Bones of the Lower Limb
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
pelvic girdle
main functions are to transfer upper body weight to the legs, provide muscle attachment for locomotion, and protect pelvic organs, offering stability rather than mobility like the pectoral girdle.
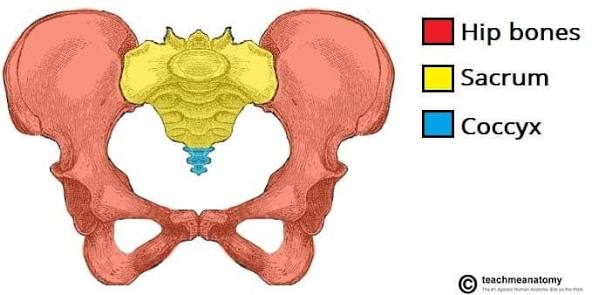
os coxae (hips)
2 hips (right and left), made up of ilium, ischium, and pubis
Supports body weight when standing and walking
Protects pelvic organs (bladder, reproductive organs, part of the intestines)
Provides attachment points for muscles of the trunk and lower limb
Transfers weight from the axial skeleton to the lower limbs
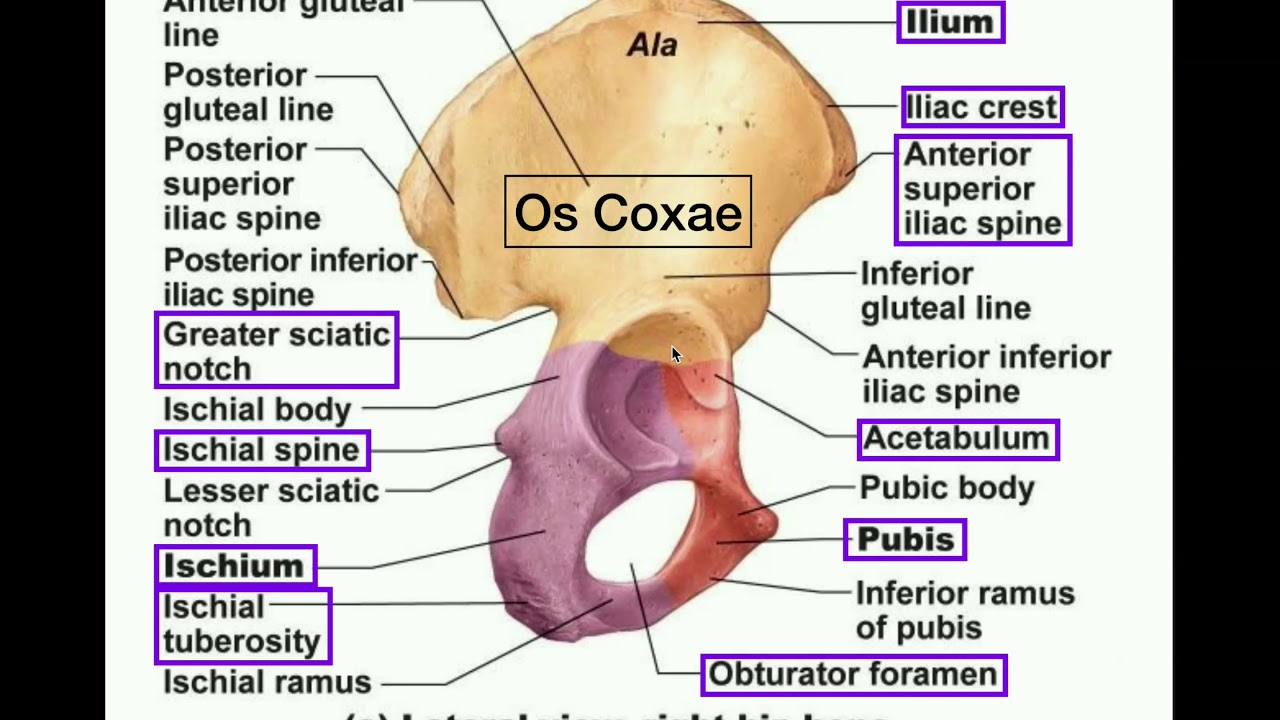
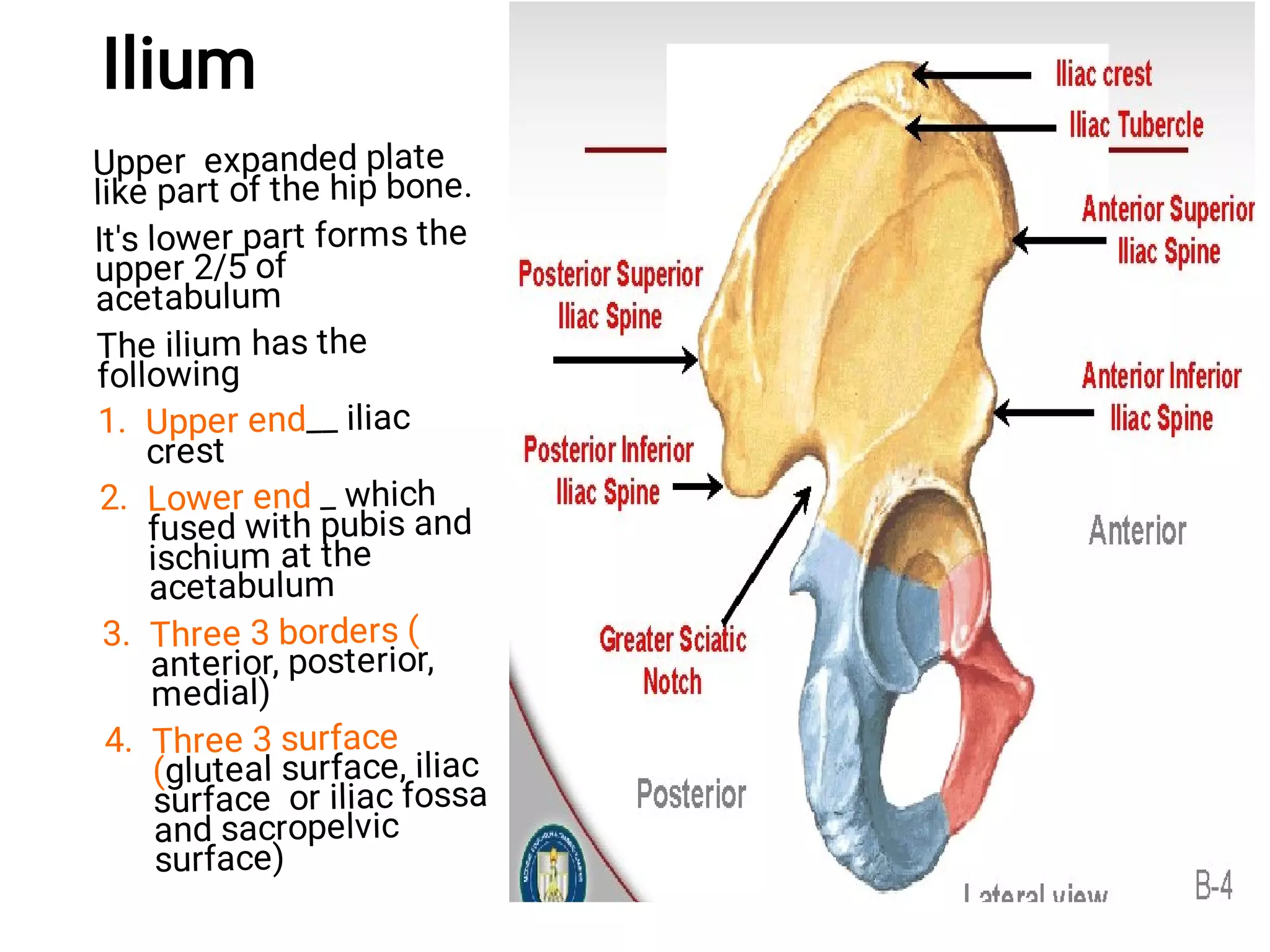
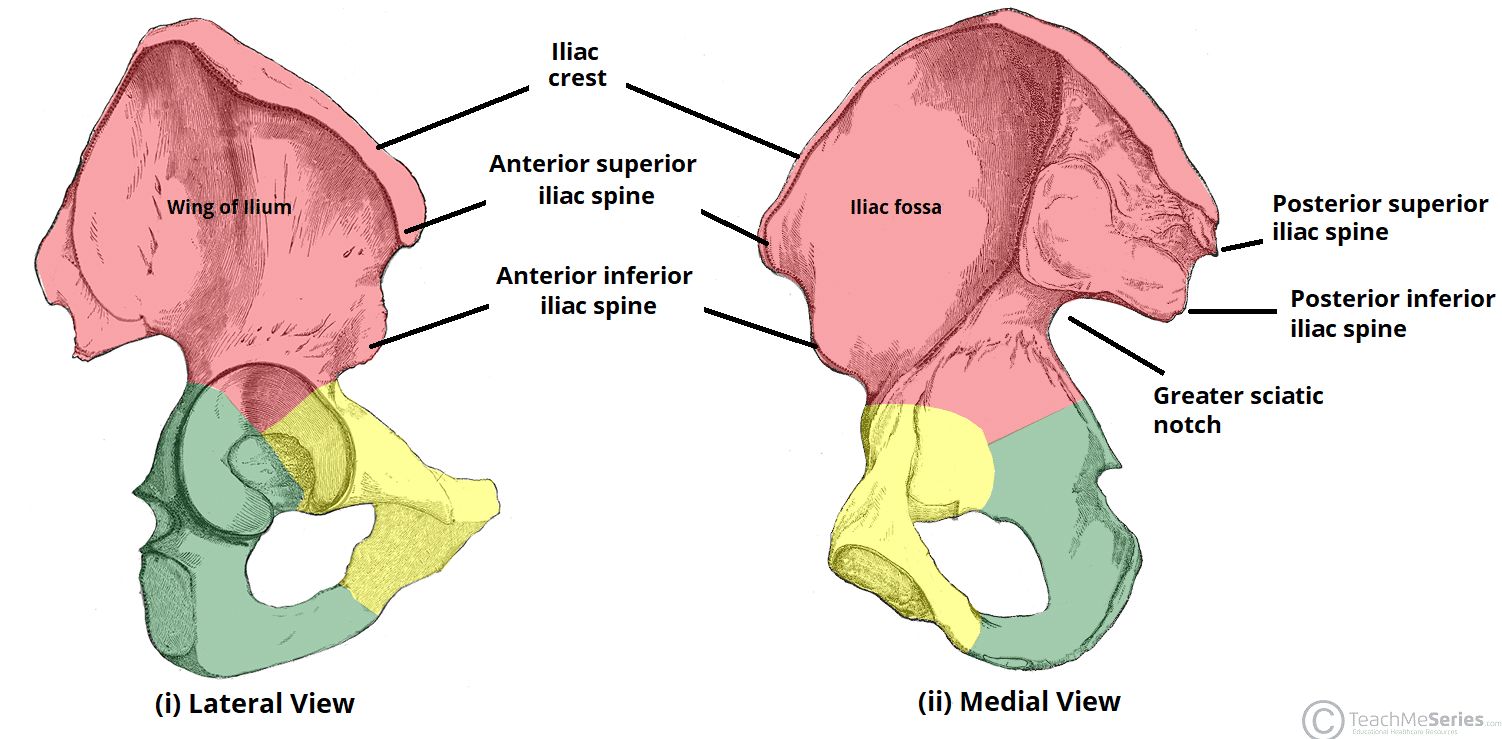
parts of ilium (lateral view)
iliac crest, anterior superior iliac spine (asis), anterior inferior spine, posterior superior iliac spine, posterior inferior iliac spine
anterior
front view
posterior
back view
inferior
towards the feet
superior
towards the head
parts of ischium (lateral view)
ischial tuberosity
parts of pubis (lateral view)
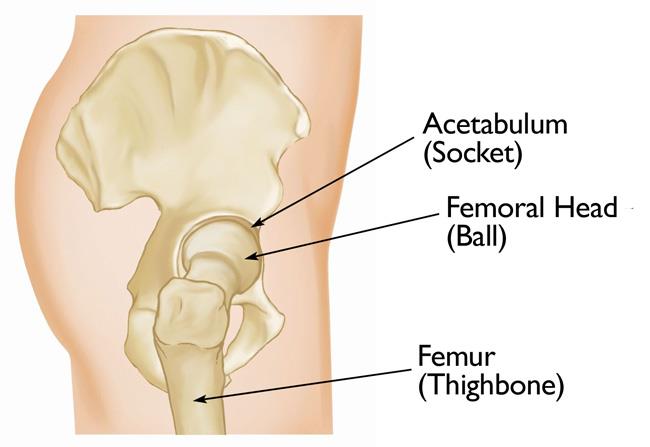
acetabulum (socket, head of femur sits here)
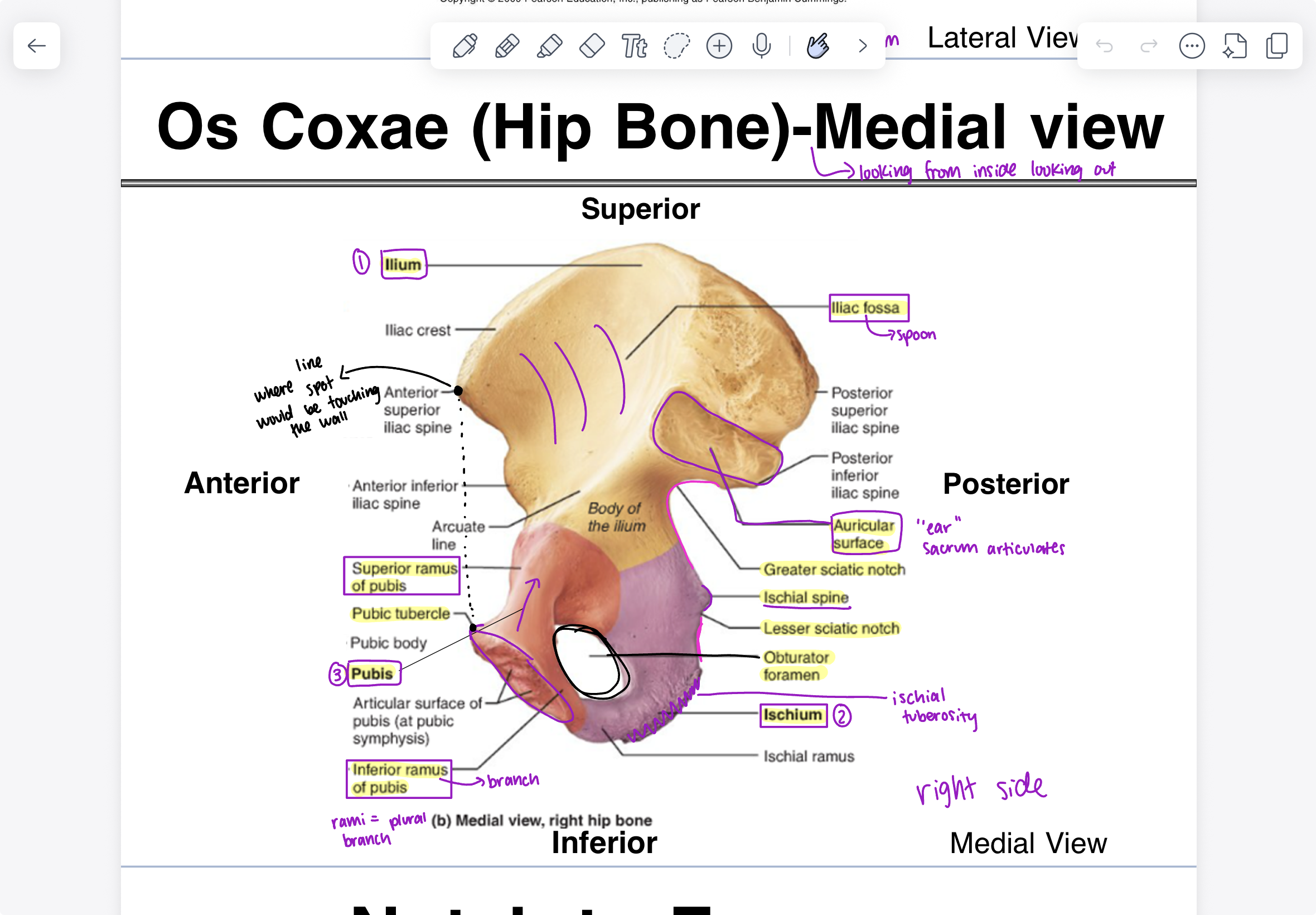
parts of ilium (medial view)
iliac fossa (spoon), auricular surface (“ear” sacrum articulates), greater sciatic notch
parts of ischium (medial view)
ischial spine, lesser sciatic notch, ischial tuberosity, obturator (hole)
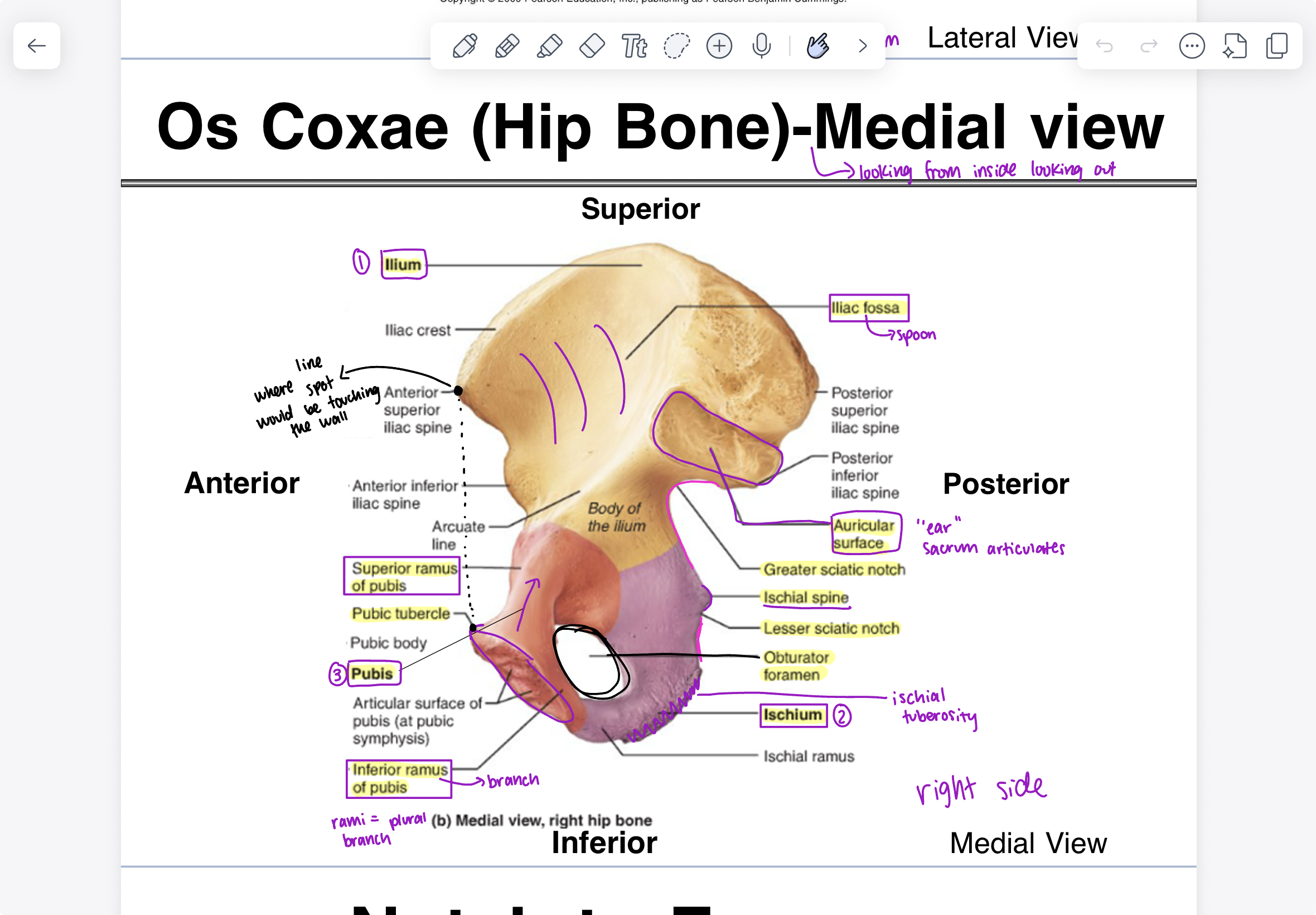
parts of pubis (medial view)
superior ramus of pubis, pubic tubercle, inferior ramus of pubis
parts of sacrum (holds together 2 os coxae) (anterior view)
lumbar (5 bones fused together forming the sacrum)
promontory (anterior most point)
foramen (hole)
anterior sacral formina (anterior side on the sacrum with foramina (holes))
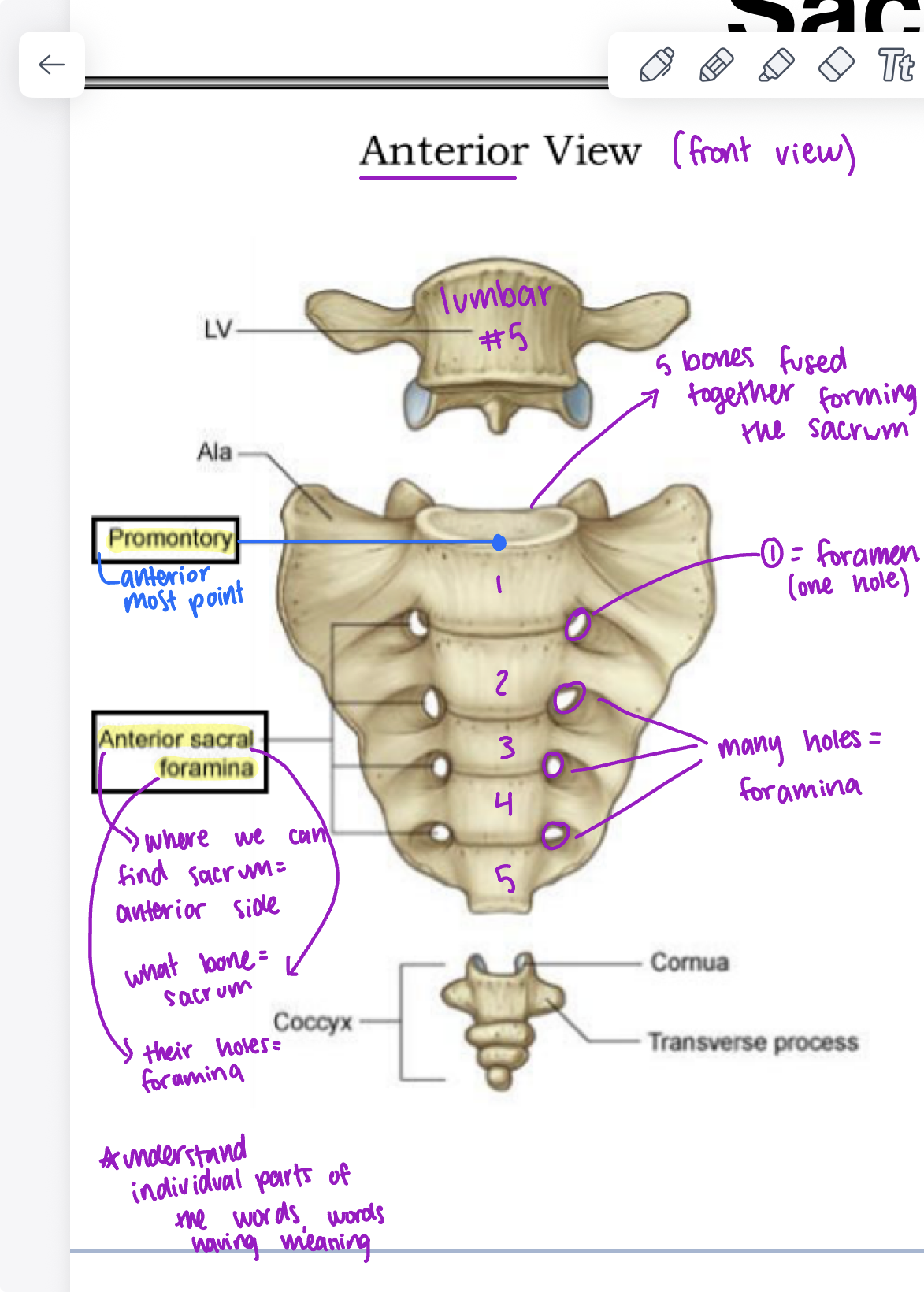
parts of sacrum (posterior view)
median sacral crest (bumps on the midline on sacrum), sacral canal, spinal cord, auricular surface “ear”, posterior sacral foramina (posterior side of sacrum with many holes), sacral hiatus
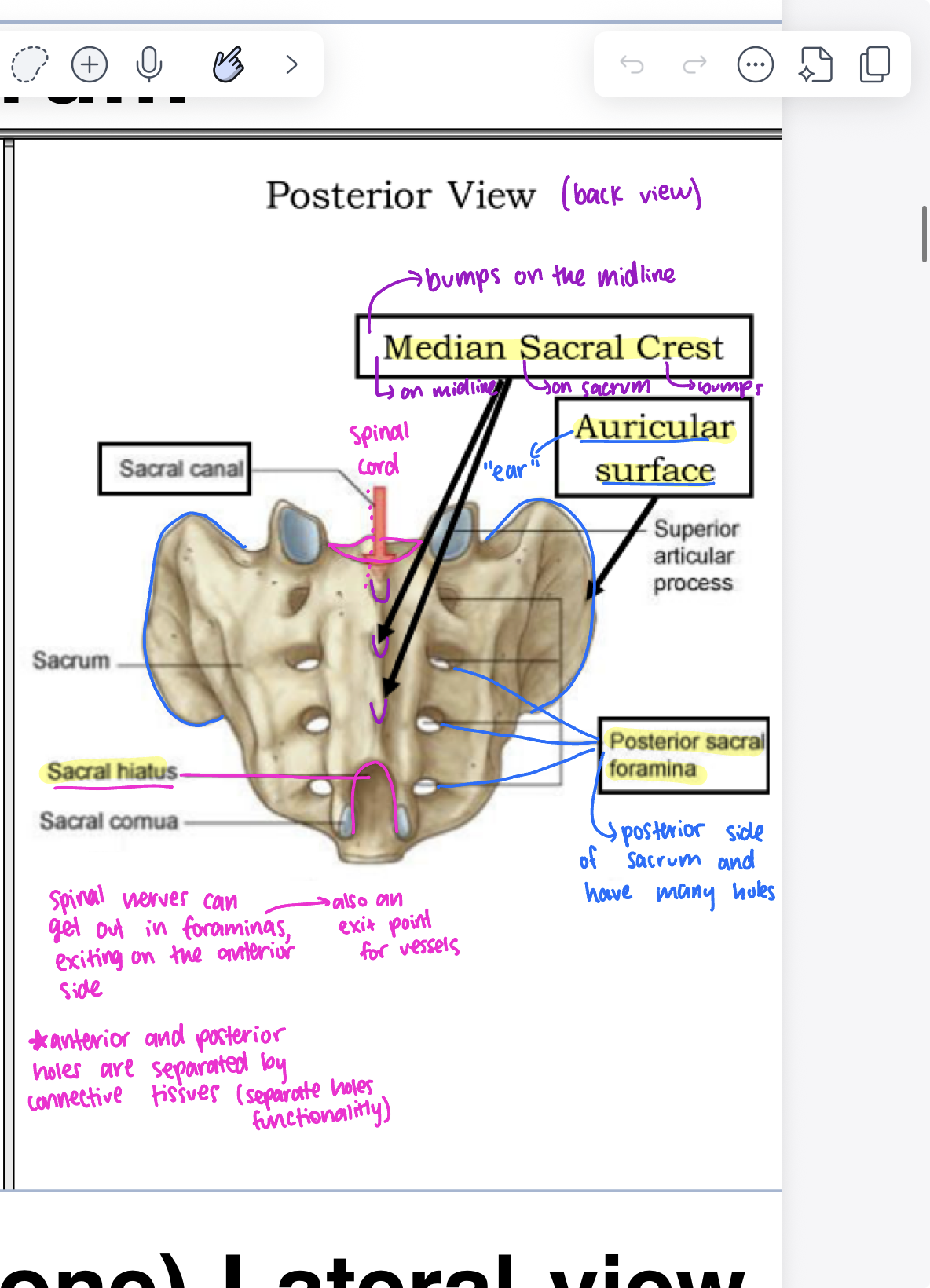
foramen parts (holes)
greater sciatic foramen (higher up), lesser sciatic foramen (lower hole), ischial spine, sacrospinous ligament (attaching to sacrum and spine), sacrotuberous ligament (attaching to ischial tuberosity), ischial tuberosity
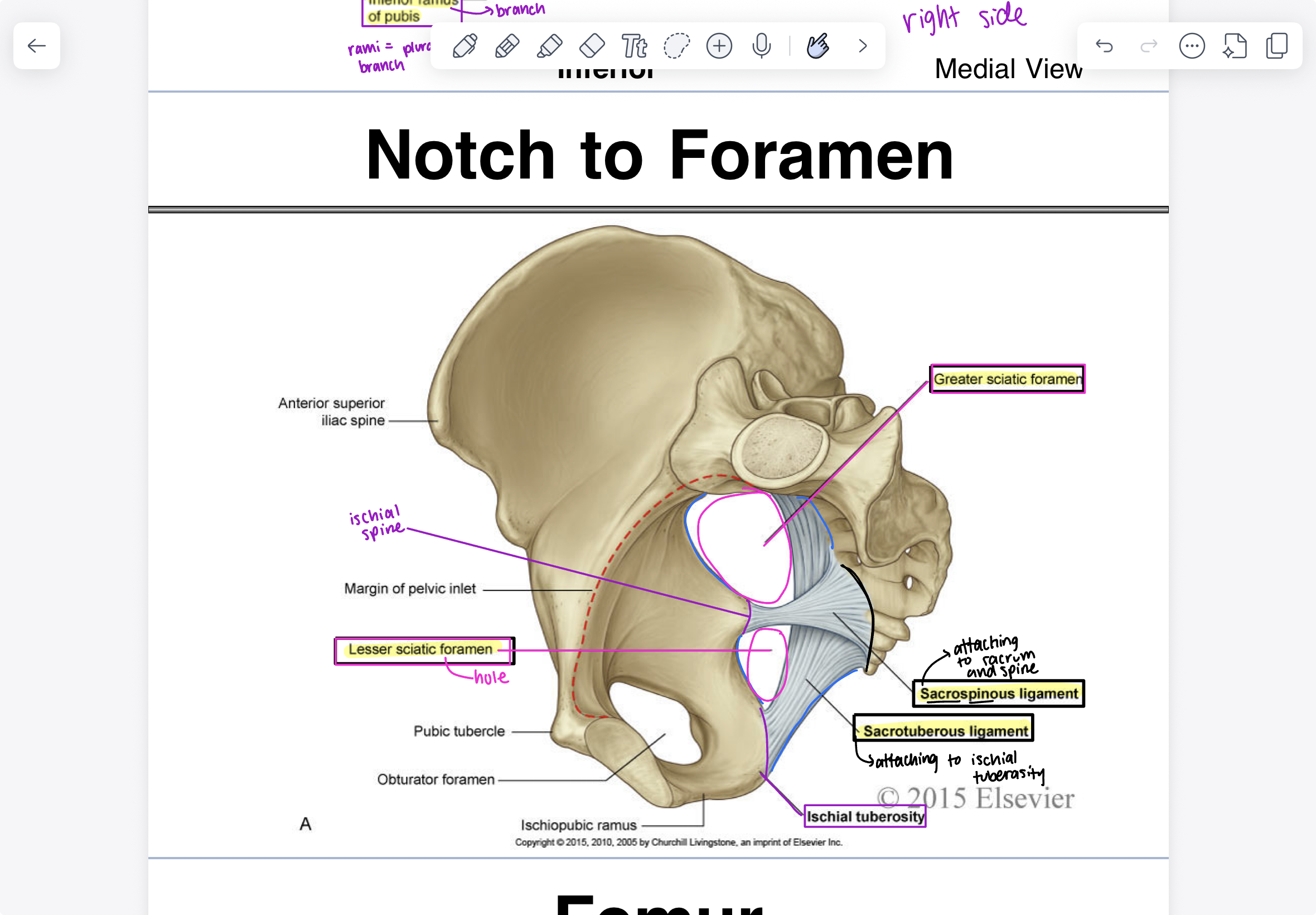
parts of femur (thigh bone) (anterior view)
femoral head (pointed medially, “ball”), neck, greater trochanter (always lateral meaning facing outwards), patellar surface (smooth surface where bones are moving across from each other), lateral epicondyle (where muscles attach), medial epicondyle (facing inside), medial condyle (smooth, U shaped)
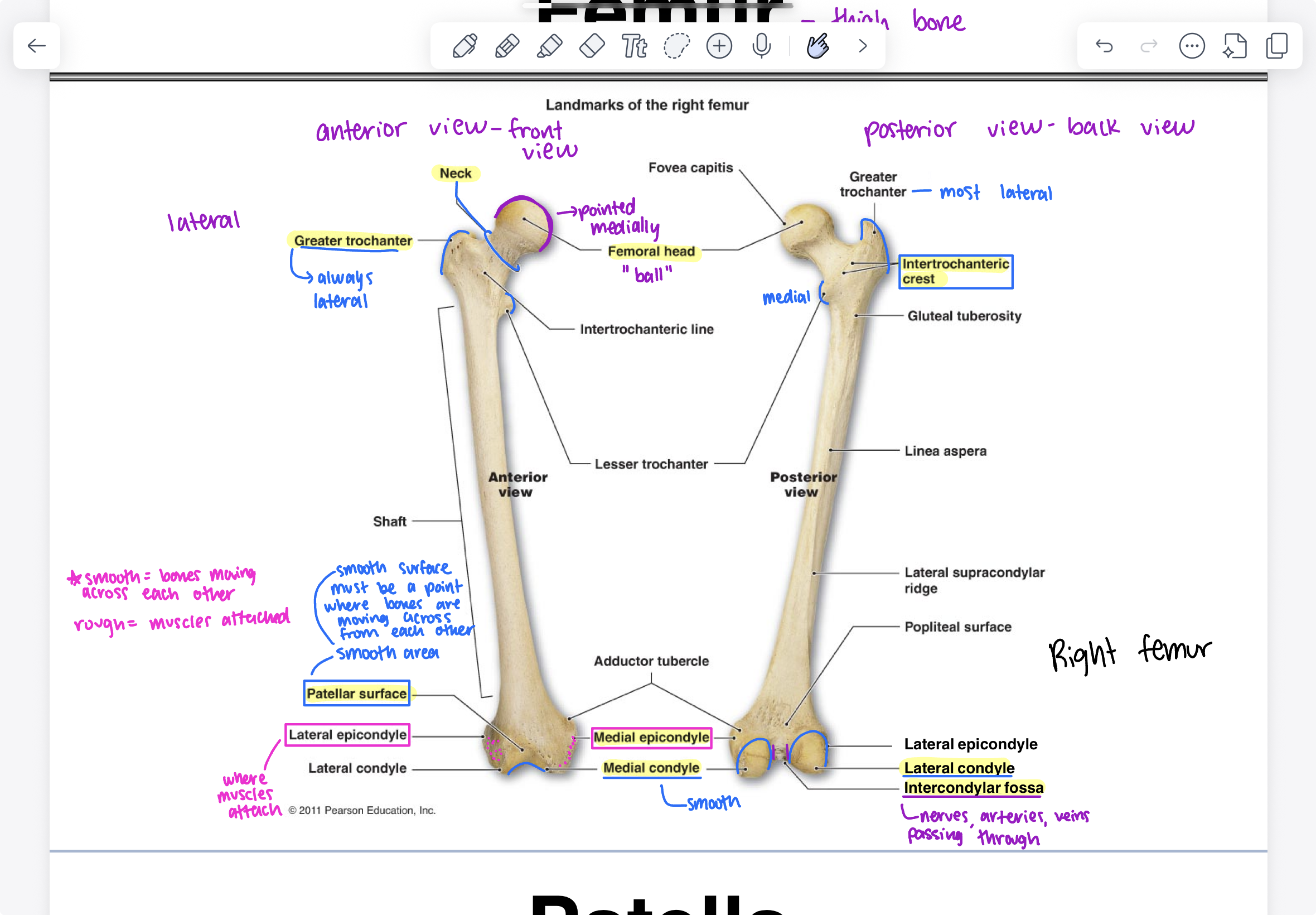
parts of femur (posterior view)
femoral head (“ball”), greater trochanter (most lateral), intertrochanteric crest, lateral condyle, intercondylar fossa (nerves, arteries, veins passing through), medial epicondyle, medial condyle (smooth, U shaped)
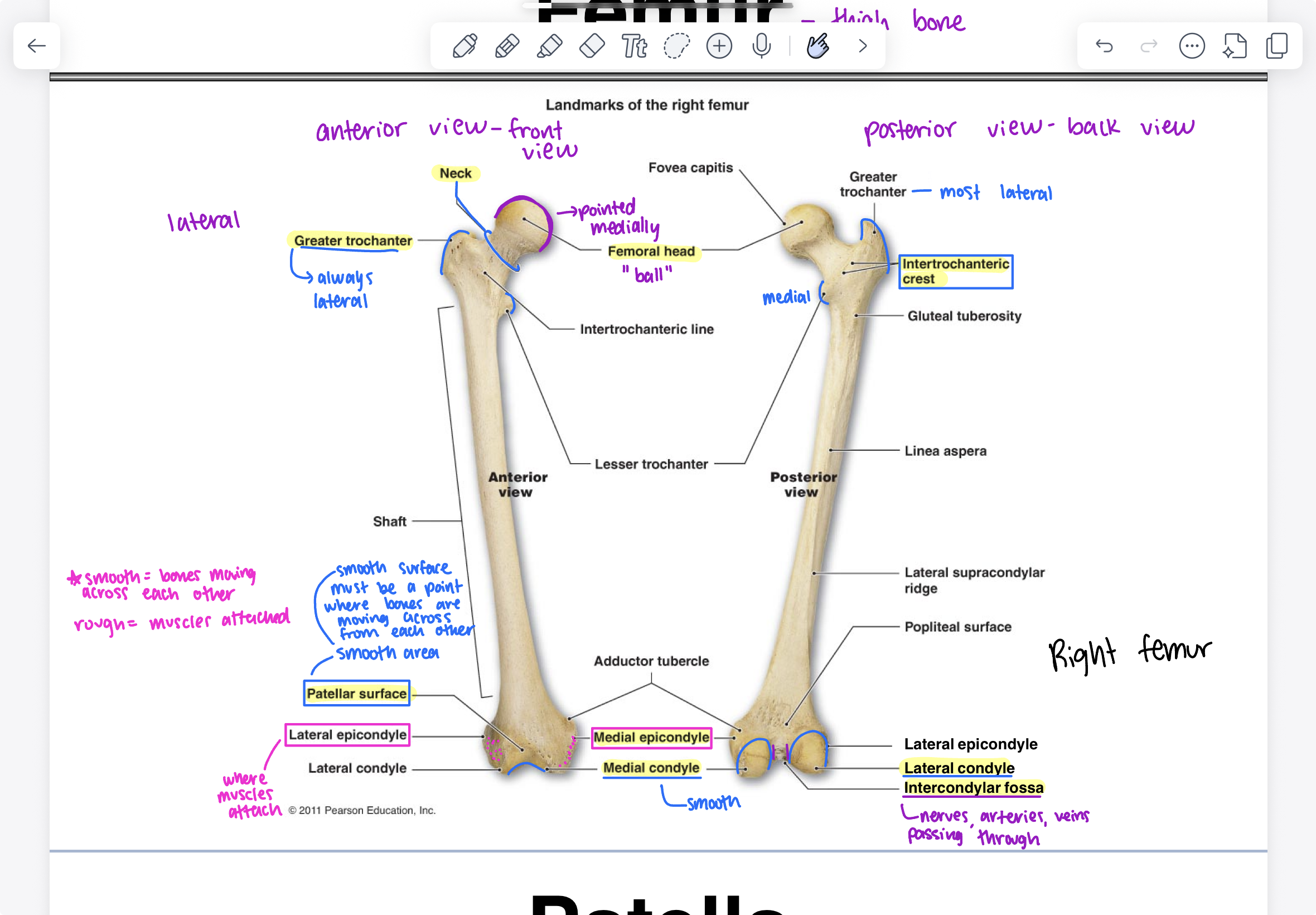
patella
sesamoid bone (bone that develops within a tendon), quadriceps tendon (quads), patellar ligament, anterior view is rough because tendons attaches to the sesamoid bone, posterior view includes femur
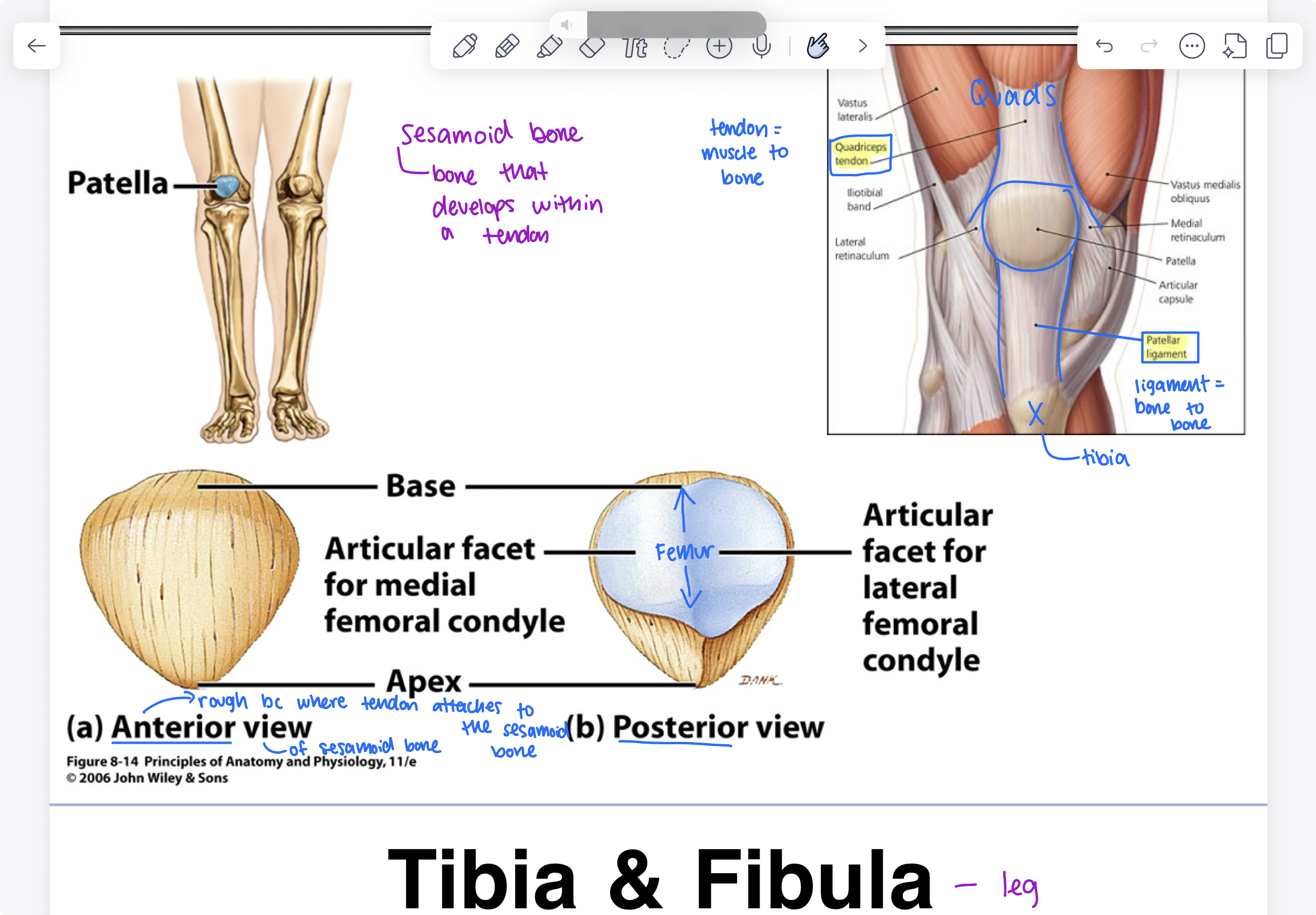
tibia and fibula
lateral condyle, medial condyle, tibial tuberosity (where ligament is attaching), fibula (on lateral side, not articulating with the tibia), lateral malleolus (bottom of fibula, grab onto ankle bones on the foot), medial malleolus (medial side of bottom of tibia)
malleolus= mallet/hammer head
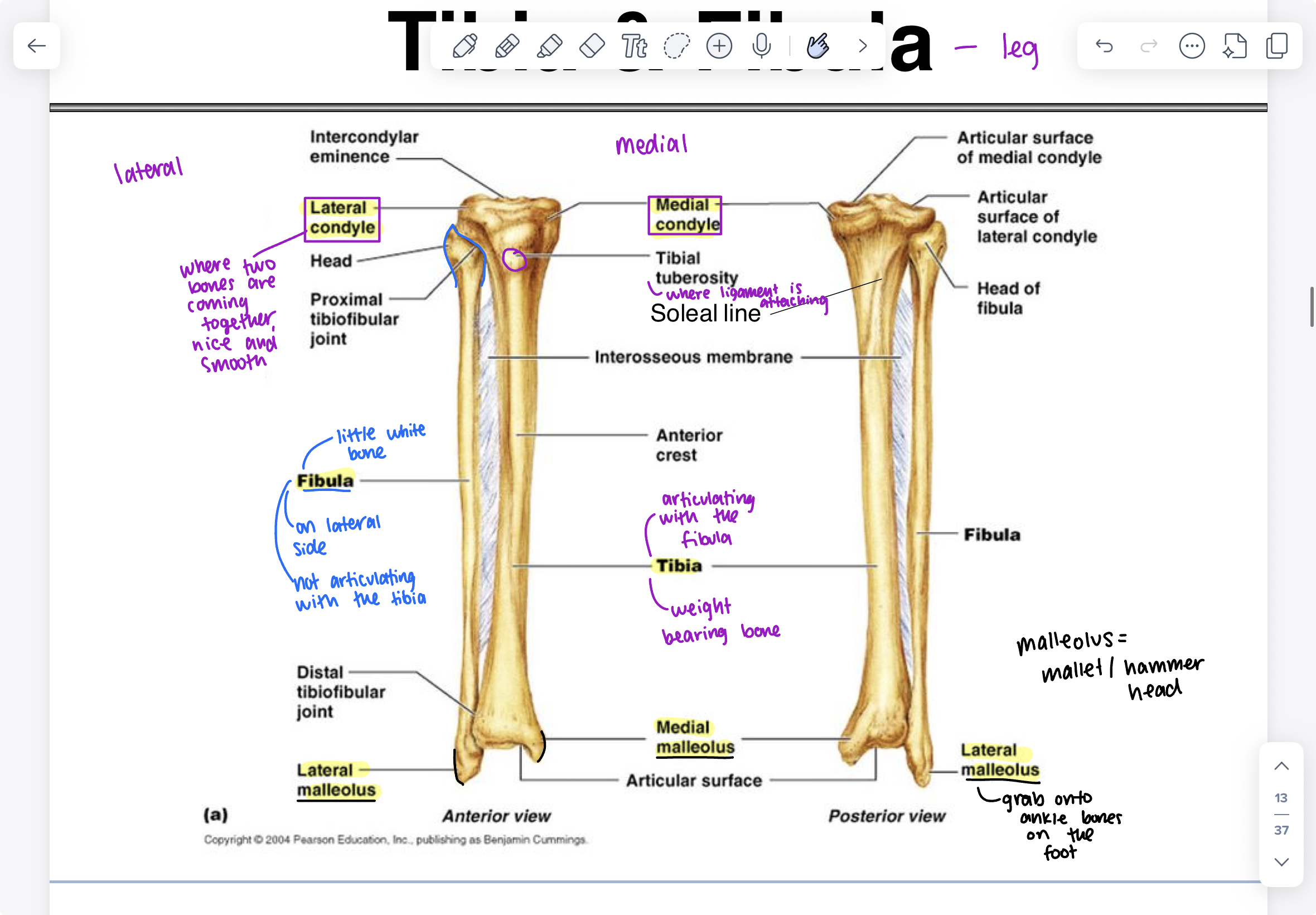
bones of the foot
tarsal bones (7): talus (smooth surface, bone to bone interaction, where tibia and fibula grab onto), calcaneus (heel), navicular (boat shaped), cuboid (lateral side), cuneiforms (medial (closes to big toe), intermediate, lateral), metatarsals (5), phalanges (14) (proximal- bottom, middle- middle, distal- top) (big toe only has middle and distal, the rest have all
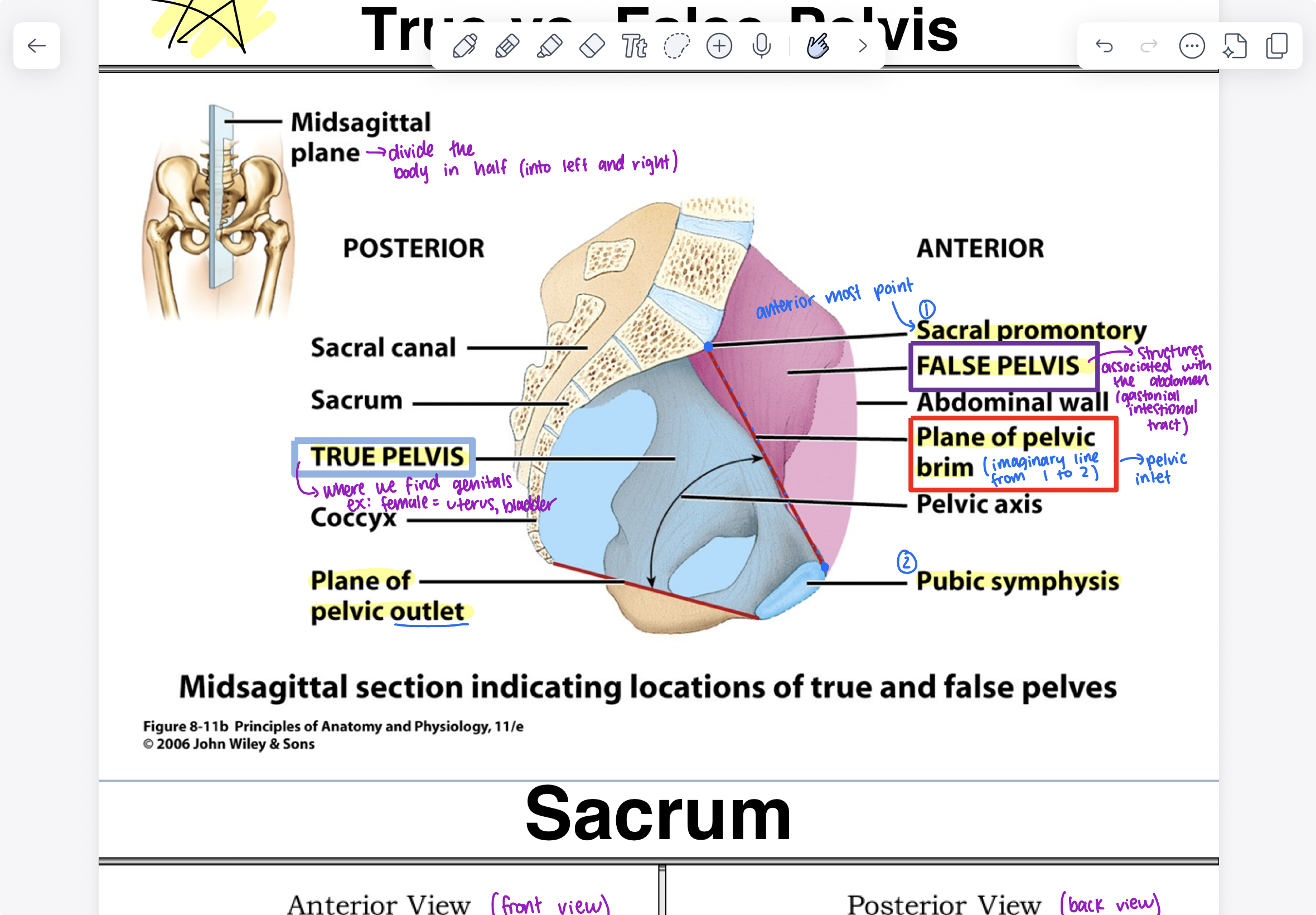
true vs. false pelvis of the pelvic girdle
midsagittal plane (divide the body in half), true pelvis (located on posterior side, where we find genitals), plane of pelvic outlet, sacral promontory (most anterior point), false pelvis (located on anterior side), plane of pelvic brim (imaginary line between the true and false pelvis), pubic symphysis (bottom)
distal
far away from center of body
proximal
closer to the center of body