parasitolgy
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what type of weather do parasites like
temperate, hot steady
what parasites are common to wisconsin
giardia lamblia
enterobius vermicularis
trichomonas vaginalis
what are the three big groups of parasites
helminths
protozoa
arthropods
helminths phylums + class
nemathelminths ( class nemotoda)
platyhelminths (class cestoda and digenea)
protozoa phylums + class
sarcomomastigophora (class lobosea and zoomastigophorea)
ciliophora (class kinetofragminophorea)
apicomplexa (class sporozoa)
athropods phylum and class
arthropoda (class insecta and arachnida)
definitive host
primary host that supports the sexually active phase of a parasites life cycle
resovoir host
host that harbors the pathogen so that it can transmit to a potential host
commensalism
relationship where parasite benefits but the host is not harmed or helped
parasitism definition
one organism benefits at the expense of the other
symbiosis
interaction of two organsisms that share a habitat
biological vector
animal hosts pathogen and it can multiply in its body
mechanical vector
can carry pathogen outside its body, but not host it
what is examined for parasites
fecal examination
how are fecal specimens collected
clean dry container, doesnt have to be sterile
two preservatives for fecal transport
PVA and SAF
can you refrigerate fecal samples
no
what does a liquid/mushy stool indicate
trophs
what does hard/firm stool indicate
cysts
wet suspensions are
direct
what are the two types of wet suspensions
saline
iodine
what is a permanent smear made of and why is it used
hematoxylin or trichrome stain
contrasts more clearly parasites vs non
what can you see on 10X
helminth ova and balantidum coli
what can you see on high dry/40X
trophs or cysts
two fecal concentration methods and which is more commonly used
sedimentation and floatation
sedimentation is more commonly used
what can you not find in concentrates
trophs
describe formalin ethyl acetate sedimentation procedure
make saline suspension pour thru gauze
centrifuge and decant
add saline resuspend
centrifuge and decant
resuspend in 7mls 10% formalin for 5min
add 4ml ethyl acetate, shake
centrifuge for 10min
decant
what parasite looks a lot like WBC
entamoeba histolytica
top to bottom name the layers of sedimentation concentration
ether and fat
fecal debris
formalin
sediment
specific gravity of floatation concentration
1.18-1.20
what is not picked up in floatation methods
ova with operculum
schistosoma ova
infertile ascaris ova
hymenolepis nana
what is the name for pinworm
enterobius vermicularis
describe the cellophane tape test for pinwor
tape on tongue depressor pressed to perianal area, then press tape onto microscope slide
what are saline wet preps good for
motility
what is very motile in saline wet preps
entamoeba histolytica
what is the iodine wet mount good for
helps see structures in cysts ( nucleus, karyosome, chomatidal bars)
helps see structures in ova (cell wall, plugs)
the iodine stain wet mount is hard on
trophs
modified acid fast stain is good for
cryptosporidium parvum
cyclospora
cystoisospora belli
microsporidia
blood smear prep is good for
plasmodium
babesia
knott technique for concentrating microfilariae is good for
suspecting filariasis
what is used to diagnose parasites quickly in immunocompromised patients
agar plate culture for strongyloides stercoralis
protozoa culture media is good for
acanthamoeba
entamoeba histolytica
naegleria fowleri
toxoplasma gondeii
trichomonas vaginalis
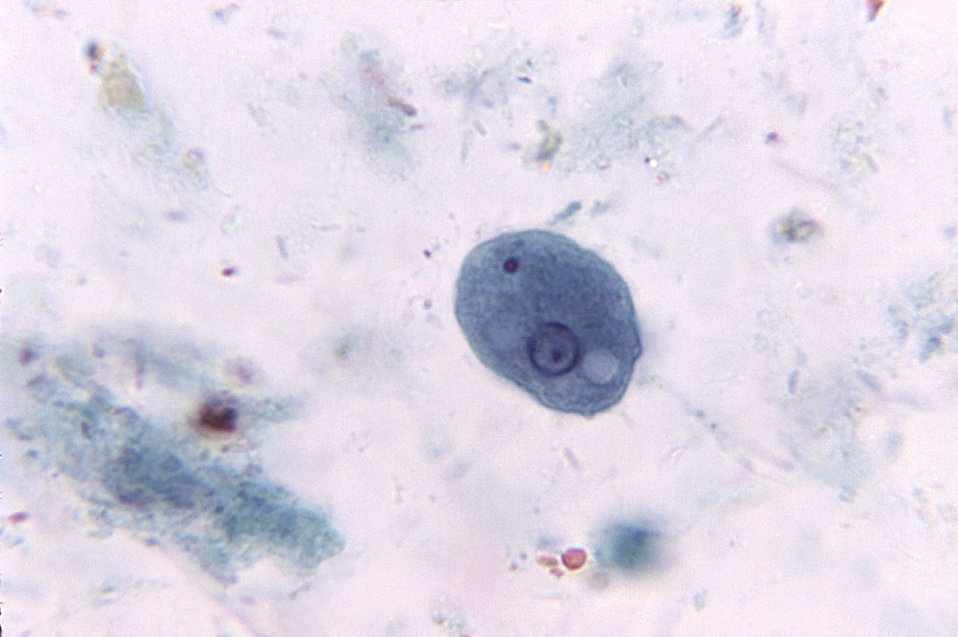
troph

cyst
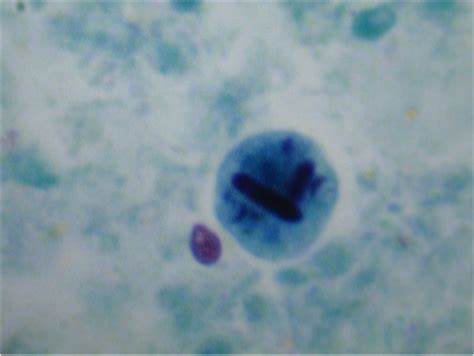
chromatoidal bars
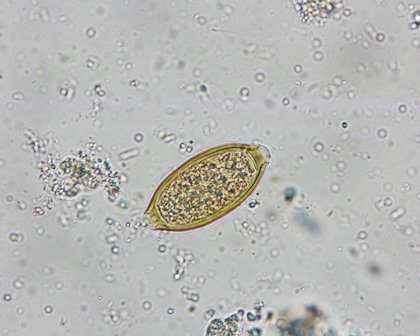
ova