Part 1 - Refresher, IFRS, Special Transactions
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Part 1 - REFRESHER
Balance Sheet
Asset = What company OWNS & = total of resources needed to operate the business
Equity = What owners CLAIM to company
Liability = What company OWES
→ L + E = total of means of financing of the assets
Theory of Assets
Asset is:
1) resource controlled by the company on the BS date
2) arising from past events or transactions
3) expected to bring future economic benefits
→ can be tangible / intangible as long as it is legally controlled
Recognition of assets:
it is probable that future economic benefits will flow to the company
its cost can be measured reliably
→ ASSET generates VALUE for the business
Assets
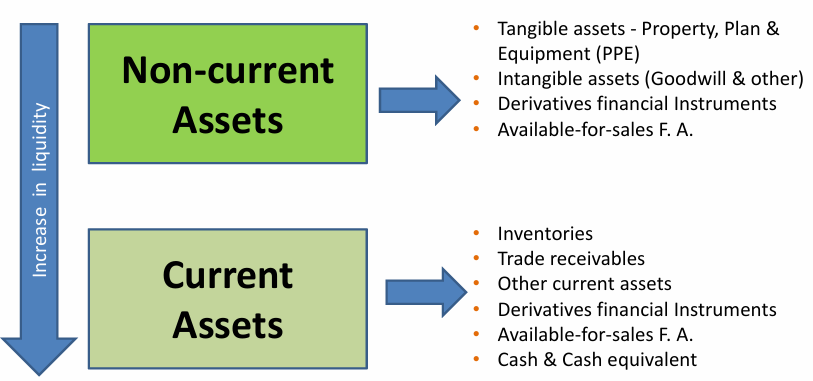
Theory of Liabilities
Liability is:
1) present obligation as of the balance sheet date
2) Arising from past events or transactions
3) That will likely lead to an outflow of resources (e.g., cash or services) to settle it
Recognition of liability:
it is probable that an outflow of economic benefits will occur
its amount of outflow can be measured reliably
→ LIABILITY represents COST or DEBT for the business
Liabilities
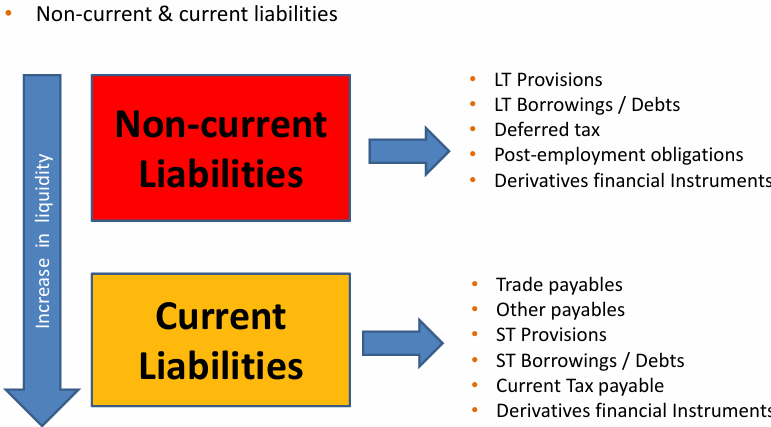
Theory of Equity
= what is left after the company paid all liabilities → what belongs to the OWNERS / SHAREHOLDERS
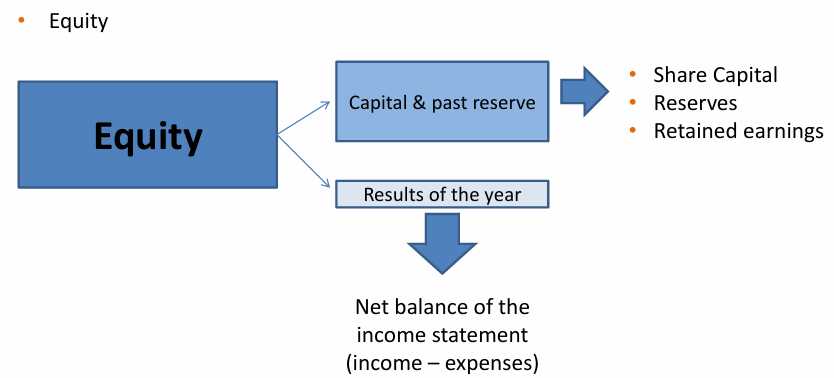
Equity = composed of:
1) Capital & Past Reserve
Share Capital = money investors put in by buying shares
Reserves = profits from past years set aside
Retained Earnings = profits kept in company instead of being paid out as dividends
2) Results of the Year
Net balance of the income statement = income - expenses = profit or loss
→ 1) + 2) = Total Equity
Equity
what can be distributed as Dividends
Dividend = Net income - DeltaReserve
Only the distributable part of equity → retained earnings or reserves
decided after allocation of the result of the year
Theory of Income
Income is:
increase in future economic benefits during an accounting period
Recognition of Income:
can be measured reliably
linked to an increase in assets (receiving cash / receivables) or decrease in liabilities (debt being forgiven)
→ results in an INCREASE in EQUITY, other than those relating to contributions by equity participants
Theory of Expenses
Expenses is:
decrease in future economic benefits during an accounting period
Recognition of Expense:
can be measured reliably
linked to a decrease in assets (using up inventory / paying salaries) or an increase in liabilities (incurring bills to pay later)
→ results in DECREASES in EQUITY, other than those relating to distributions to equity participants
Working Capital Ratio (WCR) - Definition & Formula
= a financial metric that represents a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations and fund its day-to-day operations → minimum cash company needs to operate
WCR = Inventory + Receivables - Trade payables
Depreciation = Tangible & Amortization = Intangible
= measures the portion of the cost of the non-current asset that has been used in generating the revenue → COST of USING
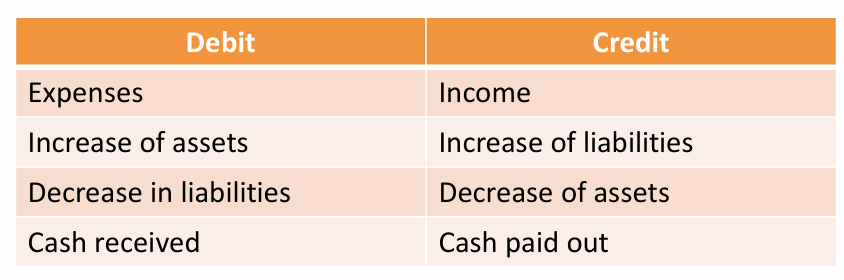
Double entry booking
Part 1 - IFRS
IFRS = International Financial Reporting Standard
= global standard used in many countries
= created bc businesses expanded on a worldwide scale, which underlined the need of having a common set of accounting rules
= ensures transparency, consistency & comparability across different countries (except US)
IFRS - Origin of the differences in accounting systems
legal system (roman law vs. common law)
companies financing (debt vs. equity ; concentrated vs. widespread)
taxation system (unicity vs. dissociation)
accidents of history (crash of 1929, Enron, Worldcom…)
IFRS - Requirements for common accounting standards
globalisation of the markets
cost of living on several markets
lack of transparency for investors
will induce a reduction of the cost of capital
IFRS - Belgium
Belgium Accounting Standard Commission follows IAS/IFRS (apply a set of IAS & IFRS standards)
IAS/IFRS :
Mandatory for all listed companies
Optional for some non-listed companies, if requested
Ongoing discussions about:
Applying IFRS to consolidated accounts of non-listed firms
Using IFRS in statutory (separate) accounts
IFRS - US
Still uses US GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)
A conversion to IFRS has been discussed but not fully adopted
Non-US companies listed in the US can file IFRS financial statements
IFRS - What are the four components of the IAS/IFRS Conceptual Framework?
The objective of financial statements
Underlying assumptions
Qualitative characteristics of financial statements
Measurement of the elements of financial statements
IFRS - What is the objective of financial statements according to IAS/IFRS?
To provide information about the financial position, performance, and changes in financial position of an entity that is useful to a wide range of users in making economic decisions
IFRS - What aspects are included under financial position?
Economic resources controlled
Financial structure
Liquidity
Solvency
IFRS - What aspects are included under financial performance?
Profitability
Variability of performance
Ability to generate cash
Predict cash flows
IFRS - What changes in financial position should be assessed?
Operating activities
Investing activities
Financing activities
IFRS - What are the two underlying assumptions in IFRS financial statements?
accural basis: effects of transaction = recognised when they OCCUR, NOT when cash = received
Accural basis accounting rely on :
Not only past transactions but obligations to pay and resources to be received
Accounting based on legal rights, as opposed to cash basis
going concern: that financial statements are prepared assuming the entity will continue operations in the foreseeable future & it ≠ the intention to liquidate or curtail operations
IFRS - What are the qualitative characteristics of financial statements?
understandability (assumes reasonable knowledge of users)
relevance (to decision making, predictive, confirmatory, materiality concept)
comparability (consistency of acc policies)
reliability (faithful representation, substance over form, neutrality, prudence, completeness)
constraints on relevant + reliable information (timeliness, balance between cost + benefit and qualitative characteristics)
true + fair presentation (use of qualitative characteristics + appropriate acc standards)
IFRS - What is measurement of financial statements in the conceptual framework?
determination of the monetary amount at which the elements of FS are to be recognised + reported
measurement bases :
Historical cost – Most commonly used
Current cost – Value to acquire now
Realizable value – Sale/settlement value
Present value – Discounted future inflows or outflows
Fair value – Market-based value representing the amount at which an asset could be exchanged or a liability settled, in a transaction between knowledgeable, willing parties acting independently and without compulsion → Mainly used for:
Business combinations
Financial instruments
Investment properties
What are the 5 IFRS Financial Reporting Basic Requirements?
The set of IFRS financial statements
IAS/IFRS Balance Sheet (« Statement of Financial Position »)
IAS Income Statement (« Statement of Comprehensive Income »)
IAS Statement of Changes in Equity
Compliance Requirement
What is the set of IFRS financial statements ?
Statement of financial position (Balance sheet)
Statement of comprehensive income: performance (Income statement)
Statement of cash flows: changes in financial position
Statement of changes in equity: shows the movements in the different components of equity
→ share capital, reserves, retained earnings,…
Statement of recognized income & expenses: details income and expenses recognized directly in equity
→ foreign currency translation gains, hedges, certain unrealized gains, available-for-sale investments, actuarial gains on pensions,…
Notes (disclosures) and supplementary schedules → gives a lot of extra information
What is the IAS/IFRS Balance Sheet?
Format of financial statement (FS):
No mandatory format or presentation (bc gives more transparency, flexibility + added value)
Lists of minimum items to be presented “on the face” of balance sheet and income statement
Items (lines) can be added or deleted as appropriate
Under Belgian GAAP, legally imposed preprinted forms for balance sheet, income statement and notes/disclosures, provided by the National Ban
→ IFRS need to show FS that is aligned with the type of activity of company (consulting firm shows less detail in FA)
What are the minimum items requires on the IAS Income Statement (IStat)?
Revenue
Financial expenses
Share of profits/losses of associates or joint ventures (equity method)
Tax expense
Gain/loss on the disposal of assets or settlement of liabilities from discontinued operations (= parts of a business that are planned to be sold → present as 1 aggregate line IStat, separately showinf activities that will no longer contribute to future operations)
Profit or loss
Allocation of result to non-controlling interests and parent equity holders
Basic and diluted earnings per share (IAS 33)
→ revenue = only specific line required for operating activities (choice between nature of expense or function of expense (= used by most companies) & BE GAAP = by nature
What is the Statement of Changes in Equity?
Purpose = Make equity movements understandable to users and show changes in components like capital, reserves, and retained earnings
CAPITAL & RESERVES = items MANDATORY shown separately in BS
movements = typically included in the Statement of Changes in Equity:
Changes in accounting policy
Revaluations (e.g., of property, plant & equipment, or investments)
Currency translation differences
Net result for the period
Dividends paid
Capital increases/decreases
Intra-equity transfers
What are the general compliance requirements for IFRS financial statements?
Full compliance with all IFRS/IAS standards is mandatory
Improper accounting can't be corrected by disclosure or notes
If IFRS compliance would be misleading, deviation is allowed only if full disclosure is made (including quantified impacts)
Departure is not allowed because another method than IFRS would also give a true and fair view
Comparative financial statements
Must be provided at least annually
If the balance sheet date changes, financial statements cover a period < or > 1 year
→ disclosure needed:
Reason for the period difference
Fact there will be no comparability for income statement, changes in equity & cash flow statement
Annual Report
Composed of 4 main sections:
Economic Report / Business Review
→ strategic presentation of economic report (company performance, strategy, key figures, invest types…)
CSR / Sustainability Report
→ mandatory in EU, not in US but often required by investors / banks
Financial Statements
→ 5 IFRS requirements seen before
Governance Report / Corporate Governance
→ how company is managed, member of board, executive comite, salary, hierarchy,…
Who reads the financial statement?
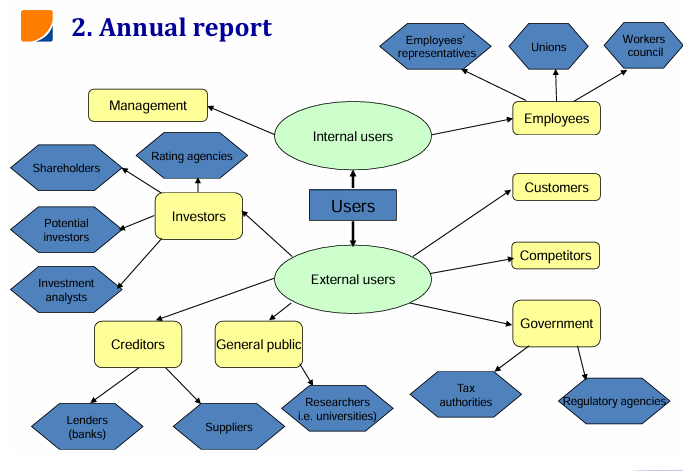
Who is the Boss of a Company?
SHAREHOLDERS are the BOSS (not CEO or BOARD)
→ in listed companies:
Shareholders:
elect the board of directors (10 - 15 people) to represent their interests
have voting rights based on the number of shares they hold
approve major decisions such as mergers, K increases, company’s strategic direction
Board of Directors:
acts as link between shareholders + management
appoints CEO + supervises top management
validates + oversees execution of company’s strategy
removes CEO if performance / alignment fails
CEO & Executive Team:
Handle the daily operations + decision-making
Implement the strategy approved by the board
Are accountable to board + by extension to shareholders
CSR = Corporate Social Responsability
= new regulation in EU which obliges companies to prepare an integrated reporting where they present financial & non-financial data (carbon emission, footprint)
= focuses on ethical, social & environmental responsabilities
Is there an equivalent to IFRS for non-financial information (CSR)?
YES
equivalent to IFRS is GRI (Global Reporting Initiative)
mission is to enable organizations to be :
transparent
take responsibility for their impacts
through the world’s most widely used standards for sustainability
In EU = CSRD:
= all things that have to be disclosed in terms of sustainability, if you are a company (harmonized reporting to avoid greenwashing)
Part 1 - SPECIAL TRANSACTIONS
IAS 18 - Revenue recognition
IAS 11 - Long term contract
IAS 16 - P. P. & E.
IAS 40 - Invest properties
IAS 2 - P. P. & E. held for sale
IFRS 16 - Accounting for leases
IAS 21 - Foreign currency transactions
IAS 37 - Provision
IAS 38 - Intangible Assets
Revenue Recognition (IAS 18):
Objective IAS 18
Issues in Rev Recognition
Objective IAS 18:
→ prescribe the accounting treatment for revenue arising from certain types of transactions
2 issues in rev recog:
measurement of revenue based on:
FV of the consideration received
hierarchy for determining FV under IAS 39
→ Use a quoted market price if available
→ If not, use a valuation method based on market inputs and parameters
moment of recog → when to credit the income statement
Revenue Recognition (IAS 18) → types of rev recog:
Recognition of a sale of GOOD when:
Significant risks and rewards of ownership have transferred to the buyer
Seller loses effective control of the goods
Revenue can be measured reliably
→ closely linked to shipping and sales cut-off rules.
Shipped but not billed → rev = recognized
Not shipped & not billed → no rev recognized
Billed but not shipped → no rev recognized
Billed & shipped → rev = recognized
Recognition of a sale of SERVICE
by using percentage of completion method
→ Revenue is only recognized when service is actually delivered, often spread across multiple periods
Recognition of FINANCIAL & other INCOME
→ when it is probable that economic benefit will flow to the entity
Royalties → on an accrual basis (per the fee agreement) = PATENT
Dividends → when the shareholder’s right to receive payment is established = DIVIDENDS
Interest → on a time-proportion basis, using the effective interest rate (pro rata temporis)
Long Term Contract (IAS 11):
Objective IAS 11
Issues in LT Contract
IAS 11 → applies to construction contracts typically lasting more than 1 year + special inventory category = used “Contracts in Progress“
Issues at year end:
Work is in progress (WIP), but the delivery to the client has not occurred yes → which creates the following problems:
advance billings = made: is this a sale then?
cost occurred: should they be recorded in IStat as charges?
contract completed and delivered a profit/loss should be recognized: hasn’t part of the profit/loss already been generated?
Long Term Contract (IAS 11) → types of LT contract recog:
Percentage of Completion (PoC) Method:
Used when revenues and costs can be reliably measured → recognize revenue over time→ % of completion
= (Cost incurred)/(Total estimated costs)
Completed Contract Method:
If not reliably measurable → recognize all revenue and profit only at delivery
in FStat :
Asset = CIP inventory =
(Incurred costs + Estimated profit × % completion) − BillingsIf result is:
Positive (debit): show as a receivable (asset)
→ company has done more work than it has billed for
Negative (credit): show as a liability (due to client)
→ company has billed more than work performed
→ shows net work done BUT not yet billed or collected
Long Term Contract (IAS 11) → BE GAAP vs IAS
BE GAAP:
Board chooses PoC or Completed
Billings = liability
CIP stays as inventory
IAS 11:
PoC mandatory if conditions are met
Deducted from CIP inventory
Reclassified to receivable or liability
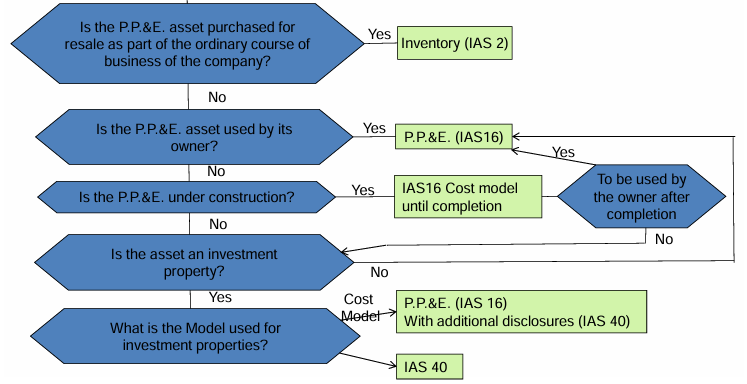
P. P. & E. - Default rules for PP&E (IAS 16):
recognition
PPE is initially recognized at cost, which includes:
Purchase price
+ Acquisition taxes & duties
+ Directly attributable costs (e.g., site prep, installation, transport, etc.)
+ Future dismantling/site cleanup costs, estimated and recorded as a provision
+ Borrowing costs: interest on loans is capitalized until the asset is ready for use (as per IAS 23, mandatory since 2009)
- Subsidies: deducted from the cost unless treated as deferred income (per IAS 20)
P. P. & E. - Default rules for PP&E (IAS 16):
depreciation rules
Depreciation* when:
PPE with a finite useful life must be depreciated.
*straight-line, degressive, SYD (not allowed under BE GAAP) / Units of production methods
NO Depreciation when:
PPE with an infinite useful life (e.g., land)
SEPERATE Depreciation when:
1 asset has multiple components with different useful lives
P. P. & E. - Investment properties (IAS 40)
When using the Fair Value Model for investment properties:
No depreciation is applied
Annual adjustments to fair value (market value) is done.
Gains/losses go directly to the income statement
IAS 40 recommends that fair value should ideally be determined by an independent real estate appraiser
P. P. & E. - Summary
Foreign Currency Transactions (IAS 21):
examples
concepts
Transactions in which the amount is denominated in a foreign currency (FC)
Common examples:
Buying or selling goods/services in FC
Borrowing or lending in FC
Entering a foreign exchange contract (contract that gives the right to buy/sell a certain currency a couple of months before )
Acquiring/disposing assets or settling liabilities in FC
Key concepts:
Realized exchange difference: occurs when the transaction is settled
Unrealized exchange difference: occurs when amounts are remeasured at period-end but not yet settled
Foreign Currency Transactions (IAS 21):
recognition
FC transactions must be recorded at the spot rate on the transaction date
Using an approximate rate (e.g., average rate for the month) is allowed for practicality
exchange differences recognition:
during year N :
Realized exchange difference = when transaction is settled in the same period
BS end of the year:
Unrealized exchange difference = possible difference between spot rate and closing rate for monetary items
during year N+1:
difference between last BS amount and subsequent settlement / subsequent BS amount
→ All differences are recognized in income or expense.
Foreign Currency Transactions (IAS 21):
exception
Certain long-term FC items (e.g., loans to foreign subsidiaries or FC borrowings funding investments) are:
Unrealized exchange differences → Not recorded in income BUT go to equity (account: translation reserve)
Cumulative translation reserve recycled into income when the investment is disposed of
Foreign Currency Transactions (IAS 21) - BE GAAP:
For unrealized gains in BS:
Treatment is to record as deferred income (liability) instead of income
Realize as income only when settled
But treating as immediate income is acceptable if consistent with group policy
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37):
objectives IAS 37
definition
IAS 37 aims to avoid:
Creating excess provisions
Misusing provisions for unrelated purposes
Reversing provisions in a way that distorts profits
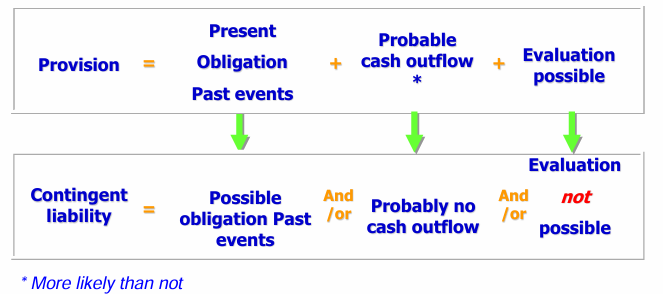
Provision:
A liability with uncertainty, e.g., about amount or timing
types: litigation, termination, remediation, dismenting, environment, pension, garantie
Liability:
A present obligation (legal or constructive), arising from past events, that is expected to lead to an outflow of economic resources.
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37):
recognition
recognize provision:
Present obligation
– Legal (contract/law) or
– Constructive (past actions created expectations)Obligation comes from a past event (not a future plan)
It is probable that the company will have to pay (outflow of economic resources)
Amount can be measured reliably
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37):
obligations
Under IAS 37 company must have a present OBLIGATION to record provision
obligation is:
legal : Required by law, contract, or regulation
constructive : Arises from past actions that create a valid expectation (e.g., company policy or announcements)
→ A board decision alone is NOT enough unless it has been communicated and created a binding expectation
Obligating event:
creates a legal or constructive obligation
independently of entity’s future actions
leaves no realistic alternative to settling the obligation
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37):
NO obligations
NO OBLIGATION → it may be a contigent liability or nothing
A possible obligation that arises from past events and whose existence will be confirmed only by the occurrence or non occurrence of one or more uncertain future events not wholly within the control of the entity
Or
A present obligation that arises from past events but is not recognized because:
it is not probable that an outflow of resources will be required to settled the obligation OR
amount cannot be measure reliably
SUMMARY of RECOGNITION
Contingent liabilities and contingent assets are not recognized in the financial statements
BUT they must be disclosed in the notes, if material
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37):
measurement
Use the best estimate of cost at the balance sheet date and consider:
Risks and uncertainties
Expert advice
Weighted average of possible outcomes
Present value (if impact is material)
Future events
Excluding gain on disposal
Reimbursements: Only recorded if virtually certain
Provisions must be reviewed yearly and reversed if not needed
Use provision only for the original purpose
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37):
special cases
Future operating losses → ❌ no provision (no present obligation)
Onerous contracts → ✅ provision allowed
Example: A contract where fulfilling it costs more than the benefits
Not for normal purchase orders or construction contracts
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37):
restructuring
Provision allowed if both:
There’s a detailed formal plan identifying:
Business or part of business concerned
Principal locations affected
Location, function and approximate number of employees to be compensated
Expenditures to be undertaken
When the plan will be implemented
Has raised valid expectation in those affected
→ measurement:
Only direct costs are included
Not future operating costs
Provisions & Contigent liabilities (IAS 37) - BE GAAP
Provisions are required if:
They result from a past event
Likely or certain to occur
May not be reliably measurable
Examples: pensions, major maintenance, guarantees, litigations
no legal or constructive obligation required
⚠ Belgian GAAP is more flexible — allows more provisions than IFRS + restructuring decision of the board of directors = sufficient
Intangible assets (IAS 38):
definition
Intangible asset is:
Identifiable, non-monetary, and has no physical substance
It must be:
Separable (can be sold or transferred) OR
Arise from contractual or legal rights
It is an asset & must be controlled by the entity and bring future economic benefits
Intangible assets (IAS 38):
measurement
An intangible asset is recognized only if:
Probable future economic benefits will flow to the entity AND
Cost can be measured reliably
Intangible assets (IAS 38):
recognition
Types of Intangible assets that are recognized:
Intangible assets purchased separately
Measured at cost, i.e.
Purchase price, including import duties and non-refundable taxes; and– Any directly attributable cost of preparing the asset for its intended use (ex; professional fees, costs of testing,…,etc.)
Intangible assets acquired as part of business combination
If it meets the definition of an asset and is identifiable
Measured at fair value
Internally generated intangible assets which meet the criteria of paragraphs 52-67 of IAS 38 (see below)
→ not recognized as intangible assets
Internally generated goodwill
Internally generated intangible assets which do not meet the definition of an intangible asset or the recognition criteria of paragraphs 52-67 of IAS 38 → i.e. brands, publishing titles, customer lists
Intangible assets (IAS 38) - Research & Development:
definition
Research: early investigation to gain new knowledge → Always expensed
Development: turning knowledge into usable or sellable products → May be capitalized if 6 criteria are met
Intangible assets (IAS 38) - Research & Development:
recognition
Qualifying internally generated intangible assets. Distinction between
Research phase
No asset recognition
Costs are expensed when incurred
Development phase: recognition of an intangible asset if, and only if, an entity can demonstrate:
The technical feasibility
Its intention to complete the intangible asset
Its ability to use and sell the asset
How the intangible asset will generate probable future economic benefits (namely, existence of a market)
Availability of resources (technical, financial and others) to complete the development and to use or sell the intangible asset
Its ability to measure reliably the expenditure
Directly attributable costs
Materials and services
Employee benefits
Fees to register legal rights
Amortisation of patents and trademarks used Recognition
NOT recognized: Internally generated brands, mastheads, publishing titles, customer lists and items similar in substance shall not be recognized Generally cannot be distinguished from the cost of developing the business
Intangible assets (IAS 38):
cost model
Intangible assets are measured at:
Cost − Accumulated amortisation − Impairment losses
Intangible assets (IAS 38):
amortization
Intangible assets with finite useful lives:
Allocate cost systematically over useful life
Assume residual value is zero unless:
A buyer commits to purchase it
There is an active market
Methods:
Reflect usage pattern of generation of economic benefit
If unknown → use straight-line
Must review every year when required by economic circumstances
Intangible assets with indefinite useful lives:
Assets with indefinite useful lives:
No amortisation
Must be tested for impairment yearly
If the carrying amount > recoverable amount → record impairment loss
Intangible assets (IAS 38) - BE GAAP
Formation/start-up expenses → may be capitalized under Belgian GAAP
R&D:
Can be expensed or capitalized if not exceeding a prudent estimate of value
Only direct costs allowed
Revaluation is not allowed
Accounting for Leases (IFRS 16):
before IFRS 16 and now
Before IFRS 16 (under IAS 17):
Only finance leases were shown on the balance sheet.
Operating leases were “off-balance sheet”: no liability or asset recorded.
Under IFRS 16:
→ all leases are on the BS - unless they are:
Short-term (less than 12 months), or
Low-value items (e.g., small office equipment)