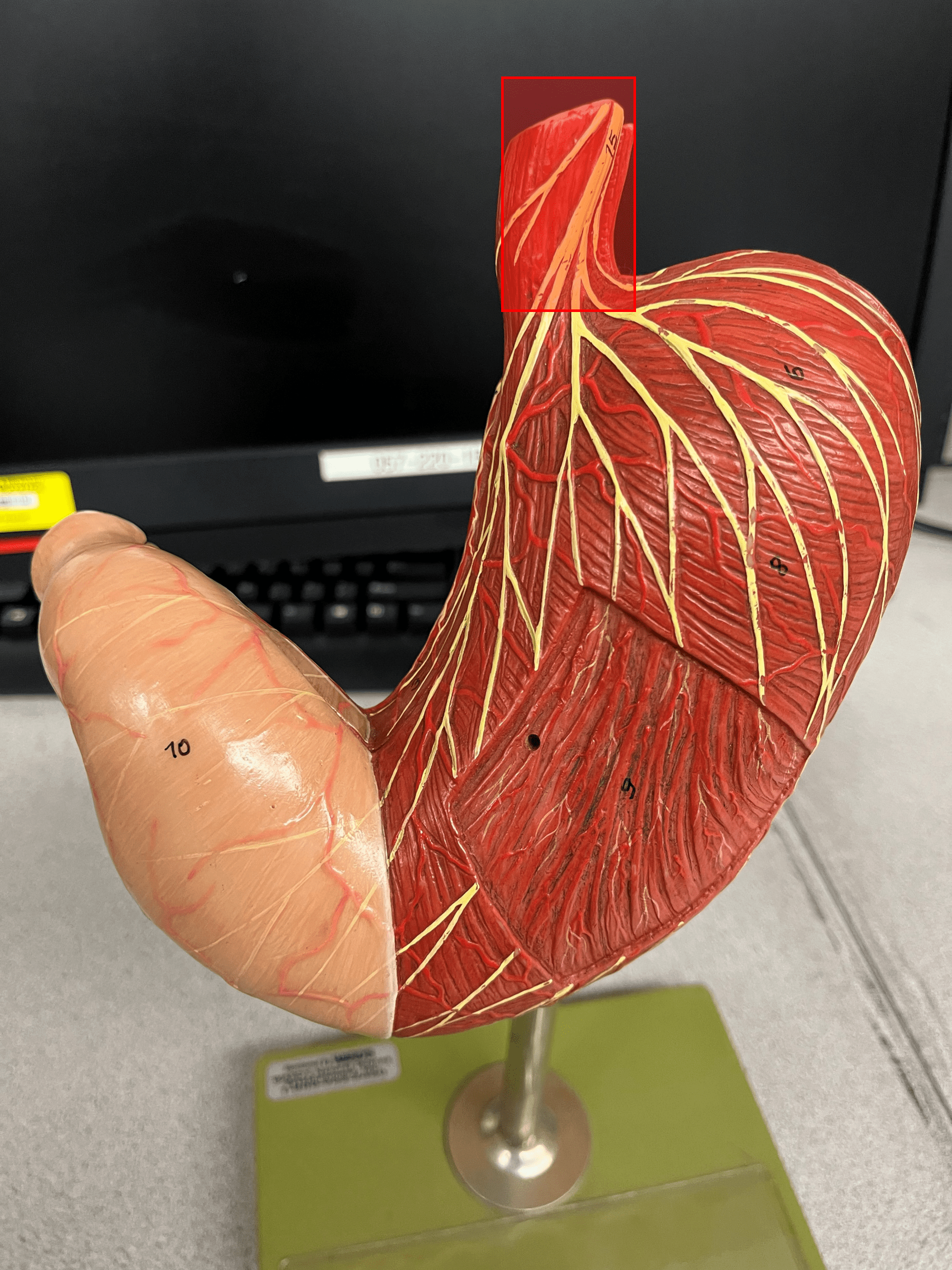
20
New cards
lower esophageal sphincter
• A sphincter that opens to allow food into the stomach.
• Abbreviated LES.
• Abbreviated LES.
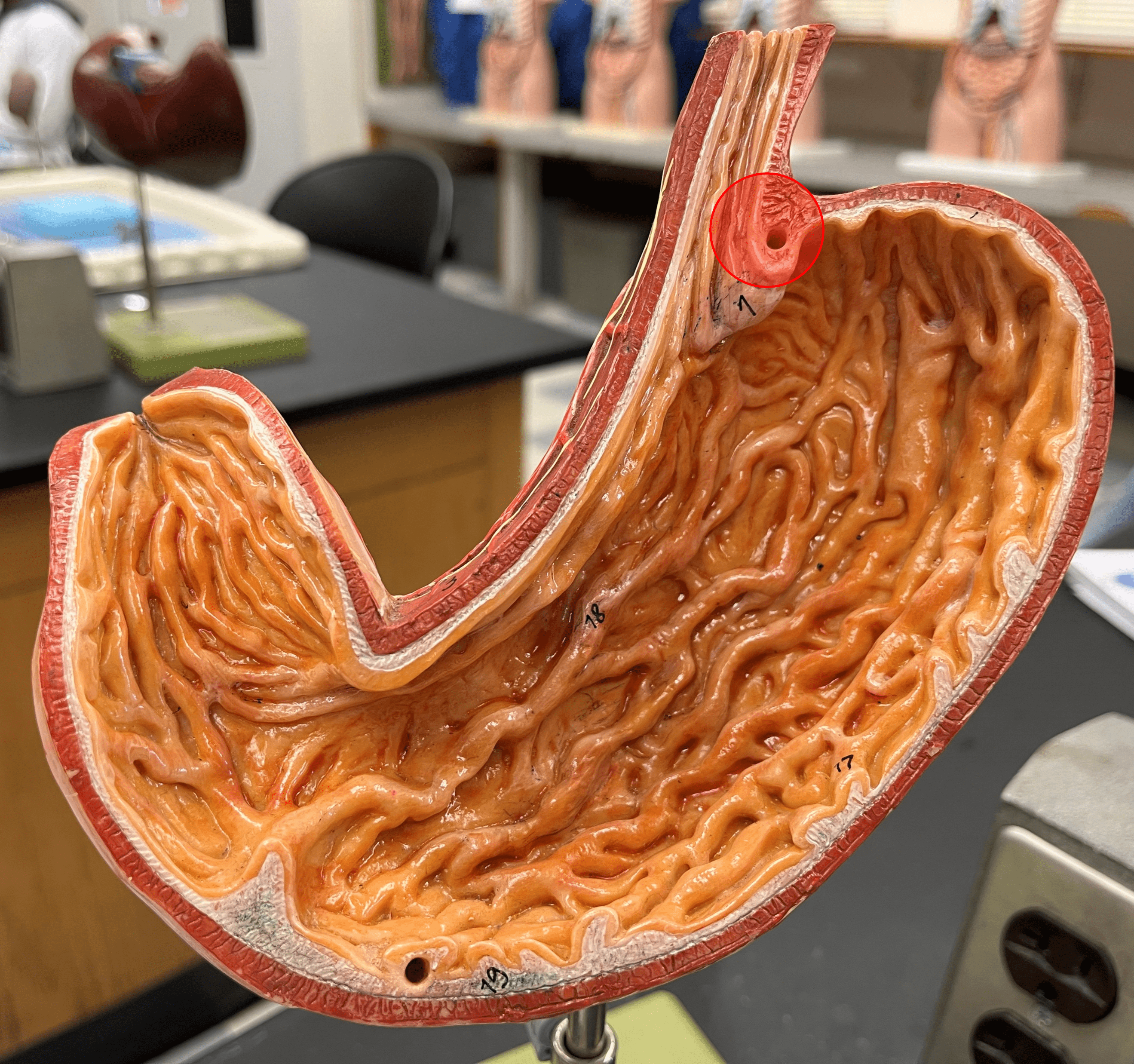
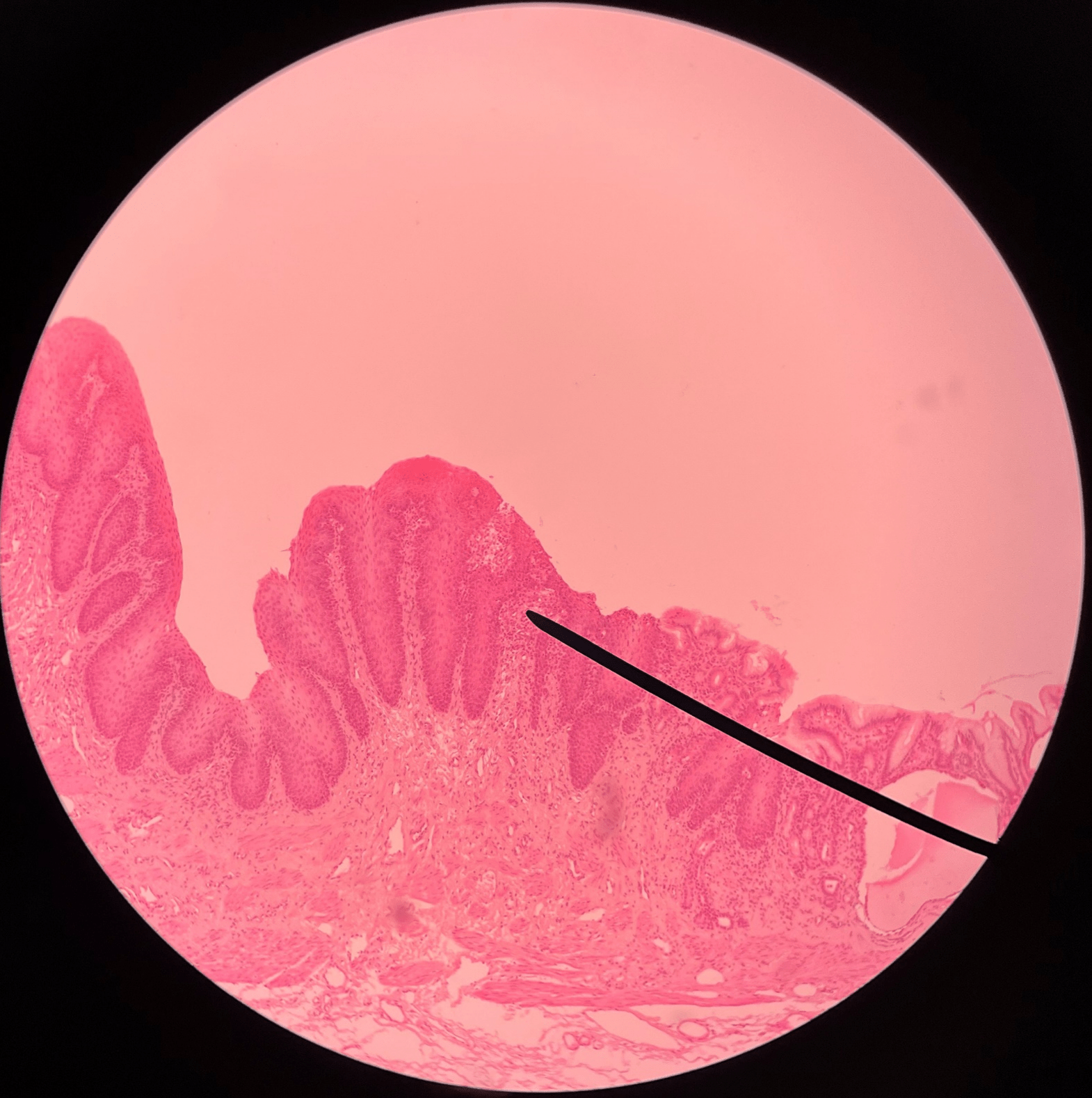
21
New cards
esophagus
• Slide of the gastroesophageal junction.
• Composed of stratified squamous epithelium.
• Composed of stratified squamous epithelium.
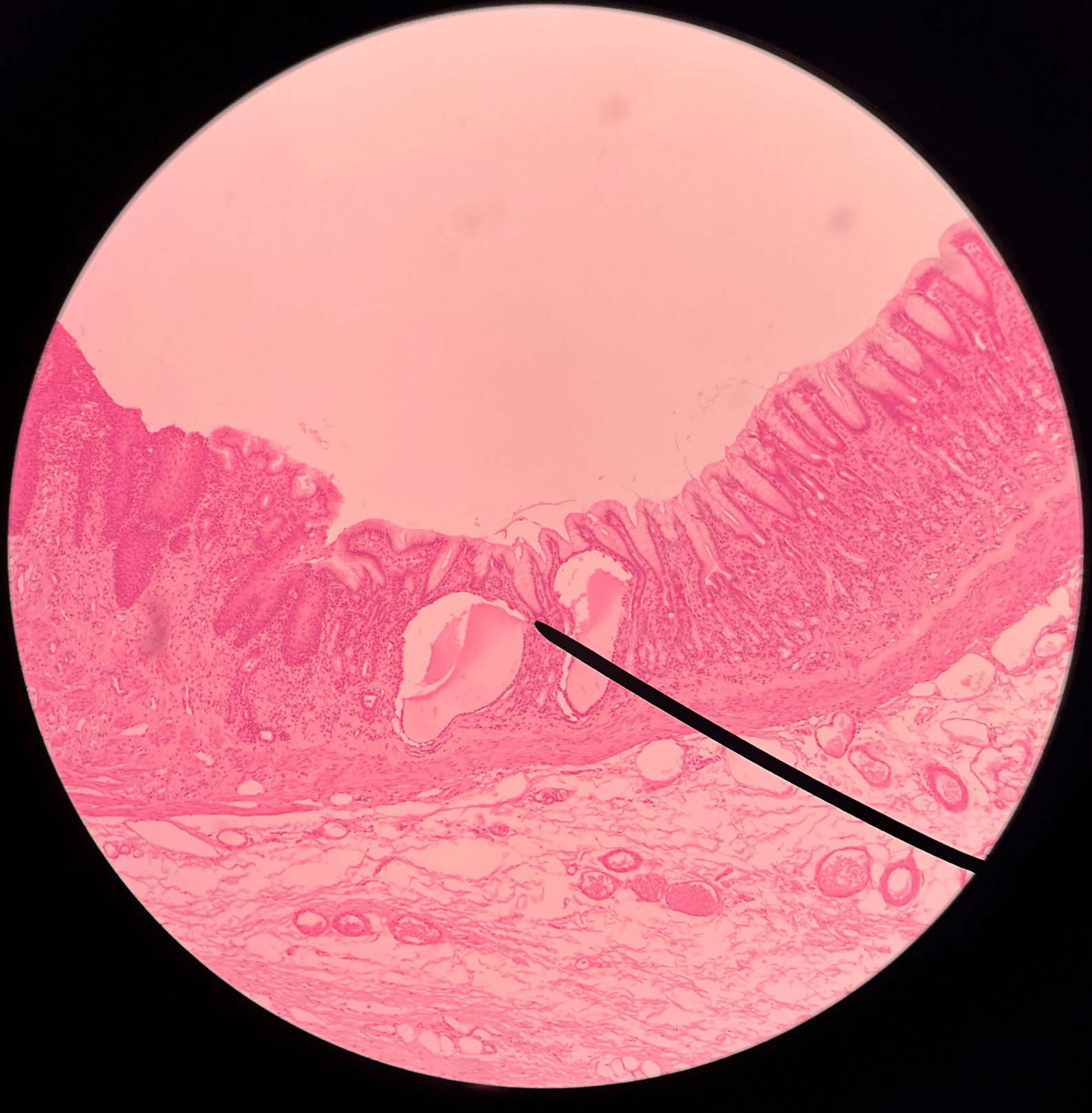
22
New cards
stomach
• Slide of the gastroesophageal junction.
• Composed of simple columnar epithelium.
• Composed of simple columnar epithelium.
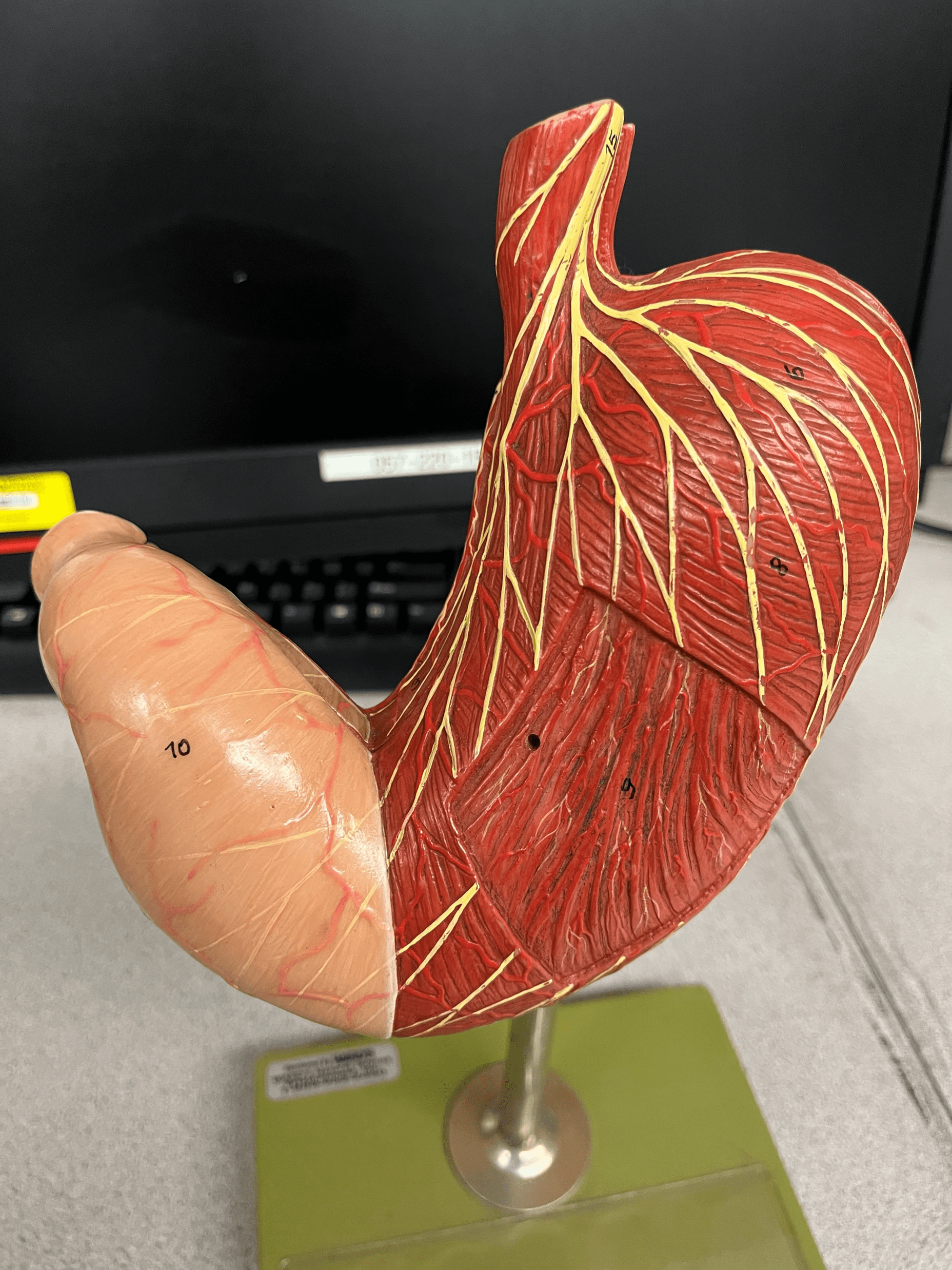
23
New cards
stomach
• A J-shaped open immediately inferior to the diaphragm on the left side of the abdominal cavity.
• Divided into four regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus.
• Mixes and churns food.
• Divided into four regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus.
• Mixes and churns food.
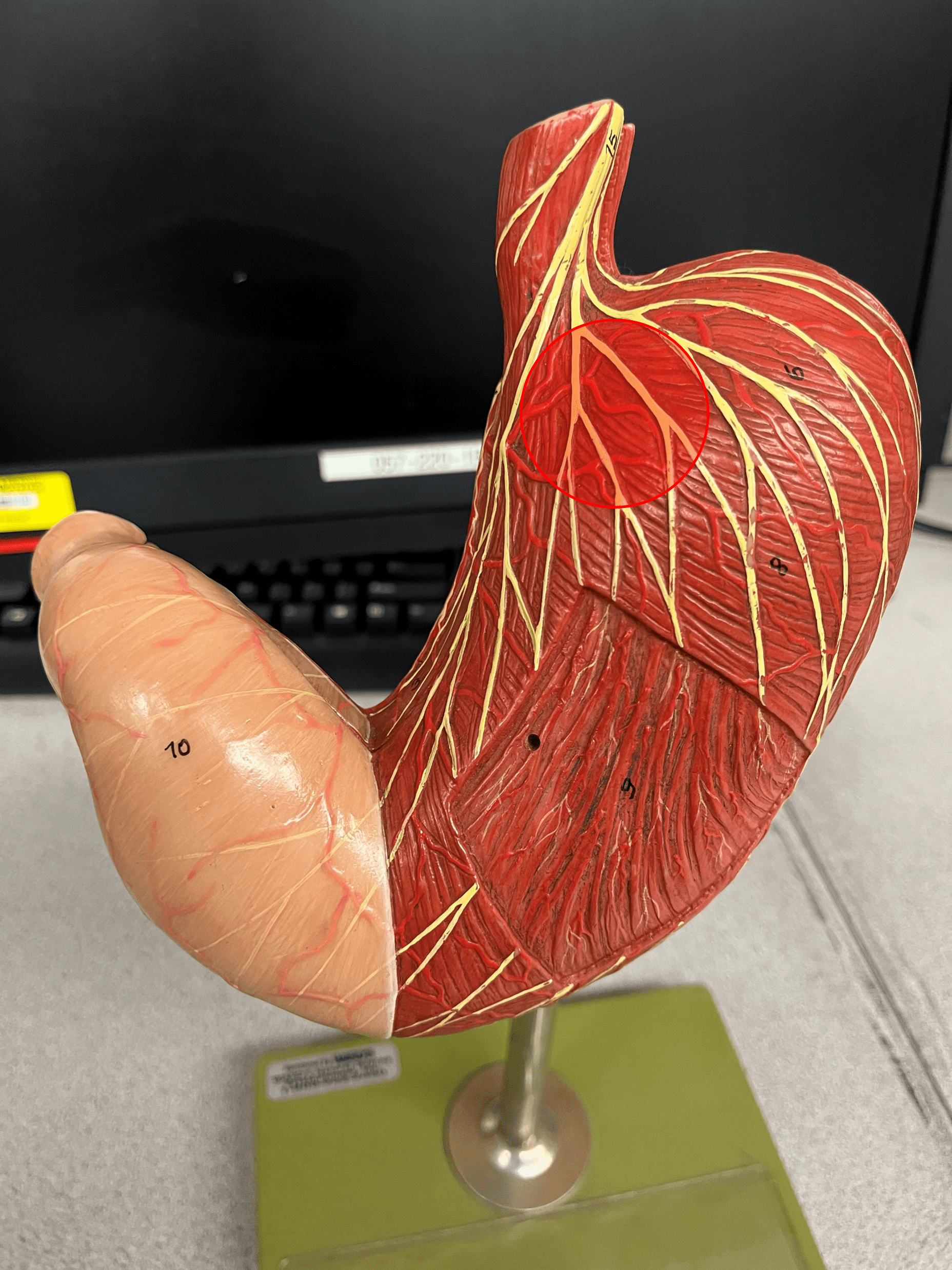
24
New cards
cardia
• A region of the stomach.
• Receives food from the esophagus in the superior part of the stomach.
• Receives food from the esophagus in the superior part of the stomach.
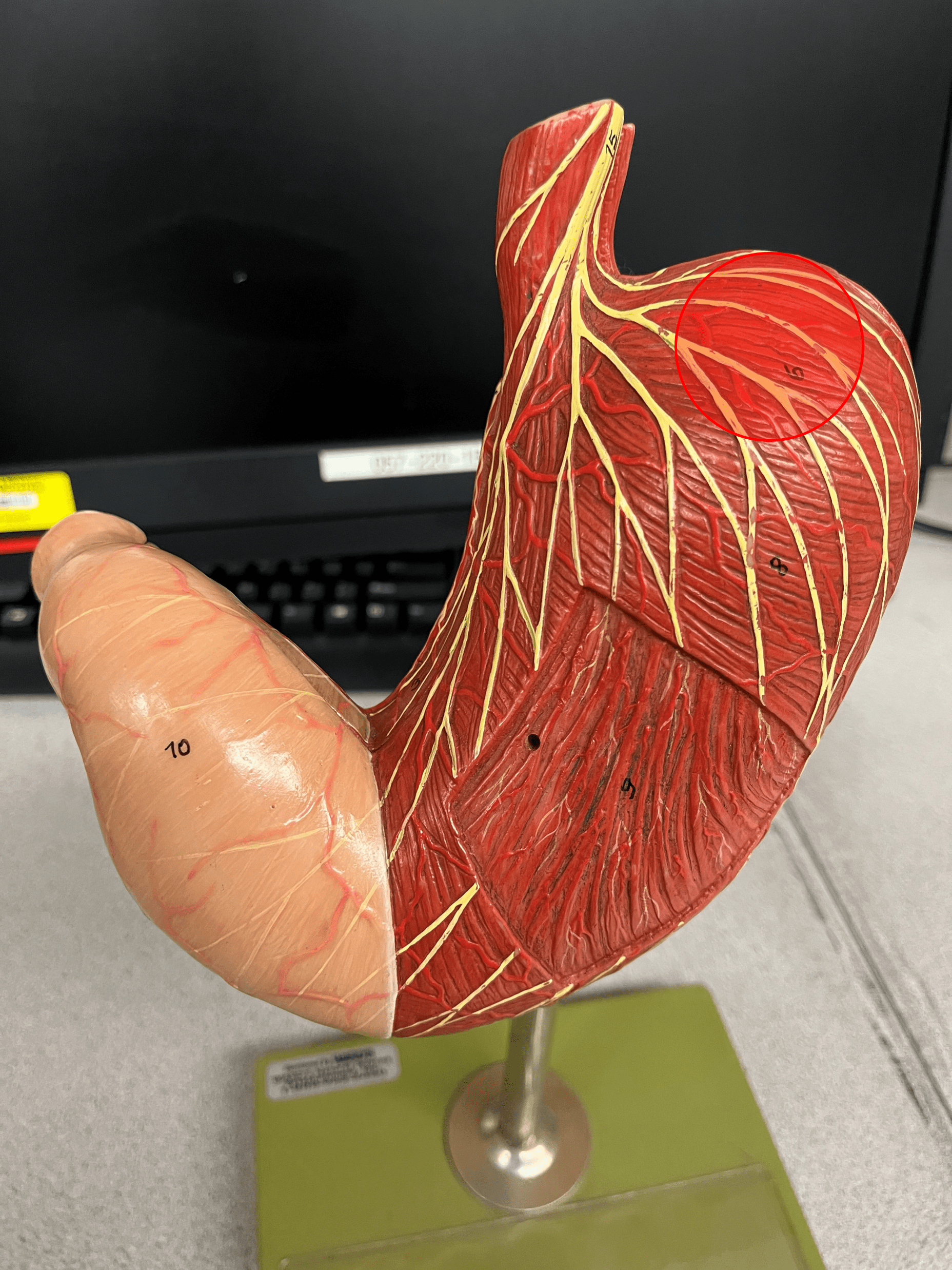
25
New cards
fundus
• A region of the stomach.
• An area that holds food and forms the superior part of the stomach.
• An area that holds food and forms the superior part of the stomach.
26
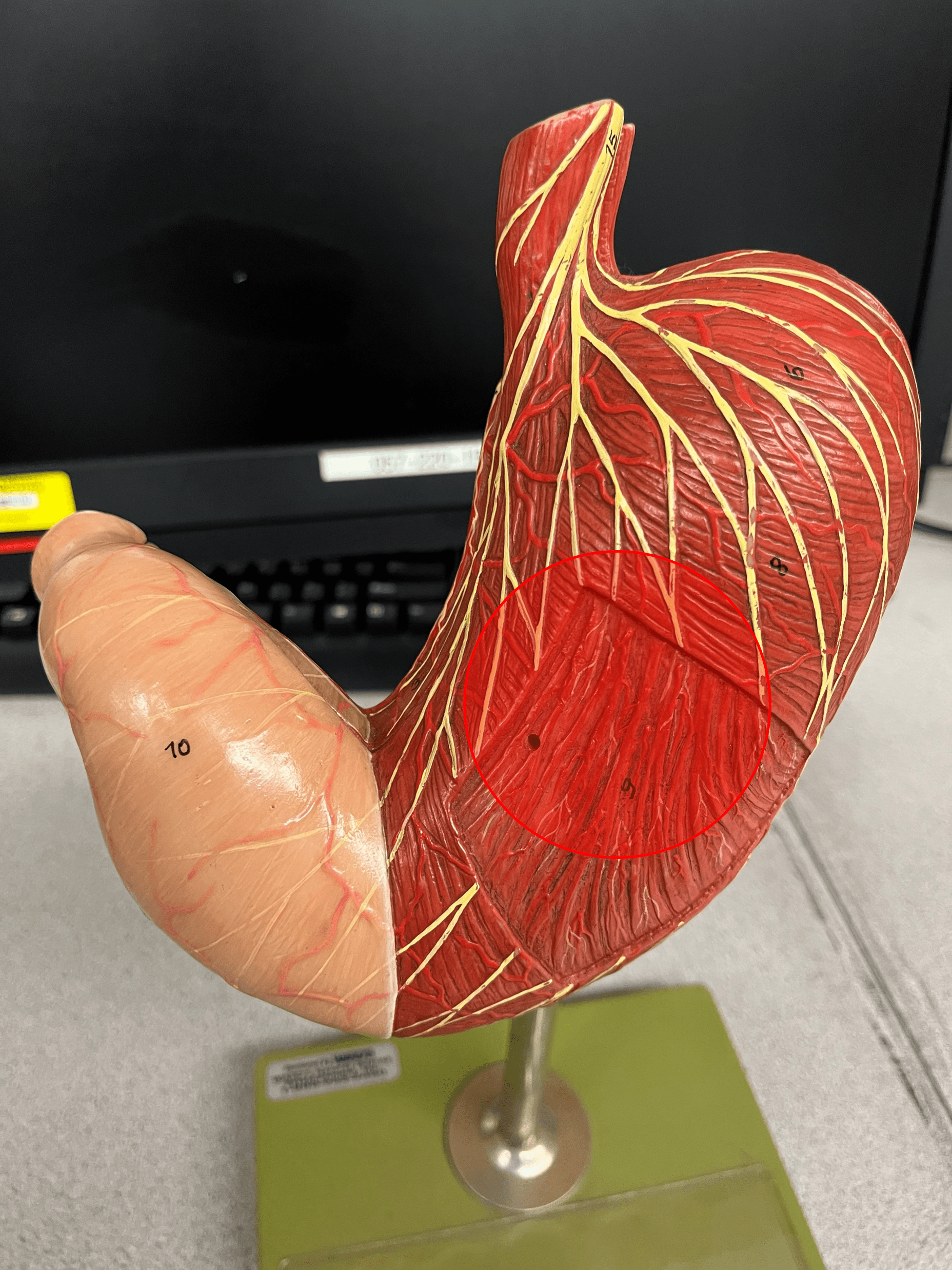
New cards
body
• A region of the stomach.
• The large, central portion of the stomach.
• The large, central portion of the stomach.
27
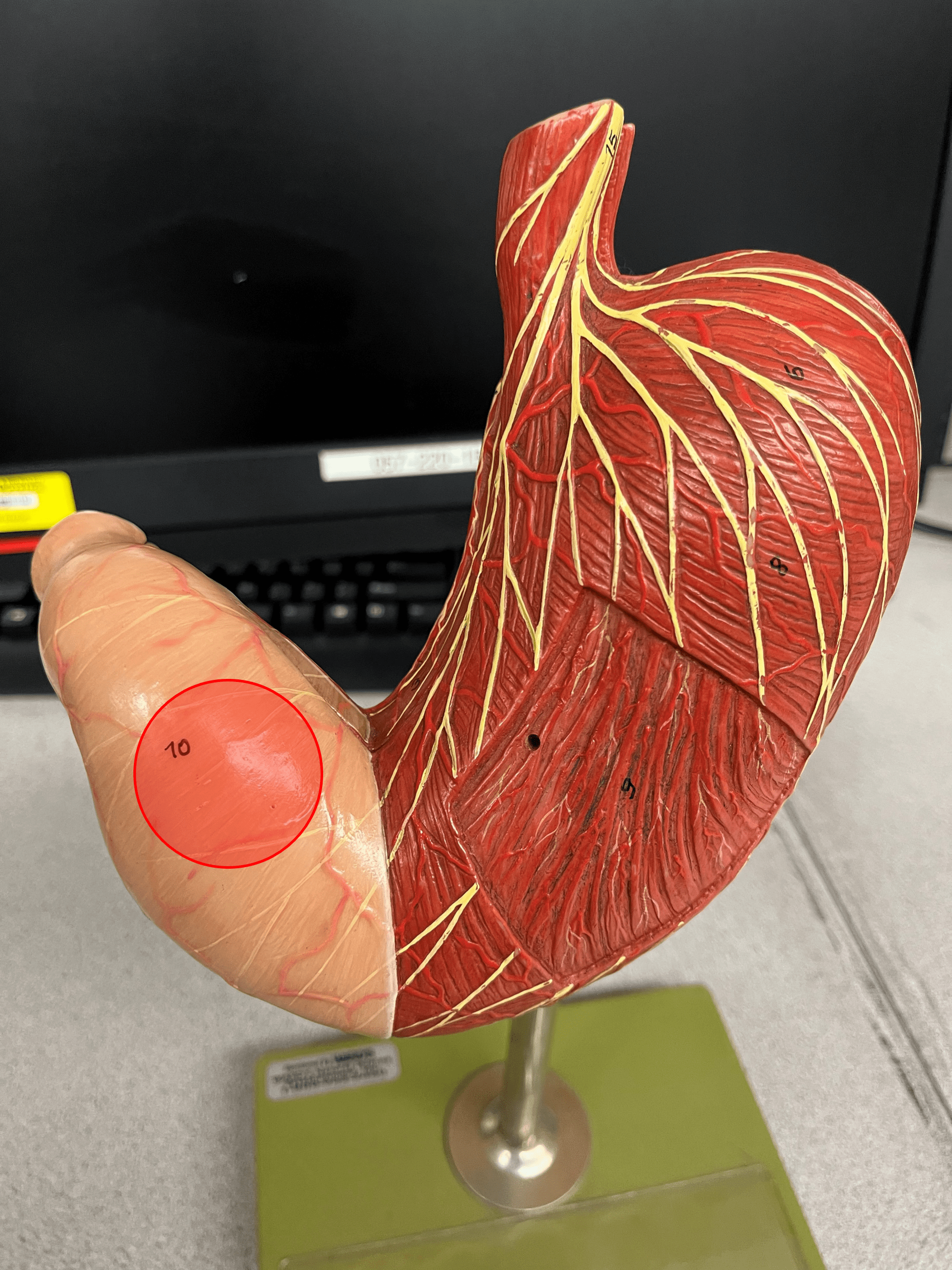
New cards
pylorus
• A region of the stomach.
• The small distal area of the stomach.
• The small distal area of the stomach.
28
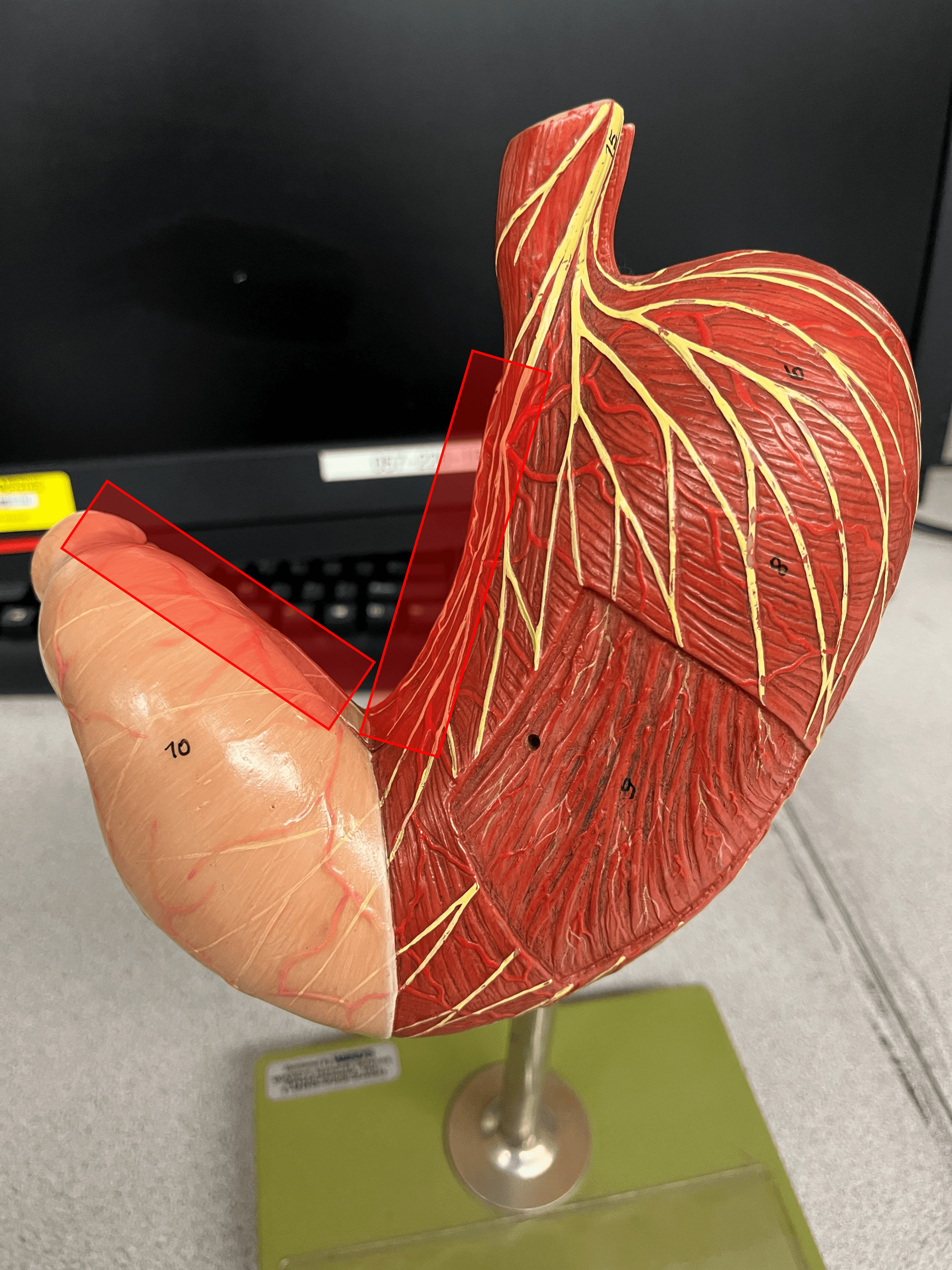
New cards
lesser curvature
The medial, concave curvature of the stomach.
29
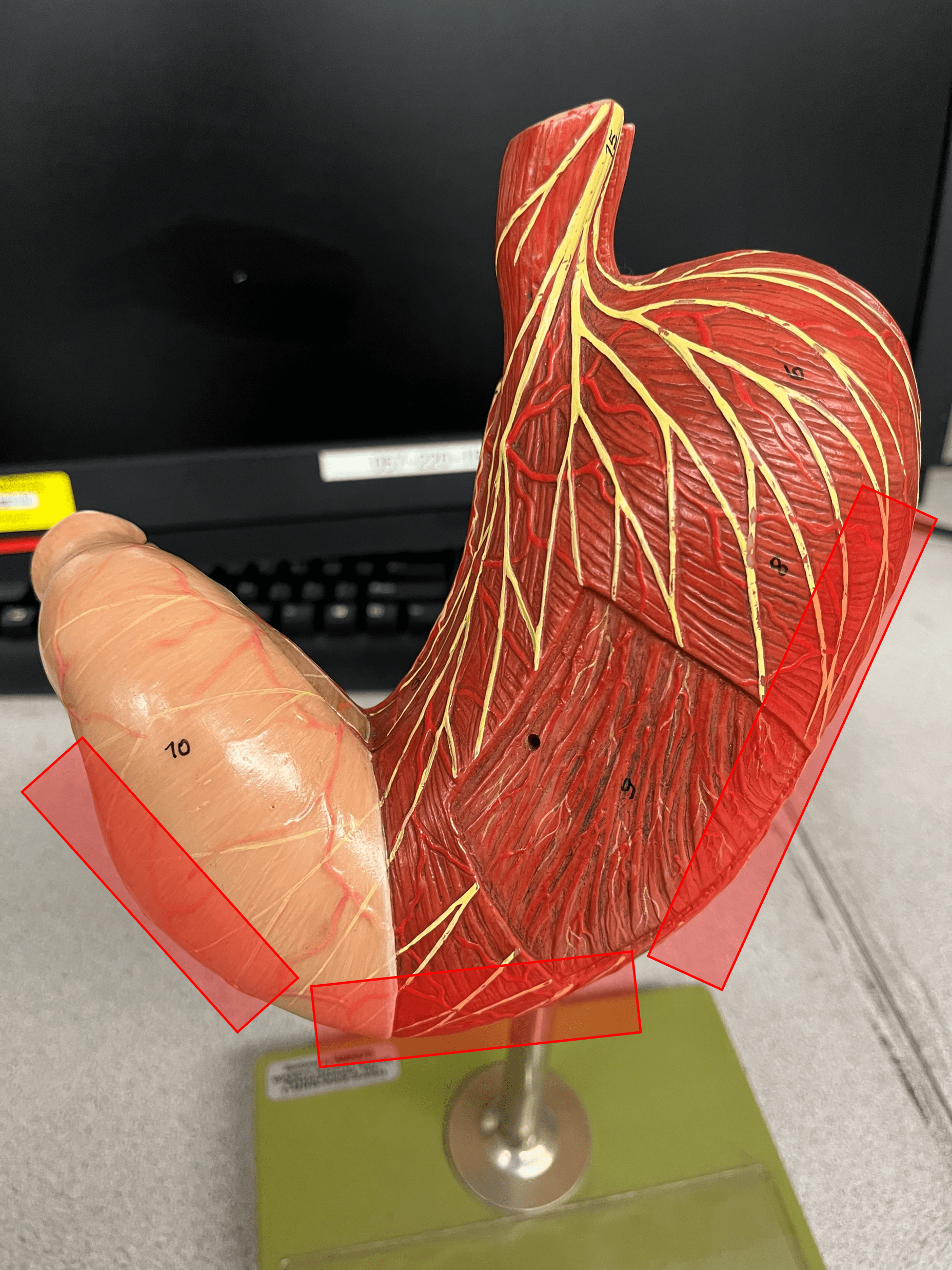
New cards
greater curvature
The lateral, convex curvature of the stomach.
30
New cards
rugae
• Ridges of the mucosa on the internal surface of the stomach.
• Stretches to accommodate a larger volume of food.
• Contains microscopic gastric pits that contain gastric glands.
• Stretches to accommodate a larger volume of food.
• Contains microscopic gastric pits that contain gastric glands.
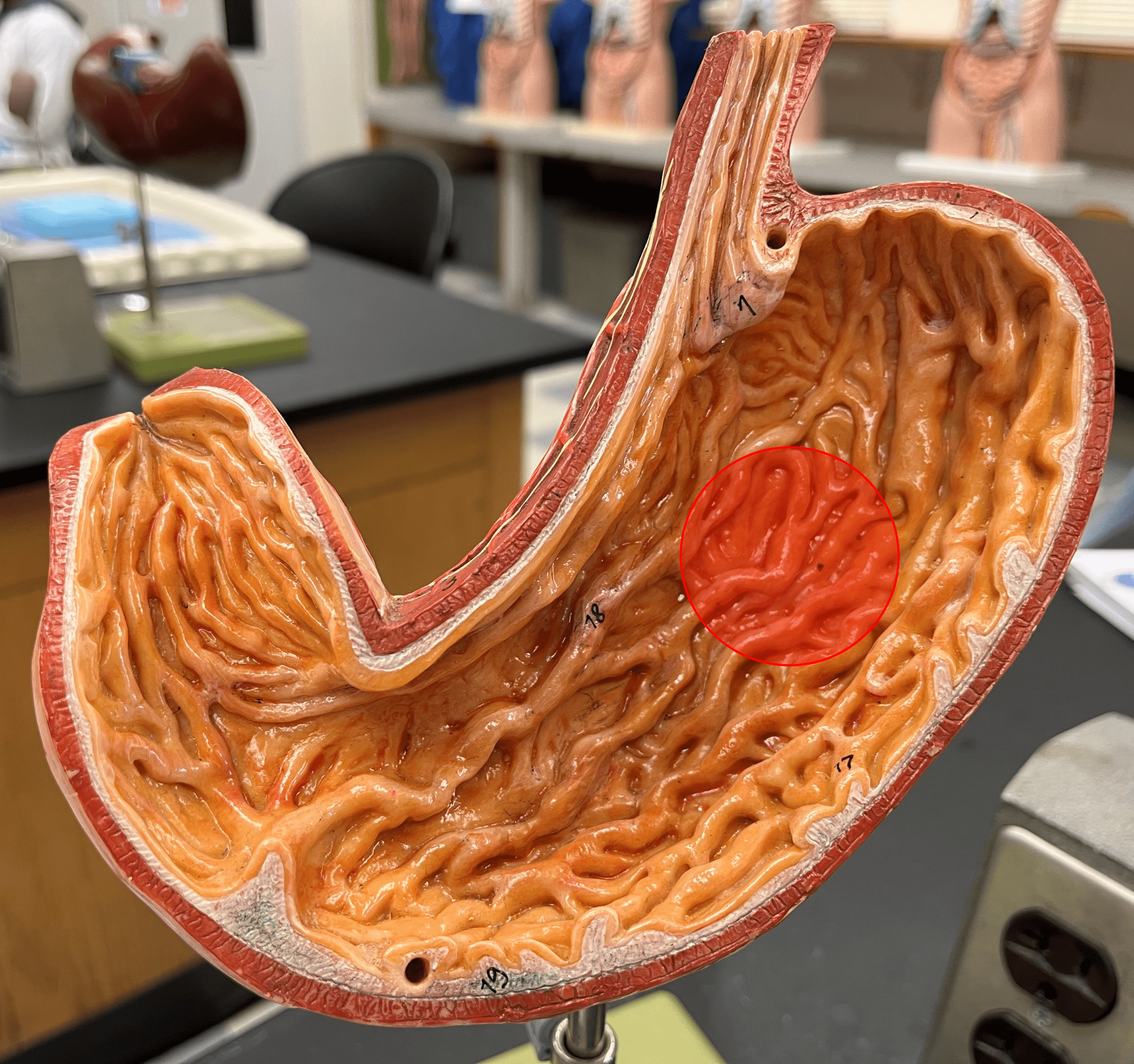
31
New cards
gastric pit
• Slide histology of the stomach.
• A microscopic invagination of the rugae of the stomach.
• A microscopic invagination of the rugae of the stomach.
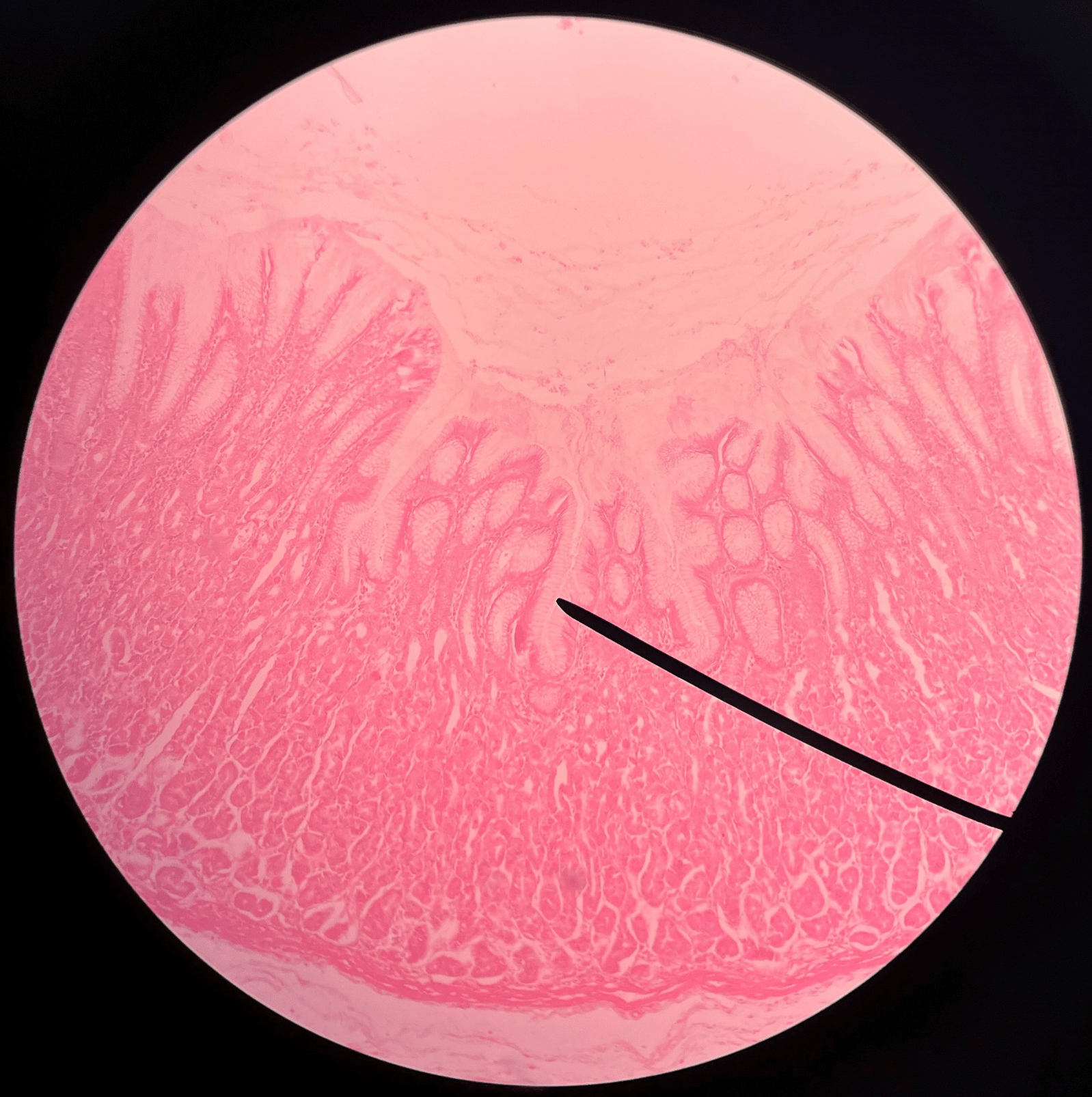
32
New cards
gastric glands
• Slide histology of the stomach.
• Located within gastric pits.
• Secretes gastric juice.
• Located within gastric pits.
• Secretes gastric juice.
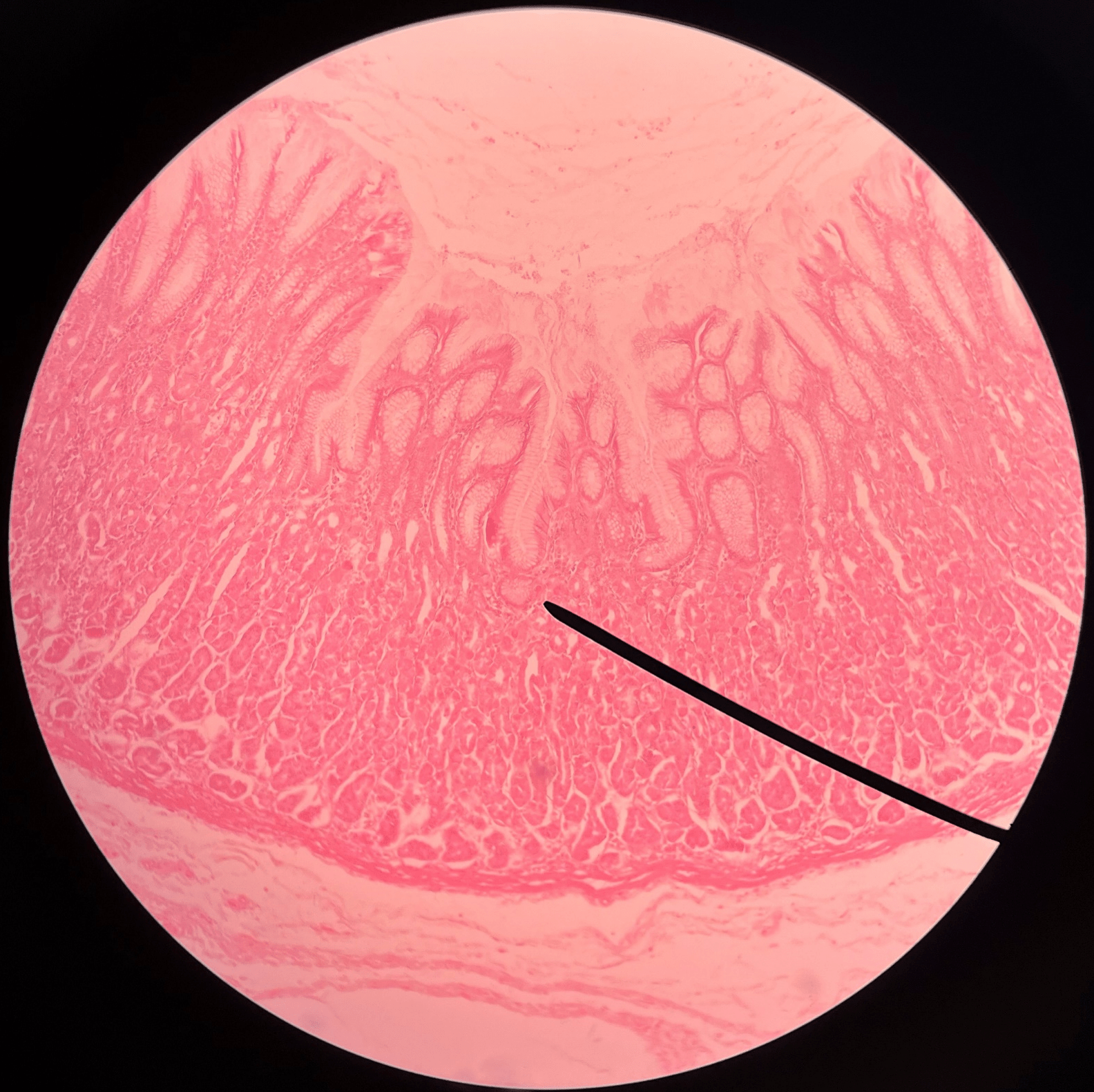
33
New cards
pyloric antrum
• Part of the pylorus of the stomach.
• The region of the pylorus adjacent to the body of the stomach.
• The region of the pylorus adjacent to the body of the stomach.
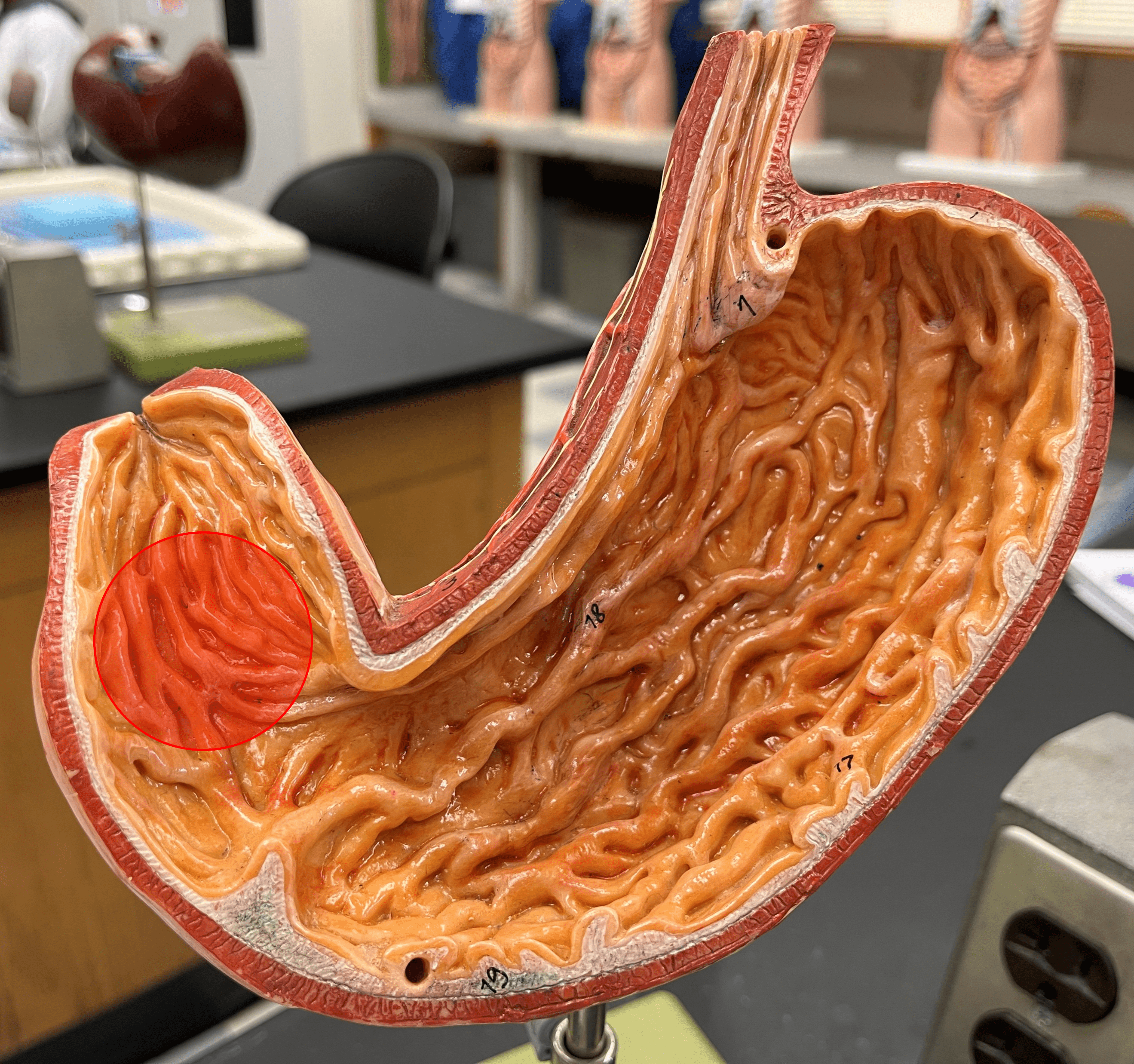
34
New cards
pyloric sphincter
• Part of the pylorus of the stomach.
• Opens to allow stomach contents into the duodenum.
• Also known as the pyloric valve.
• Opens to allow stomach contents into the duodenum.
• Also known as the pyloric valve.
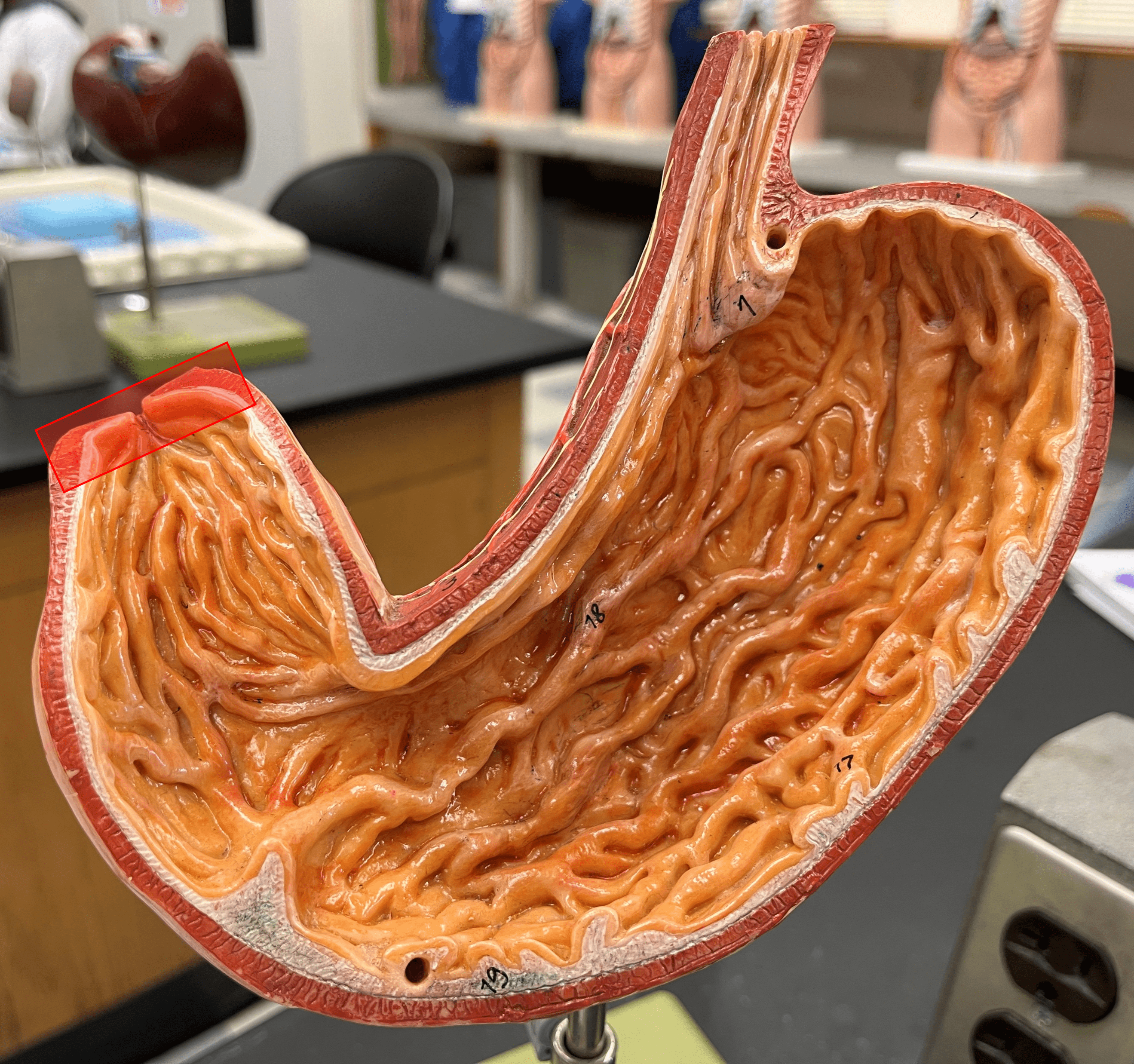
35
New cards
pyloric canal
• Part of the pylorus of the stomach.
• The opening between the stomach and the duodenum.
• The opening between the stomach and the duodenum.
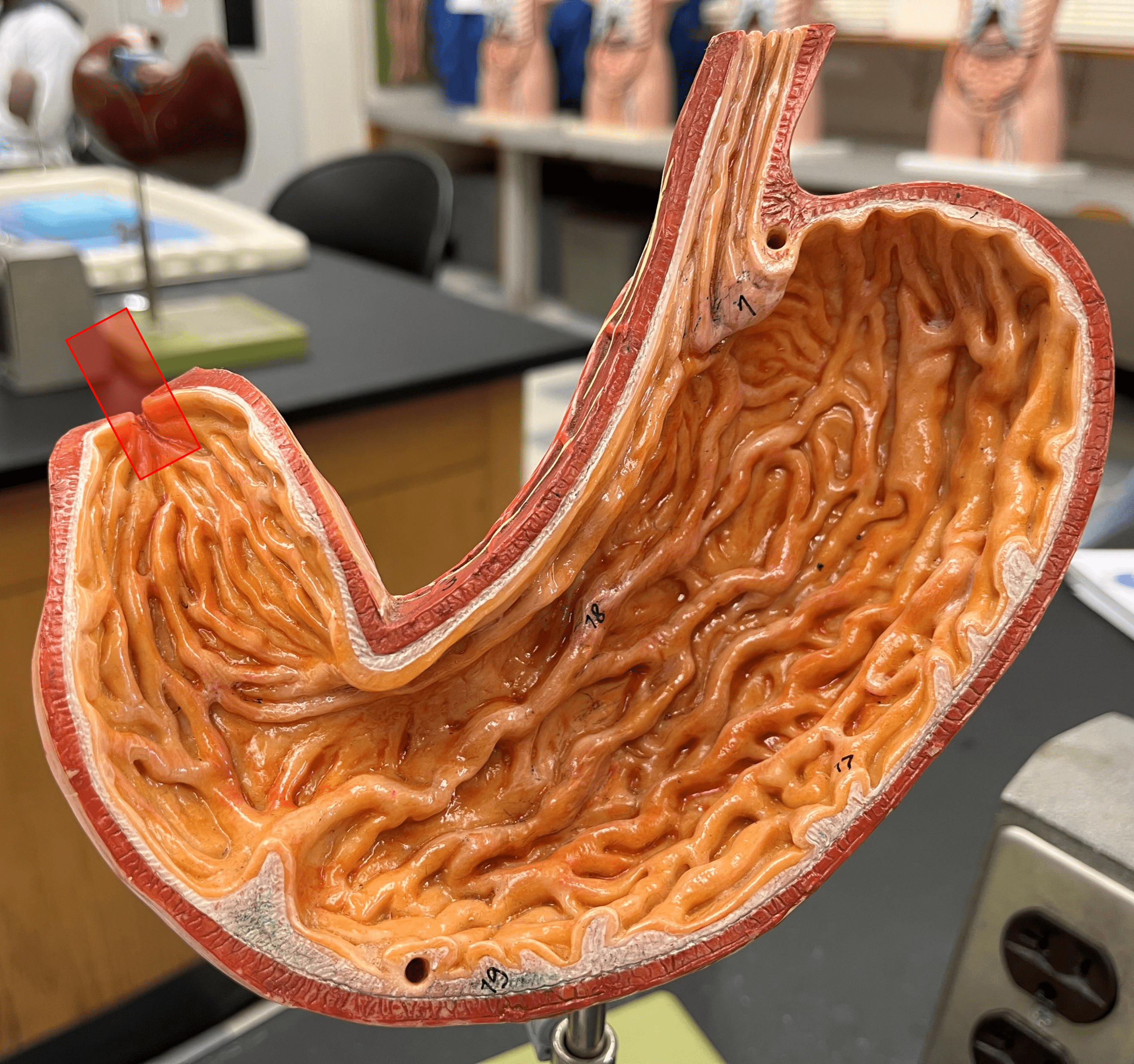
36
New cards
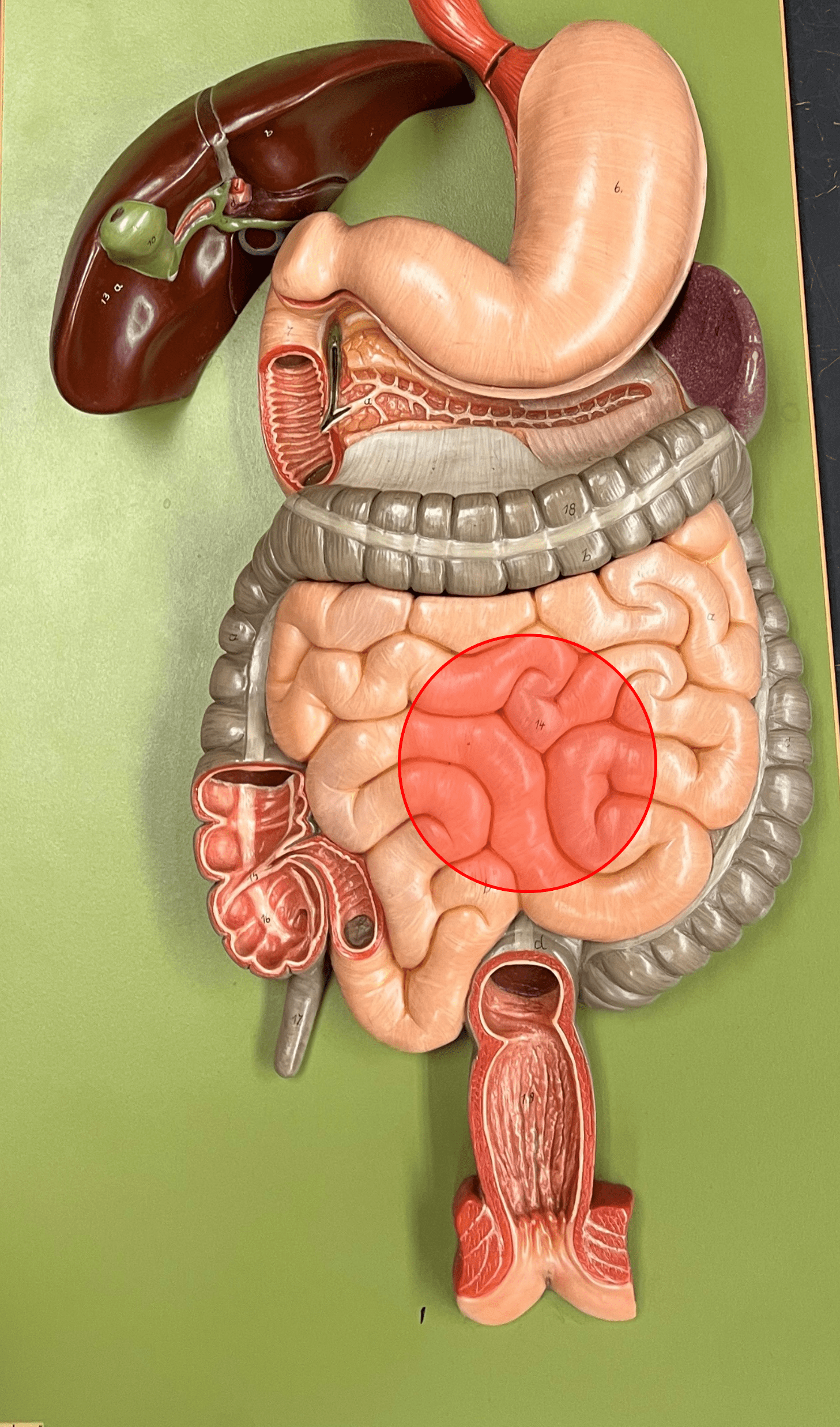
small intestine
• A long tube-shaped organ.
• Divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
• Site of most digestion and nutrient absorption.
• Divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
• Site of most digestion and nutrient absorption.
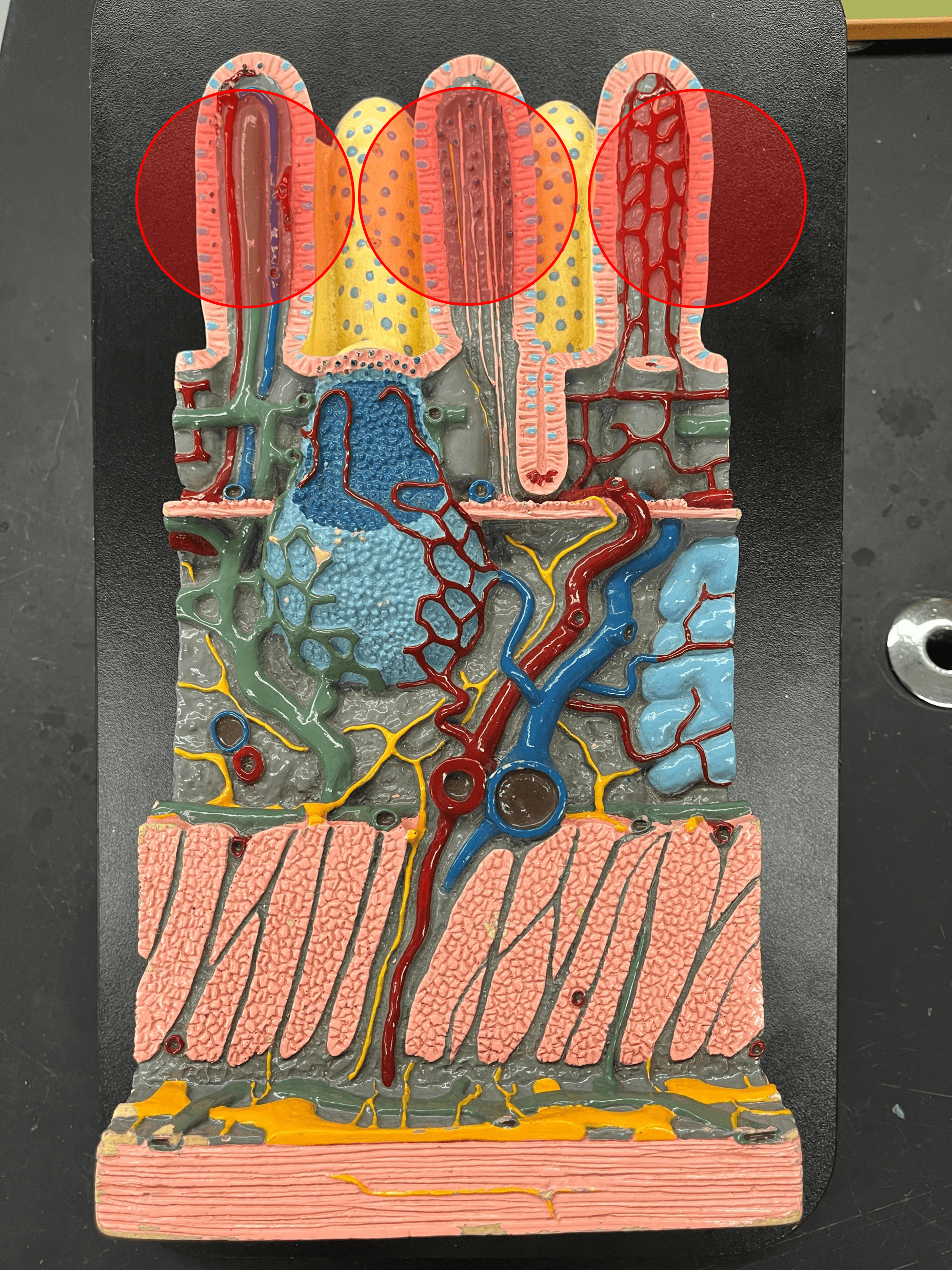
37
New cards
villi
• Located in the small intestine.
• Finger-like projections that increases the absorptive surface of the small intestine.
• Finger-like projections that increases the absorptive surface of the small intestine.
38
New cards
lacteal
• Located in the villi of the small intestine.
• A part of a lymphatic vessel that absorbs digested fats into the circulatory system.
• A part of a lymphatic vessel that absorbs digested fats into the circulatory system.
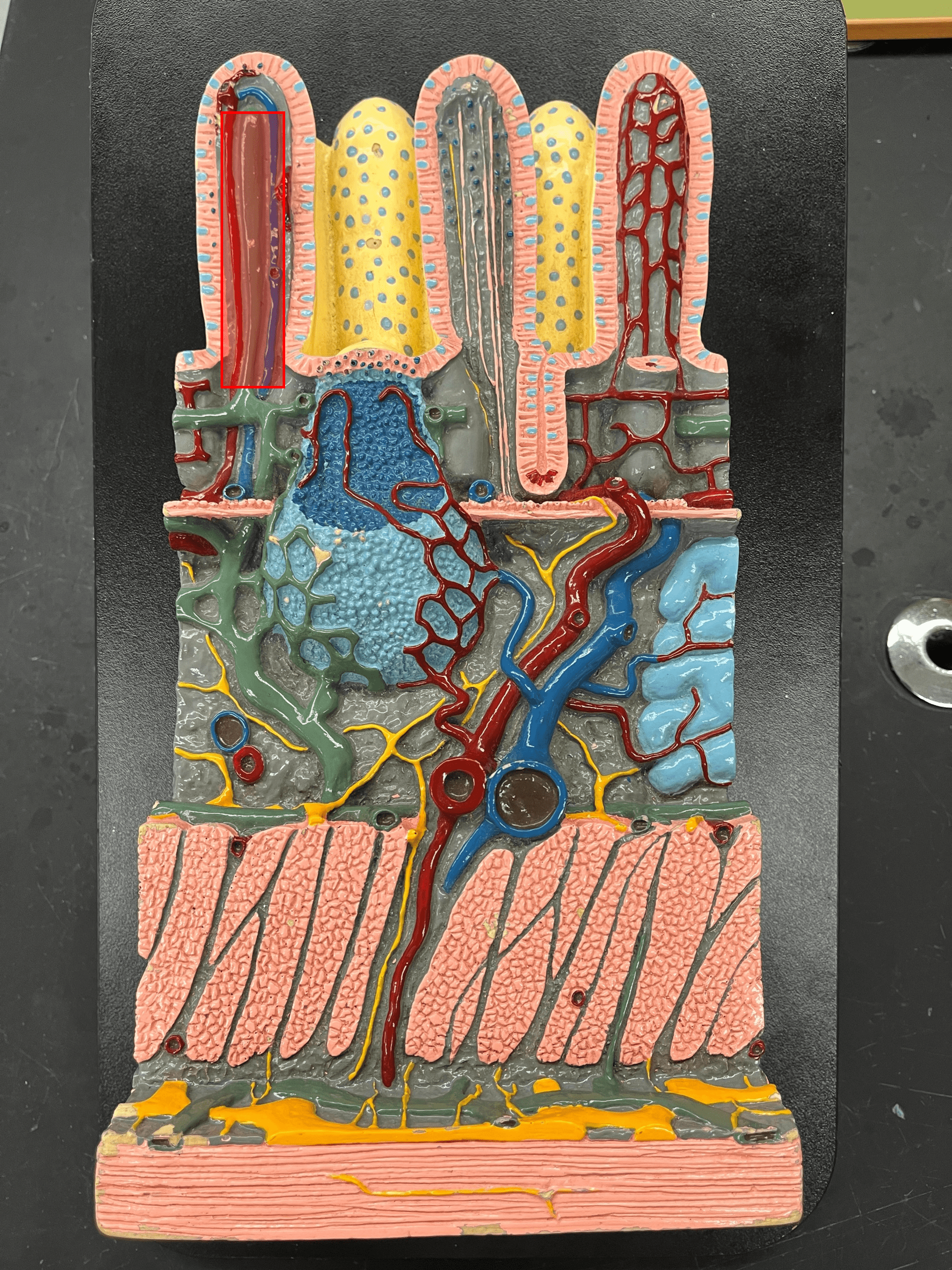
39
New cards
duodenum
• Slide histology.
• The proximal region of the small intestine.
• The proximal region of the small intestine.
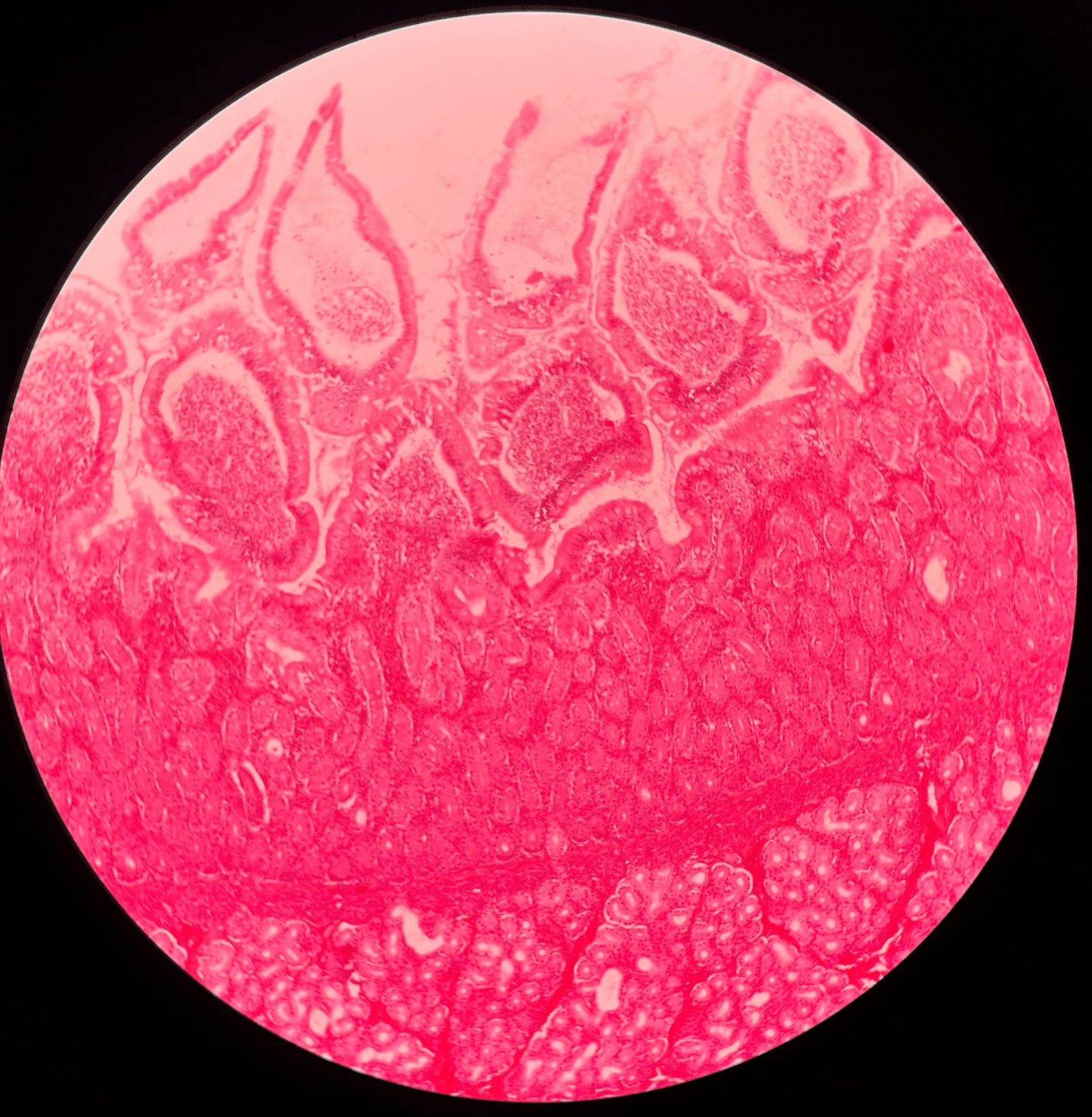
40
New cards
villi
• Slide histology of the duodenum.
• Located in the mucosa layer of the duodenum.
• Increases the absorptive surface of the lining epithelium.
• Located in the mucosa layer of the duodenum.
• Increases the absorptive surface of the lining epithelium.
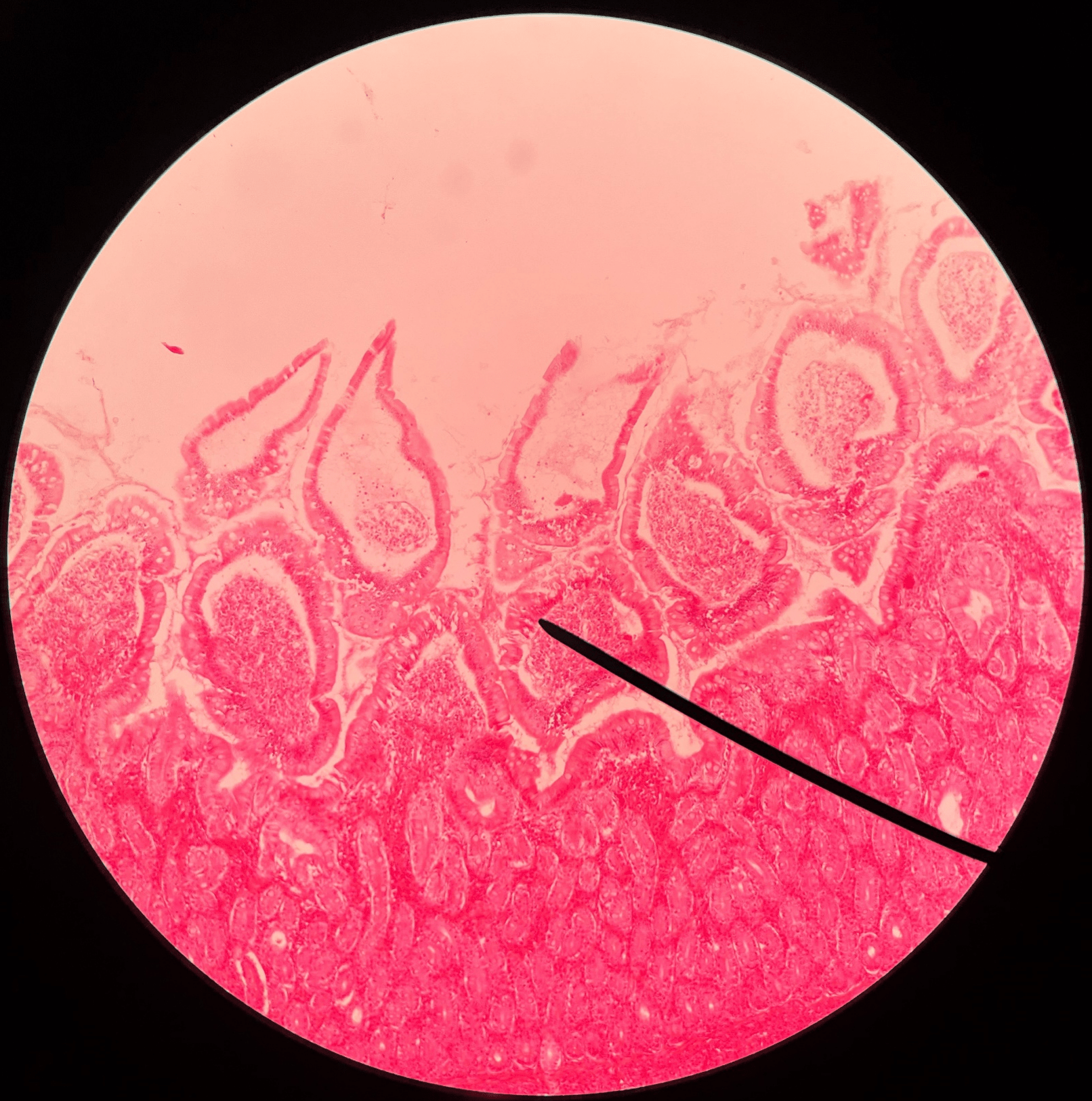
41
New cards
intestinal glands
• Slide histology of the duodenum.
• Located in the mucosa layer of the duodenum.
• Produces hormones that participate in digestion.
• Located in the mucosa layer of the duodenum.
• Produces hormones that participate in digestion.
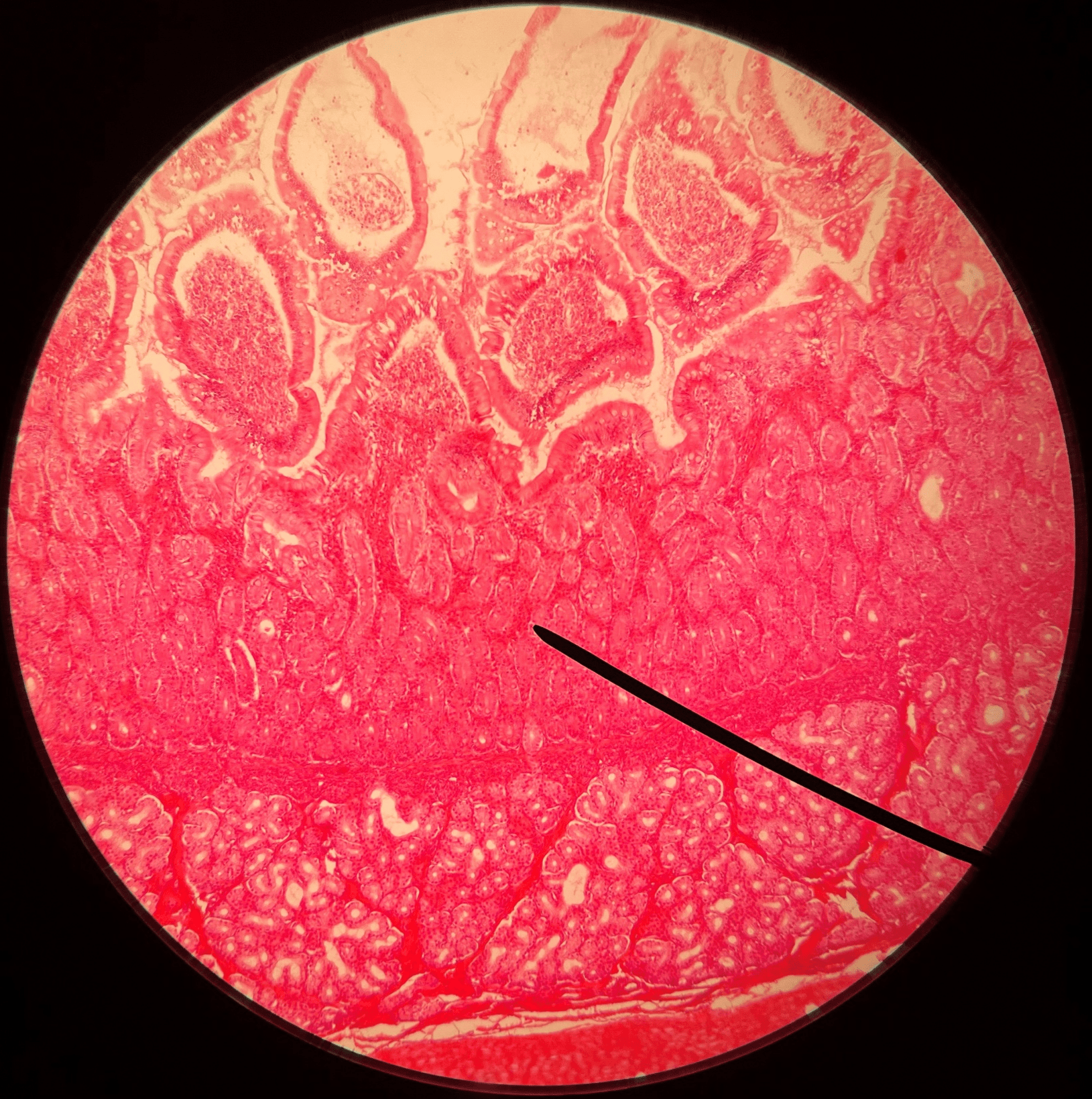
42
New cards
duodenal glands
• Slide histology of the duodenum.
• Located in the submucosa layer of the duodenum.
• Produces mucus to protect the intestinal lining from stomach acid.
• Located in the submucosa layer of the duodenum.
• Produces mucus to protect the intestinal lining from stomach acid.
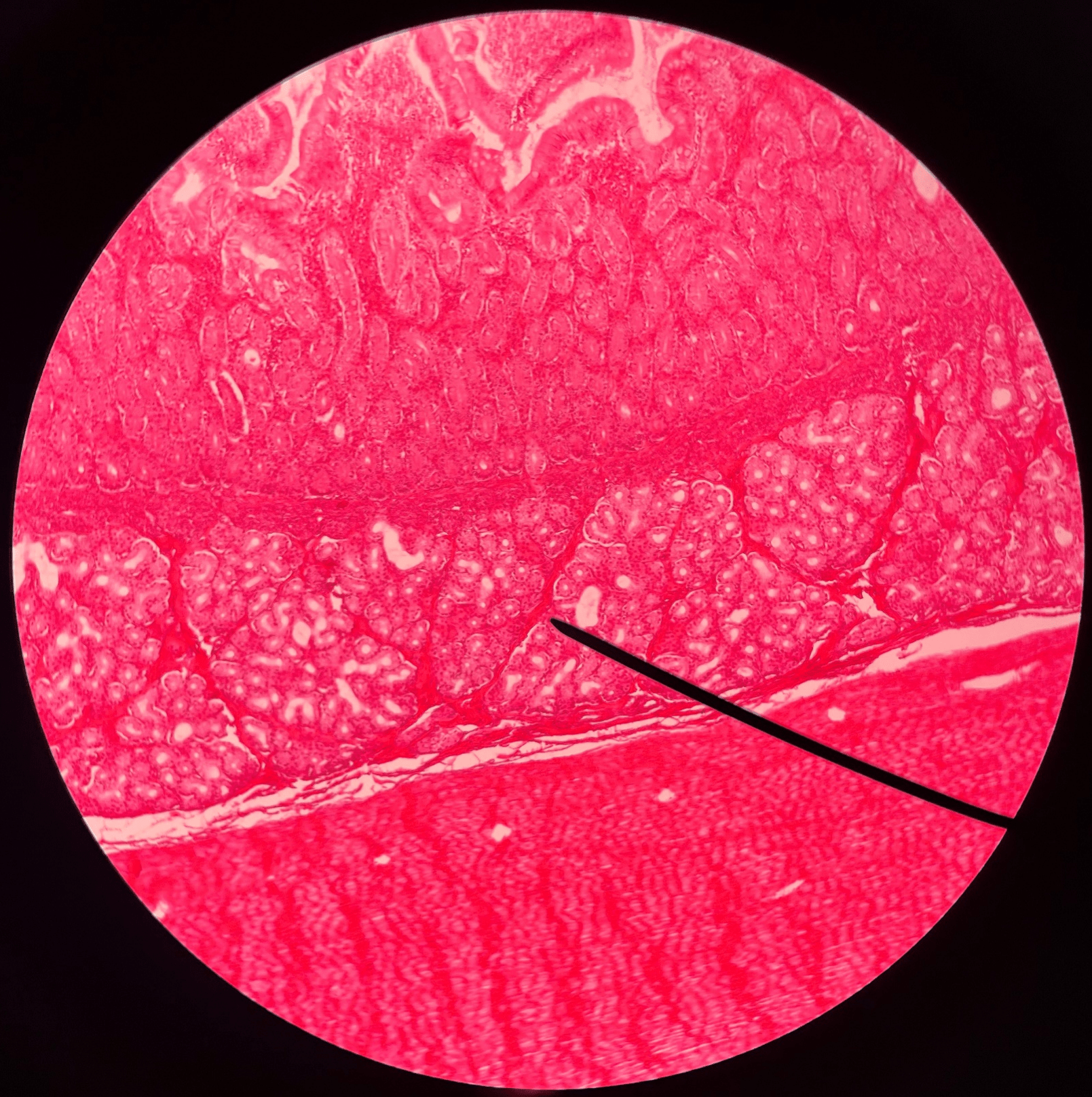
43
New cards
muscularis
• Slide histology of the duodenum.
• The layer of the duodenum deep to the submucosa.
• The layer of the duodenum deep to the submucosa.
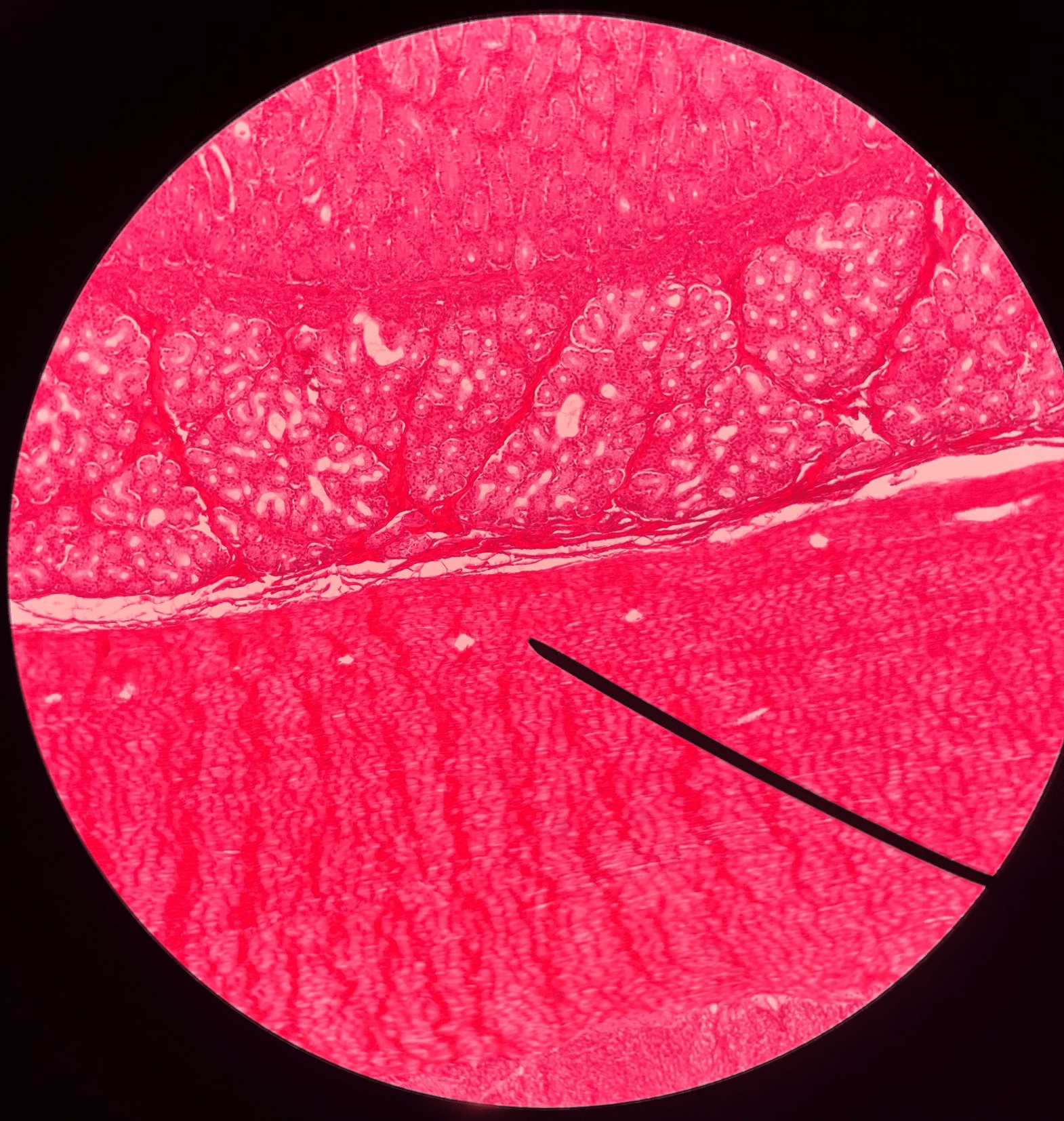
44
New cards
ileum
• Slide histology.
• The distal region of the small intestine.
• The distal region of the small intestine.
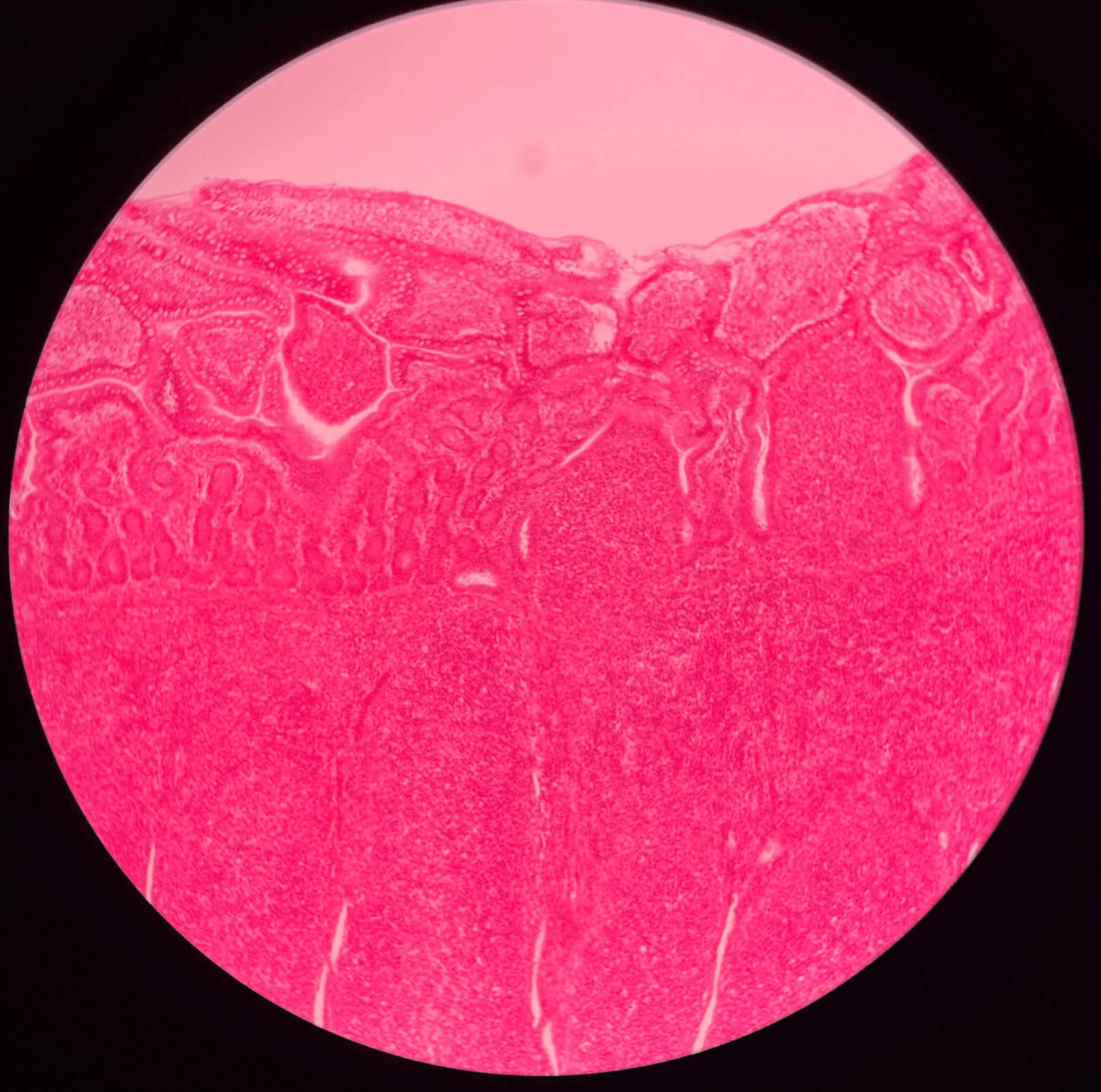
45
New cards
villi
• Slide histology of the ileum.
• Located in the mucosa layer of the ileum.
• Increases the absorptive surface of the lining epithelium.
• Located in the mucosa layer of the ileum.
• Increases the absorptive surface of the lining epithelium.
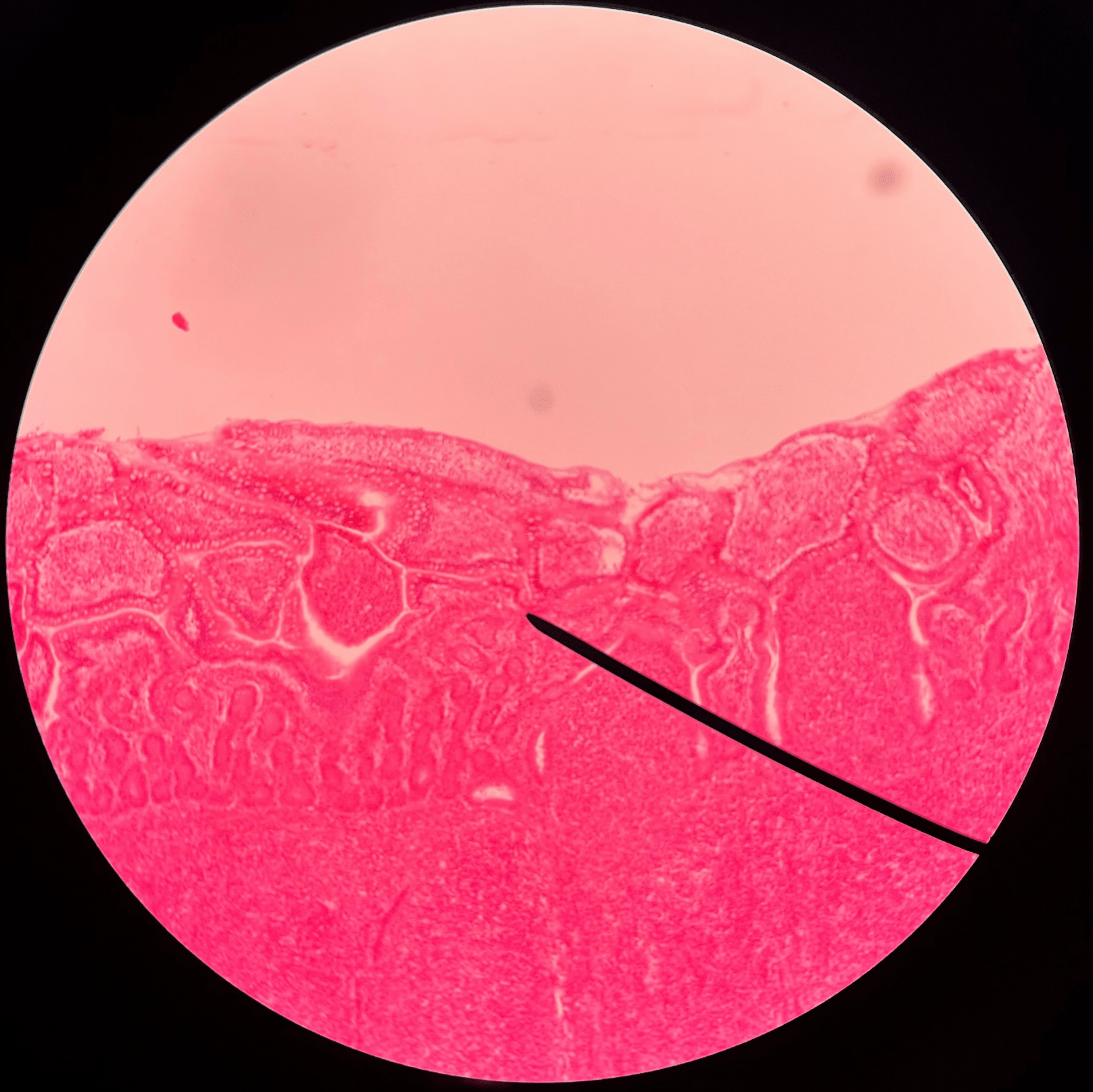
46
New cards
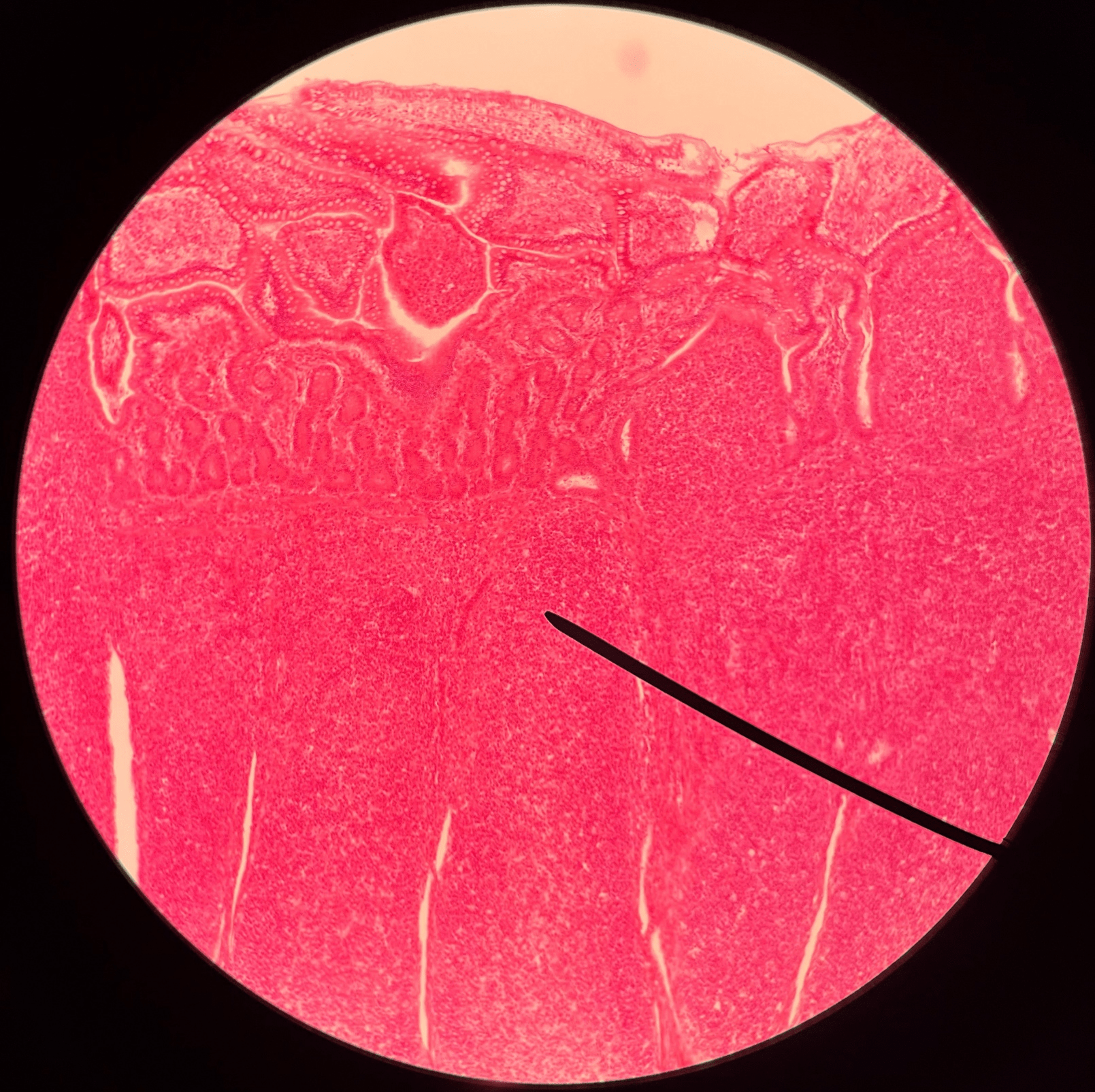
Peyer’s patch
• Slide histology of the ileum.
• Located in the submucosa layer of the ileum.
• A round cluster of dark-staining lymphocytes and macrophages.
• Located in the submucosa layer of the ileum.
• A round cluster of dark-staining lymphocytes and macrophages.
47
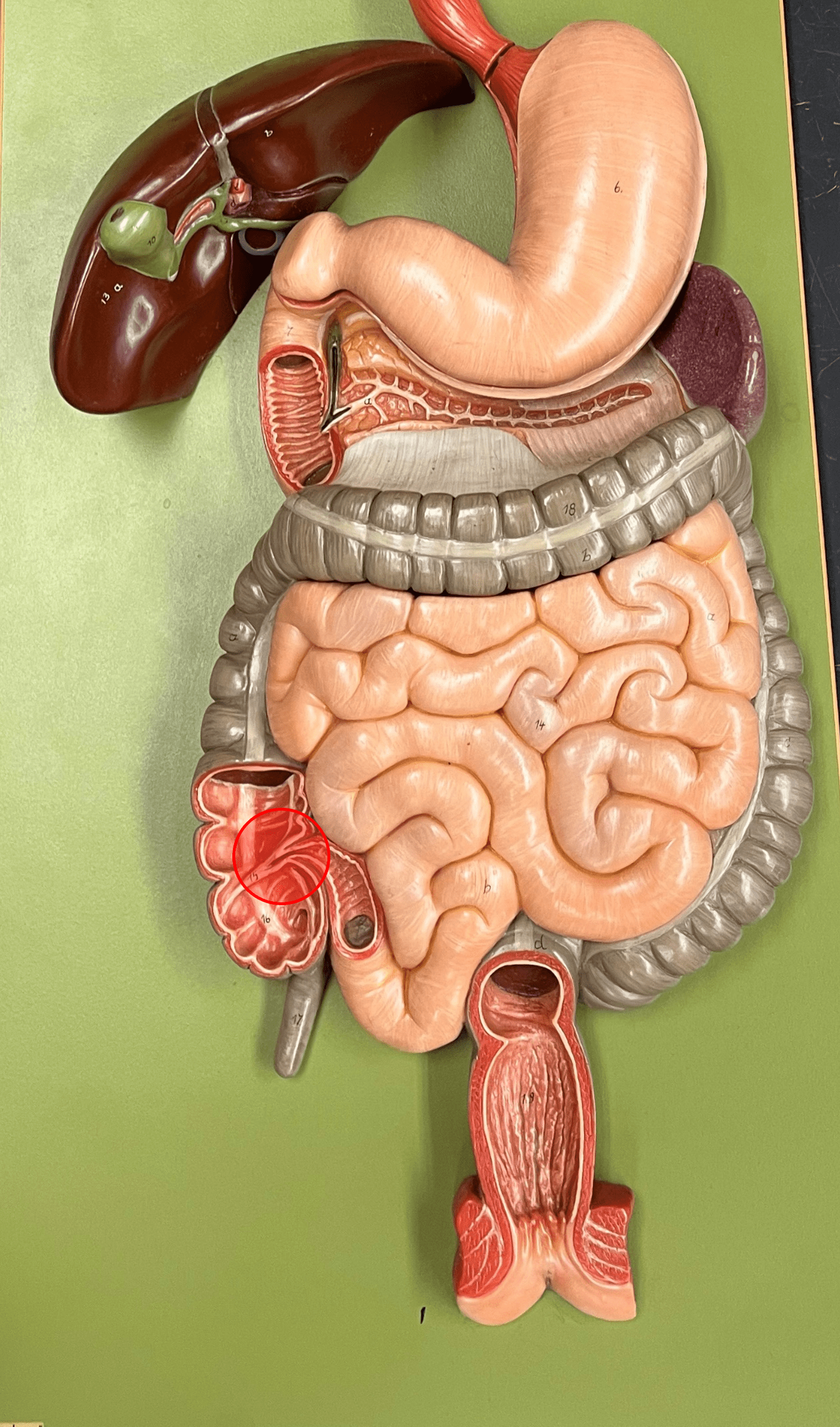
New cards
ileocecal valve
• The termination of the ileum.
• Allows small intestine contents into the large intestine.
• Allows small intestine contents into the large intestine.
48
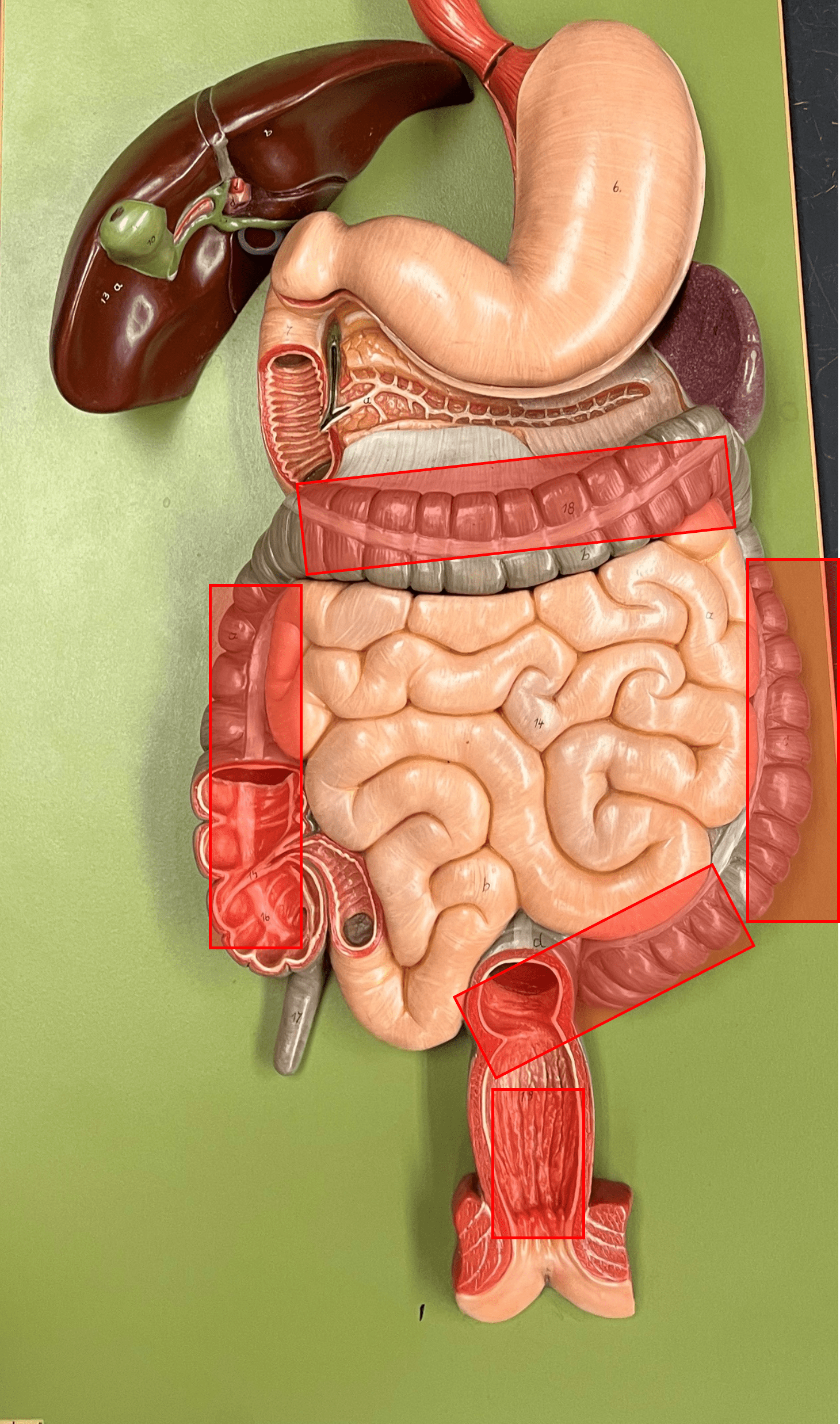
New cards
large intestine
• A tube-shaped organ.
• Divided into the cecum, colon, and rectum.
• Site of feces formation.
• Divided into the cecum, colon, and rectum.
• Site of feces formation.
49
New cards
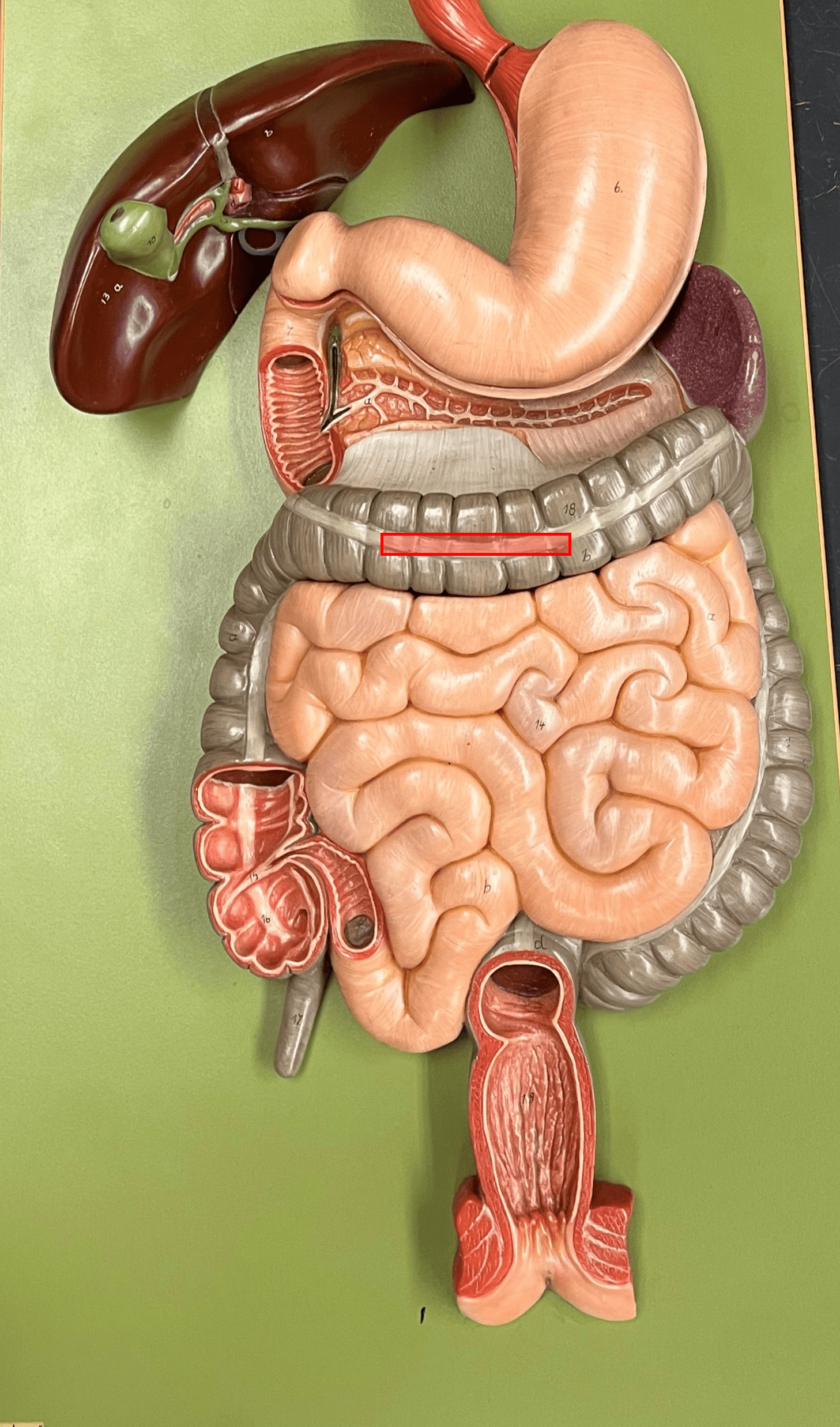
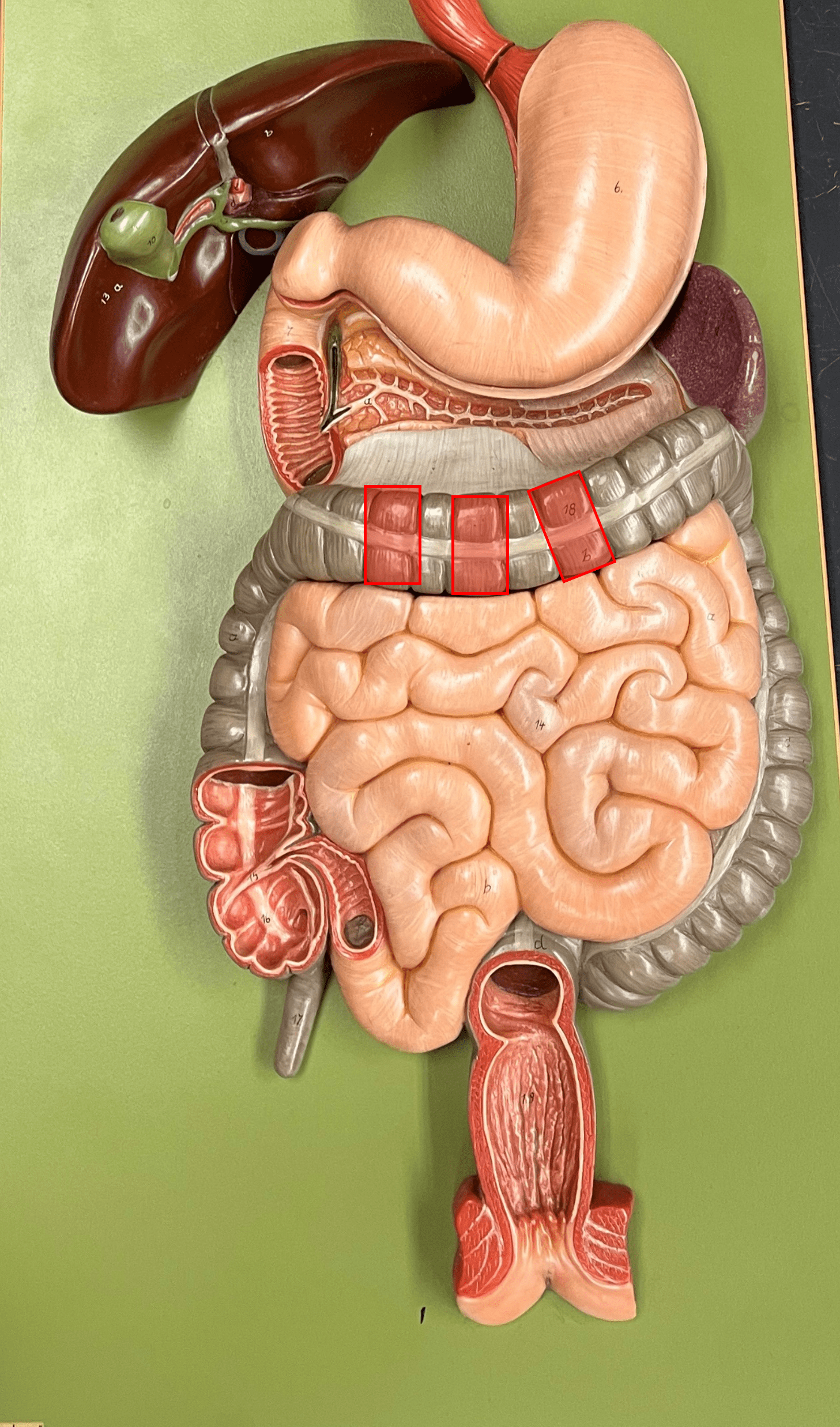
taenia coli
• The three longitudinal bands of smooth muscle separating parts of the colon into haustra.
• Found only on the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
• Found only on the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
50
New cards
haustra
• Pouches of the colon formed by the taenia coli.
• Present on the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
• Present on the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
51
New cards
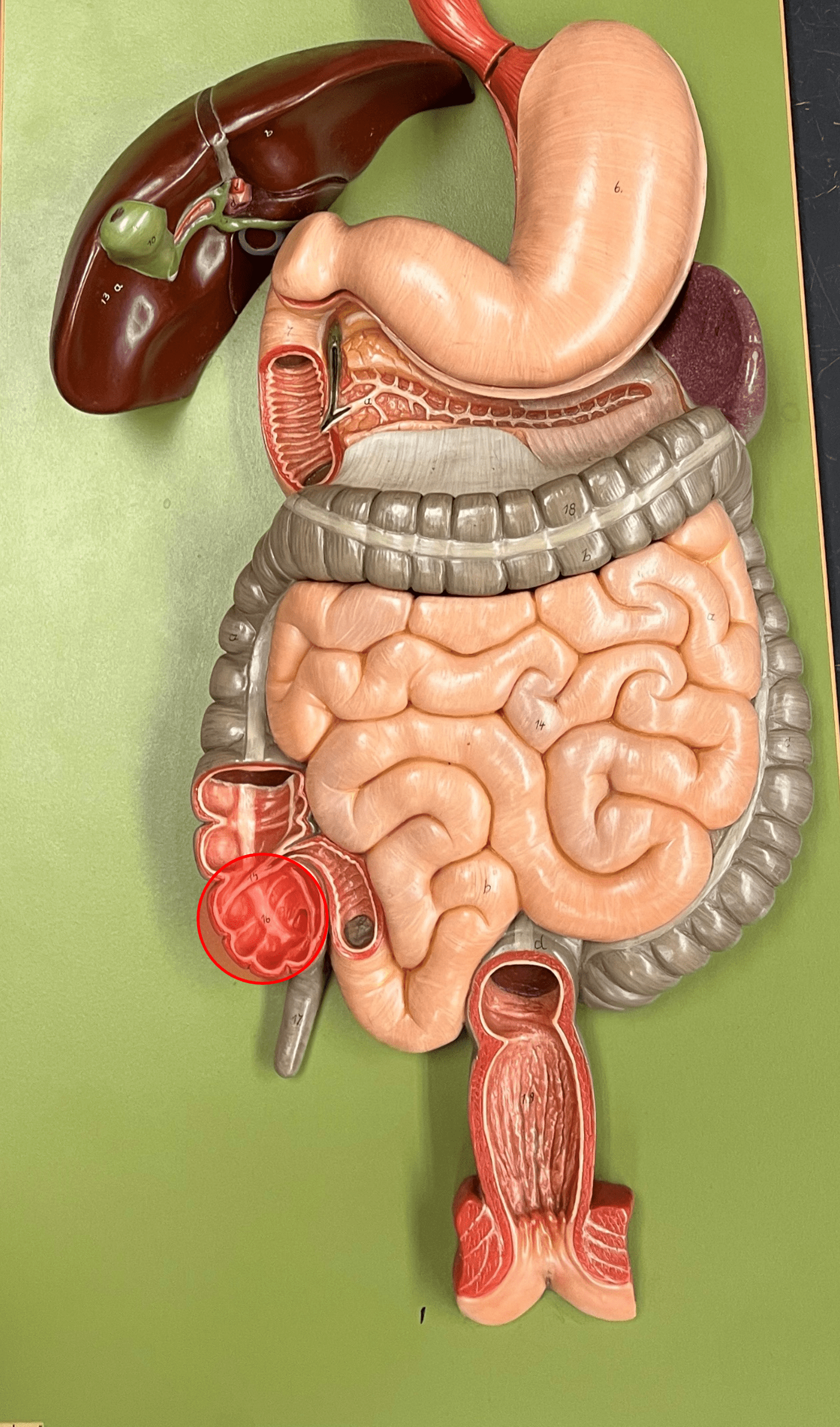
cecum
• A region of the large intestine.
• A blind pouch arising from the ileocecal valve.
• A blind pouch arising from the ileocecal valve.
52
New cards
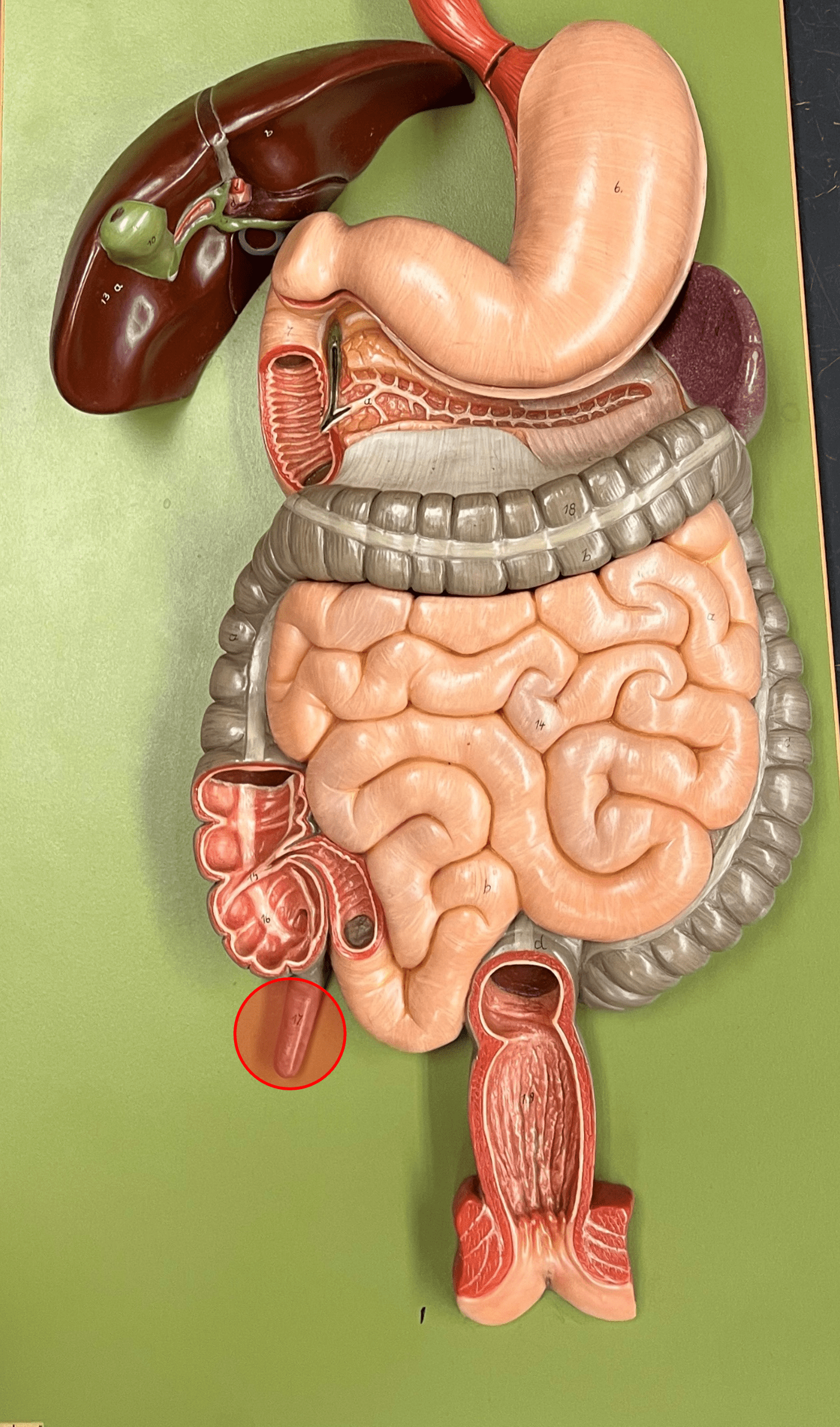
appendix
• Part of the cecum.
• A slender appendage extending from the medial wall of the cecum.
• A slender appendage extending from the medial wall of the cecum.
53
New cards
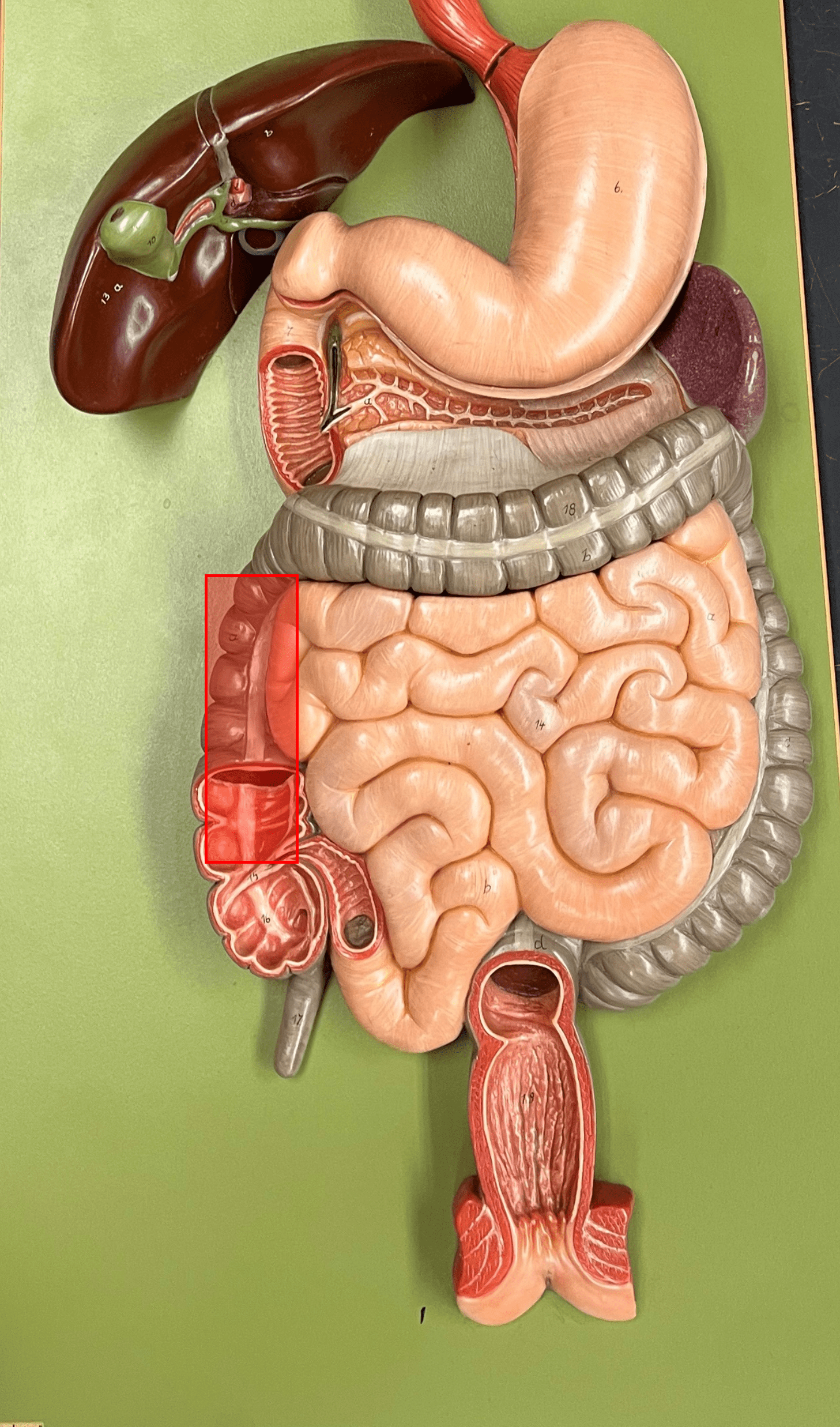
ascending colon
• The first part of the colon of the large intestine.
• The part of the colon moving upwards toward the liver on the right side of the abdominopelvic cavity.
• The part of the colon moving upwards toward the liver on the right side of the abdominopelvic cavity.
54
New cards
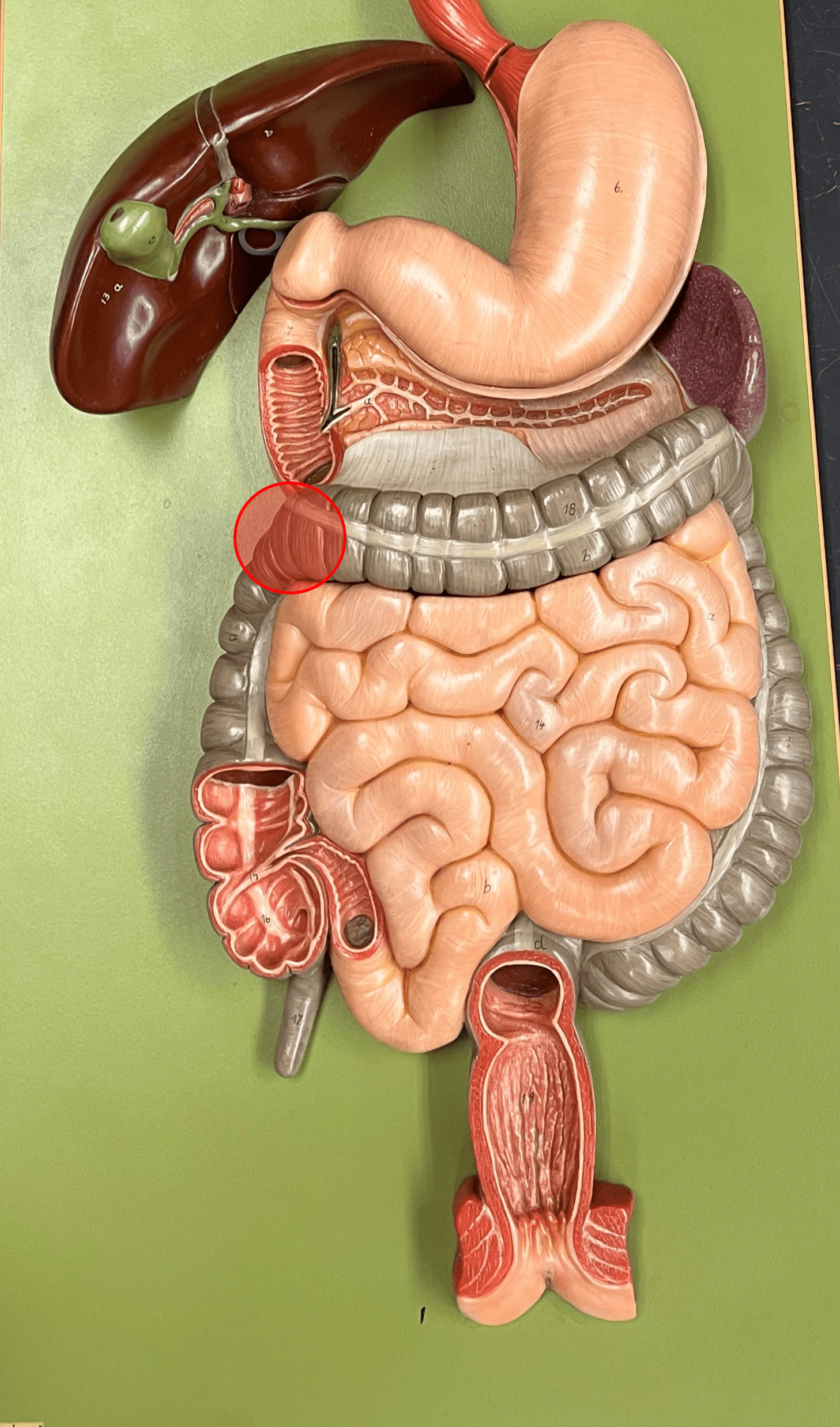
right colic flexure
• The 90° turn of the ascending colon into the transverse colon.
• Occurs just beneath the liver.
• Also known as the hepatic flexure.
• Occurs just beneath the liver.
• Also known as the hepatic flexure.
55
New cards
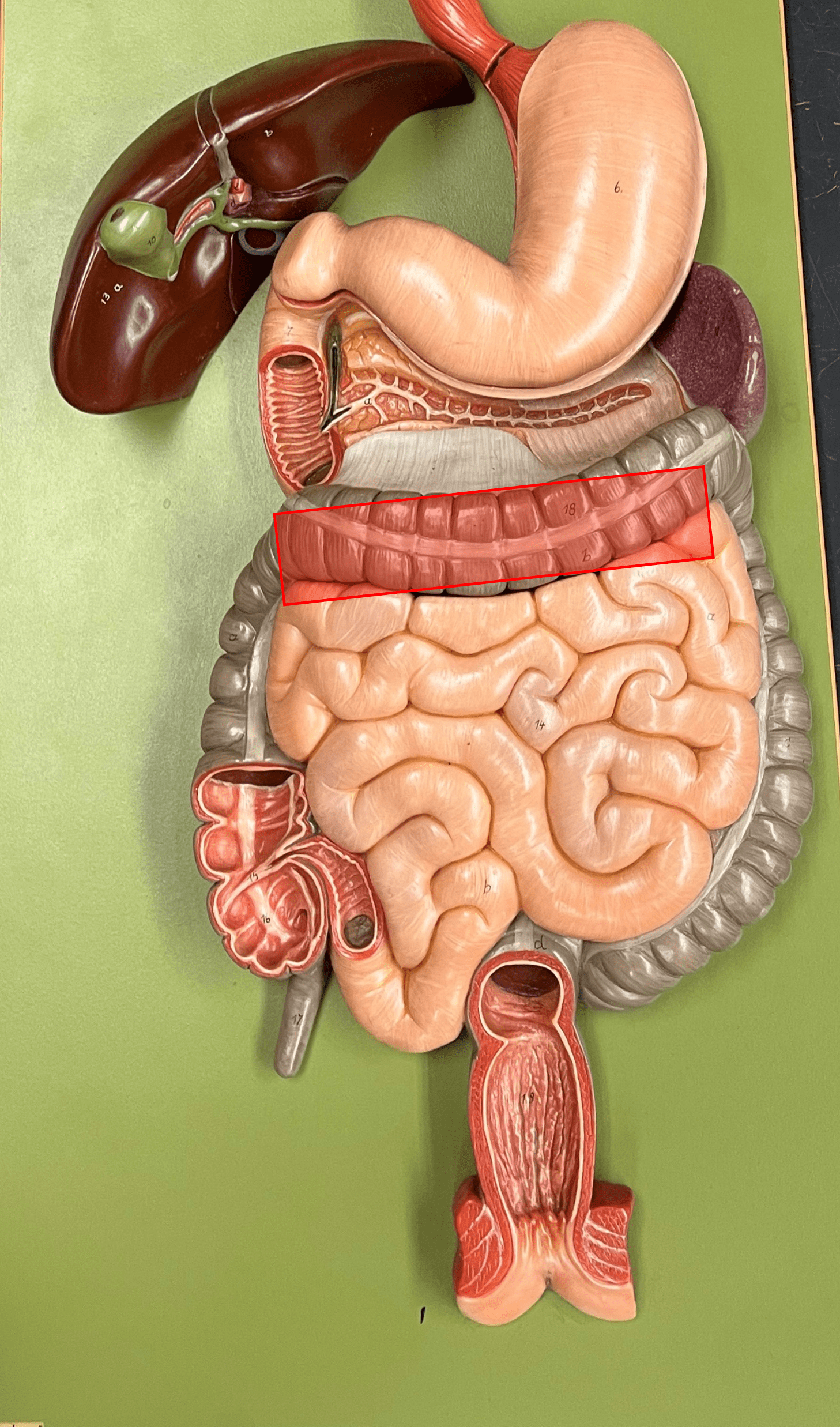
transverse colon
• The second part of the colon of the large intestine.
• The part of the colon moving leftwards across the abdominopelvic cavity.
• The part of the colon moving leftwards across the abdominopelvic cavity.
56
New cards
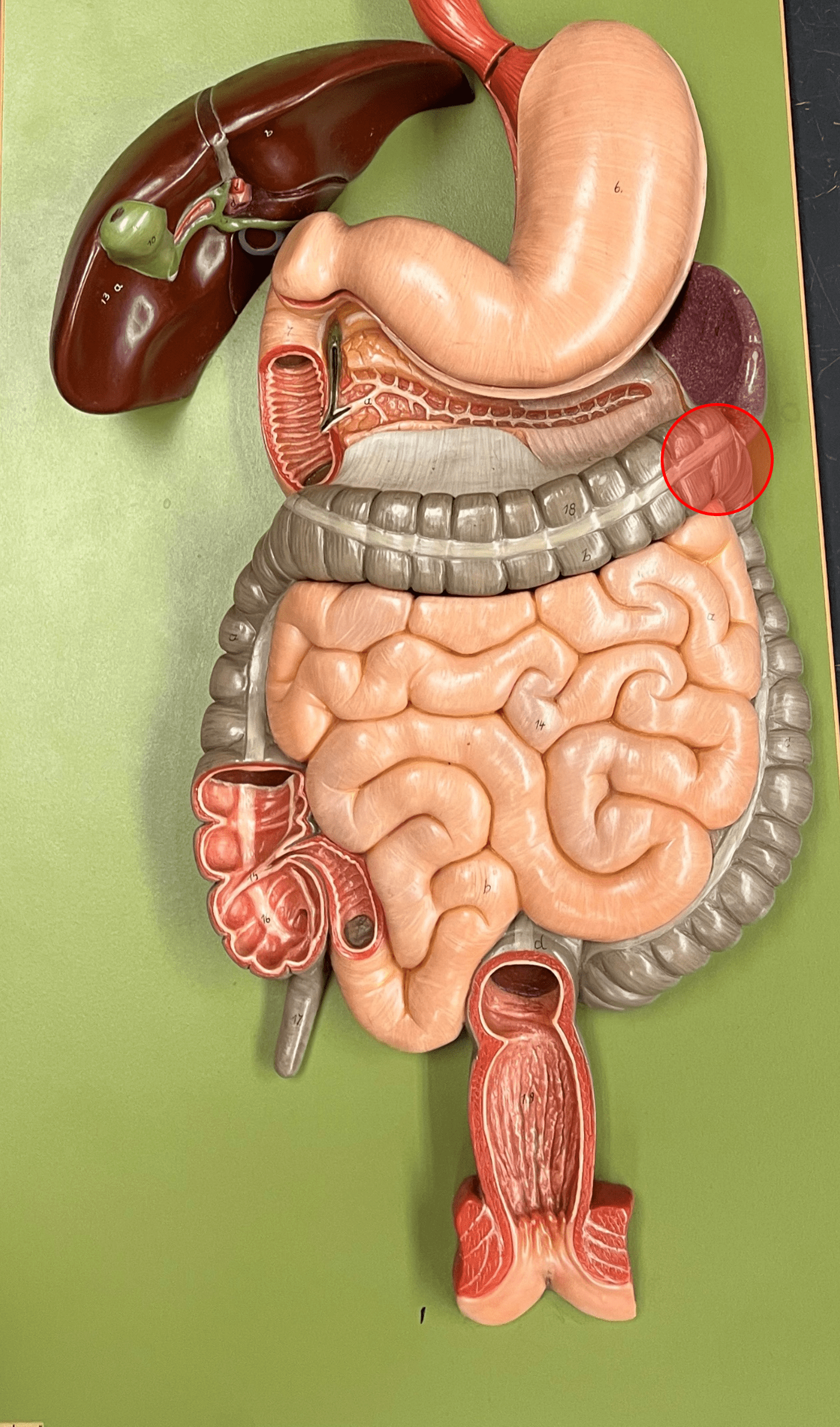
left colic flexure
• The 90° turn of the transverse colon into the descending colon.
• Occurs near the spleen.
• Also known as the splenic flexure.
• Occurs near the spleen.
• Also known as the splenic flexure.
57
New cards
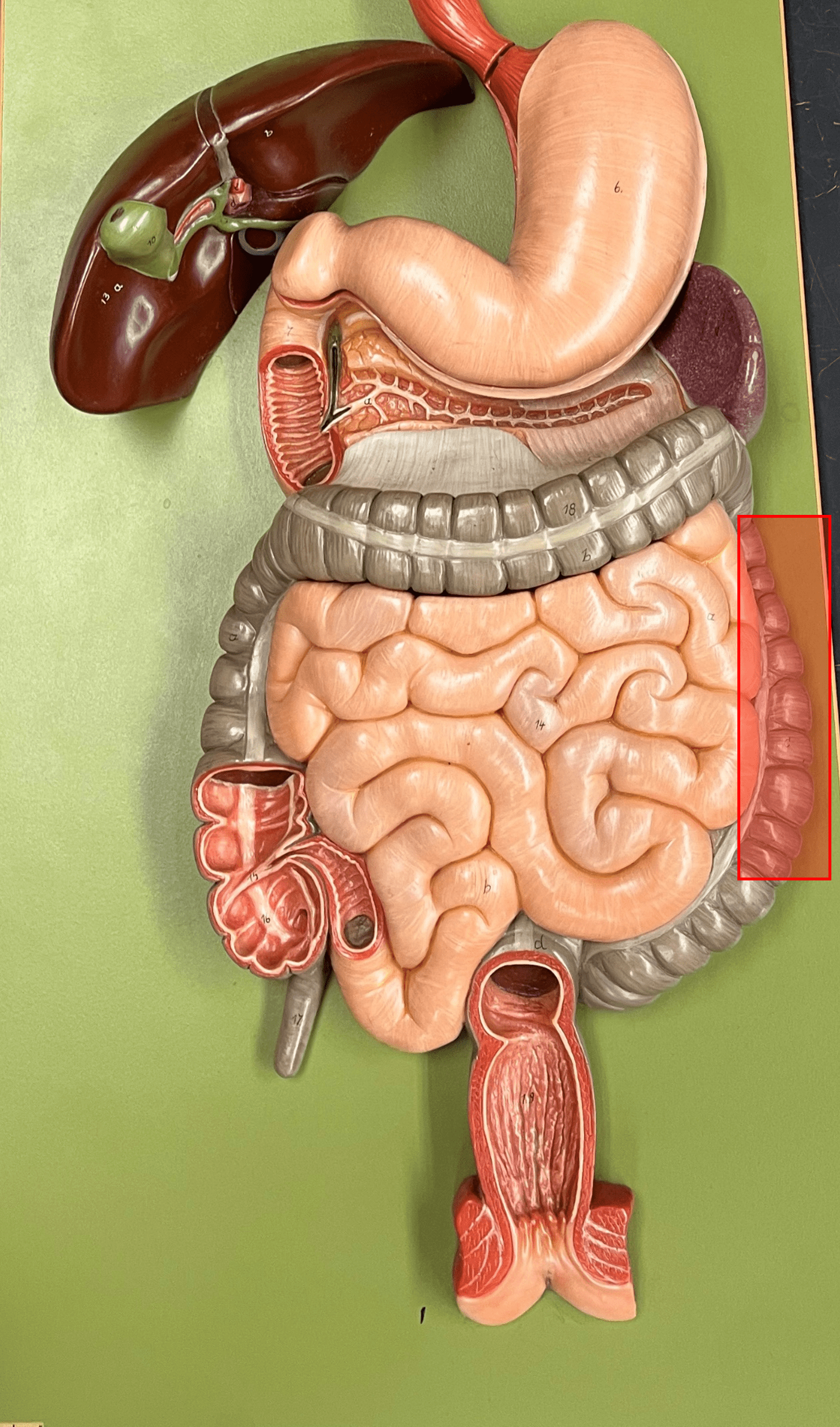
descending colon
• The third part of the colon of the large intestine.
• The part of the colon moving downwards on the left side of the abdominopelvic cavity.
• The part of the colon moving downwards on the left side of the abdominopelvic cavity.
58
New cards
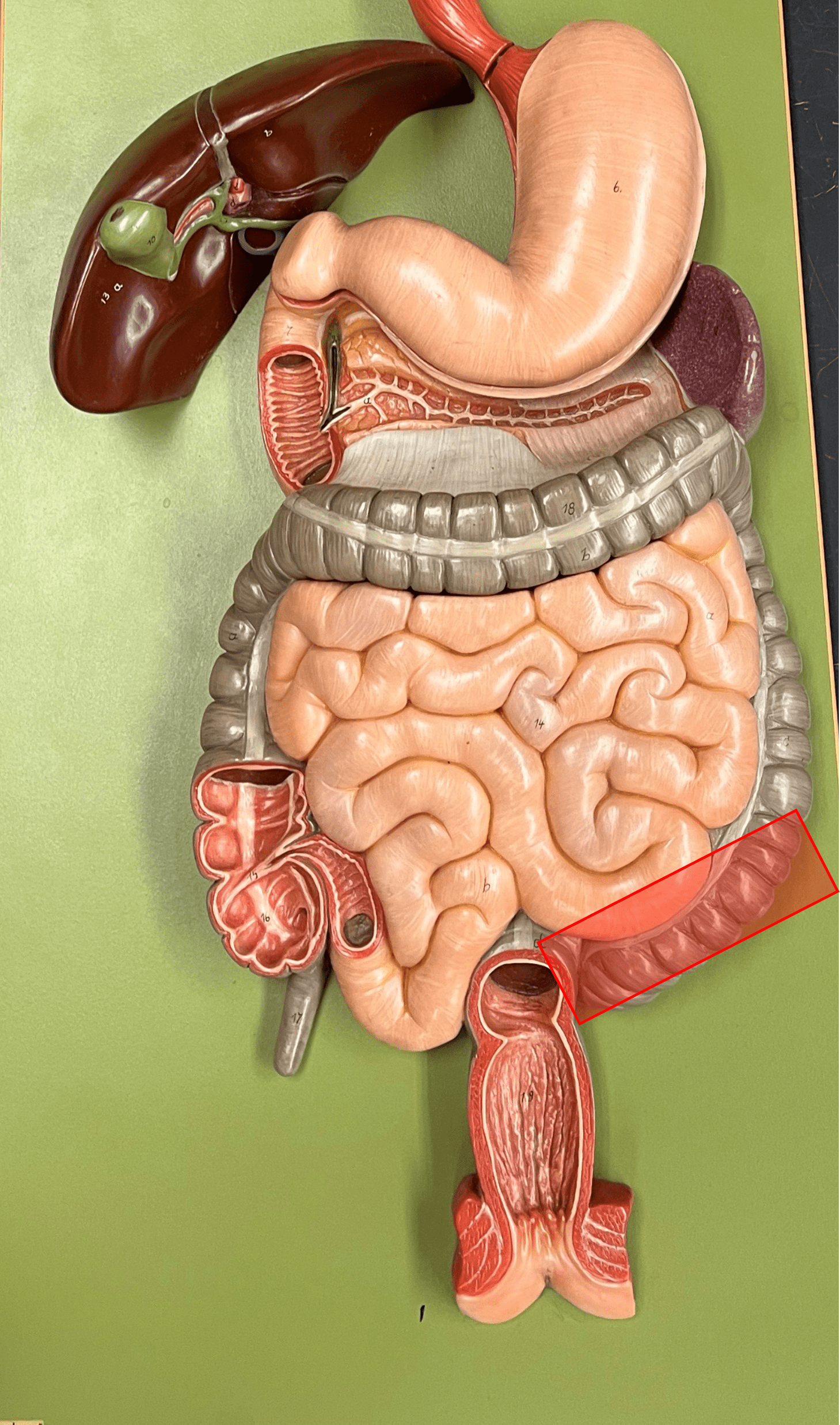
sigmoid colon
• The fourth part of the colon of the large intestine.
• The S-shaped segment at the level of the iliac crest.
• The S-shaped segment at the level of the iliac crest.
59
New cards
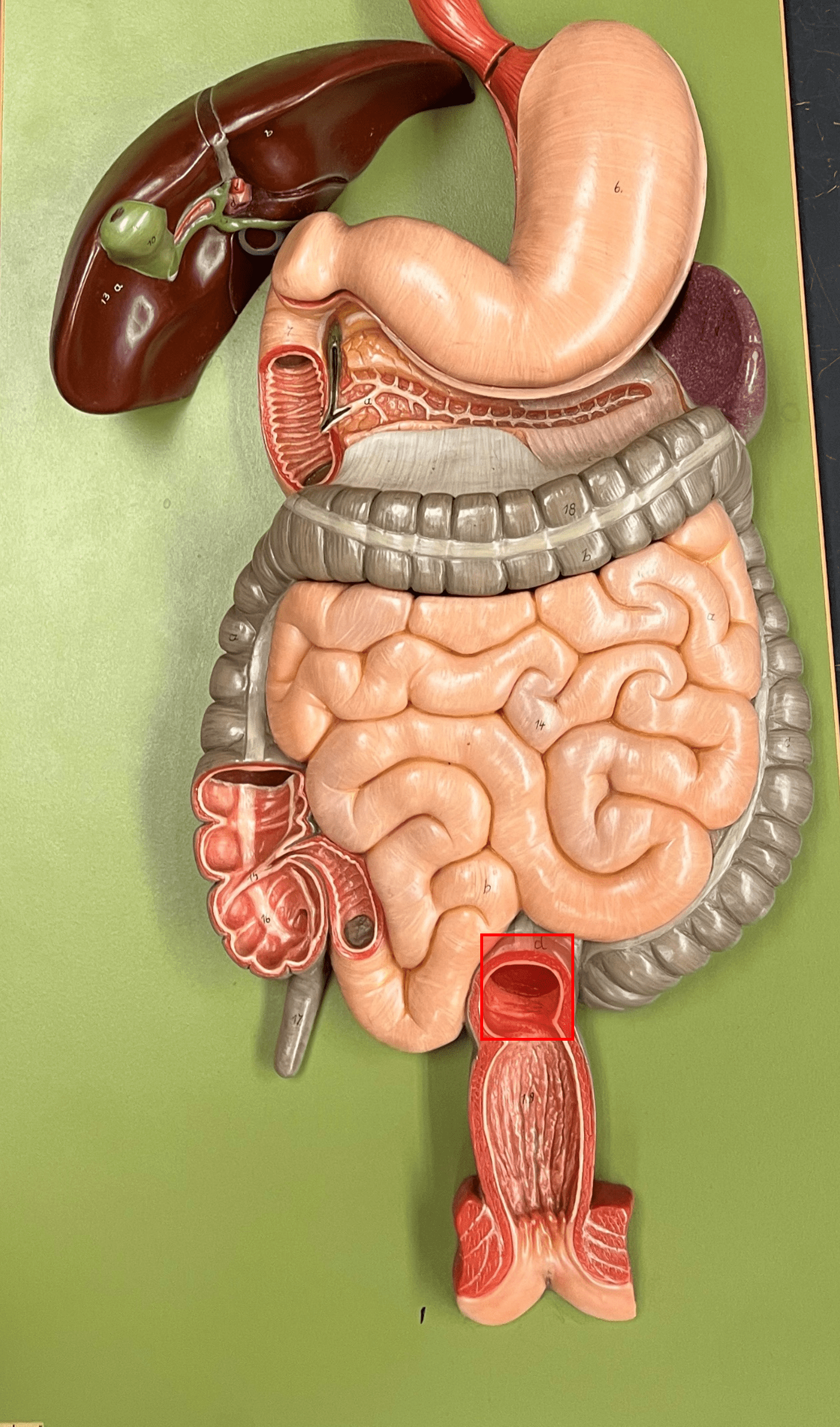
rectum
• A region of the large intestine.
• An area for holding feces until defecation.
• An area for holding feces until defecation.
60
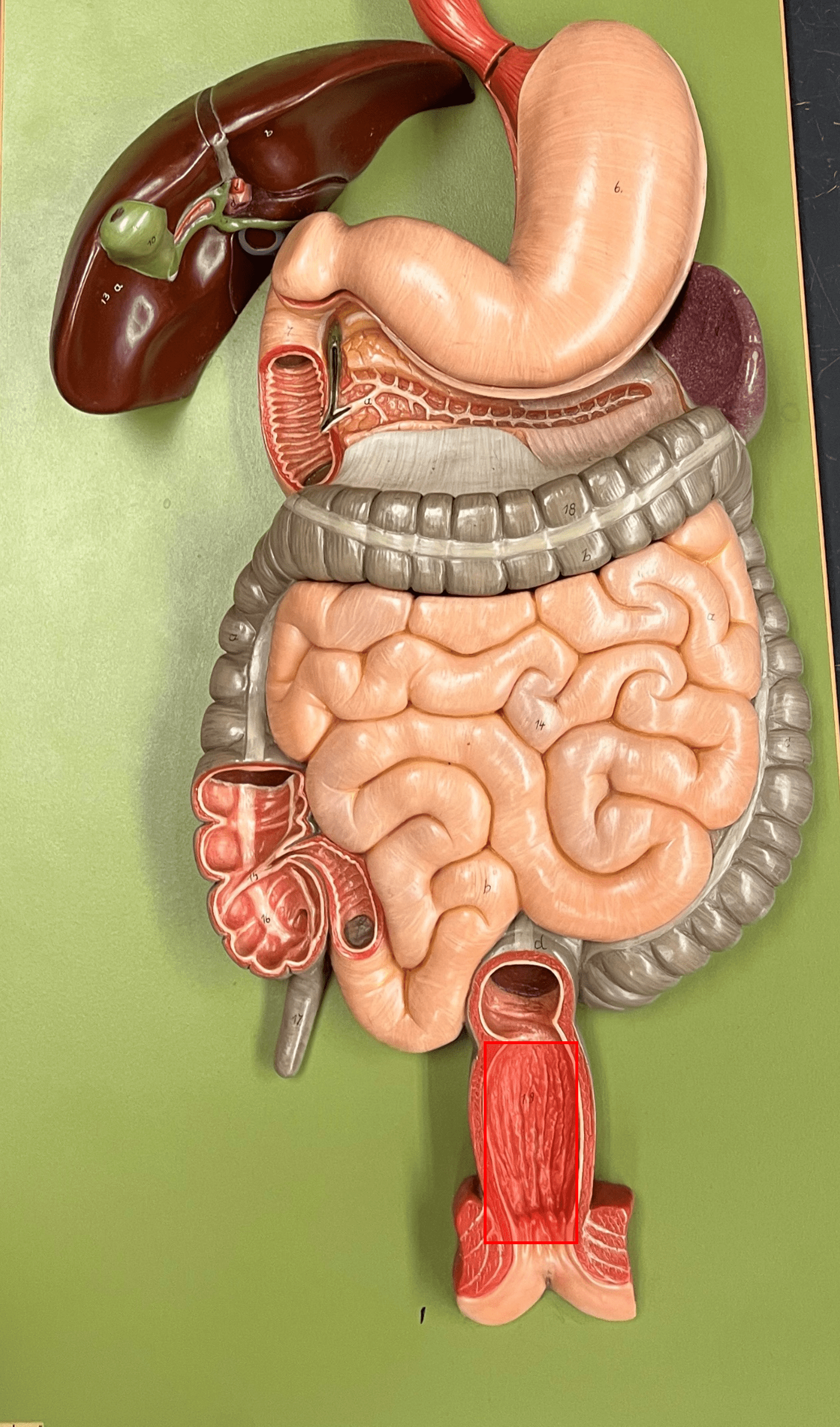
New cards
anal canal
• The final two inches of the rectum.
• Contains anal columns along the inner wall.
• Contains anal columns along the inner wall.
61
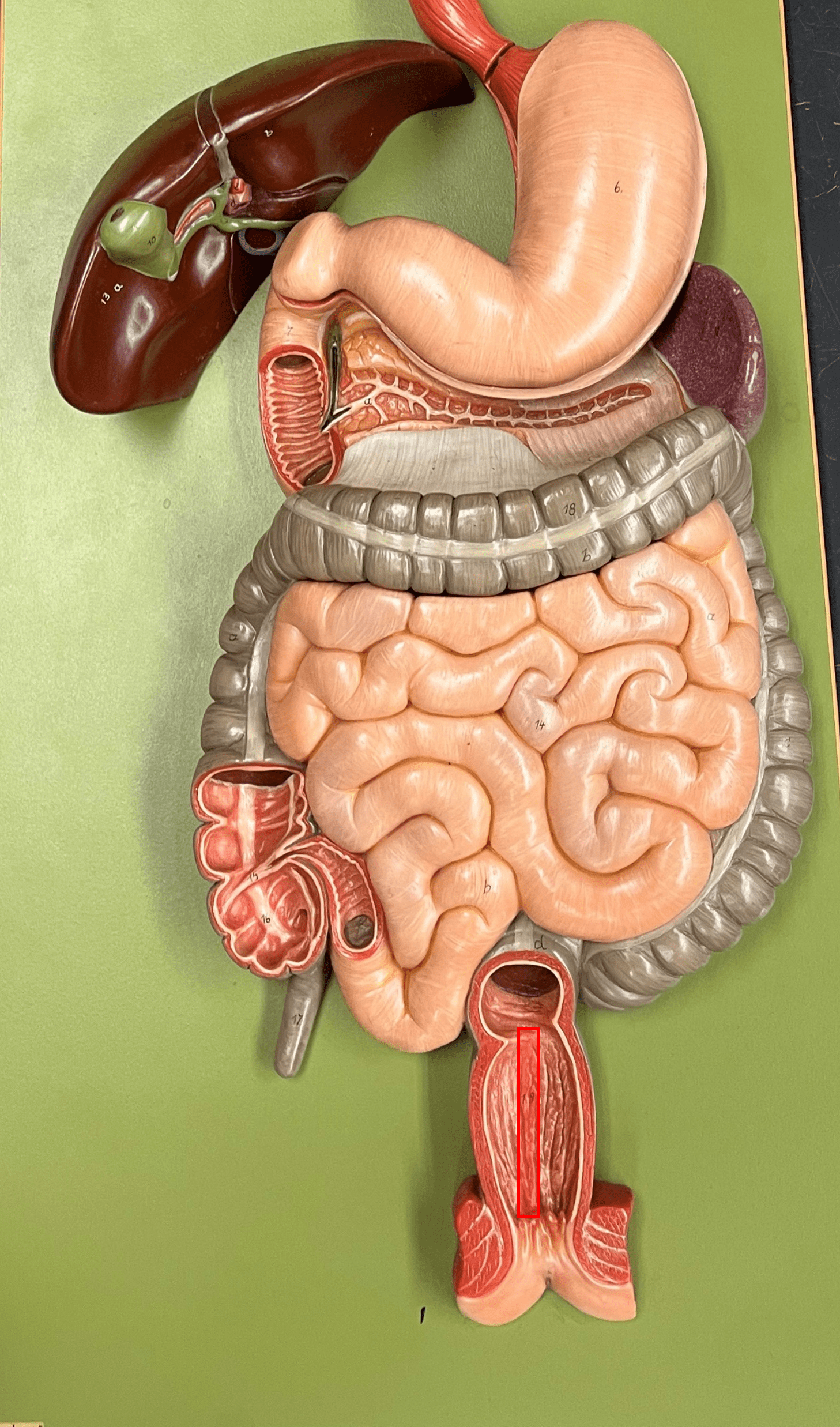
New cards
anal column
A fold of the anal canal along the inner wall.
62
New cards
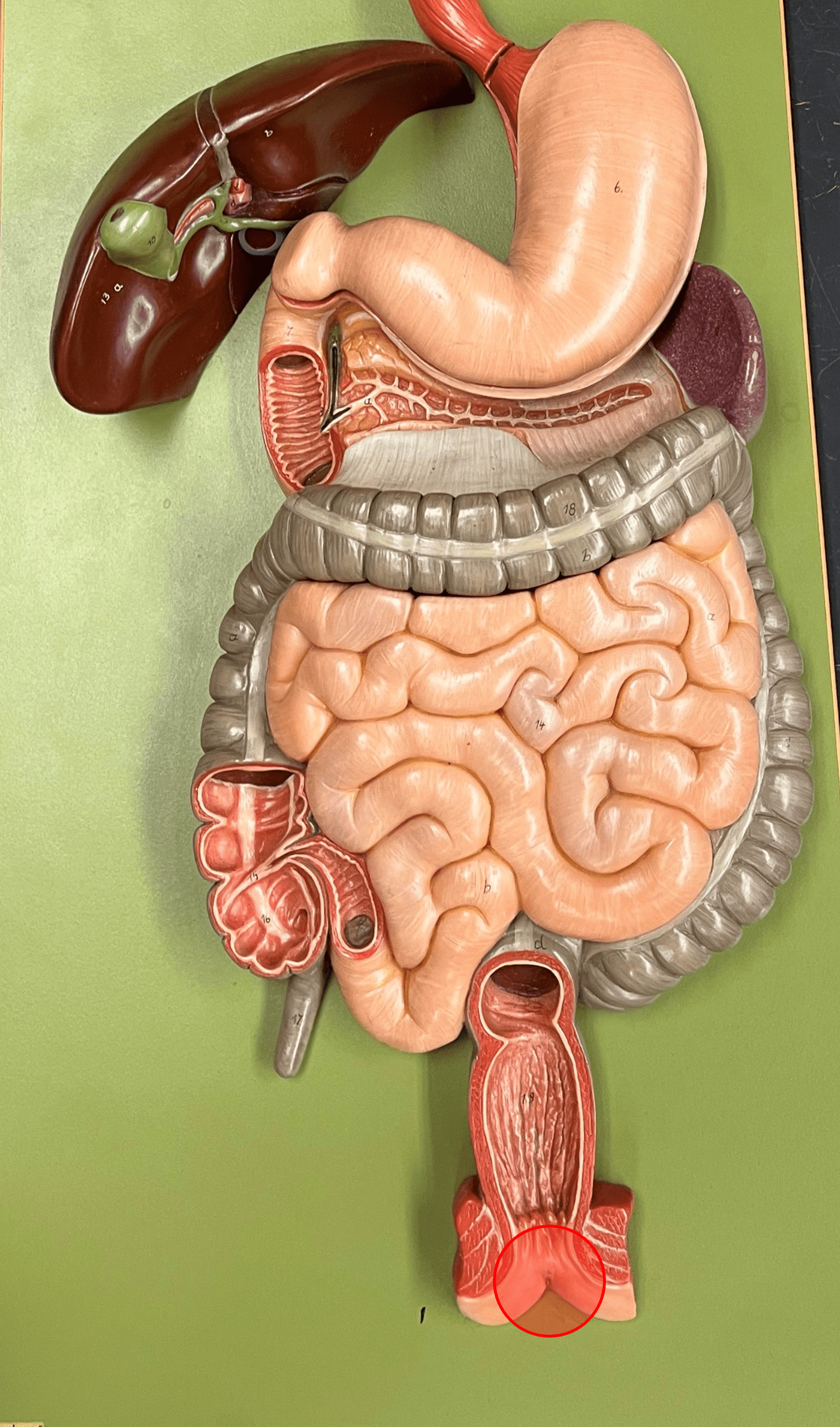
anus
• The opening of the rectum into the exterior.
• Bordered by internal and external sphincters of smooth and skeletal muscle.
• Bordered by internal and external sphincters of smooth and skeletal muscle.
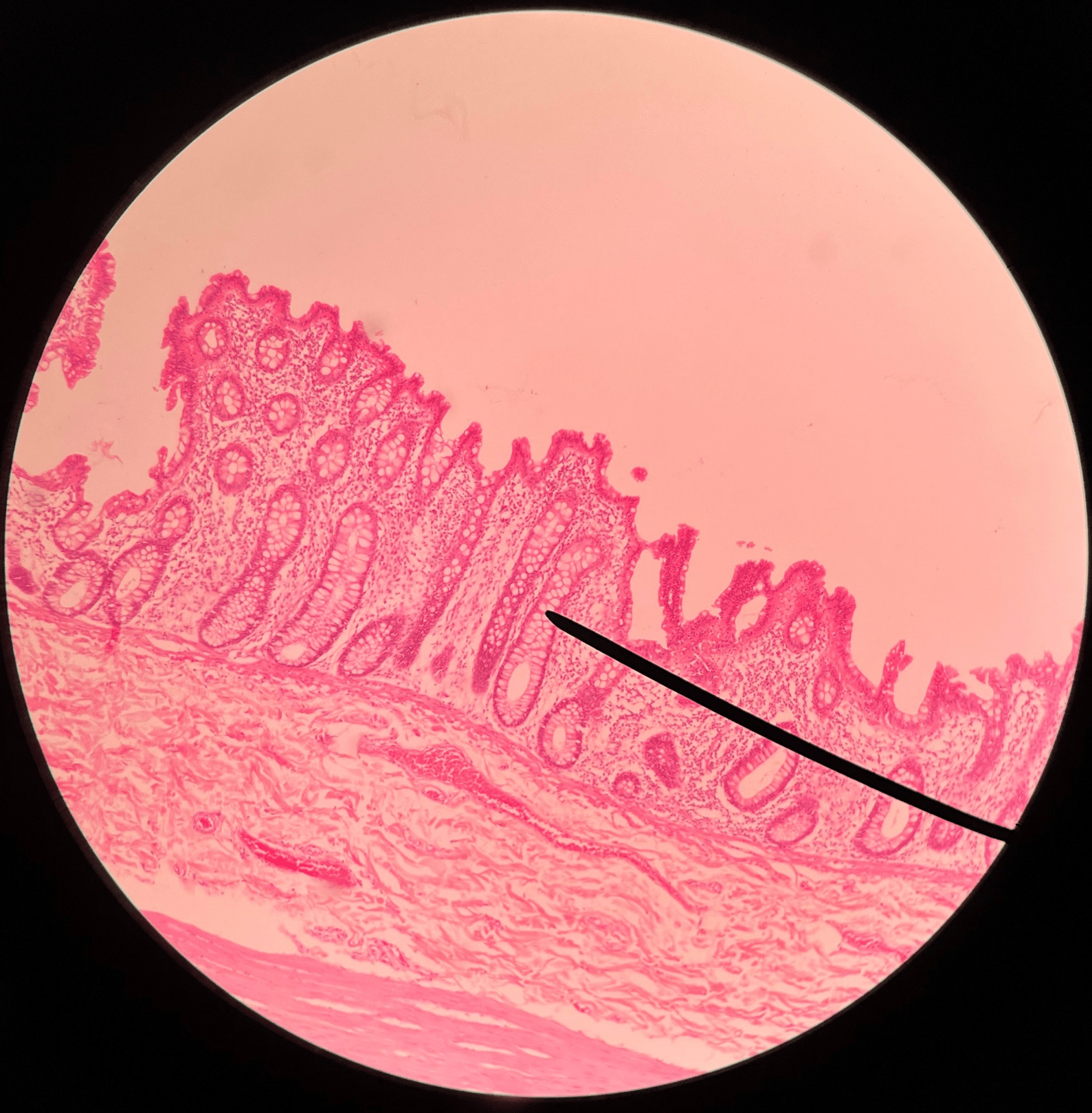
63
New cards
goblet cell
• Slide histology of the large intestine.
• Secretes mucus.
• Secretes mucus.
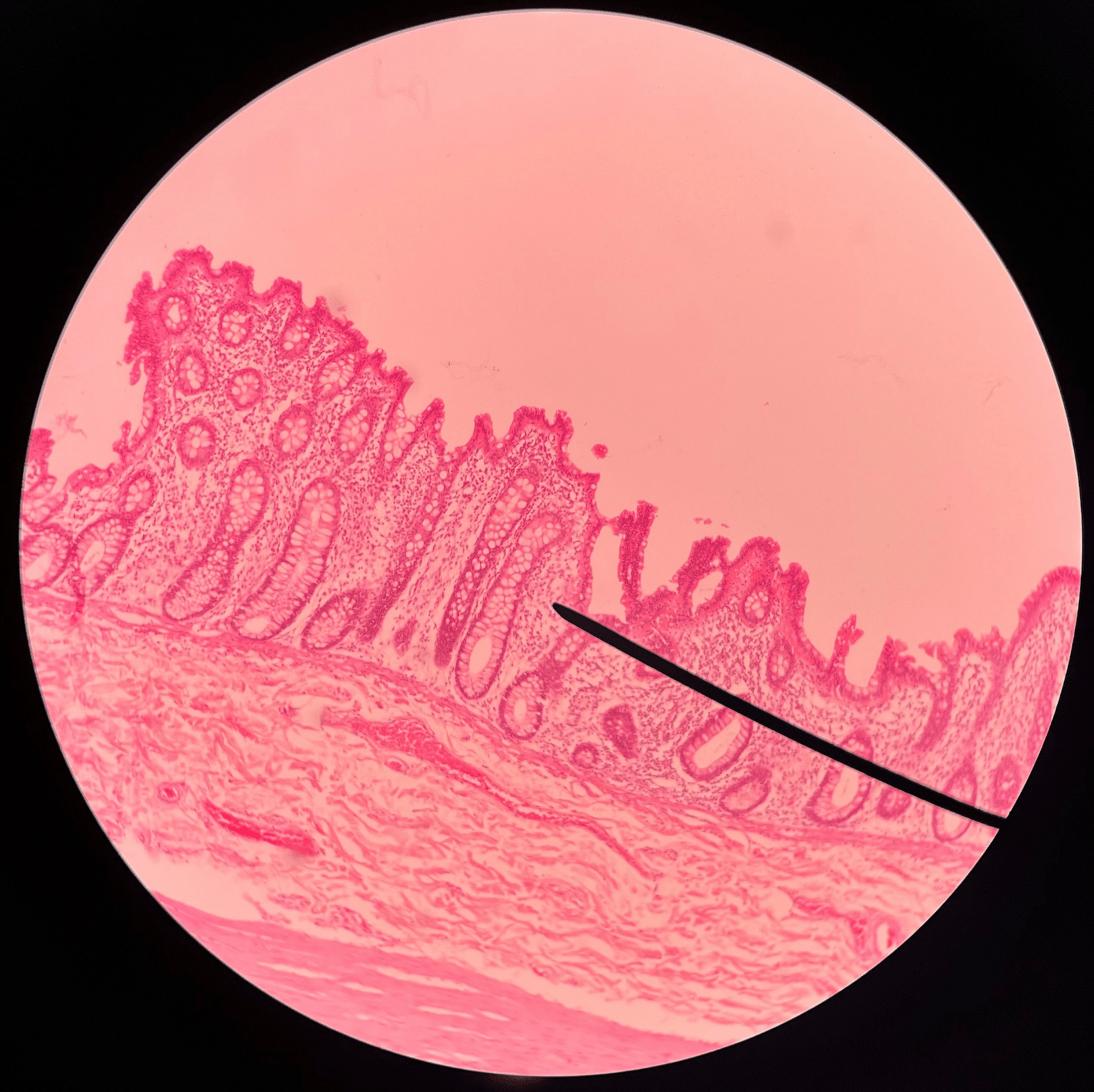
64
New cards
mucosa
• Slide histology of the large intestine.
• The deepest layer of the large intestine.
• Deep to the submucosa.
• The deepest layer of the large intestine.
• Deep to the submucosa.
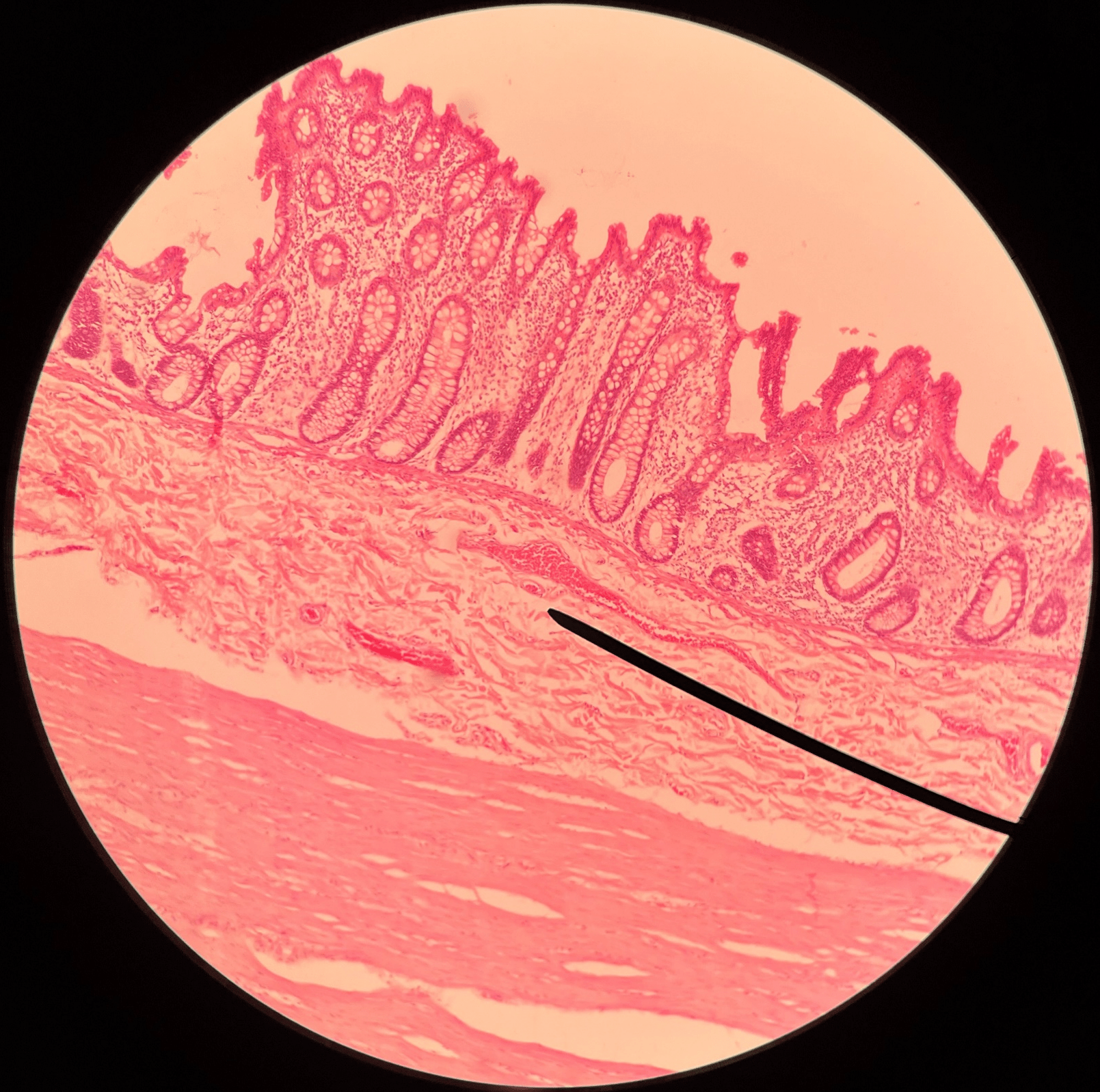
65
New cards
submucosa
• Slide histology of the large intestine.
• The second-deepest layer of the large intestine.
• Superficial to the mucosa.
• Deep to the muscularis.
• The second-deepest layer of the large intestine.
• Superficial to the mucosa.
• Deep to the muscularis.
66
New cards
gingiva
• Anchors the teeth.
• Also known as a gum.
• Also known as a gum.
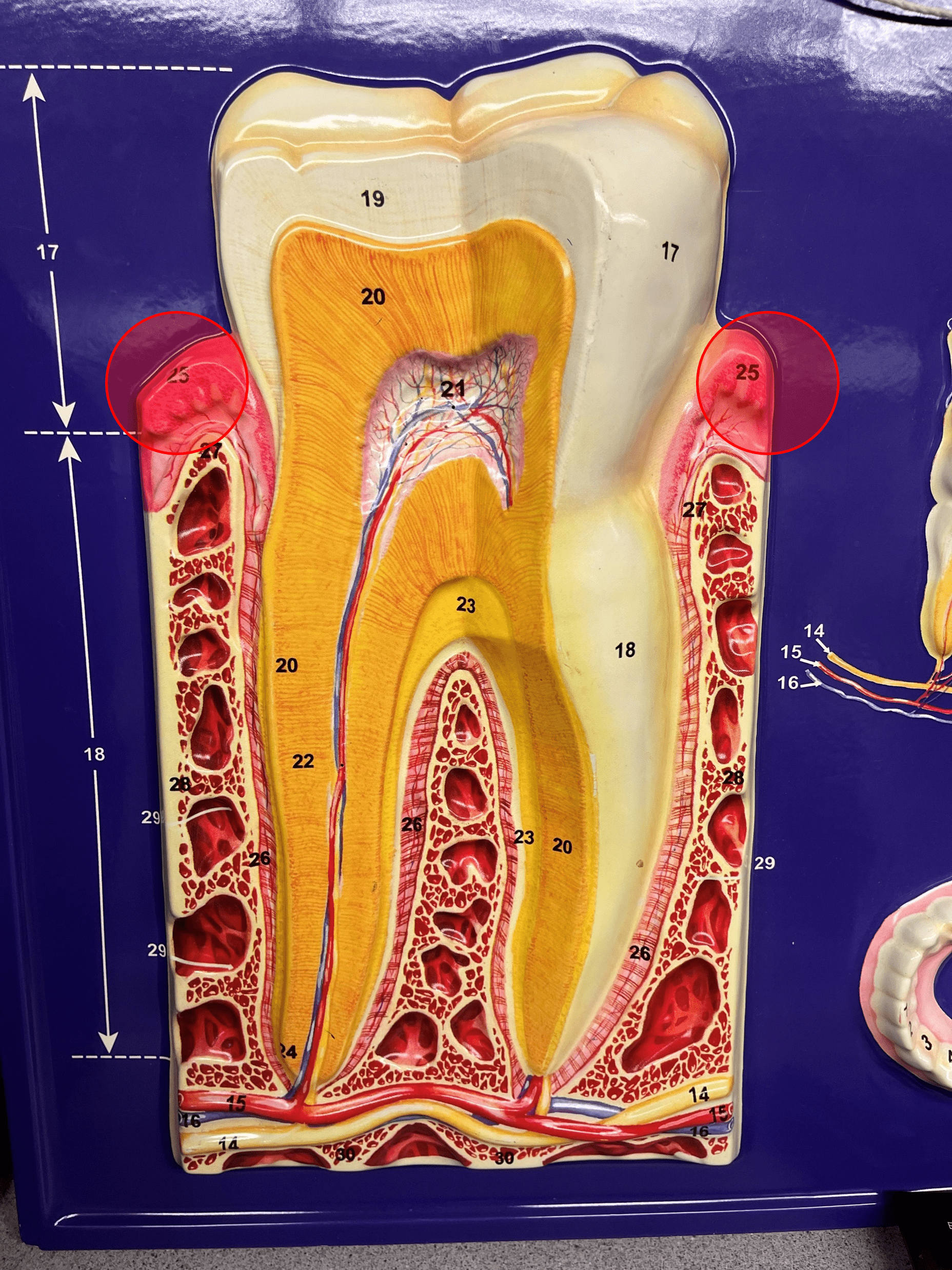
67
New cards
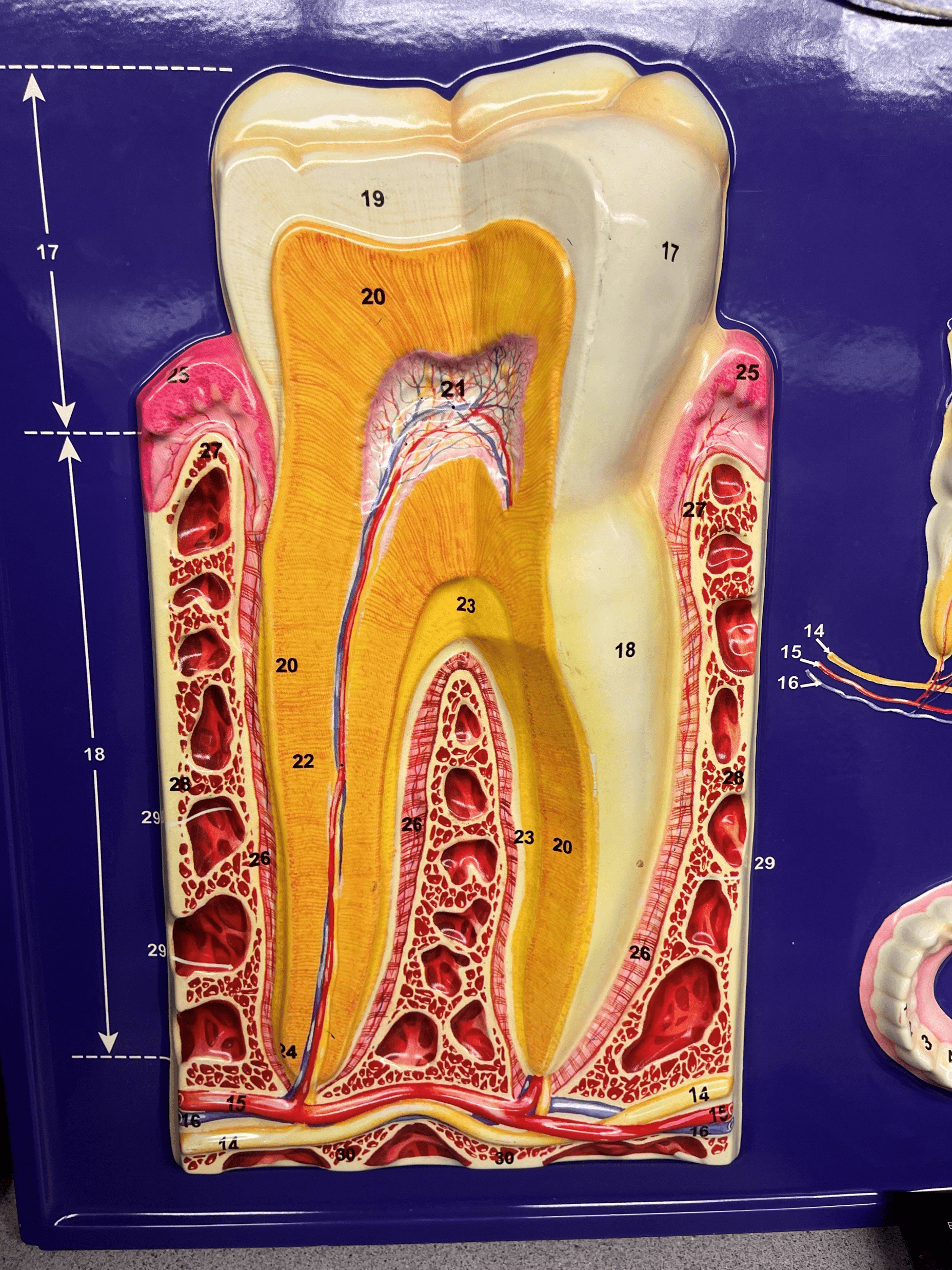
tooth
• Provides mechanical digestion by breaking up food particles in the mouth.
• Composed of a crown and the root.
• Composed of a crown and the root.
68
New cards
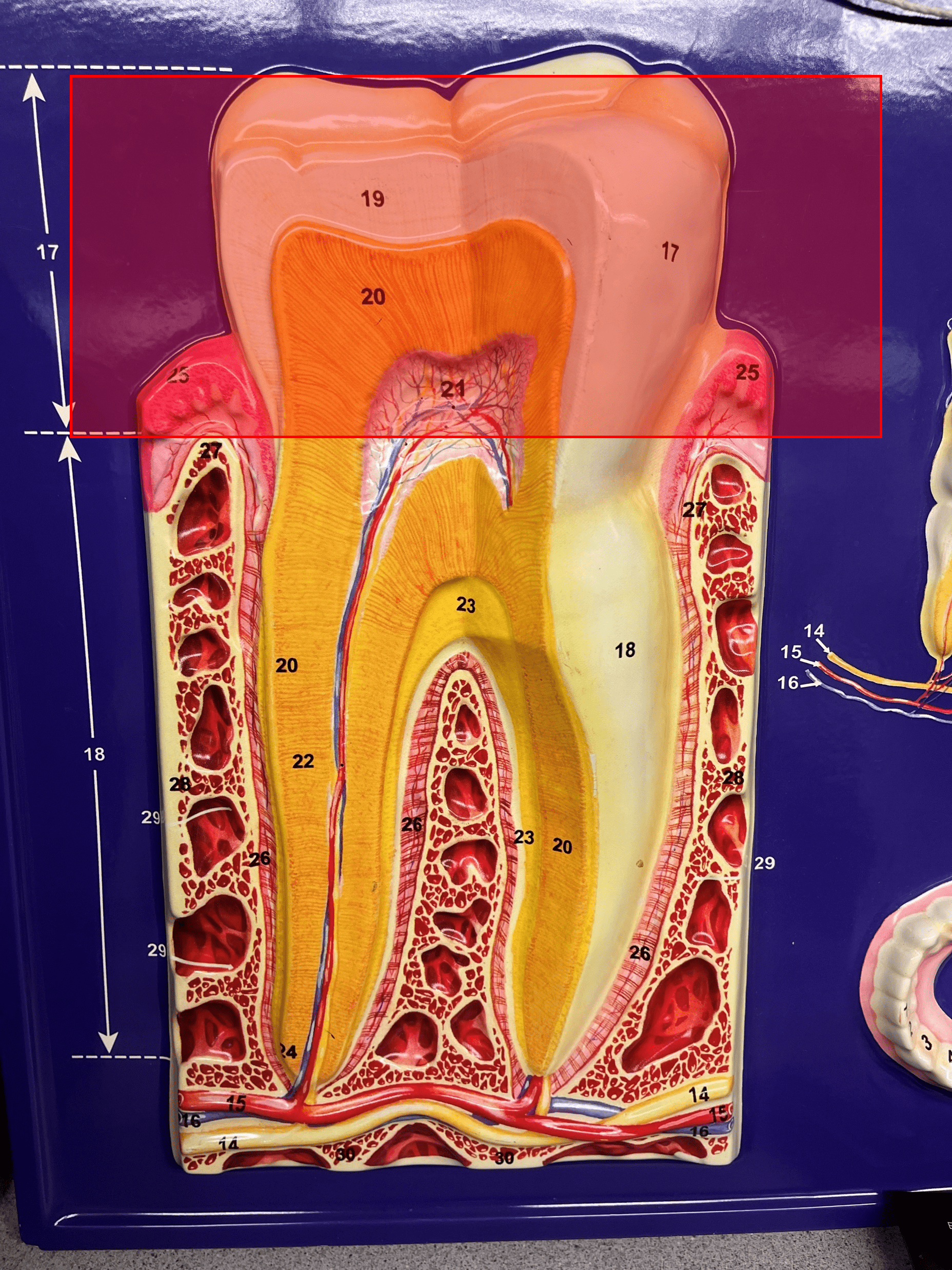
crown
• A region of the tooth.
• The area of the tooth visible above the gum line.
• The area of the tooth visible above the gum line.
69
New cards
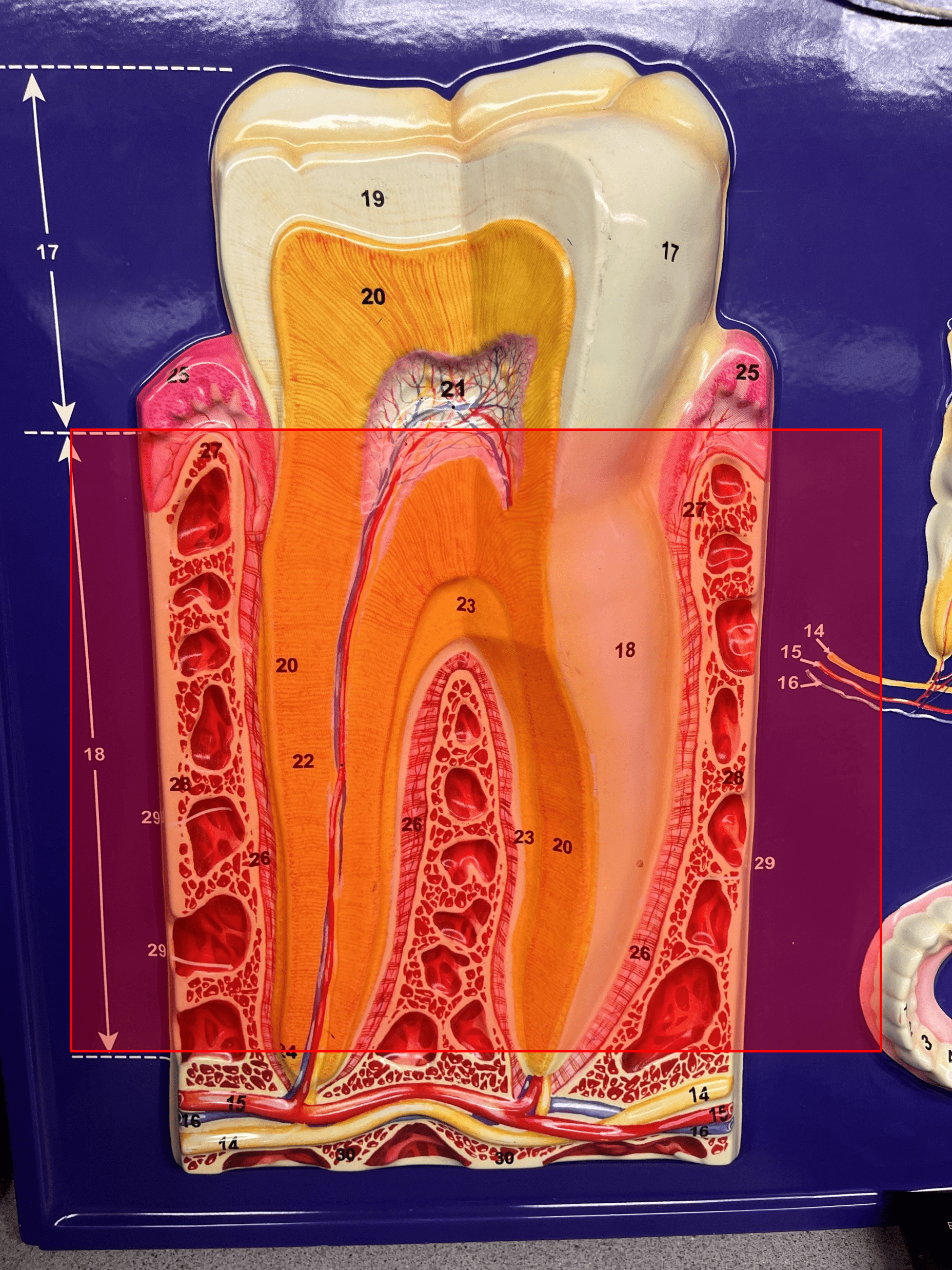
root
• A region of the tooth.
• The area of the tooth below the gum line.
• The area of the tooth below the gum line.
70
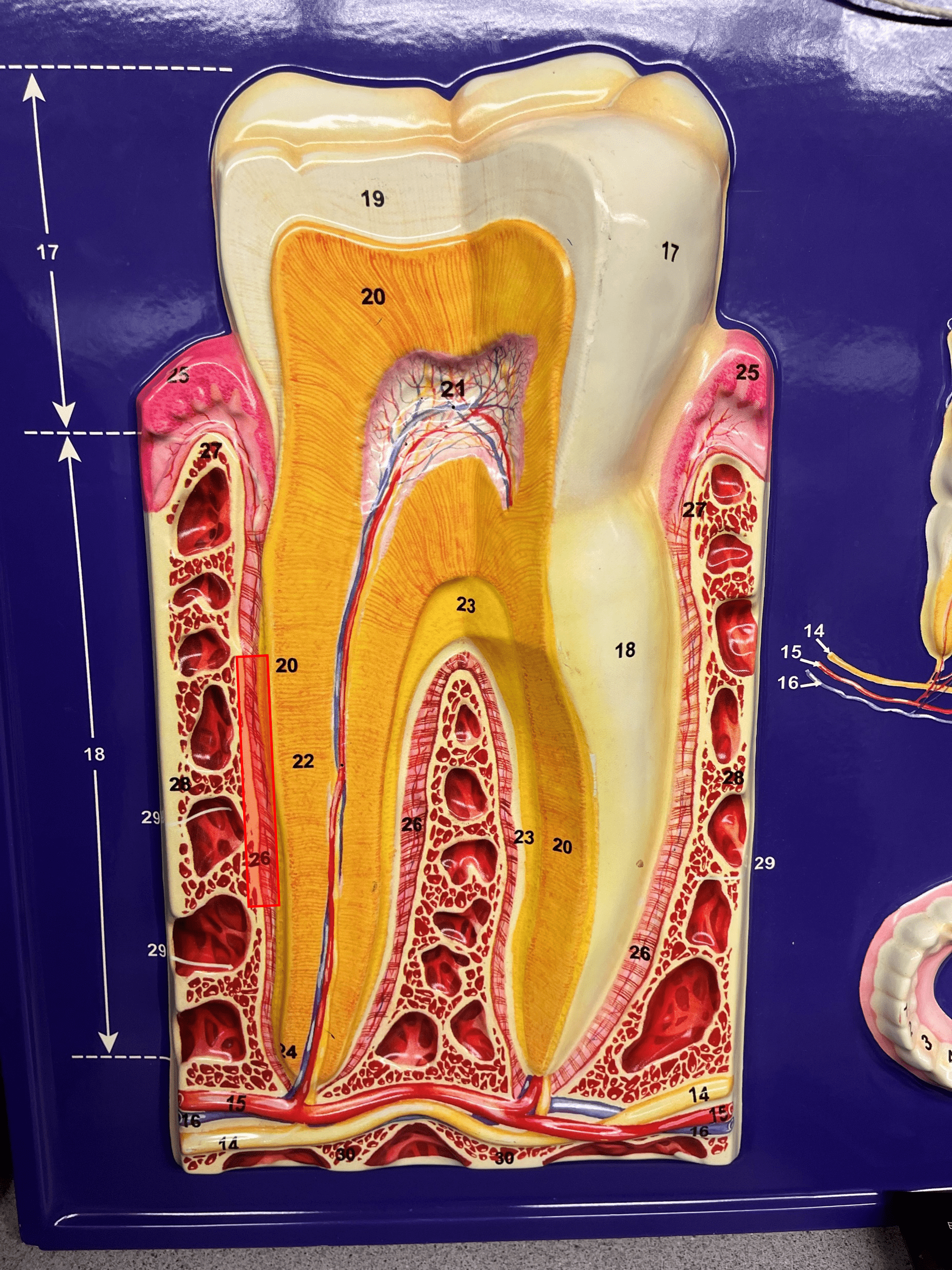
New cards
periodontal ligament
• Lines the alveolar socket of the tooth.
• Anchors the root of the tooth to the gingiva.
• Anchors the root of the tooth to the gingiva.
71
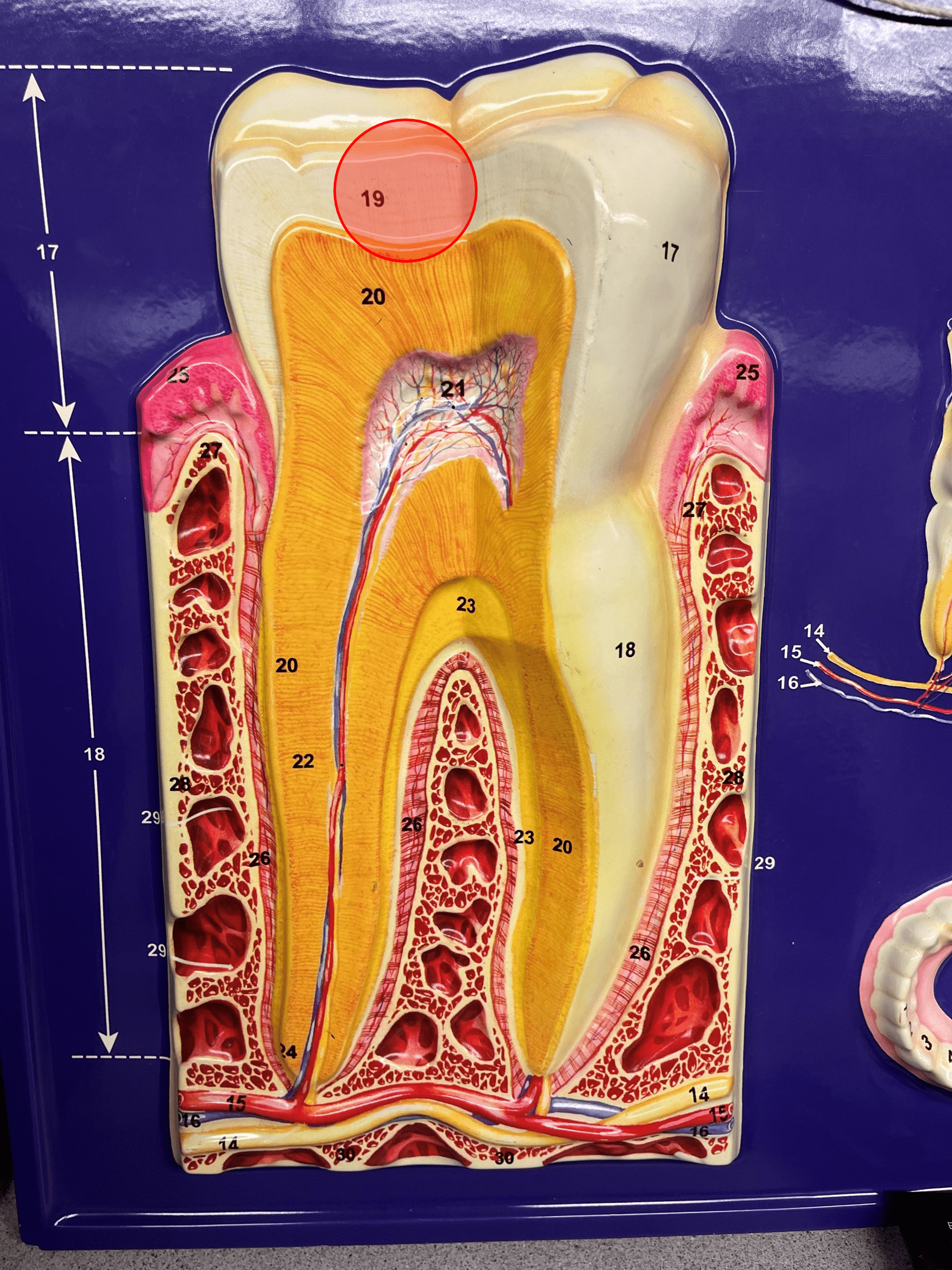
New cards
enamel
• A very hard substance.
• Covers the crown of the tooth.
• Covers the crown of the tooth.
72
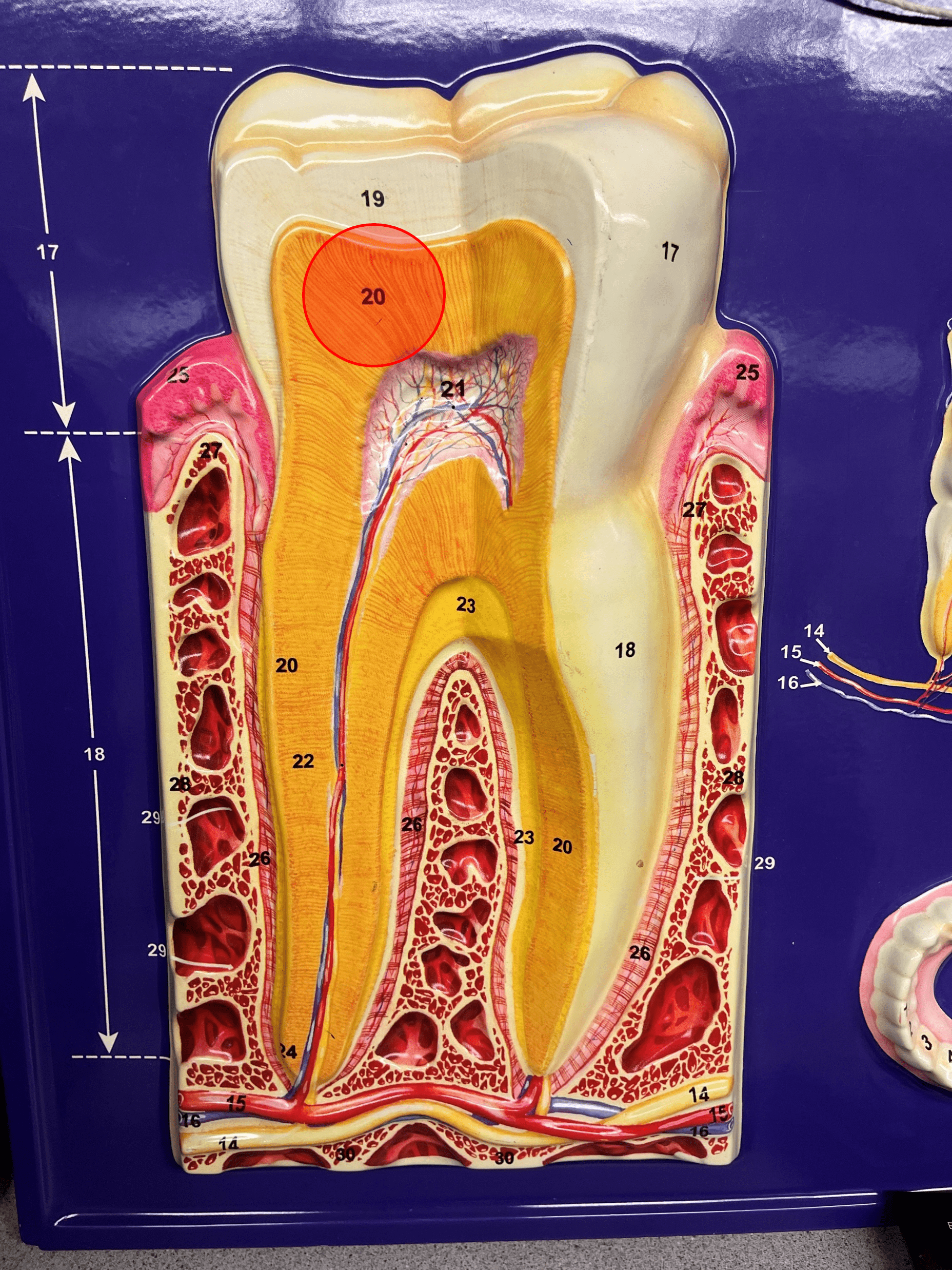
New cards
dentin
• Calcified connective tissue.
• Composes most of the internal tooth.
• Composes most of the internal tooth.
73
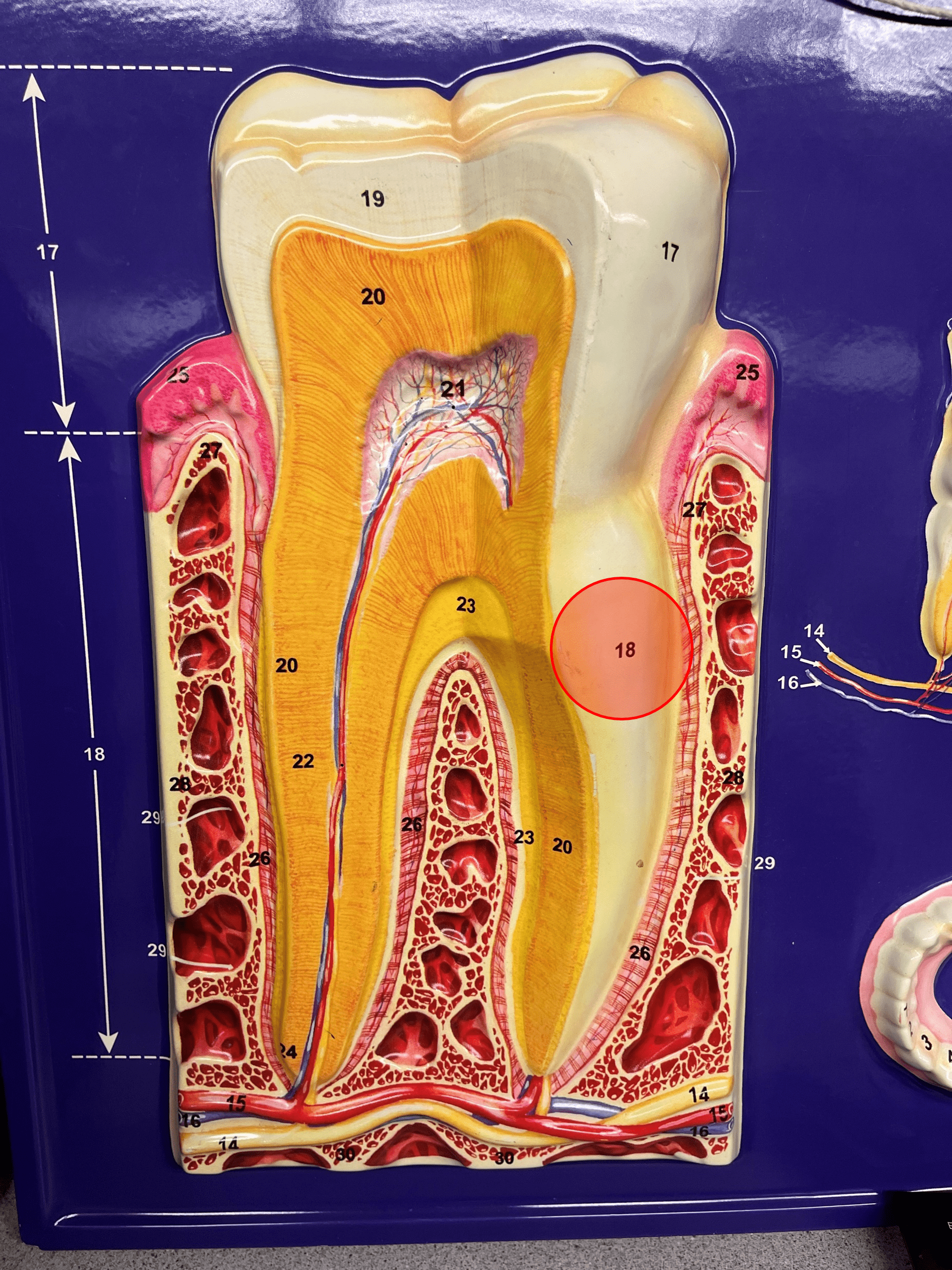
New cards
cementum
• An adhesive connective tissue.
• Adheres the dentin to the periodontal ligament.
• Adheres the dentin to the periodontal ligament.
74
New cards
pulp cavity
• Located in the center of the crown of the tooth.
• Filled with pulp containing blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.
• Filled with pulp containing blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.
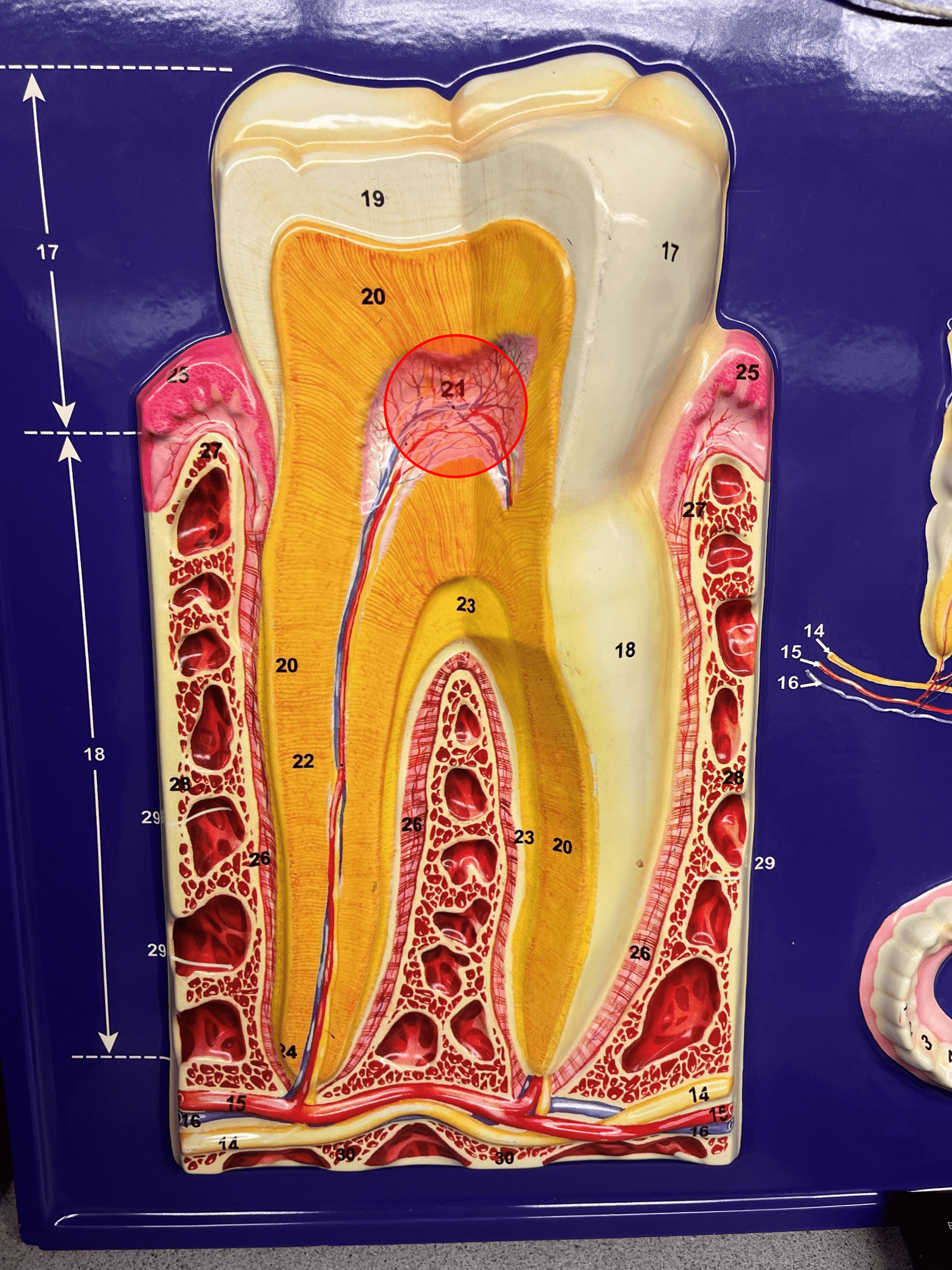
75
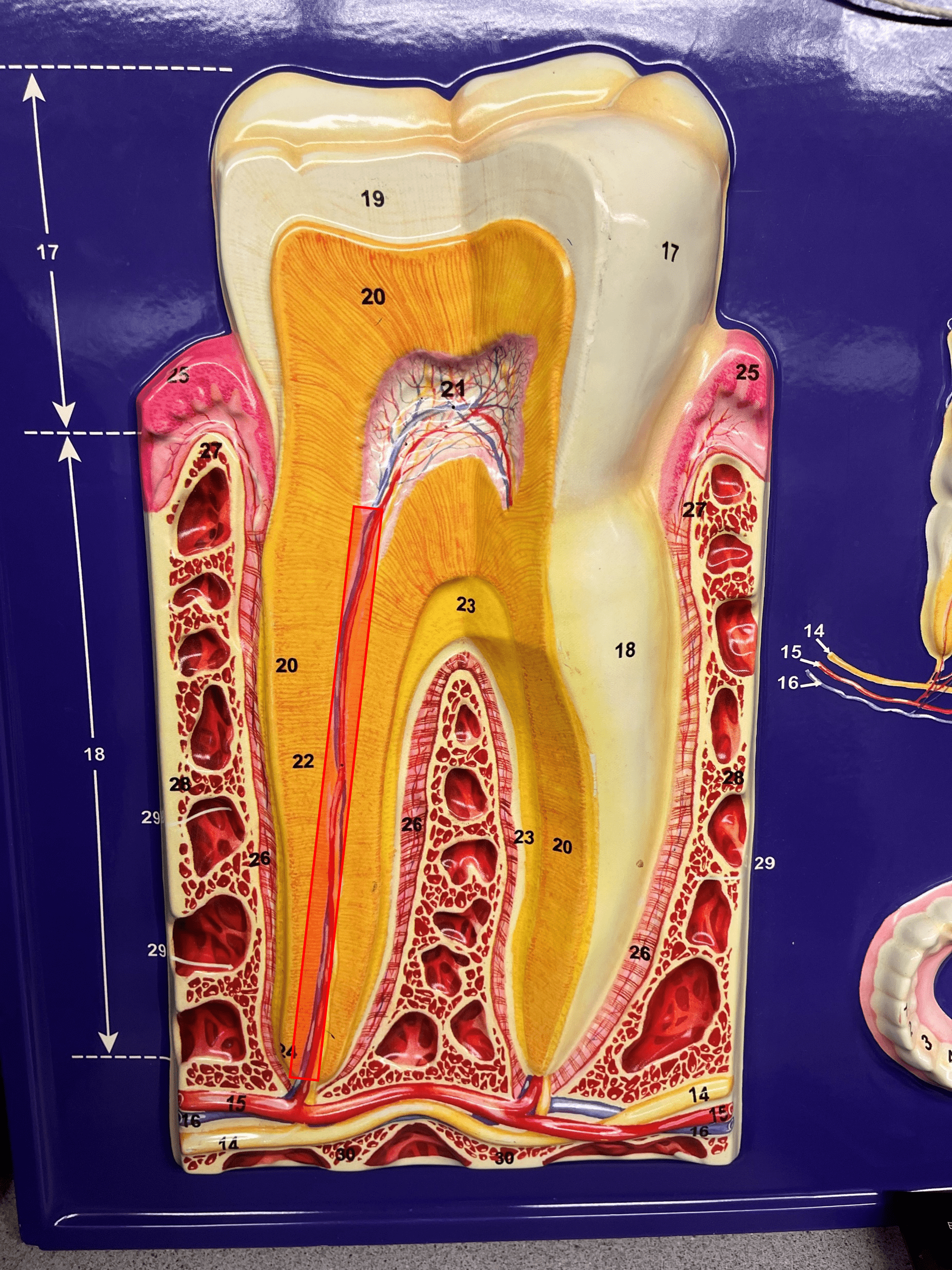
New cards
root canal
• A slender channel in the root of the tooth.
• The continuation of the pulp cavity and pulp into the root of the tooth.
• The continuation of the pulp cavity and pulp into the root of the tooth.
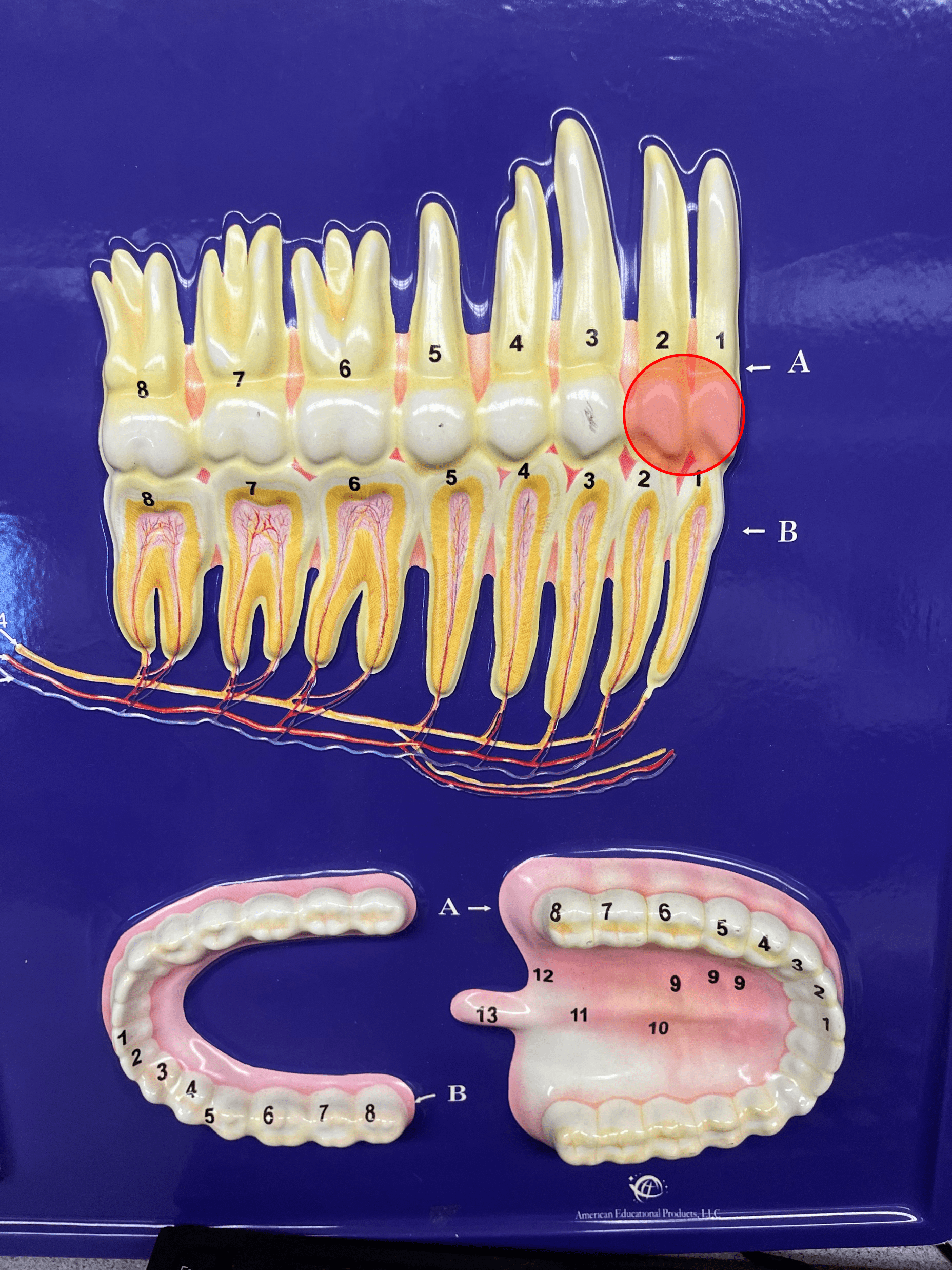
76
New cards
incisor
• A type of tooth.
• Has narrow edges for cutting food.
• Has narrow edges for cutting food.
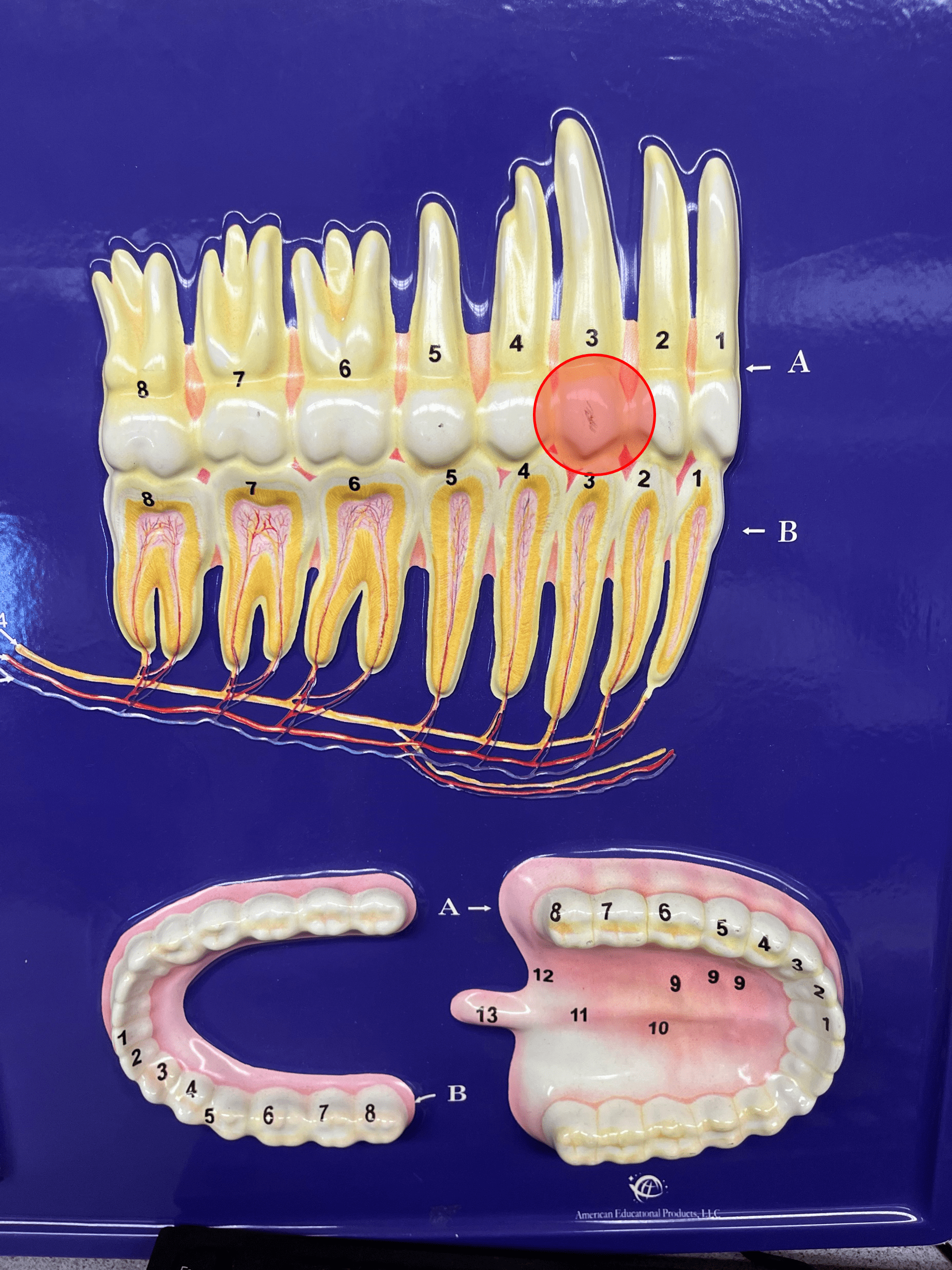
77
New cards
canine
• A type of tooth.
• Has a pointed edge for tearing food.
• Has a pointed edge for tearing food.
78
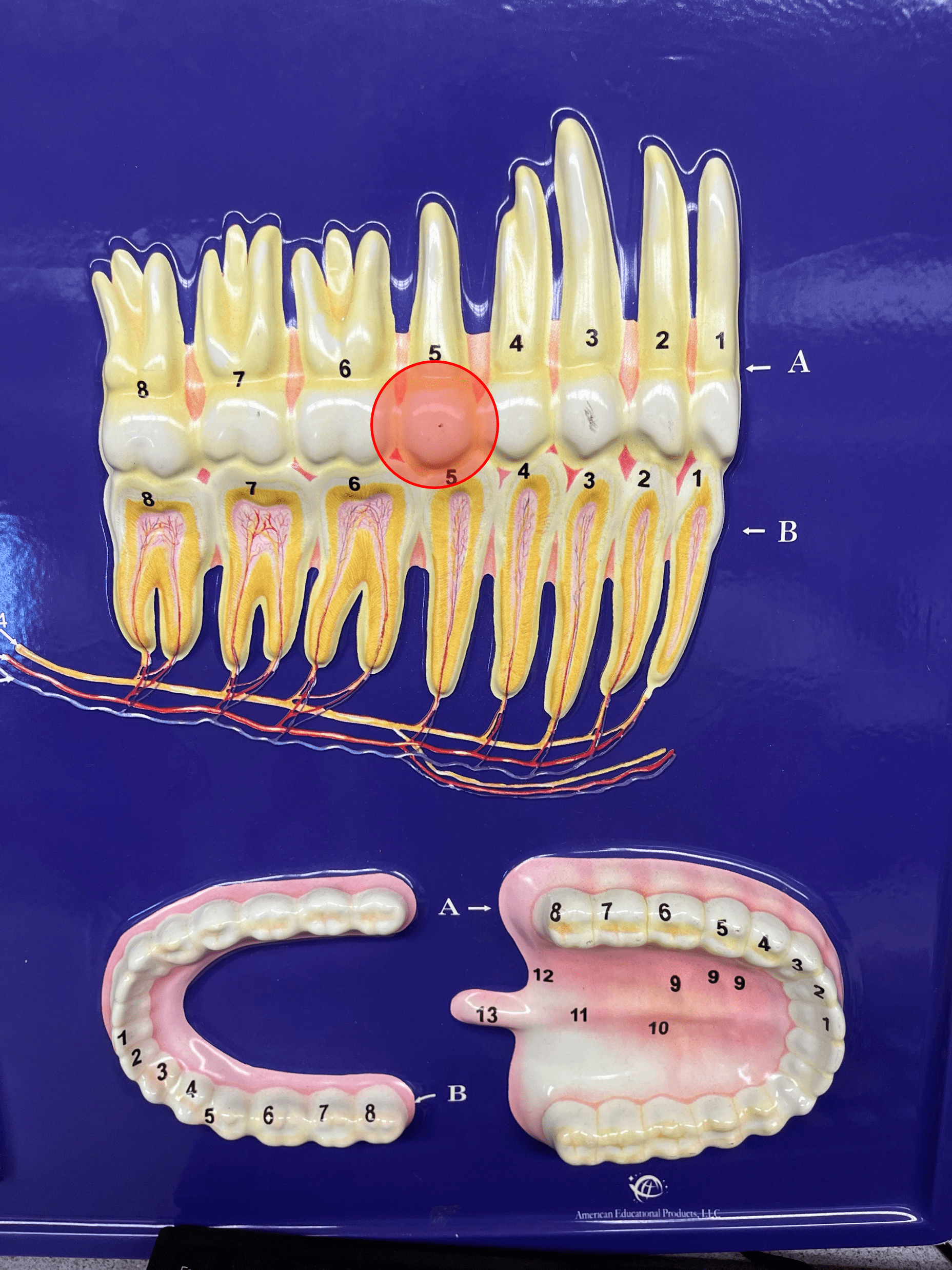
New cards
premolar
• A type of tooth.
• Has two flat cusps for grinding food.
• Has two flat cusps for grinding food.
79
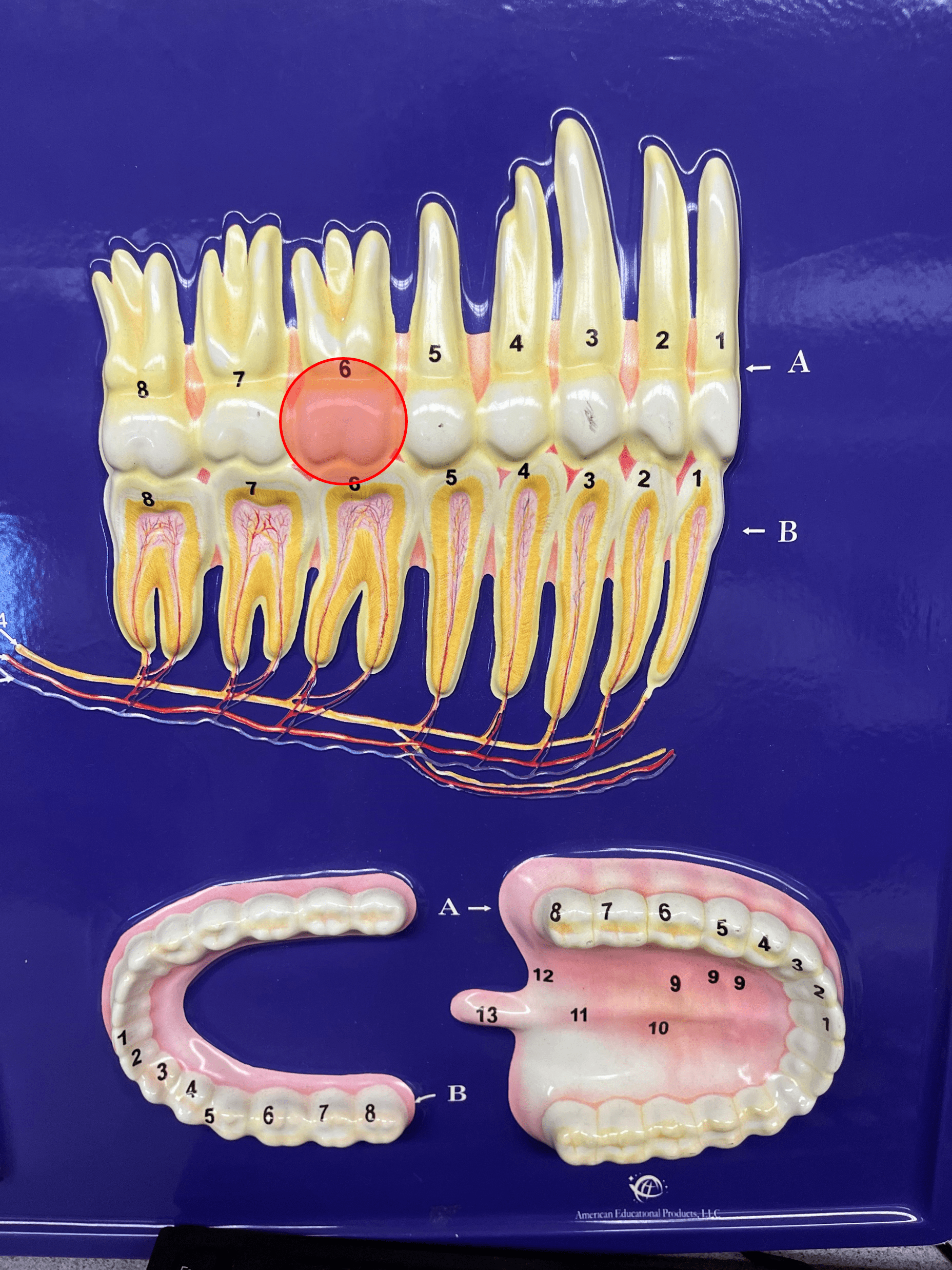
New cards
molar
• A type of tooth.
• Has broad or rounded cusps for grinding food.
• Has broad or rounded cusps for grinding food.
80
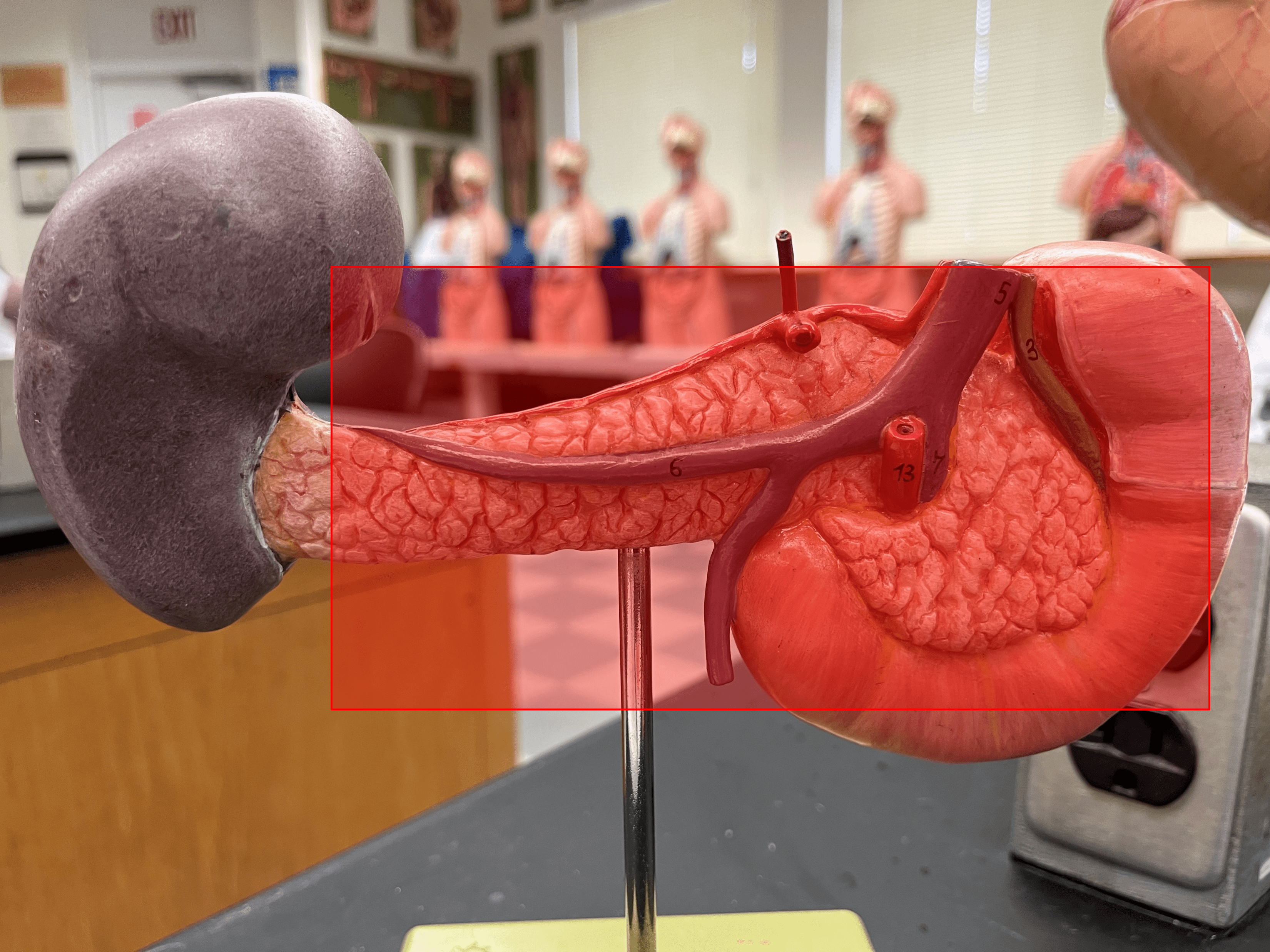
New cards
pancreas
• An organ located within the abdominal cavity posterior to the stomach and proximal end of the duodenum.
• Composed of a head, body, and tail.
• Secretes digestive enzymes and hormones.
• Composed of a head, body, and tail.
• Secretes digestive enzymes and hormones.
81
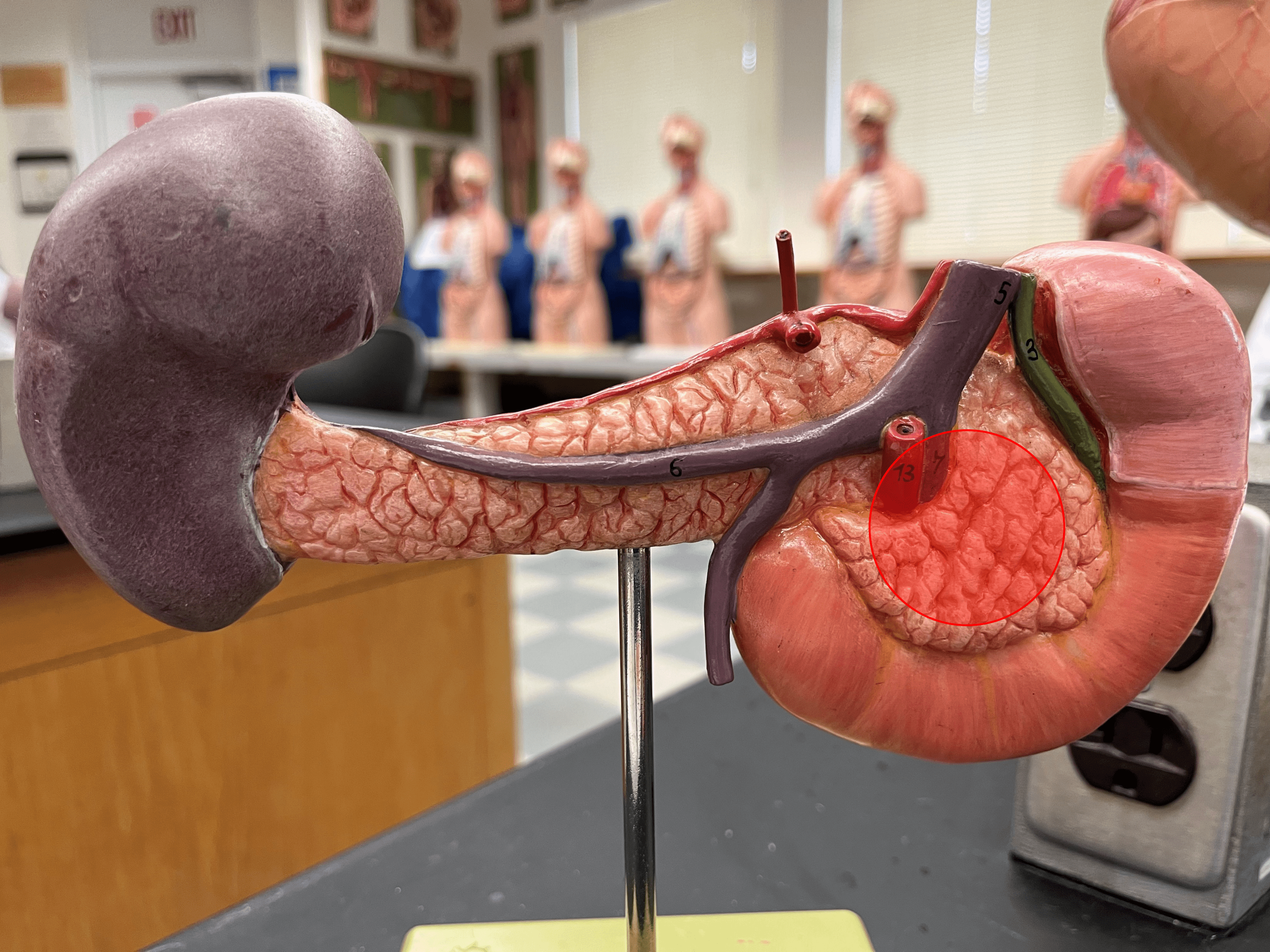
New cards
head
• A region of the pancreas.
• The expanded portion of the pancreas located posterior to the duodenum.
• The expanded portion of the pancreas located posterior to the duodenum.
82
New cards
body
• A region of the pancreas.
• The central portion of the pancreas behind the pylorus of the stomach.
• The central portion of the pancreas behind the pylorus of the stomach.
83
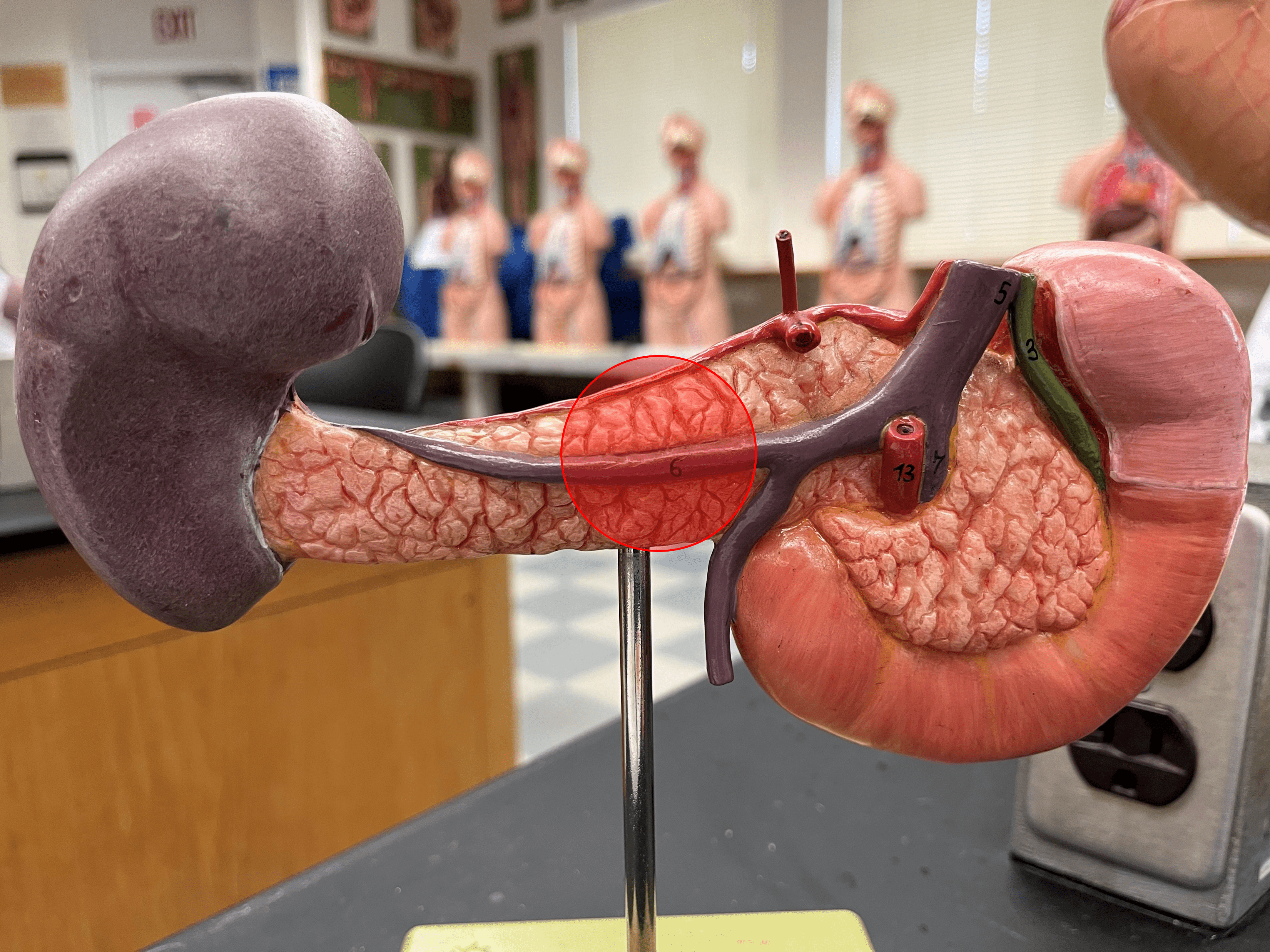
New cards
tail
• A region of the pancreas.
• The narrow portion of the pancreas behind the body of the stomach.
• The narrow portion of the pancreas behind the body of the stomach.
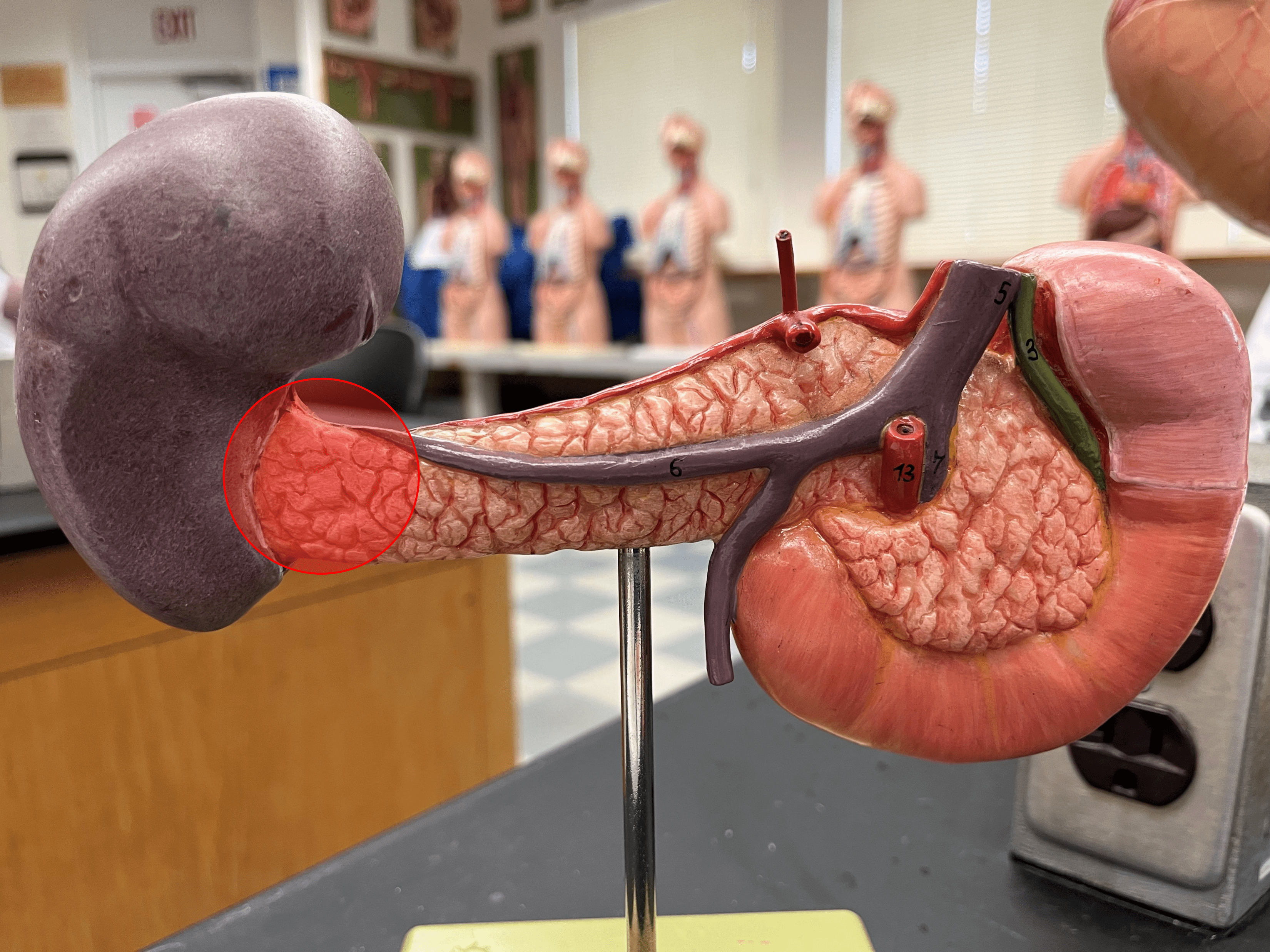
84
New cards
main pancreatic duct
• A central duct extending from the tail to the head of the pancreas.
• Secretions from acinar cells travel by this duct.
• Joins the common bile duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla.
• Opens into the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla.
• Secretions from acinar cells travel by this duct.
• Joins the common bile duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla.
• Opens into the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla.
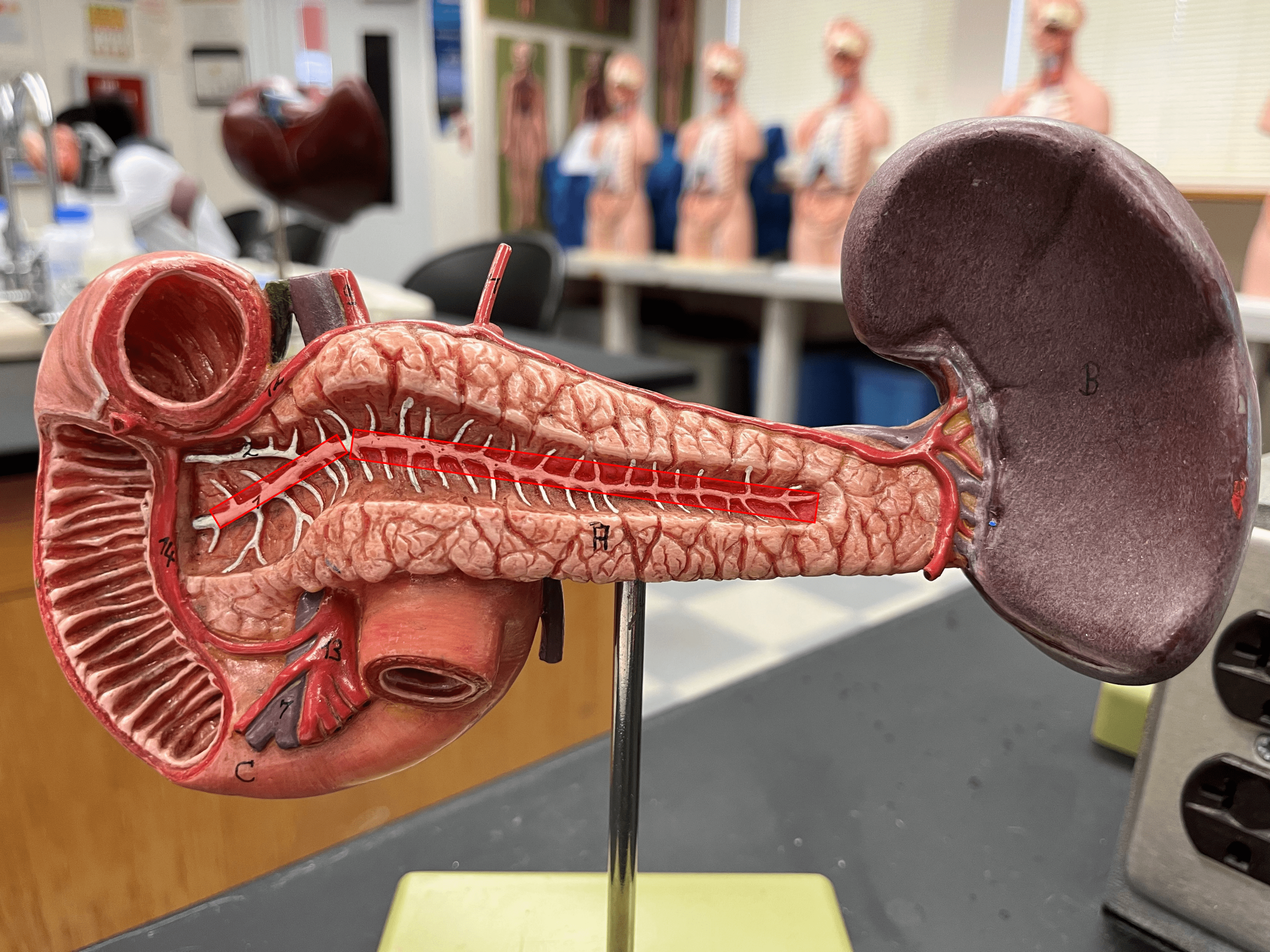
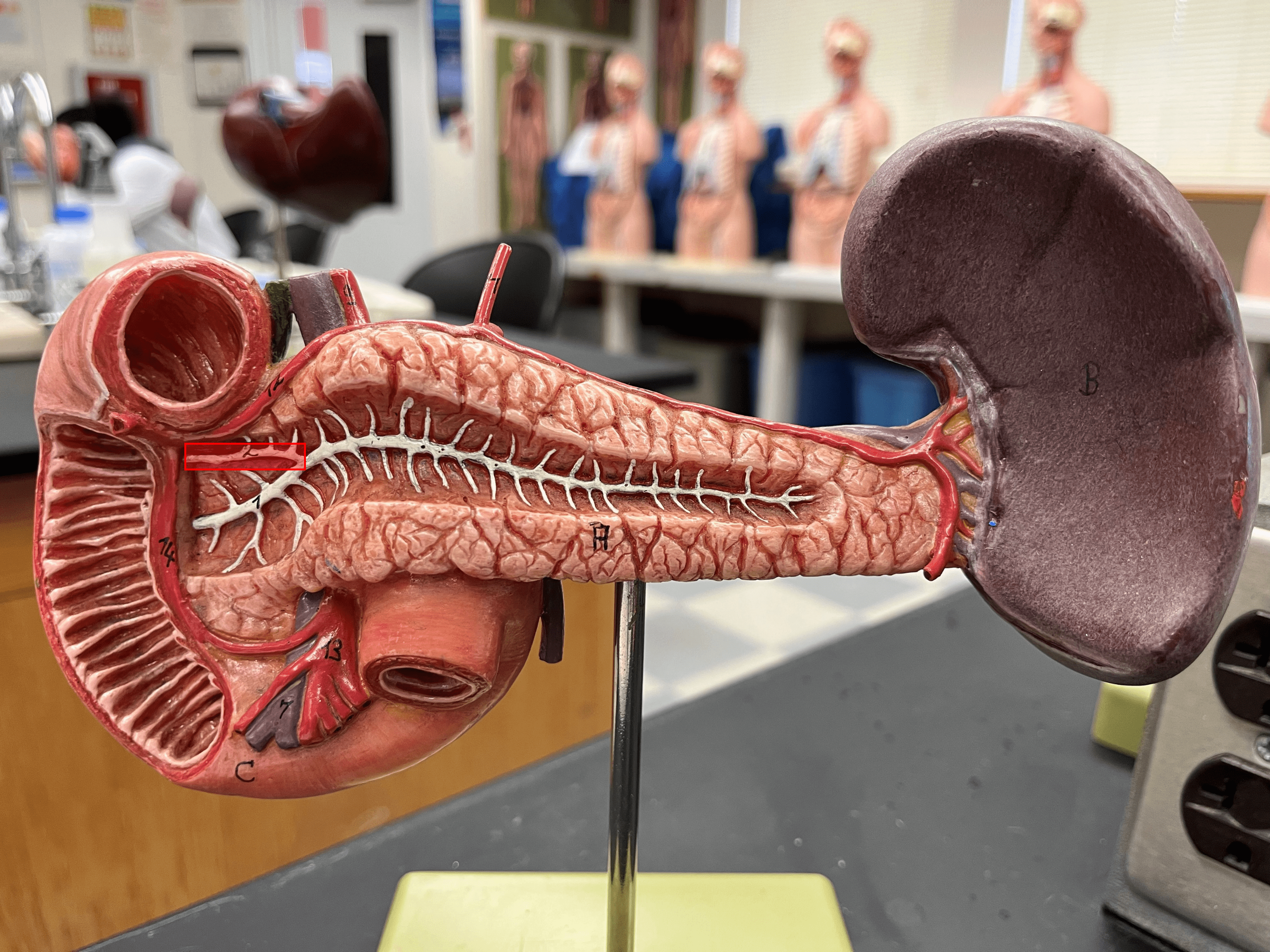
85
New cards
accessory pancreatic duct
• A division of the main pancreatic duct.
• Secretions from acinar cells travel by this duct.
• Opens into the duodenum at the minor duodenal papilla.
• Secretions from acinar cells travel by this duct.
• Opens into the duodenum at the minor duodenal papilla.
86
New cards
acinar cells
• Slide histology of the pancreas.
• Dark-staining cells that produce digestive enzymes.
• Dark-staining cells that produce digestive enzymes.
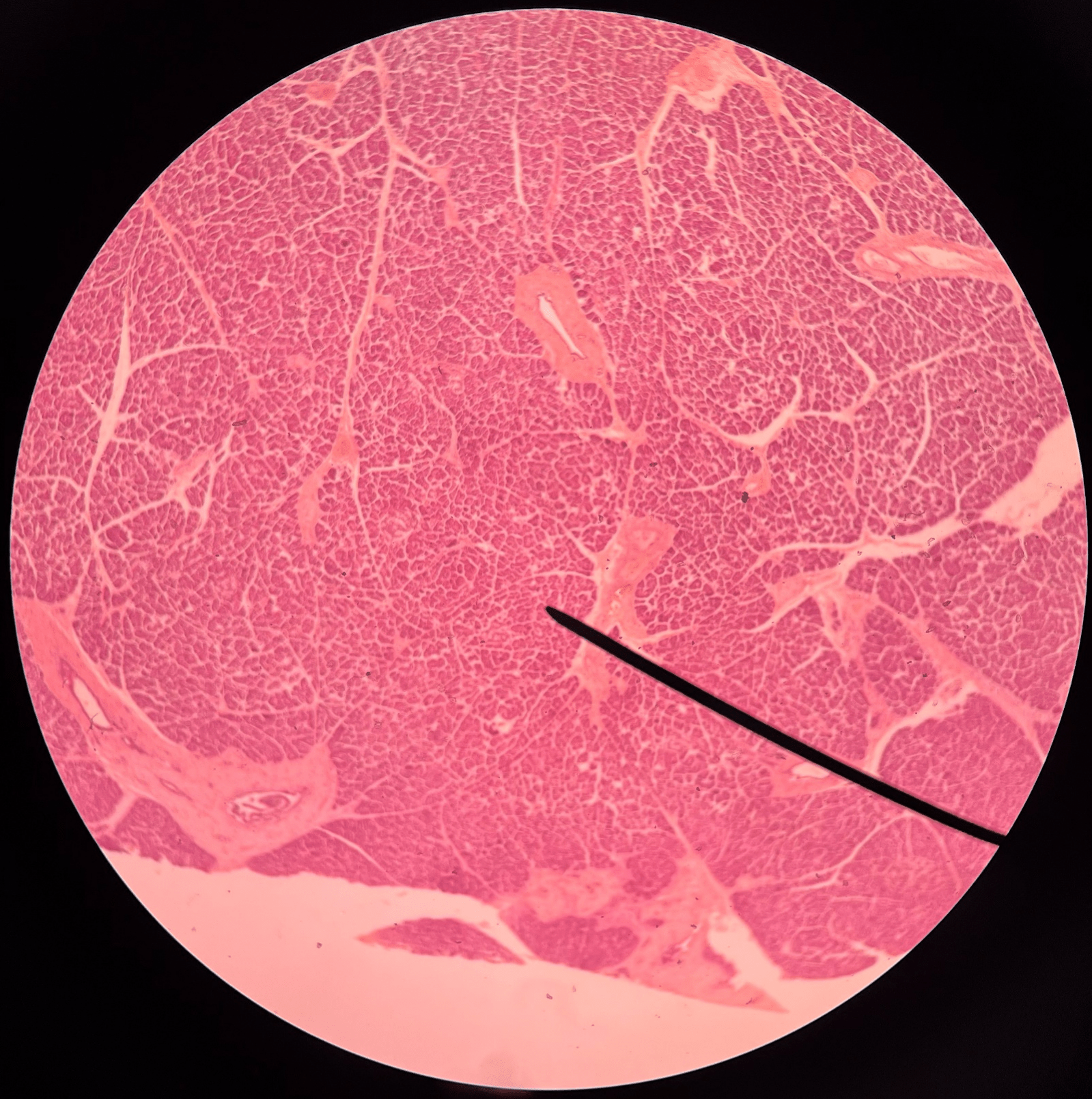
87
New cards
pancreatic islets
• Slide histology of the pancreas.
• Light-staining cells that produce hormones.
• Also known as islets of Langerhans.
• Light-staining cells that produce hormones.
• Also known as islets of Langerhans.
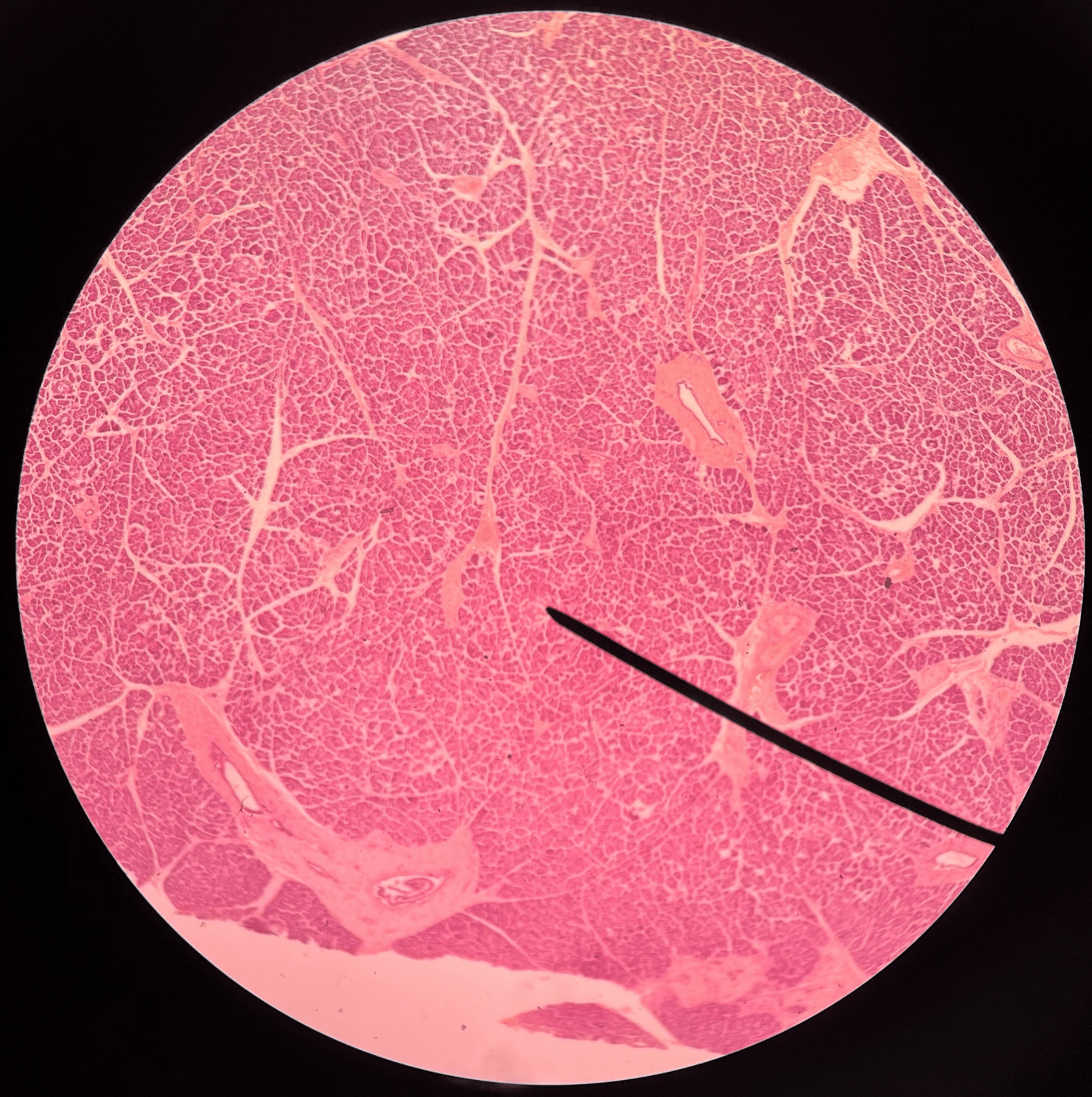
88
New cards
liver
• A large, soft organ located on the right side of the abdominal cavity pressing against the diaphragm.
• Consists of right, left, caudate, and quadrate lobes.
• Detoxifies blood, processes nutrients, and produces bile.
• Consists of right, left, caudate, and quadrate lobes.
• Detoxifies blood, processes nutrients, and produces bile.
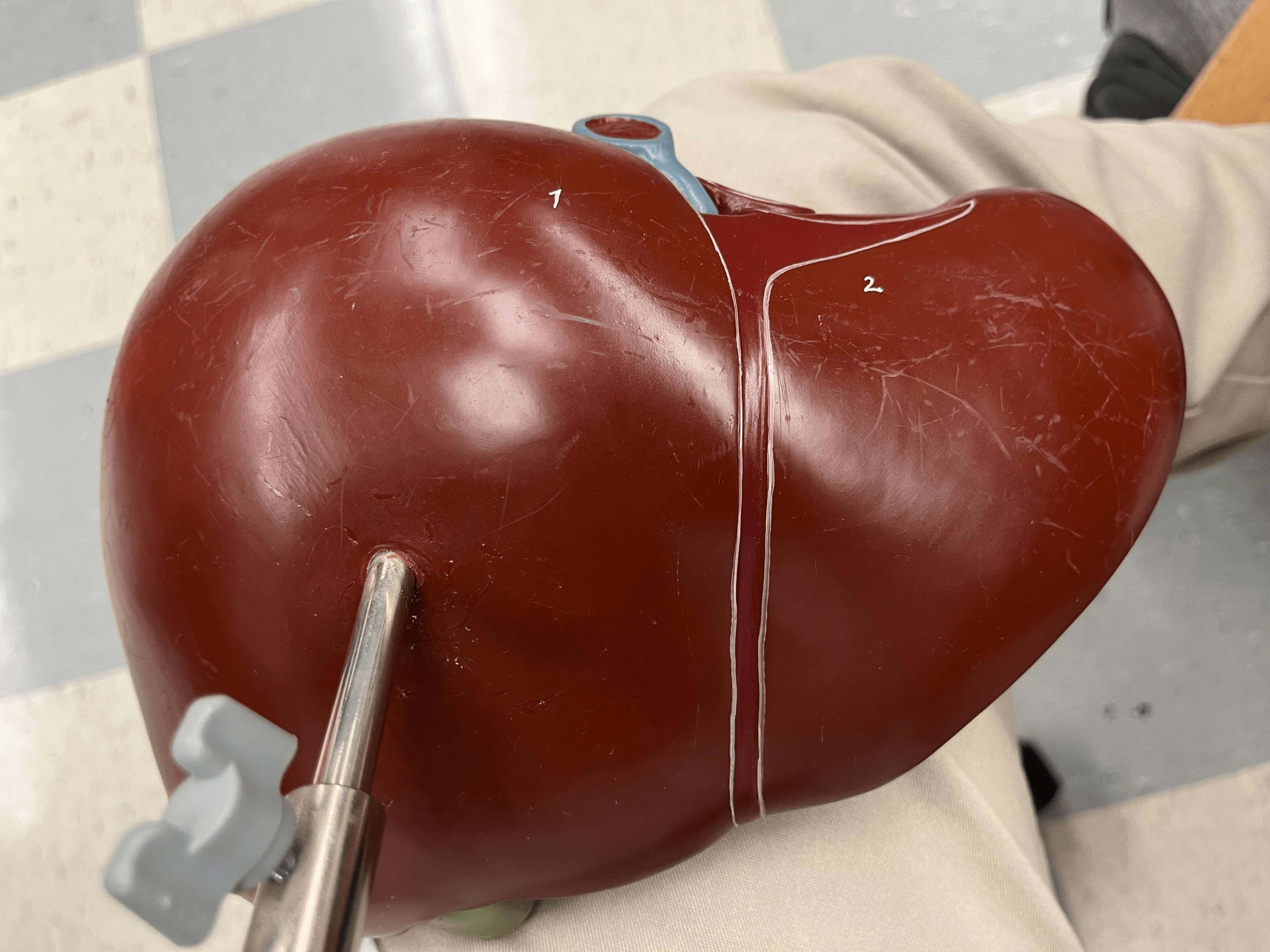
89
New cards
falciform ligament
• Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and the anterior abdominal wall.
• Separates the right and left lobes of the liver.
• Separates the right and left lobes of the liver.
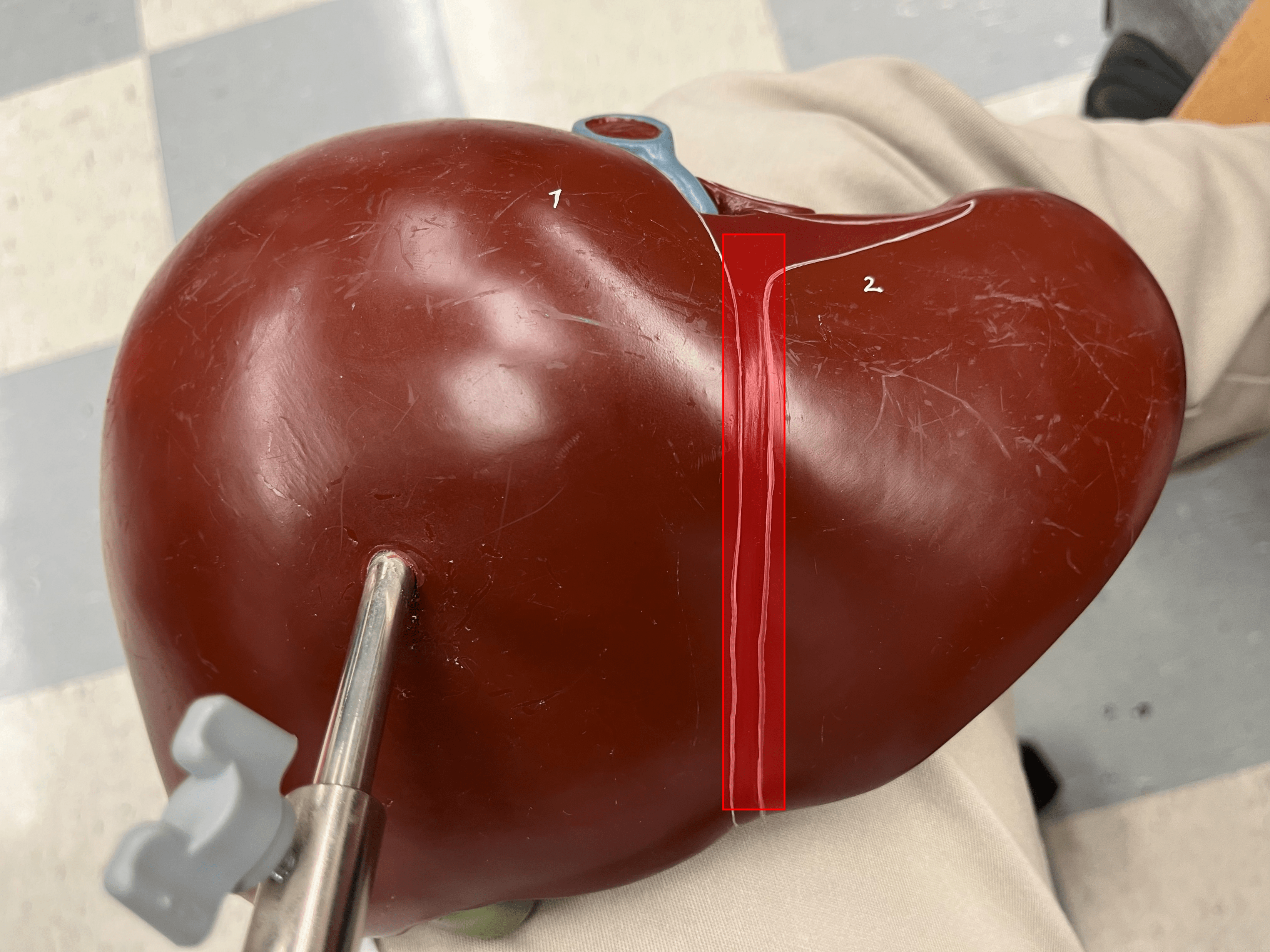
90
New cards
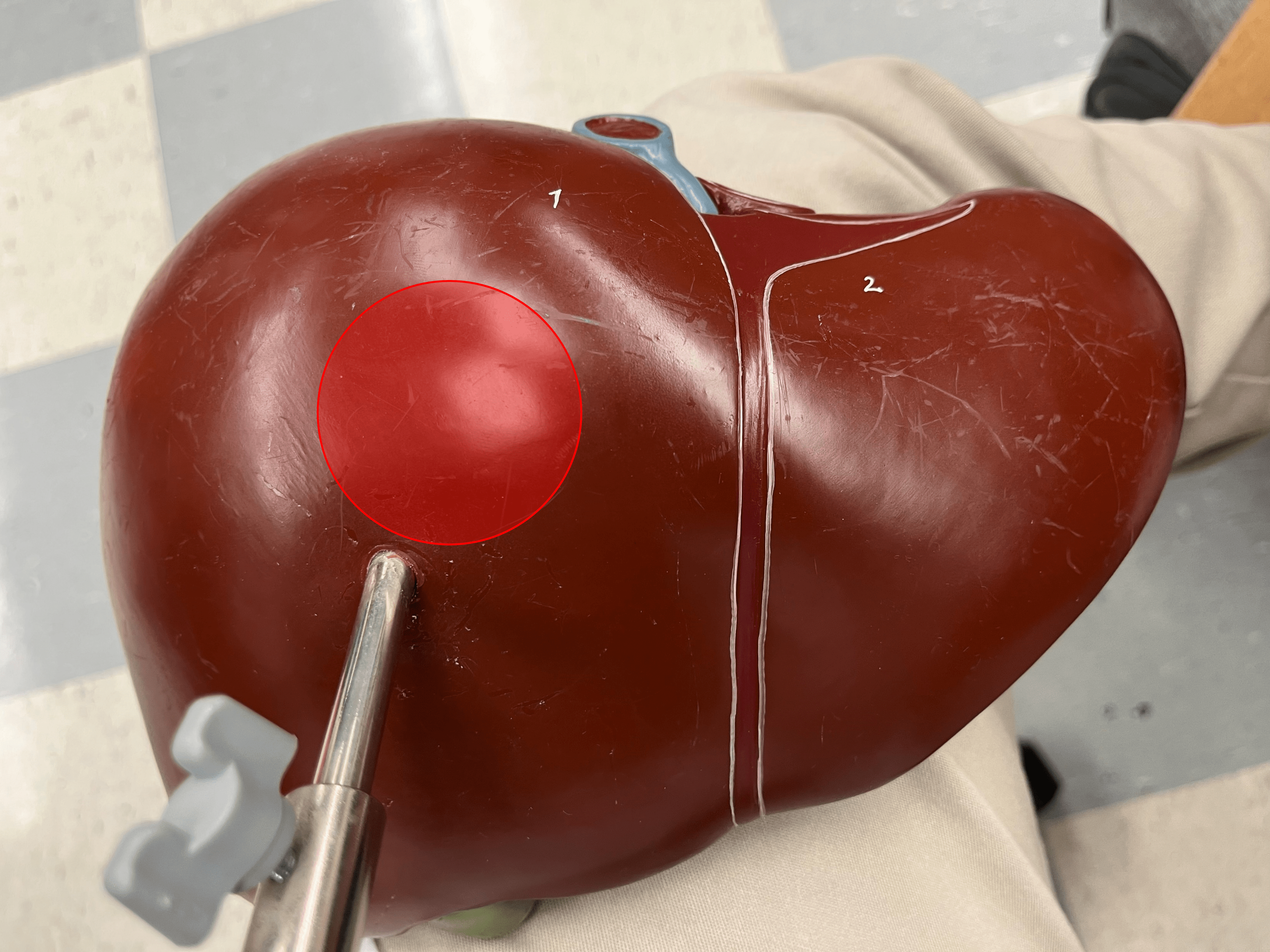
right lobe
• A lobe of the liver.
• The larger lobe on the anterior of the liver.
• The larger lobe on the anterior of the liver.
91
New cards
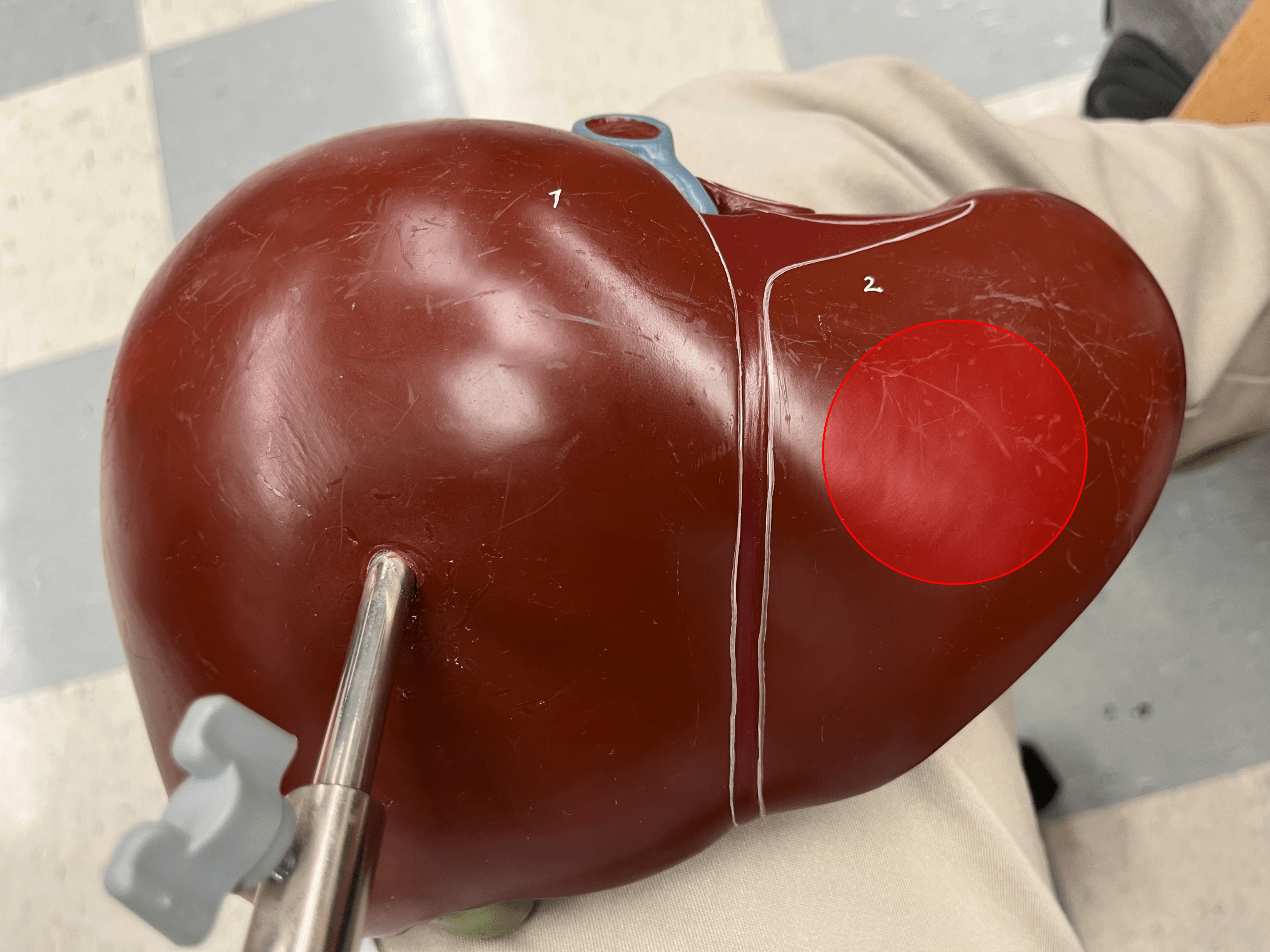
left lobe
• A lobe of the liver.
• The smaller lobe on the anterior of the liver.
• The smaller lobe on the anterior of the liver.
92
New cards
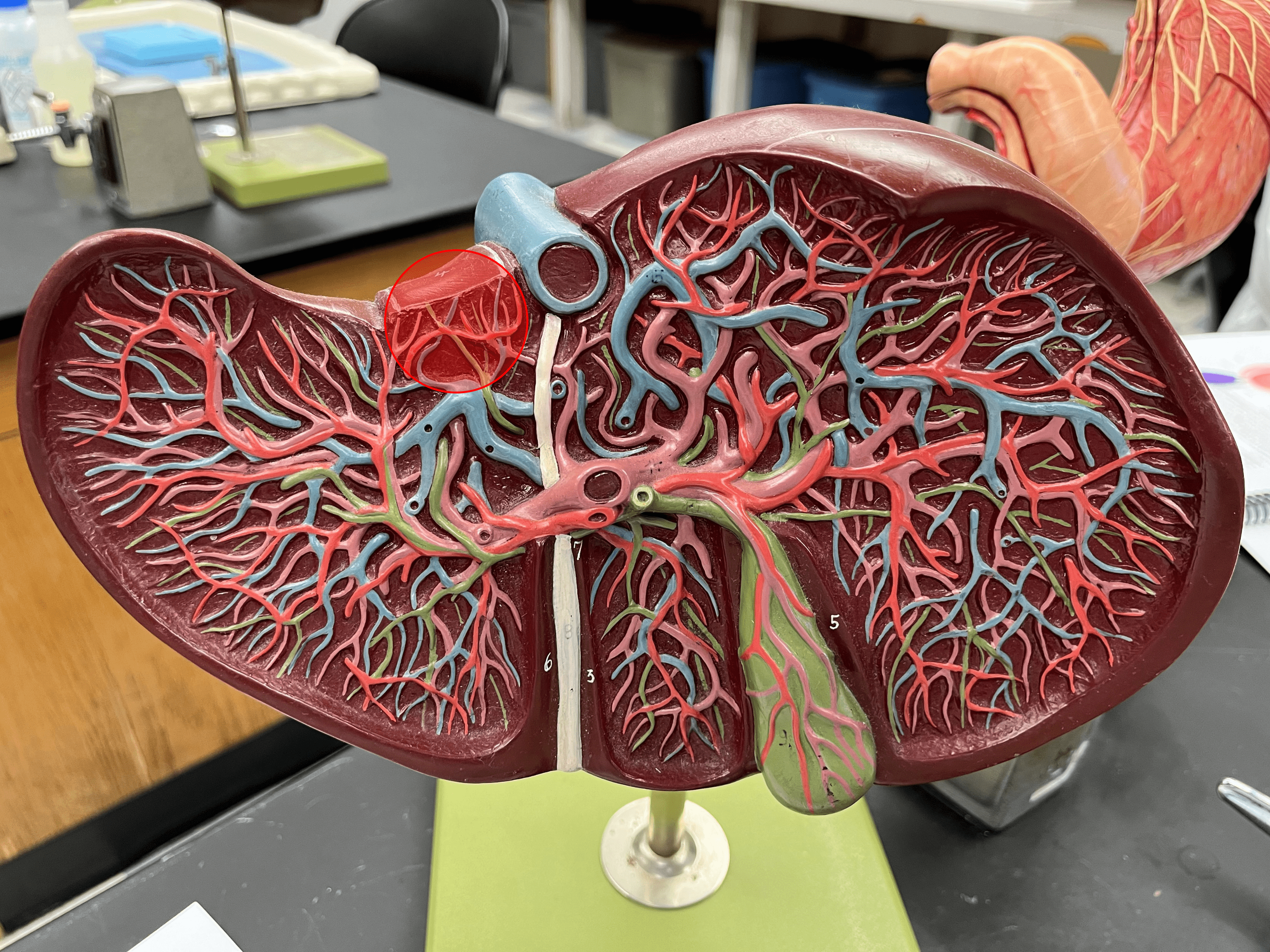
caudate lobe
• A lobe of the liver.
• The superior lobe on the posterior of the liver, next to the inferior vena cava.
• The superior lobe on the posterior of the liver, next to the inferior vena cava.
93
New cards
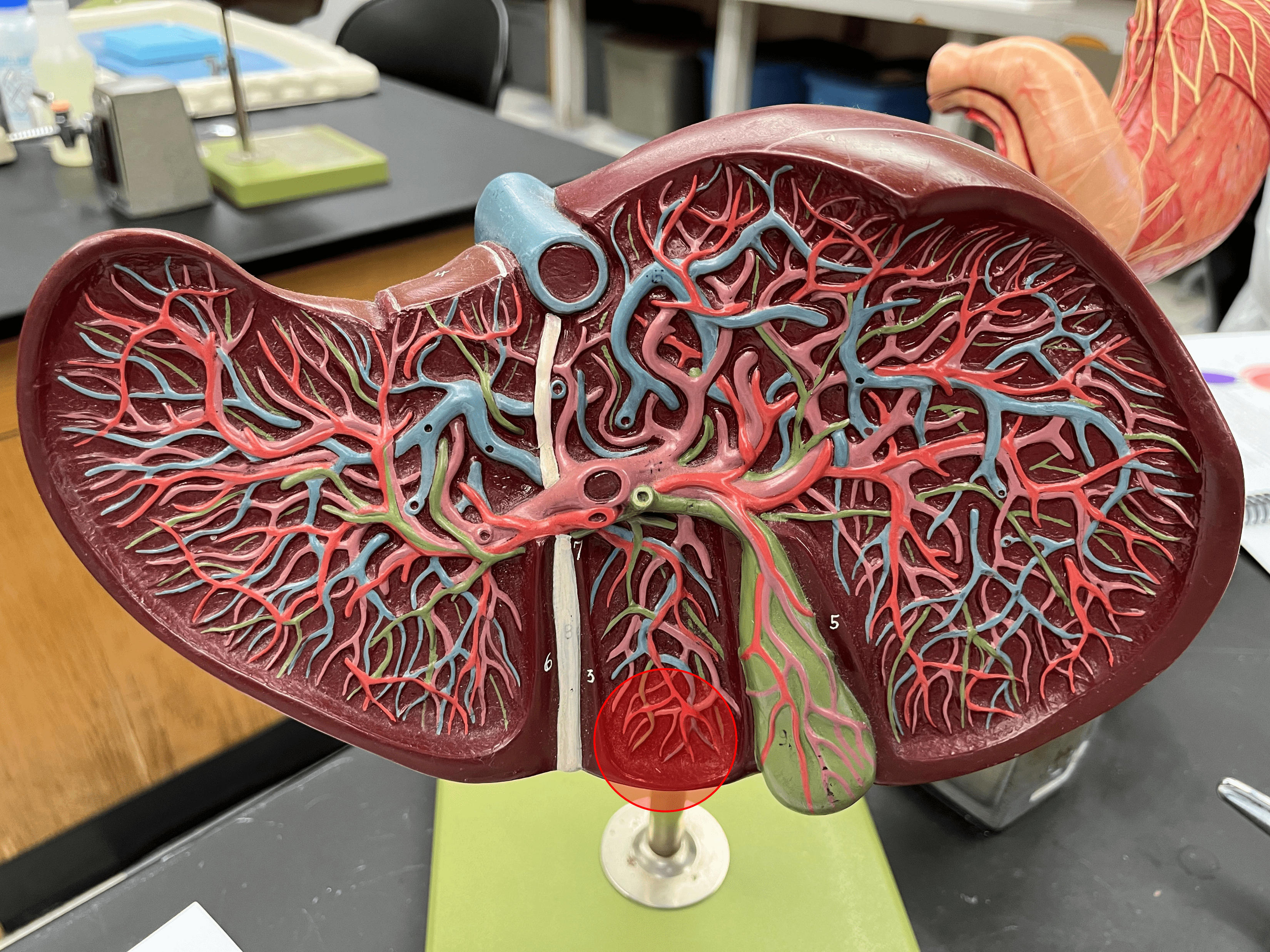
quadrate lobe
• A lobe of the liver.
• The inferior lobe on the posterior of the liver, next to the gallbladder.
• The inferior lobe on the posterior of the liver, next to the gallbladder.
94
New cards
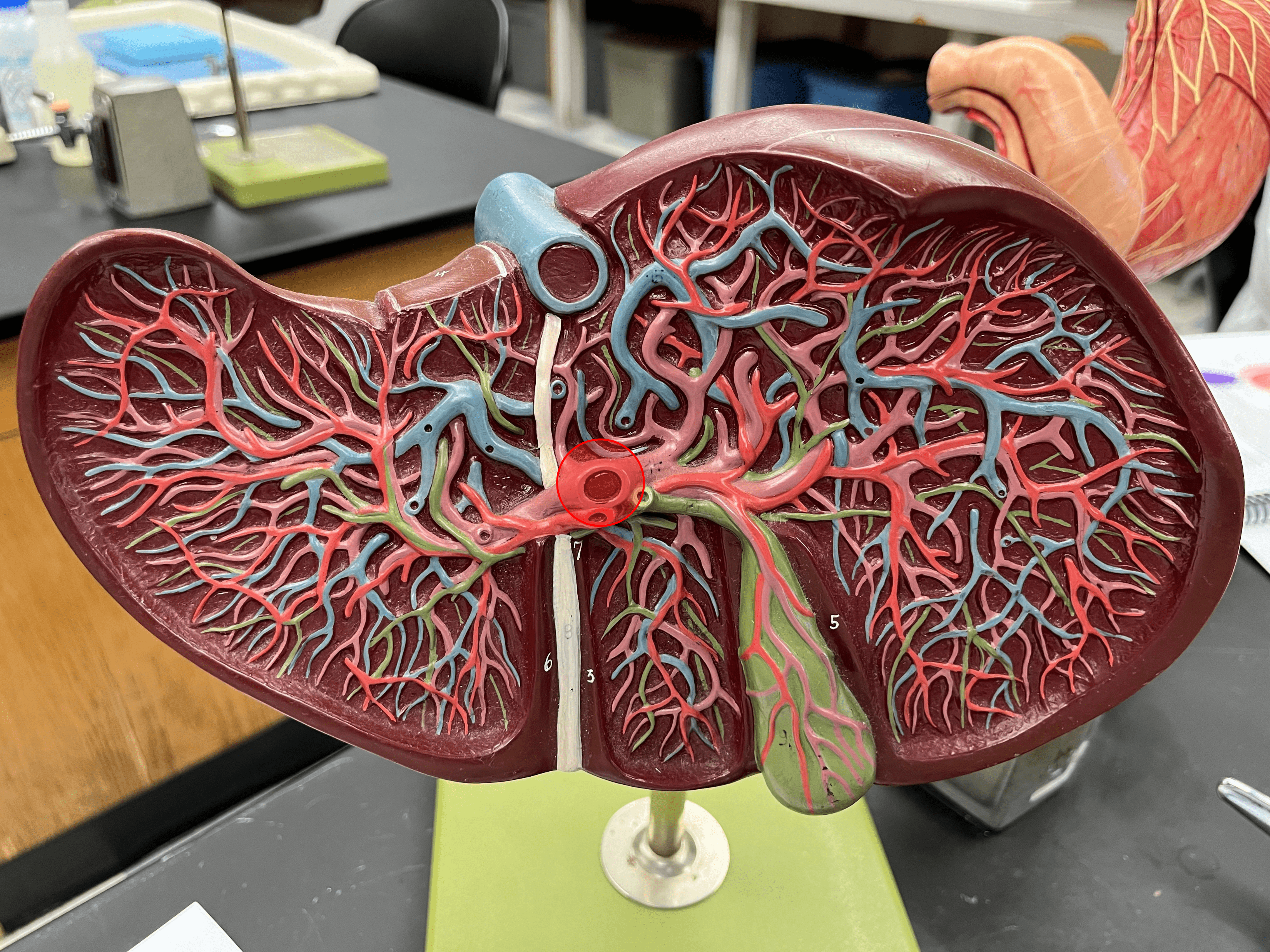
hepatic portal vein
Carries blood from the digestive tract to the liver for nutrient processing and detoxification.
95
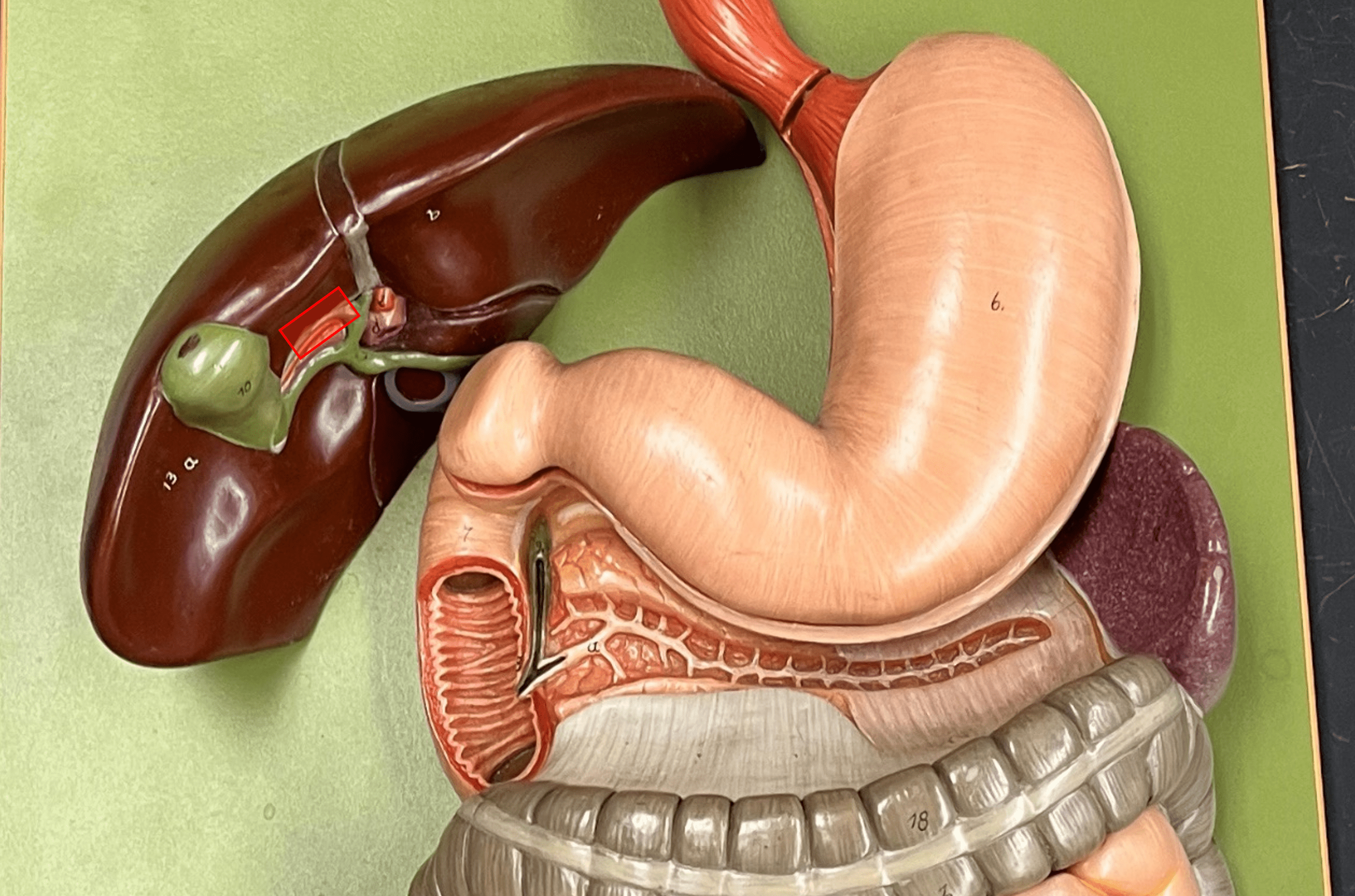
New cards
right hepatic duct
• A bile duct.
• The R. duct transports bile directly from the liver.
• Converges with the L. hepatic duct to form the common hepatic duct.
• The R. duct transports bile directly from the liver.
• Converges with the L. hepatic duct to form the common hepatic duct.
96
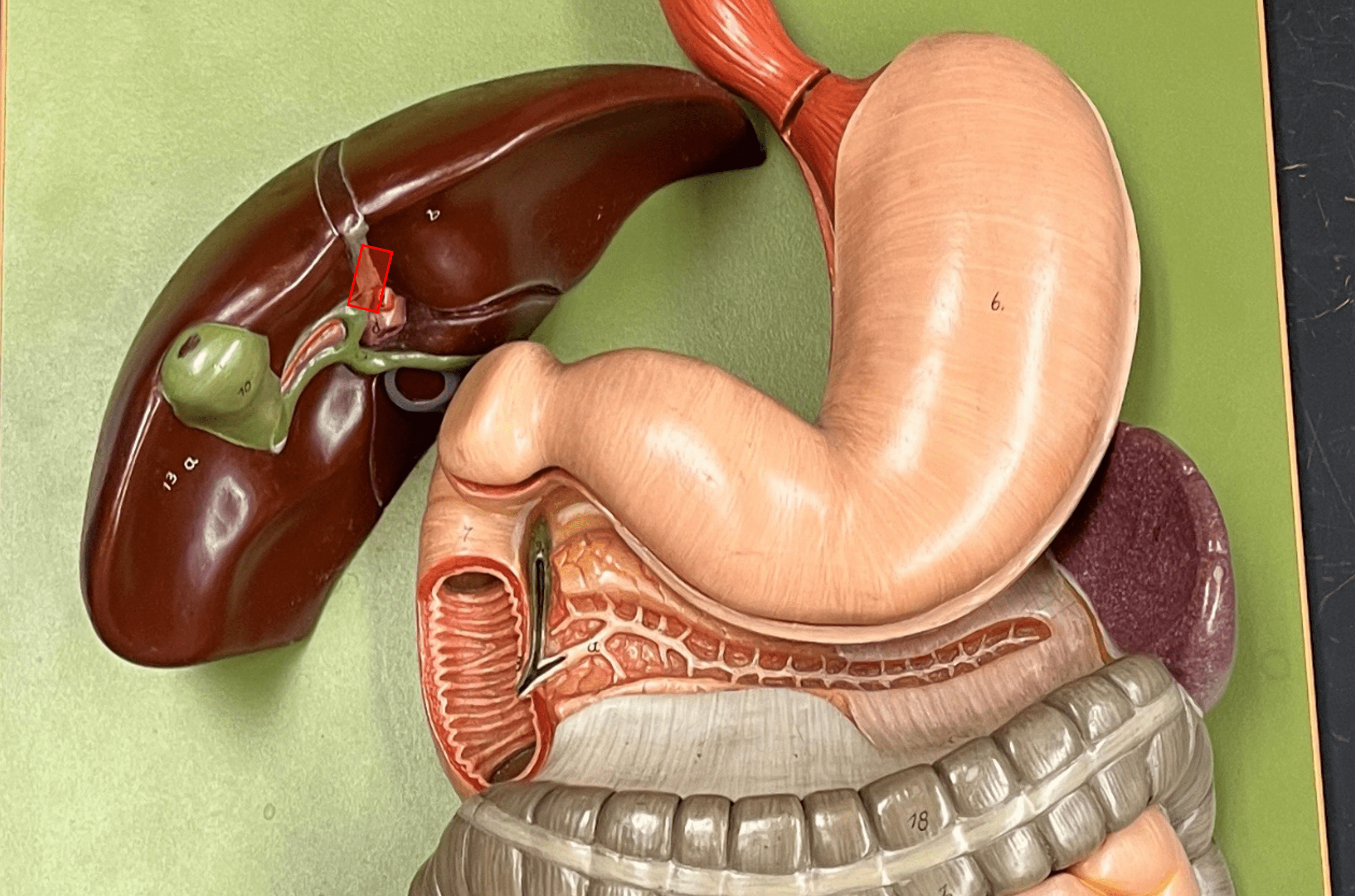
New cards
left hepatic duct
• A bile duct.
• The L. duct transports bile directly from the liver.
• Converges with the R. hepatic duct to form the common hepatic duct.
• The L. duct transports bile directly from the liver.
• Converges with the R. hepatic duct to form the common hepatic duct.
97
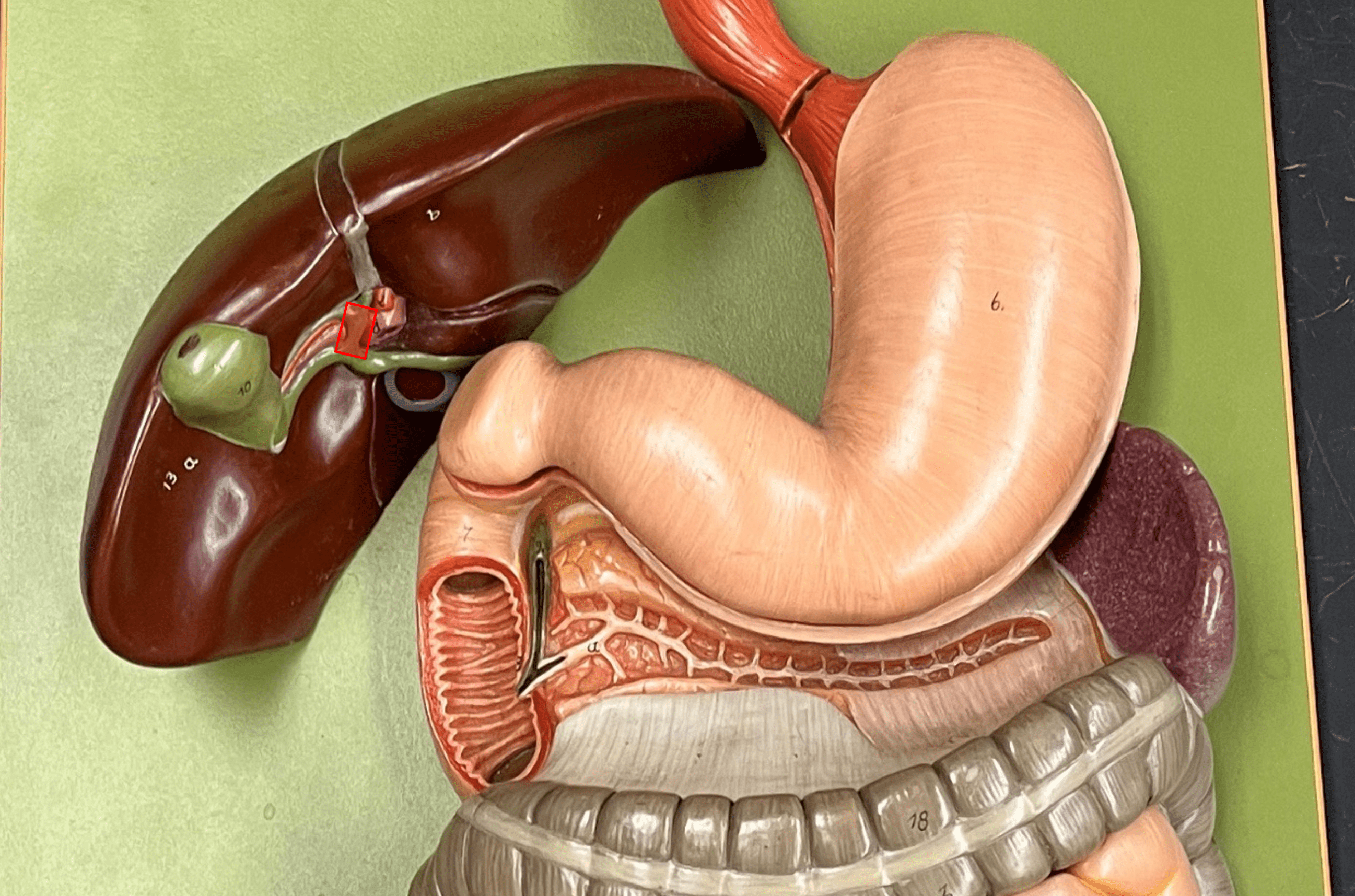
New cards
common hepatic duct
• A bile duct.
• The convergence of the R. and L. hepatic ducts.
• Converges with the cystic duct to form the common bile duct.
• The convergence of the R. and L. hepatic ducts.
• Converges with the cystic duct to form the common bile duct.
98
New cards
gallbladder
• A hollow organ located between the right and quadrate lobes of the liver.
• Receives and stores bile from the liver until digestion occurs.
• Receives and stores bile from the liver until digestion occurs.
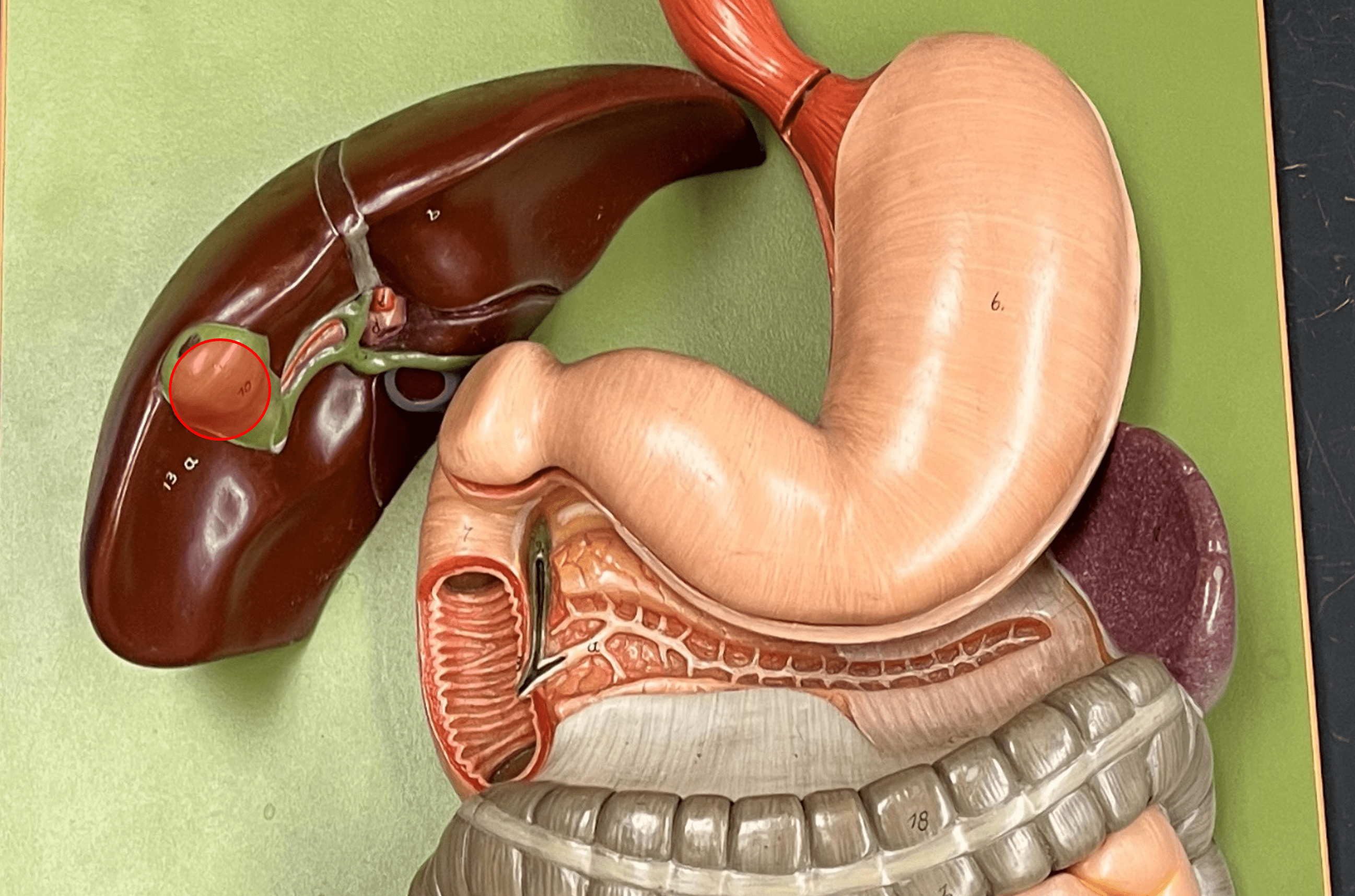
99
New cards
cystic duct
• A bile duct.
• Transports bile to and from the gallbladder.
• Converges with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct.
• Transports bile to and from the gallbladder.
• Converges with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct.
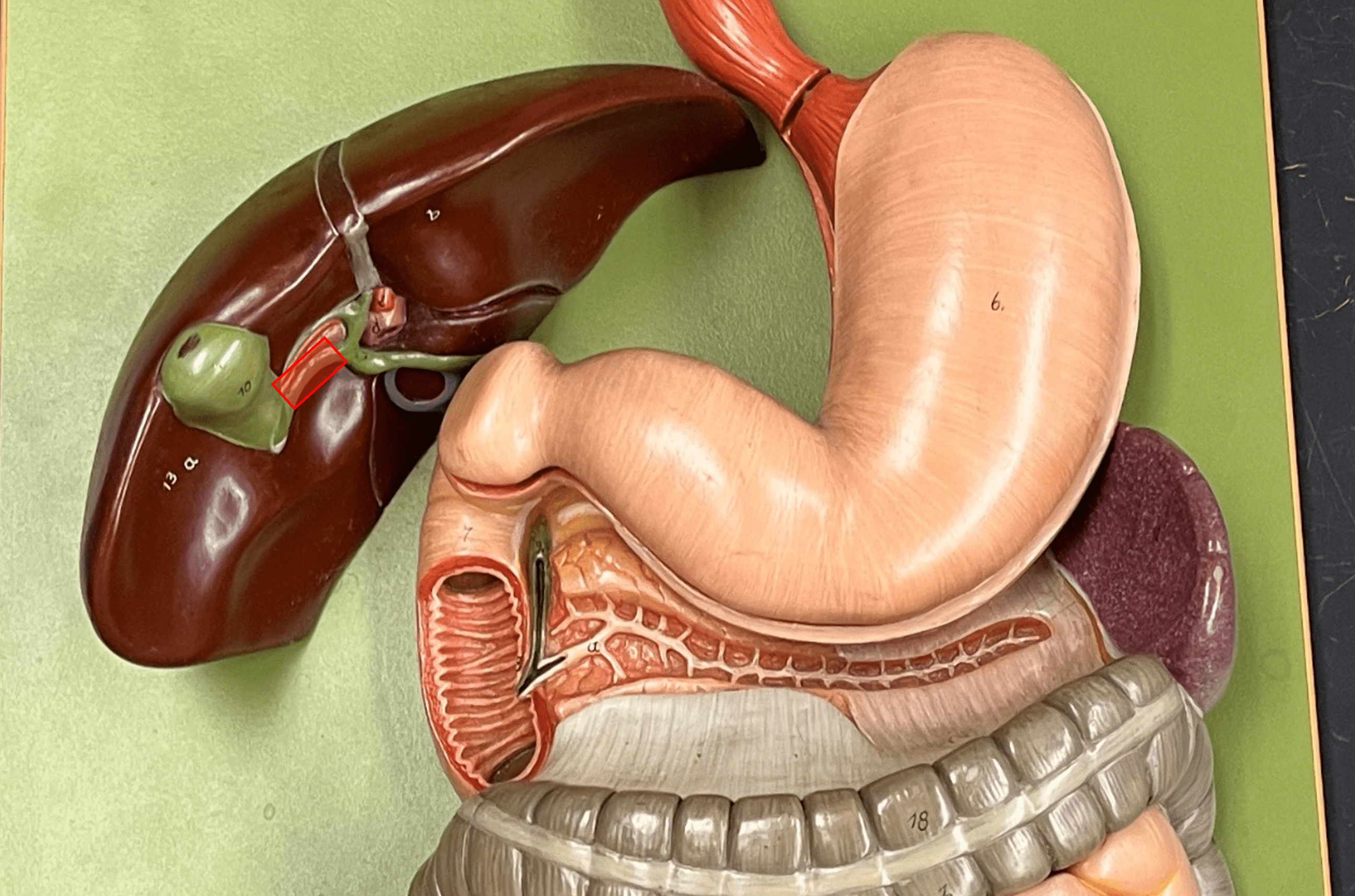
100
New cards
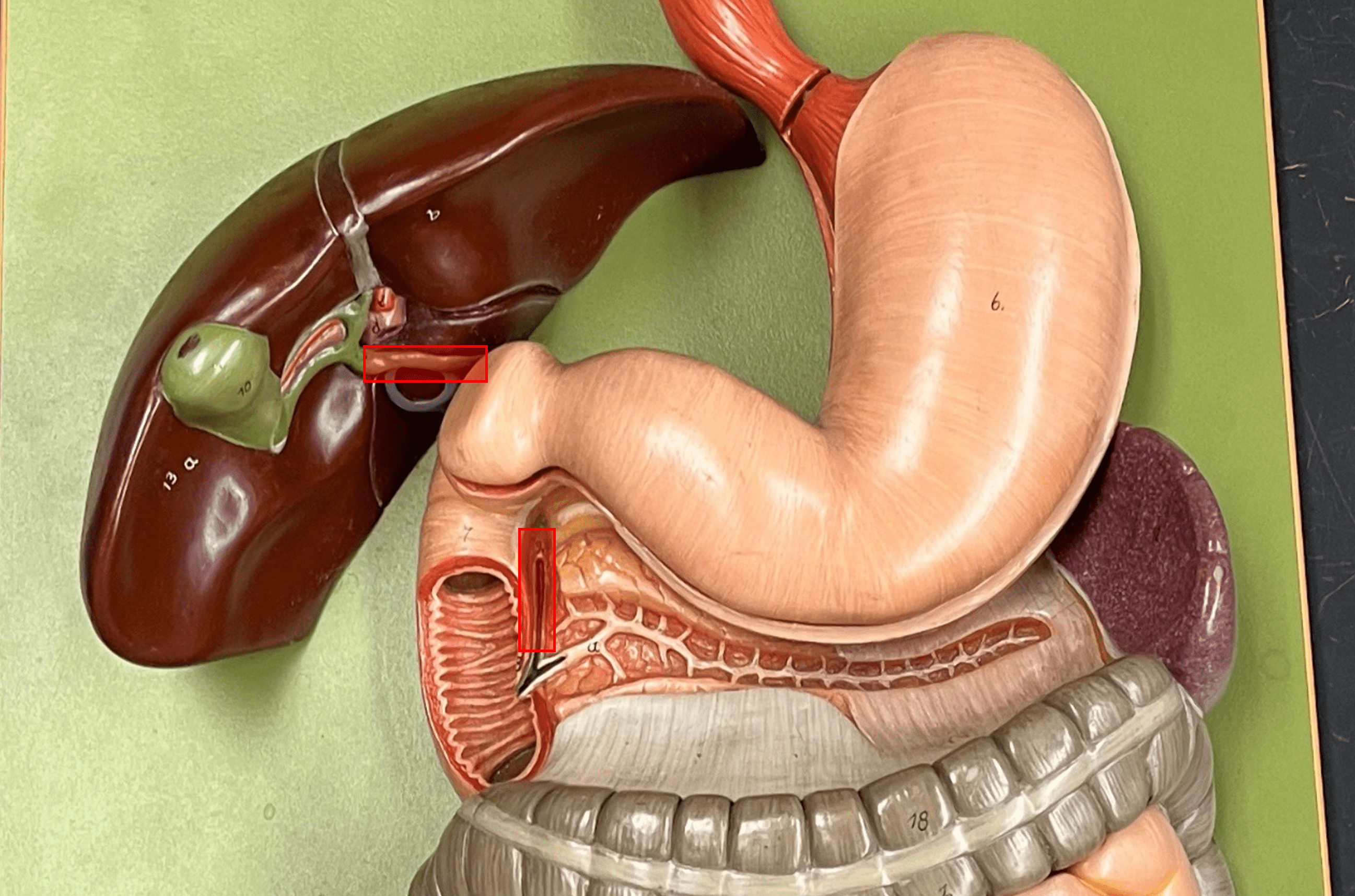
common bile duct
• A bile duct.
• The convergence of the common hepatic and cystic ducts.
• Converges with the major duodenal papilla of the pancreas to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla.
• The convergence of the common hepatic and cystic ducts.
• Converges with the major duodenal papilla of the pancreas to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla.