PPO: Pupils
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Pupil definition
Dynamic aperture within anterior chamber that controls the amount of light entering the globe
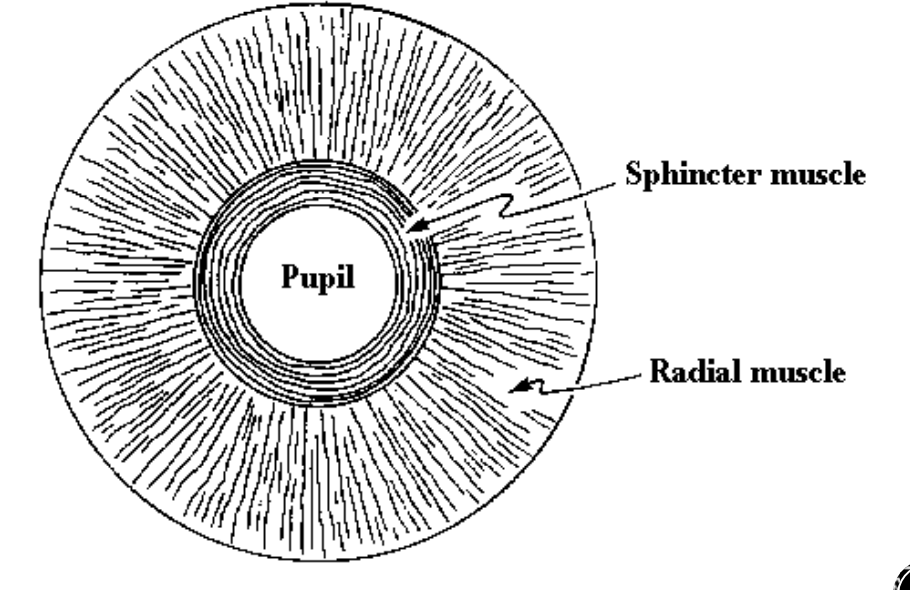
Muscles of the iris
Sphincter
Dilator
Sphincter of iris
Circular, smooth muscle
Courses circumferentially (Around the pupil in a circle)
Constricts the eye
Parasympathetic activation
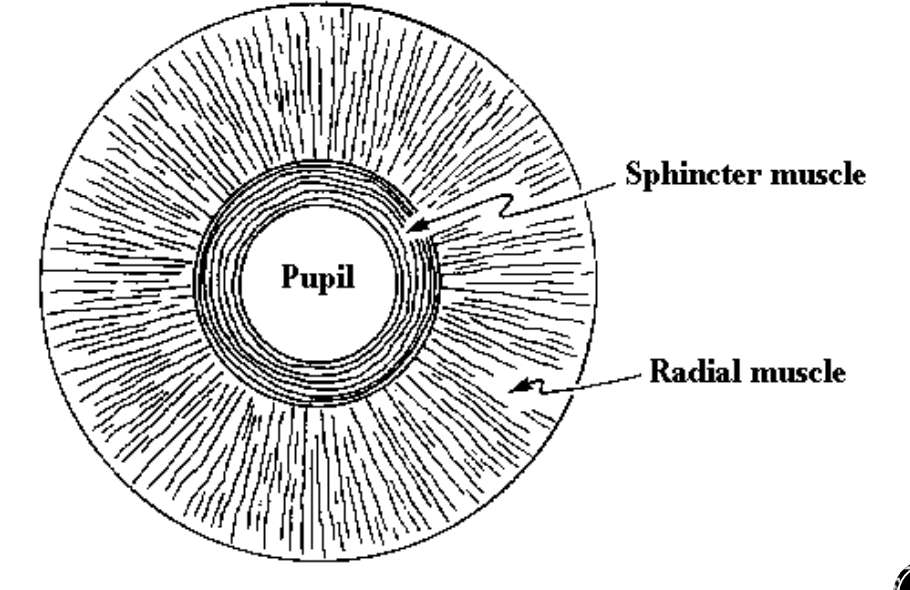
Dilator
Myoepithelial cells
Courses radially (Limbus → pupil)
Dilates the eye
Sympathetic activation
Pupil size
1.1 - 8.5 mm
What does pupil size depend on
Light intensity
Accommodation
Convergence
Emotional state
Age
Hippus
“Pupilary unrest”
Oscillations of the iris
Independent of illumination, convergence, psychological state
Function of pupils
Control retinal illumination
Reduce optical aberrations (Pinhole effect)
Indicate emotional state
Why do we check pupils?
One of the most important data points in an EE
Performed on every patient
Abnormal result may indicate life-threatening medical issue
Shining light into one will eye cause…
Both pupils to constrict
Mydriasis
Dilation of the pupil
Sympathetic
Miosis of the pupil
Parasympathetic
Constriction of the pupil
Parasympathetic funciton of pupil
Coordinates the pupillary light reflex
Responsible for constricting the pupil
Three pathways for the pupillary light reflex
Afferent
Interneural
Efferent
Afferent pathway
Path of light
Retina → brain
Begins at retinal ganglion cells
Ends in upper midbrain at the Pretectal olivary nuclei (PON)
Pretectal olivary nuclei (PON)
End of afferent pathway
Synpase with interneurons on both R and L side of brain
Entire afferent pathway
Ganglion cells (Retina) → Optic nerve → Chiasm → Optic tract → PON
Interneauronal pathway
PON → Edinger-westphal nuclei
Connects afferent and efferent pathway
Entire efferent pathway
Edinger-westphal nucleus → Ciliary ganglion → Iris
Parasympathetic fibers travel with CN III
Terminate at the ciliary ganglion
Synketic triad
Eye’s response to a near target
-Constriction
-Convergence
-Accomodation
All related, but not dependent on eachother
Accomodative system’s relationship to pupillary system
Both follow the same course (CN III)
Accomodative fibers out number pupillary fiber’s 30:1
Sympathetic pupil innervation
Three neuron chain
-Hypothalamus
-Cliliospinal center of budge
-Superior cervical ganglion
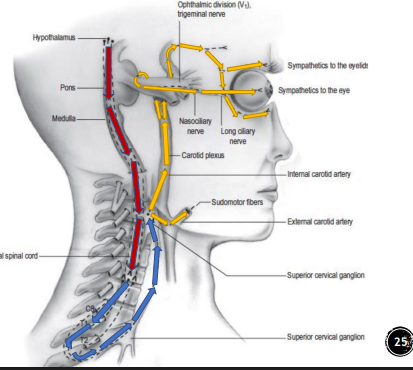
Effects of sympathetic pupil innervation
1. Eyelids → open
2. Iris → dilates
3. Glands → sweat
Parasympathetic antagonist drugs
Stop the parasympathetic pathway from constricting the pupil
Tropicamide
Cycopentolate
Sympathetic agonists
Helps the sympathetic system to dilate the pupil
Phenylephrine
Hydroxyamphetamine
Paremyd
Eye drop that contains parasympathetic antagonists and sympathetic agonists
Anisocoria
Inequality in pupil size
Defect in the pupillary pathway from brain → Iris
May be harmless or a life-threatening medical issue
Physiological anisocoria
Difference in pupil size in absence of pathology
Long standing
Difference in size remains the same in bright/dim lighting
May switch eyes
Pathological anisocoria
Significant change of anisocoria in bright v. dim illumination
Concern about life-threatening if:
-Newly noted
-Ptosis
-EOM abnormalities
-Pain
If pathological anisocoria is greater in bright light, which eye is affected?
The larger pupil → Trouble with constriction
Parasympathetic defect
If pathological anisocoria is greater in dim light, which eye is affected
Smaller pupil →Trouble with dilation
Sympathetic defect
Parasympathetic causes of anisocoria
-Adie’s tonic pupil
-Trauma → Damage to iris sphincter
-CN III Palsy
CN III Palsy and anisocoria
Parasympathetic defect
Concern is raised if there is a large ptosis the same side as dilated pupil
Neurological emergency
Adie’s tonic pupil
Lesion of the ciliary ganglion
Pupil doesnt respond to illumination
Pupil does respond when converging
Parasympathetic deffect
-Benign
-Young females
-Diminished deep tendom reflexes
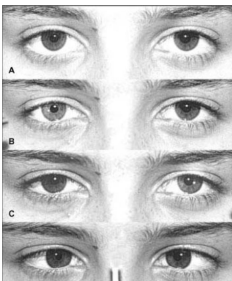
Sympathetic causes of anisocoria
Horner’s syndrome
Trauma to iris dilator
Horner’s syndrome
Sympathetic defect
Ptosis (Eyelid closure)
Miosis (Pupil constricted)
Anhidrosis (Lack of sweating on that side of face)
New DX is neurological emergency
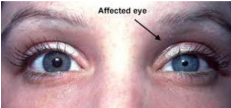
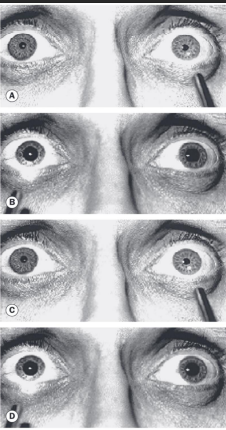
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD or APD)
Prescence of unilateral or asymmetric pathology
Indicates inhibition anterior to the optic chiasm
Shining light into one eye constricts both pupils, while shining it into the other does nothing
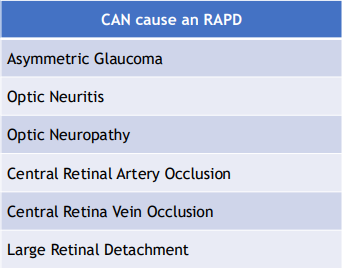
Conditions that CAN cause RAPD
Conditions that DO NOT CAUSE RAPD
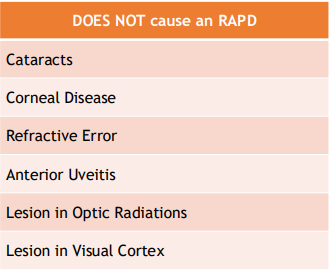
Why catarcts do not cause RAPD
Cataracts scatter light, do not block it from reaching the retina
Makes things blurry, but does not constrict light
Drugs that dilate the pupil
MDMA
LSD
Cocain
Methamphetamine
Drus that constrict the pupils
Heroin
Oxycodone
Morphine
Methadone
Static pupllary measurements
Measurement of pupil size under constant stimulus
Quantitative
Dynamic measurement of pupils
Measurement of pupils with changes in stimulus condition
Qualititave
Achieved using either light or accomodation
How to prevent induving a pseudo APD?
Shine light slightly temporally to avoid stray light hitting opposite eye
What do you do to measure pupils if there is no PD ruler?
Use the iris’s measurements
Iris diamete = 12 mm
What if you are unsure if RAPD is present?
Ask patient if one light is dimmer than the other
Neutral density filters
Objective way to quantify RAPD
Hold ND filter over normal eye and perform swinging flashlight test
As you go up in the density, you will reach a point where pupillary reaction is equal OD and OS