AP Human Geography - Unit 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Human Geography
a branch of geography that focuses on the study of patterns and processes that shape human interaction with the built environment, with particular reference to the causes and consequences of the spatial distribution of human activity on the Earth's surface
Globalization
The act of becoming global. The spread of information, ideas, etc from one place in the world to another.
Spatial Perspective
observing variations in geographic phenomena across space
Location
The position of anything on Earth's surface.
Absolute Location
Coordinates, Address, Etc.
Relative Location
Location of a place in relation to another place or landmark. (LANDMARK)
Site
The exact location's physical spot. (think construction)
Situation
The areas around the location which contribute to the sense of the place.
Human-Environment Interactions
How people interact/change the place/location.
Place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by particular characteristics. Uniqueness of the point.
Sense of Place
What makes a place unique
Perception of Place
belief or "understanding" about a place developed through books, movies, stories or pictures
Movement
the change from one location to another
Landscape
the overall appearance of an area. Most are comprised of a combination of natural and human-induced influences.
Cultural Landscape
How a culture affects the landscape of an area/shapes the world around it.
Distortion
Inaccuracies in a map due to the translation of a 3D image to a 2D surface.
Absolute directions
relative to a fixed frame of reference and always point in the same direction, regardless of their location. Directions like north/south and east/west are examples of absolute direction.
Scale
The scope
Generally, the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole, specifically the relationship between the size of an object on a map and the size of the actual feature on Earth's surface. (Scope of view.)
Reference Maps
Used for transportation and locating places.
Thematic Maps
Used to display data about a location.
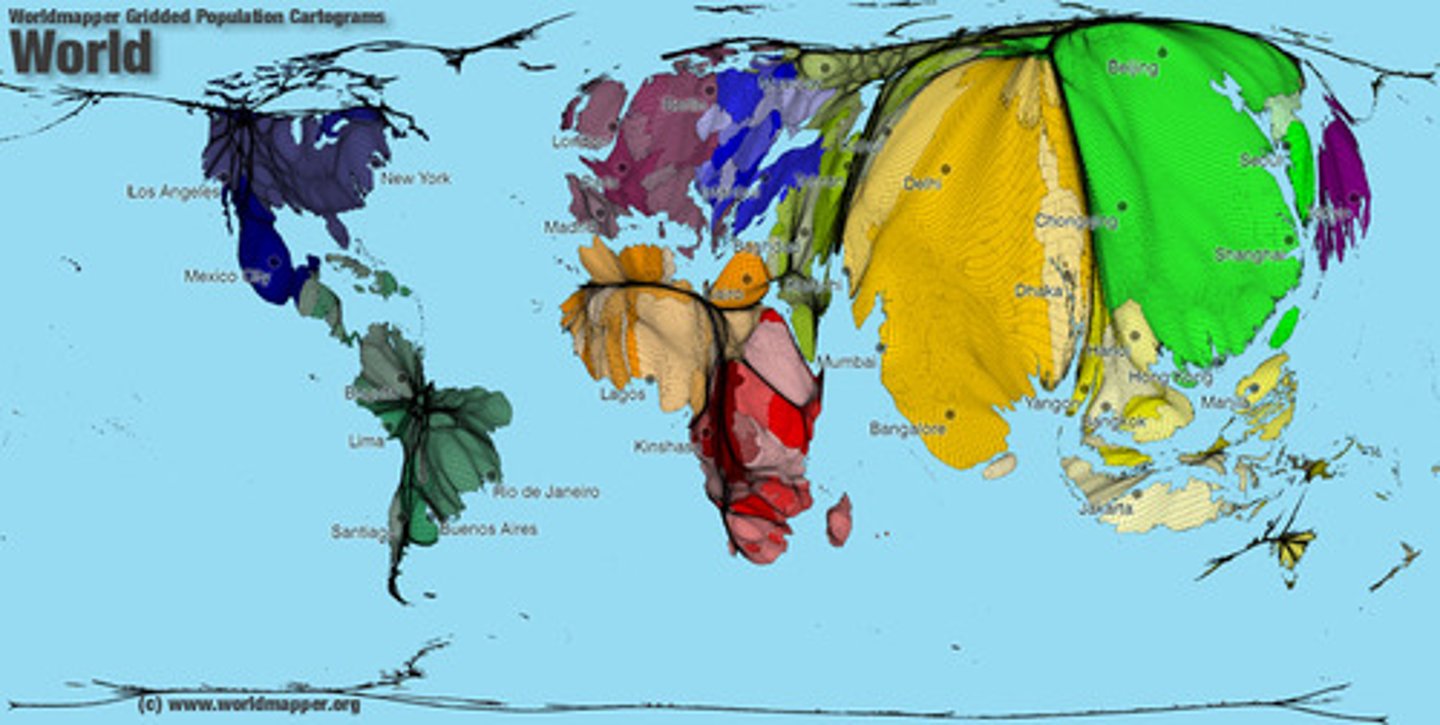
Cartograms
Shows data in relation to size
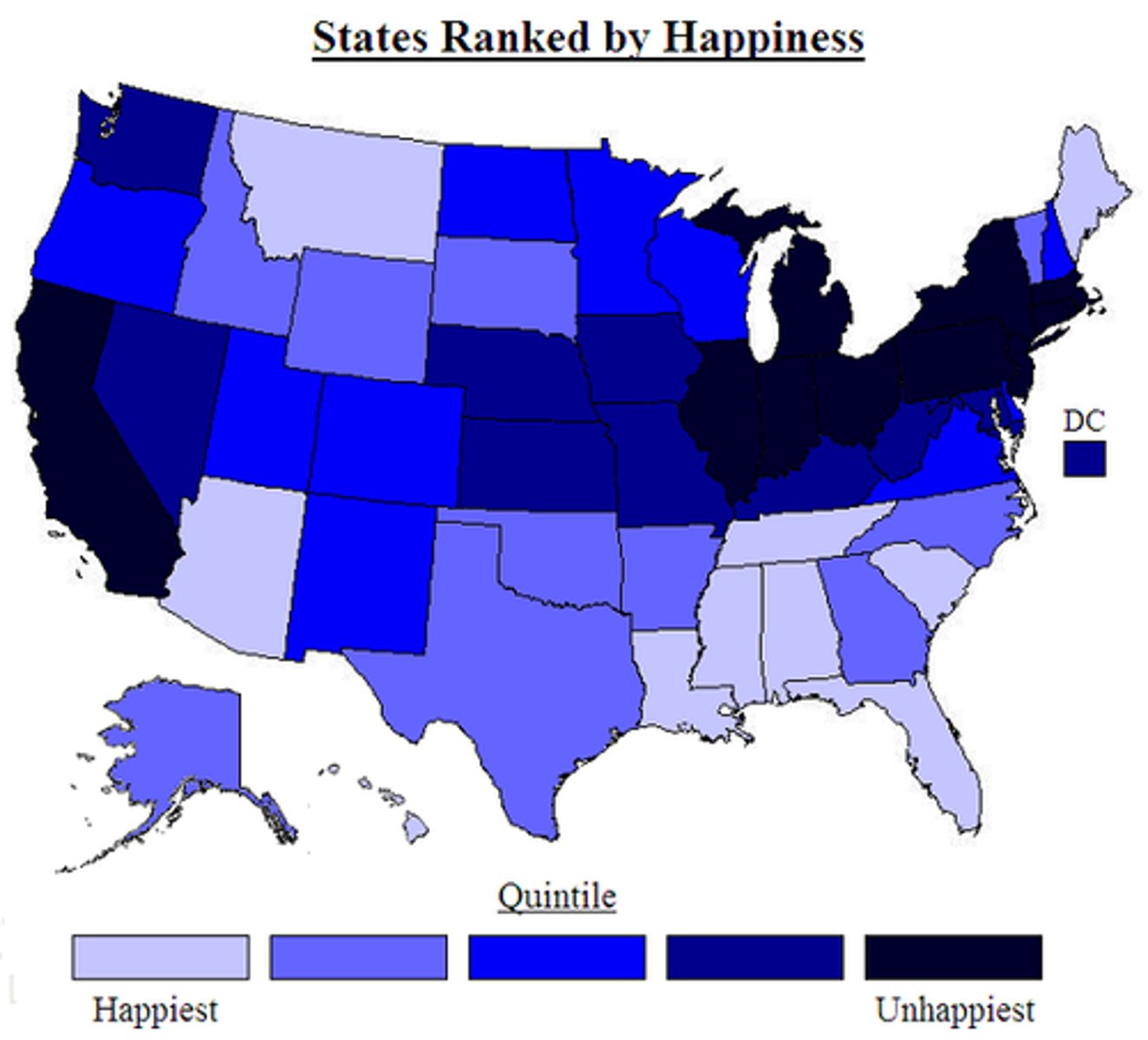
Choropleth Maps
Shows data in relation to color/intensity/shade
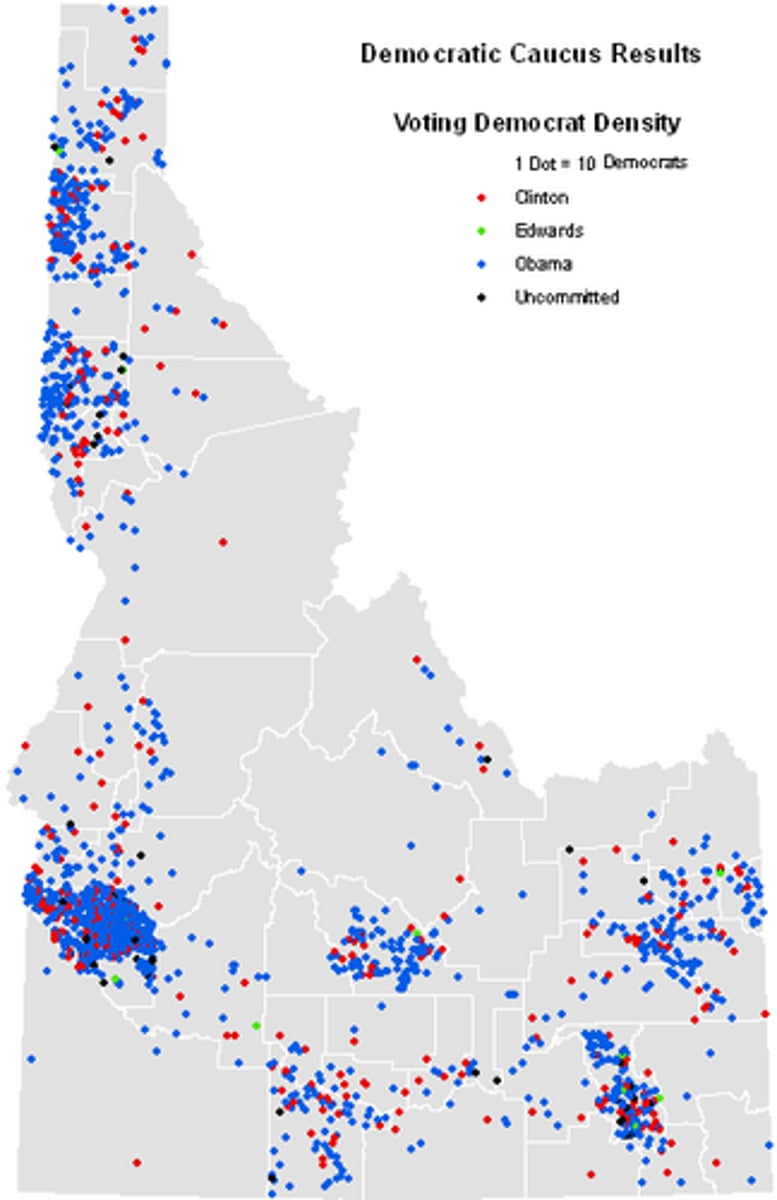
Dot Maps
Each dot represents an amount of data. More dots = more of the variable
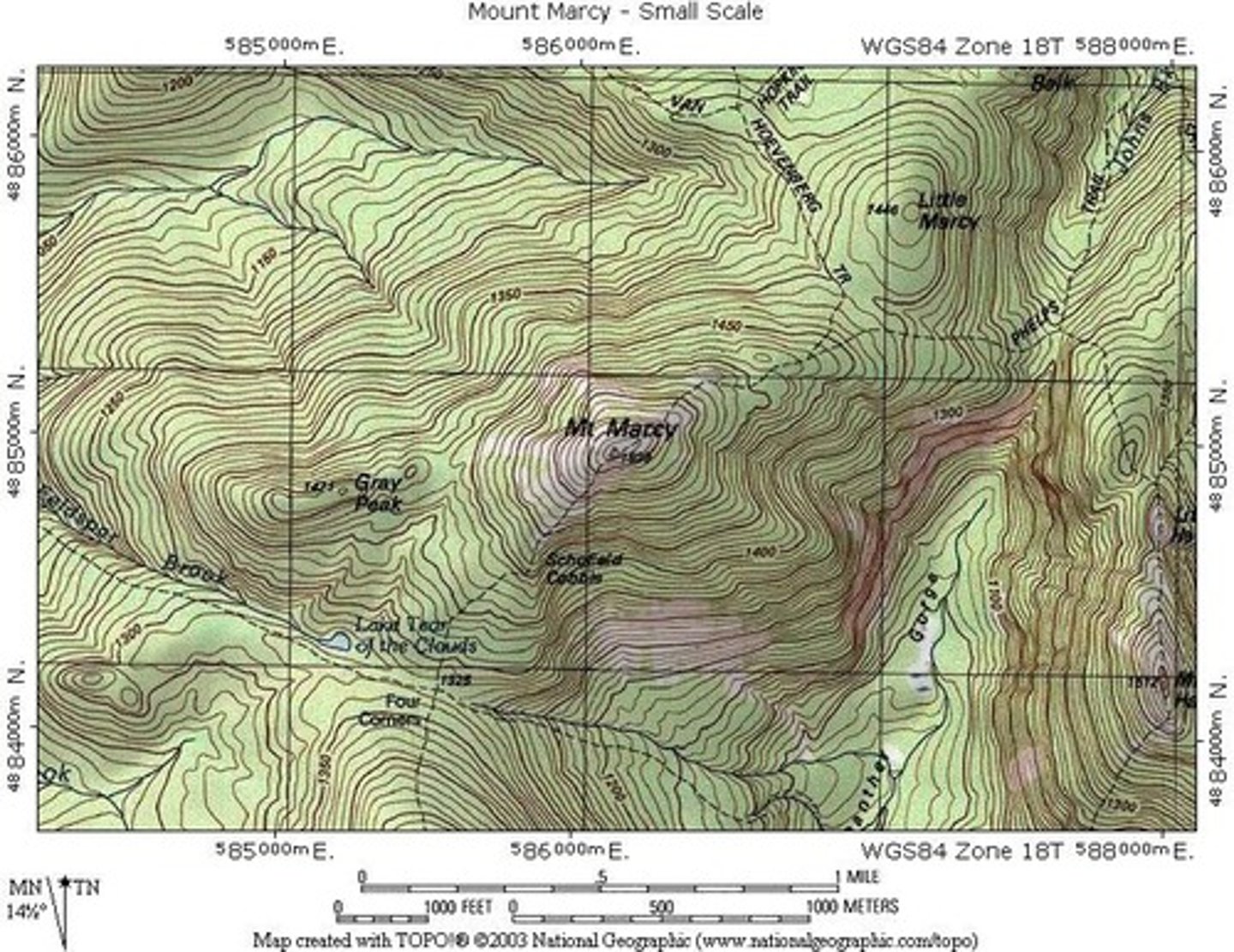
Isoline Map
Map that uses continuous lines connecting areas of same value. (Topographic Maps do this)
Parallels/Latitude
Lines measuring location on earth that wrap around, don't touch.
Meridians/Longitude
Lines measuring location and time zones (1 hr each 15 degrees) on earth that wrap around and touch at the poles.
Equator
The longest line of latitude at 0 degrees and has a constant amount of sun exposure.
census data
data about the nation's people and economy
Prime Meridian
Runs through Greenwich, England. 0 longitude. Could have been placed anywhere in the world, but was placed there.
International Date Line
An arc that for the most part follows 180° longitude, although it deviates in several places to avoid dividing land areas. When you cross it heading east (toward America), the clock moves back 24 hours, or one entire day. When you go west (toward Asia), the calendar moves ahead one day.
Mental Maps
Image or picture of the way space is organized as determined by an individual's perception, impression, and knowledge of that space
Global Positioning System
Tells you where you are on the earth.
Remote Sensing
Collecting data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet.
Geographic Information Systems
Organizes, stores, analyzes, and displays geographic data. Each layer of information is a thematic layer.
Regions
An area or division, especially part of a country or the world having definable characteristics but not always fixed boundaries.
Formal Region
Formally recognized areas determined by a governing body. Sometimes called Uniform Region.
Functional/nodel region
A region around a central node tied by transportation and communication or by economic or functional associations
Perceptual/vernacular region
A place believed to exist as a part of cultural identity. (The South, The North, The Deep South)
Culture
Comprised of shared practices, technologies, attitudes, and behaviors transmitted by a society.
Cultural Trait
The specific customs that are part of the everyday life of a particular culture, such as language, religion, ethnicity, social institutions, and aspects of popular culture.
Absolute distance
Exact measurement of the physical space between two places
Cultural Diffusion
The spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another.
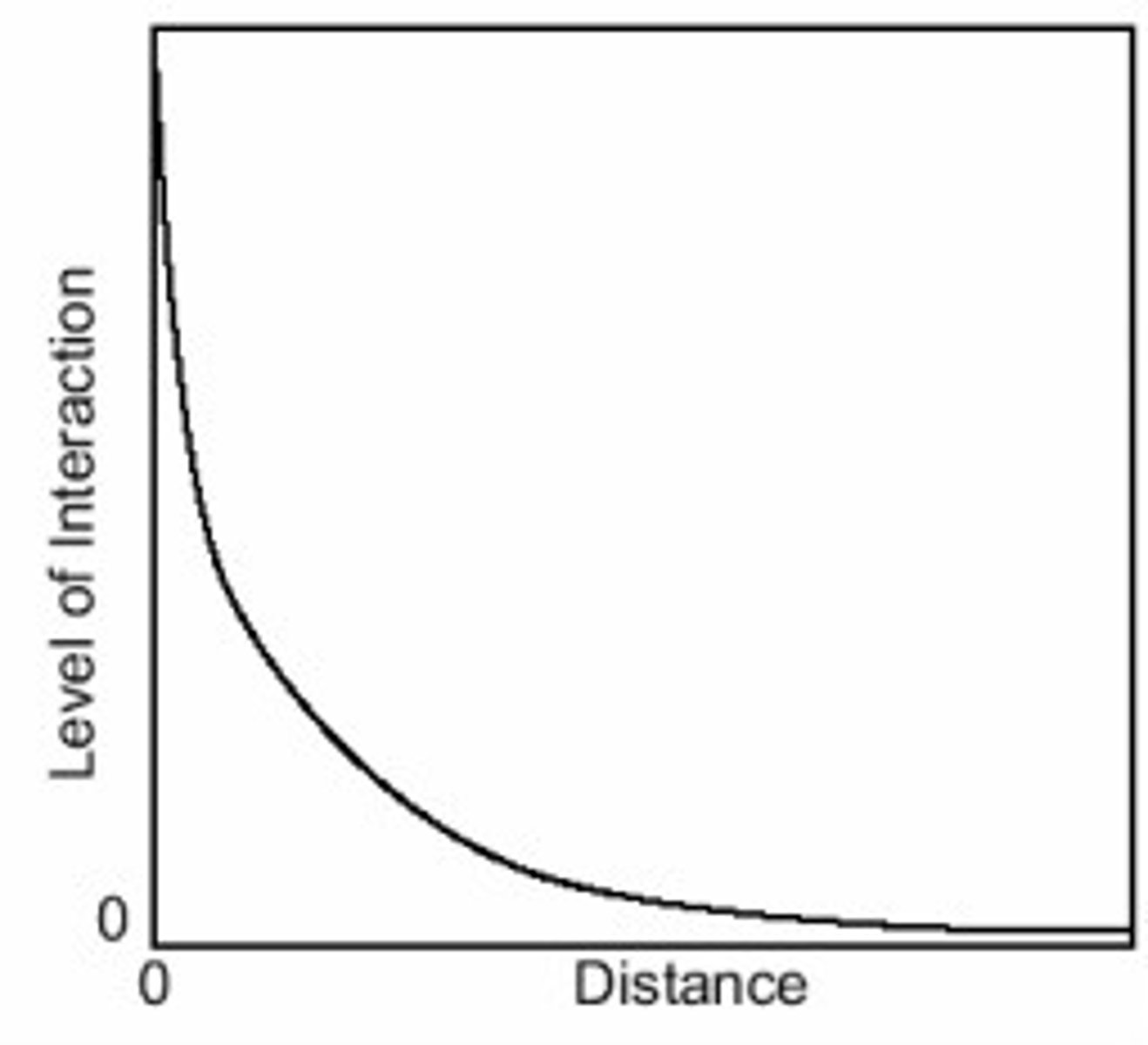
distance decay
The idea that the further something is away/more inconvenient it is, the less frequent/intense interaction with it will be.
Cultural Barriers
Prevailing cultural attitude rendering certain innovations, ideas or practices unacceptable or unadoptable in that particular culture
Expansion Diffusion
When the idea/thing being spread continues to exist in it's original location as well as spreading to new locations.
Contagious/Viral Diffusion
The spread of a disease, an innovation, or cultural traits through direct contact with another person or another place.
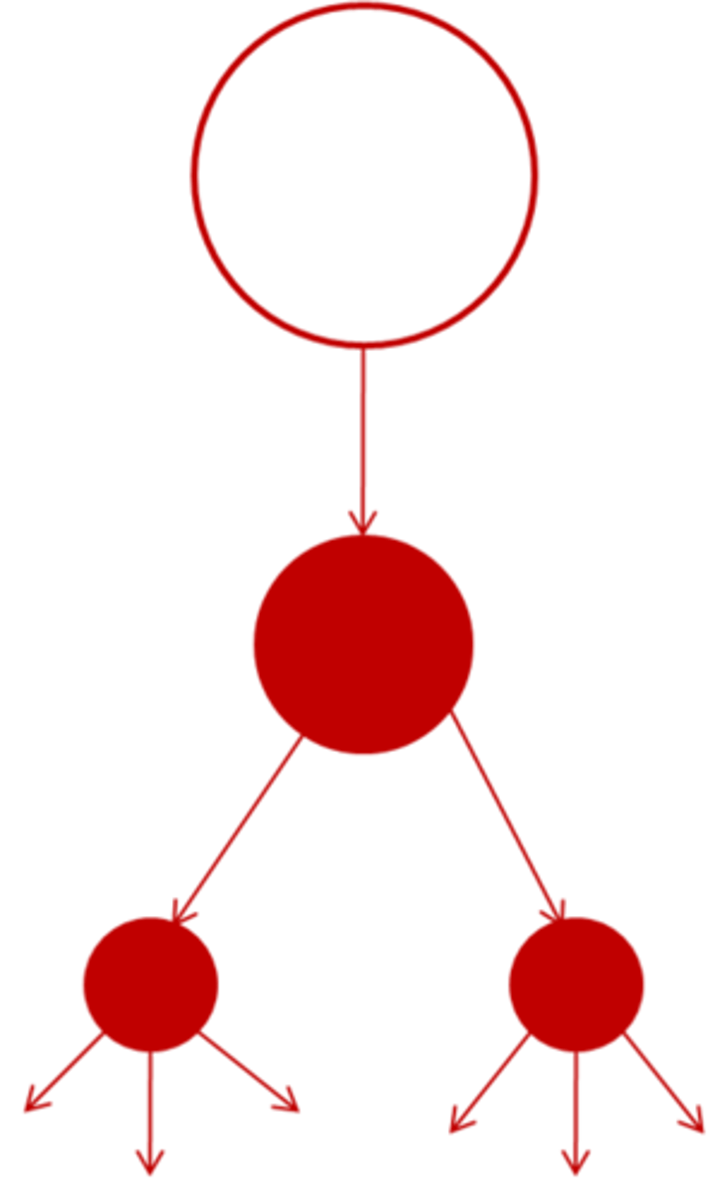
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places
Stimulus Diffusion
A form of diffusion in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place
Relocation Diffusion
Diffusion from one place to another where the idea does not stay in the origin and moves with the people.
Distribution
Spread of some data set over a given space
Density
The amount of something in a given space.
Concentration
the frequency or occurrence of some data set
Pattern
a consistent or characteristic arrangement
Enviornmental Determinism
The belief that physical environment determines potential for societal development.
Possibilism
The theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives.
Cultural Ecology
Geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships.
clustering
when objects in an area are close together
land use
Various ways humans use the land such as agricultural, industrial, residential, or recreational
local
relating to or occurring in a particular area, city, or town; located or living nearby
map projection
a way of representing the spherical Earth on a flat surface
natural resources
Materials or substances such as minerals, forests, water, and fertile land that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain
relative distance
Distance measured in terms such as cost or time which are more meaningful for the space relationship in question
relative direction
Directions such as left, right, forward, backward, up, and down based on people's perception of places
space
The physical gap or interval between two objects