Unit 3: Hypersensitivity Objectives
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivity?
Type I: Anaphylaxis
Type II: Cytotoxic
Type III: Immune complex reactions
Type IV: Cell-mediated
What is type I hypersensitivity?
Type I: Anaphylaxis: Many hypersensitivity reactions are not life-threatening, severe systemic reactions like anaphylaxis carry a significant risk of death.
Example: anaphylaxis, seasonal hay fever, food allergies, drug allergies
What is Type II hypersensitivity?
1. Type II: Cytotoxic reactions involve antibodies targeting cells or tissues resulting in organ damage;
Hemolytic transfusion (recipient’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys RBCs during a blood transfusion)
body turns against itself
Graves disease, myasthenia gravis
What is Type III hypersensitivity?
1. Type III: Immune complex reactions – involve immune complexes that deposit in tissues and cause inflammation leading to vasculitis and serum sickness;
Severe cases lead to irreversible organ damage such as kidney failure which can contribute to mortality
Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erthematosus,
What is Type IV hypersensitivity?
1. Type IV: Cell-mediated reactions – delayed type – mortality associated with type IV hypersensitivity is generally low
Most severe is DRESS – mortality rate of 5-10%
Death due to organ failure
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) caused by immunological dysfunction
Examples: TB skin test, contact dermatitis, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
What type of hypersensitivity?
1. immediate hypersensitivity – mediated by fast IgE mediated allergic response that occurs within minutes of exposure to an antigen (allergen)
1. Symptoms: mild (hay fever, hives) to severe (anaphylaxis)
Type I
What type of hypersensitivity?
1. Cytotoxic hypersensitivity – mediated by IgG or IgM antibodies (protective proteins produced by immune system) that bind directly to antigens on the surface of specific body cells or tissues – immune system mistakenly recognizes certain antibodies as foreign
1. Responsible for incompatible blood transfusion reactions and autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Type II
What type of hypersensitivity?
1. Immune complex hypersensitivity – involves formation of circulating antigen antibody (immune) complexes that deposit in tissues, triggering an inflammatory response
1. Conditions caused by this include serum sickness, systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis
Type III
What type of hypersensitivity?
1. Delayed type (cell-mediated) hypersensitivity – mediated by T cells rather than antibodies and is delayed – appearing 24 to 72 hours after antigen exposure
1. Examples include contact dermatitis (poison ivy), tuberculin skin test, and transplant rejection; Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Type IV
Etiology of hypersensitivity?
Hypersensitivity (AKA as an allergic reaction) occurs when the immune system overreacts to a typically harmless substance (allergen)
pathophysiology of hypersensitivity?
immune-mediated tissue damage from inappropriate or exaggerated responses to antigens
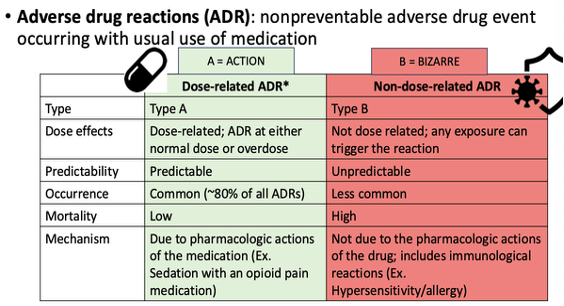
What is the most common ADR?
Dose related ADRs which are Type A (Action)
What is a type A dose related ADR?
1. MOA: an extension or exaggeration of the therapeutic effect; effects predictable based on the drug’s action
2. The reaction is expected based on how the drug works and can be anticipated
3. Dose-dependent: the severity of the ADR increases with a higher dose
What is a type B non dose related ADR?
1. MOA: mechanism is bizarre meaning it is not related to the drug’s intended pharmacological effect
2. The reaction is rare, sporadic, and not a feature of the drug’s normal use
3. Not-dose dependent: the reaction can occur at any therapeutic dose
Identify common drug classes that may result in hypersensitivity reactions. (1b, 1d)
1. Antibiotics: beta-lactams (penicillin and cephalosporins); sulfa drugs; other antibiotics (vancomycin)
2. NSAIDs: aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen; opiates: morphine and codeine; acetaminophen
Describe the long-term complications of hypersensitivities. (1e, 1f)
1. Depend on type of reaction and the affected organ system
Chronic inflammation leads to permanent tissue damage
Contact dermatitis
DRESS
Autoimmune conditions
Food allergies
Eczema
Allergic asthma
Identify drug classes that may decrease the manifestations of hypersensitivity reactions. (2a)
1. Corticosteroids, antihistamines, epinephrine, leukotriene modifiers, mast cell stabilizers
What is the first line treatment for anaphylaxis?
Epinephrine: rapidly constricts blood vessels to increase BP, relaxes smooth muscles in the airways to improve breathing and reduces swelling, hives, and itching (for Type 1 hypersensitivity)
What do corticosteroids do?
1. MOA: decrease inflammation by inhibiting inflammatory mediators
What do antihistamines do?
1. MOA: reduce itching, rash, hives by blocking effects of histamine
First generation: diphenhydramine (sedative effects)
Second generation: loratadine (non-sedating)
What is an allergy?
an adverse drug reaction and type of drug hypersensitivity reaction mediated by an immune response
What is a hypersensitivity?
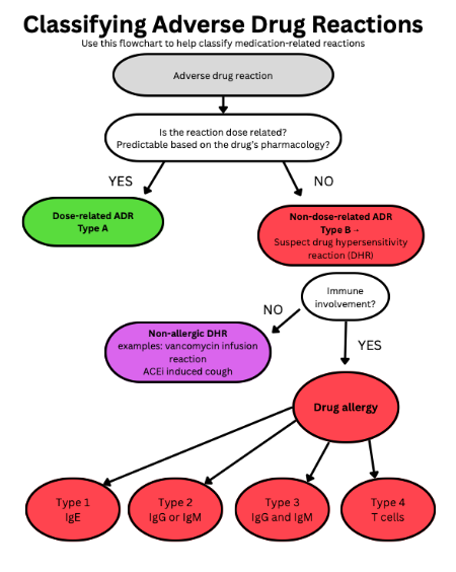
an adverse drug reaction that clinically resemble an allergic reaction but may or may not be immunologically mediated (medium bubble)
Non-immune HSR (not allergies)
Vancomycin infusion reaction
ACE inhibitor cough and angioedema (increased bradykinin)
Opioid induced histamine release
What is an adverse drug reaction?
nonpreventable adverse drug event occurring with usual use of medication
Review ADR Type A and B
How to classify Adverse Drug Reactions?
What are 3 common examples of non-immune HSR?
1) vancomycin infusion reaction
2) ACE inhibitor cough and angioedema
3) opioid induced histamine release
A patient is experiencing bradycardia after taking metoprolol (beta blocker). What type of ADR?
Type A because bradycardia is a side effect for beta blockers (not an allergy)
A patient is experiencing urticaria (hives) after taking losartan (ARBs). What type of ADR?
non dose related ADR (type B - unusual symptom) - allergy
A patient is experiencing urticaria (hives) after taking hydrochlorothiazide, what ADR is this?
non dose related ADR - Type B - wouldn’t expect a rash - non-immune example
A patient is experiencing urticaria after taking HCTZ and it occurred an hour after taking medication, what type of hypersensitivity is this?
Type 1 - immediate reaction
A patient is taking amlodipine and experiences peripheral edema, what type of ADR is this?
-dose related ADR - type A - would expect it because it is a disease effect
A patient is taking enalapril (ACEi) and develops a cough (bradykinin), what type of ADR is this?
Type B - non-allergic (dose) drug hypersensitivity
A patient takes HCTZ and complains of a rash, what type of reaction is this?
Type B - non dose related allergy (hypersensitivity)
A patient takes amoxicillin and complains of diarrhea, what type of ADR is this?
Type A - dose related ADR - not an allergy
A patient takes IV vancomycin and complains of an itchy scalp, what type of ADR is this?
Type B - non allergic drug hypersensitivity (not immune related)
A patient is allergic to lisinopril and has an anaphylactic reaction, what type of ADR is this?
Type B non dose hypersensitivity (allergy) - Type 1 Hypersensitivity
What are anticholinergic effects?
Can’t see (blurred vision), Can’t spit (dry cough), Can’t pee (urinary retention), Can’t poop (constipation)