Biology Test/Quiz #2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
characteristics that all living things share
made up of units called cells
reproduce
based on universal genetic code
grow and develop
obtain and use materials and energy
respond to their environment
maintain homeostasis
change over time/ evolve
what is a virus
a noncellular particle of nucleic acids, protein, and in some cases, lipids
can only reproduce by infecting living cells
what is a virus composed of
a core of nucleic acids (RNA or DNA)
surrounded by a protein coat (capsid)
come in a variety of shapes
vary in size (10-400 nanometers)
how does a virus enter an a cell
the capsid proteins bind to the receptors on the surface of the cell and “trick” the cell into allowing it inside
bacteriophage
viruses that infect only bacteria
two types of infections
lysogenic infection
lytic infection
characteristics of a lytic infection
enters the cell
uses the cell to make copies of itself
cause the cell to lyse or burst releasing new viruses and killing the cell
characteristics of a lysogenic infection
a virus integrates its DNA into the DNA of the host cell
the viral genetic information replicates along with the new host cell’s DNA possibly for many generations
viral DNA eventually becomes active and creates new virus particles and lyses the cell wall releasing new viruses
why is a retrovirus different from a regular virus
it contains RNA instead of DNA as its genetic information
how do retroviruses work
by infecting cells and making a DNA copy of their RNA
the DNA is then inserted into the DNA of the host’s cells
what is a prokaryote
unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus
** also the smallest and most common microorganisms
Eubacteria
have a cell wall that protects the cell and determines its shape
cell walls contain peptidoglycan
have a cell membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm
what kind of environments do eubacteria live in
fresh water
on land
the human body
Archaebacteria
cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan
have different membrane lipids
the DNA sequences are more like eukaryotes than eubacteria
live in extreme environments
where do archaebacteria live
methanogens live in oxygen-free environments, such as thick mud and animal digestive tracts
others live in salty environments or in hot springs where water temperatures approach the boiling point
how can scientists identify prokaryotes
shape
chemical nature of their cell walls
the way they move
the way they obtain energy
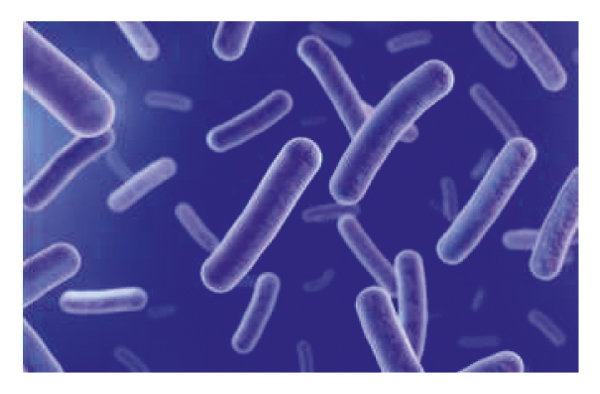
rod shaped prokaryote
bacilli
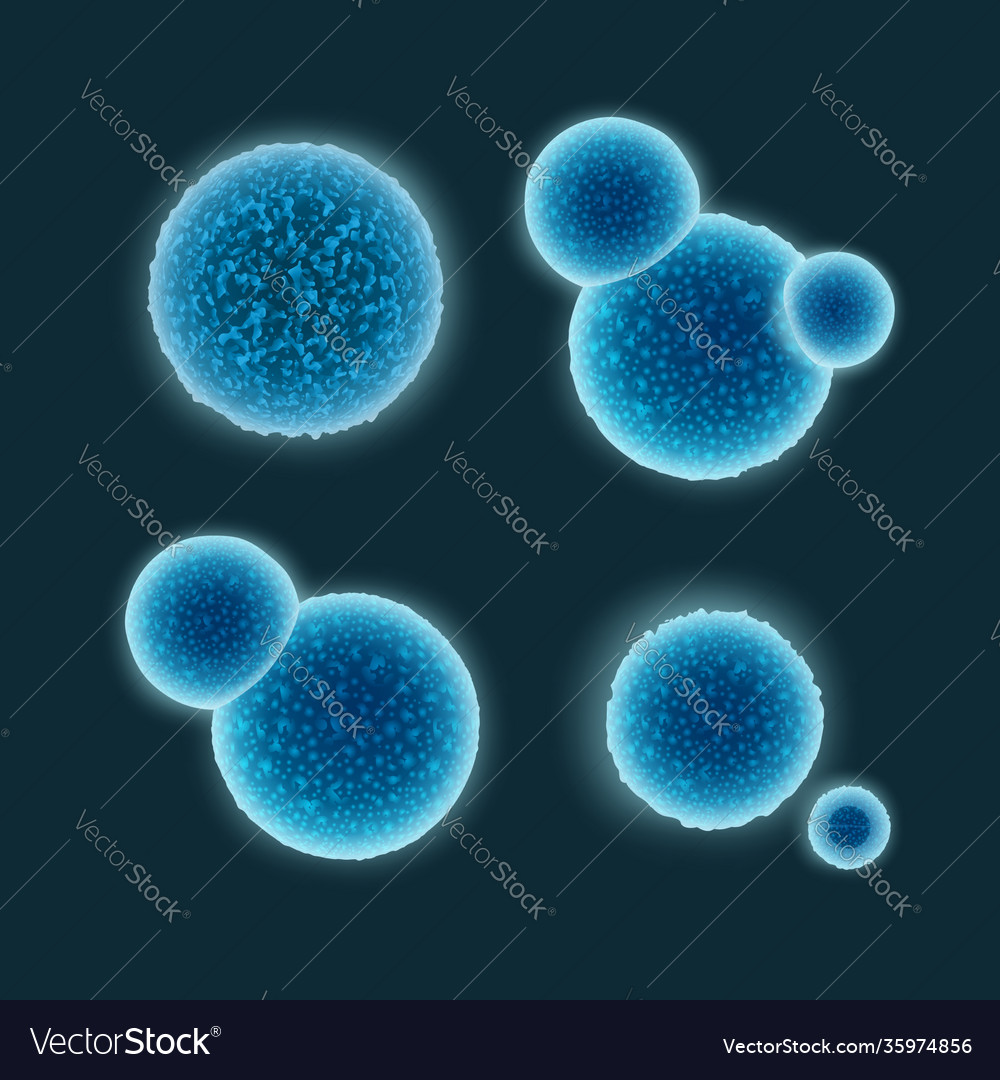
spherical shaped prokaryote
cocci
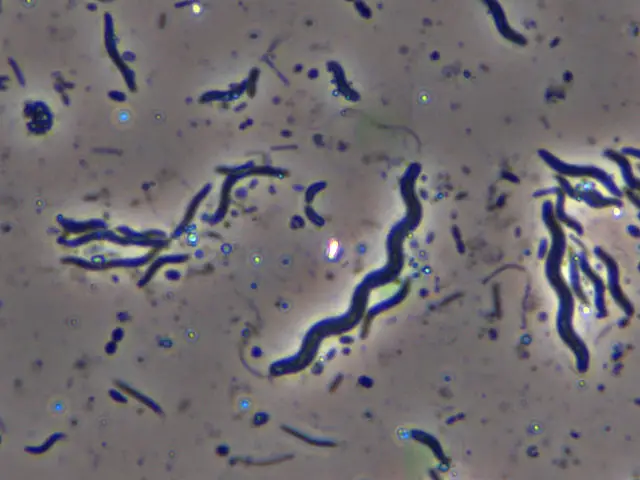
spiral and corkscrew shaped prokaryotes
spirilla
two types of cell walls
gram-positive
gram-negative
gram-positive cell walls
bacteria have thick cell walls with large amounts of peptidoglycan (take up crystal violet)
gram-negative cell walls
bacteria have thinner cell walls inside an outer lipid layer (take up safranine)
how can scientists identify what kind of cell wall they are dealing with?
gram staining- tells them apart by using crystal violet and safranine
types of movement for prokaryotes
flagella
lash, snake, or spiral forward
glide along a layer of slime
or don’t move at all
what are the two main groups of prokaryotes obtaining energy
heterotrophs
autotrophs
heterotroph
get their energy by consuming organic molecules made by other organisms
autotroph
make their own food from inorganic molecules
chemoheterotrophs
take in organic molecules for both energy and a supply of carbon
most animals
most bacteria
photoheterotrophs
use sunlight for energy but take in organic compounds
cant use carbon dioxide as sole carbon source
photoautotrophs
use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water to carbon compounds and oxygen
similar to plants
chemoautotrophs
make organic compounds from carbon dioxide but do not require light as energy instead use inorganic molecules including hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and sulfur
how is needed energy released
cellular respiration or fermentation
respiration
involves breaking down food molecules to release energy
fermentation
enables cells to carry out energy production without the use of oxygen
obligate anaerobes
must live without the presence of oxygen because they may be killed by it (EX// food poisoning)
facultative anaerobes
can survive with or without oxygen
how does bacteria reproduce through binary fission
also known as asexual reproduction, bacteria doubles in size, replicates its DNA, and divides in half
how does bacteria reproduce through sexual reproduction
a hollow bridge forms between two bacterial cells, and genes move from one cell to another
when done each cell has a different set of genes
increases genetic diversity
when does an endospore form?
when bacterium produces a thick internal wall that encloses its DNA and some of its cytoplasm
shapes of bacteria
rod-shaped
tadpole-shaped
many sided
helical
cube-like
obligate aerobe
organism that requires a constant supply of oxygen in order to live
types of important bacteria we need
decomposers
nitrogen fixers
decomposers
bacteria recycle nutrients and maintain equilibrium in the environment
bacteria also help in the treatment of sewage
nitrogen fixers
atmosphere is approximately 80 percent nitrogen
plants can’t use nitrogen gas but need nitrogen
many plants have symbiotic relationships with nitrogen fixing bacteria which take nitrogen gas from the air and convert it to a form plants can use
humans uses for bacteria
foods
removal of waste
clean up oil spills
synthesis of drugs and chemicals via genetic engineering
production is vitamins in human intestines