HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 HELP GUIDE
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Dorsal
Back
Ventral
Front
Anterior
Front end
Posterior
Back end
Superior
toward head
inferior
away from head
medial
toward midline
laterial
away from midline
proximal
close to origin/pt
distal
farther from orgin/pt
superficial
towards surface
deep
away from surface
The femoral region is _____ to the crural region
proximal
the hypogastric region is____ to the umbilical region
inferior
the heart is ____ to the diaphragm
superior
which type of section separates ventral from dorsal
coronal
a surgeon asked the surgical technician to help create an opening in the chest during open heart surgery along a plane that equally separated the right and left halves of the thoracic cavity. This section is known as
saggital section
The part of homeostasis control system that provides the control centers response is called the
effector
The result of the effect is to shut off the original_____ or reduce it’s an intensity during the negative feedback mechanism to restore homeostasis
stimulus
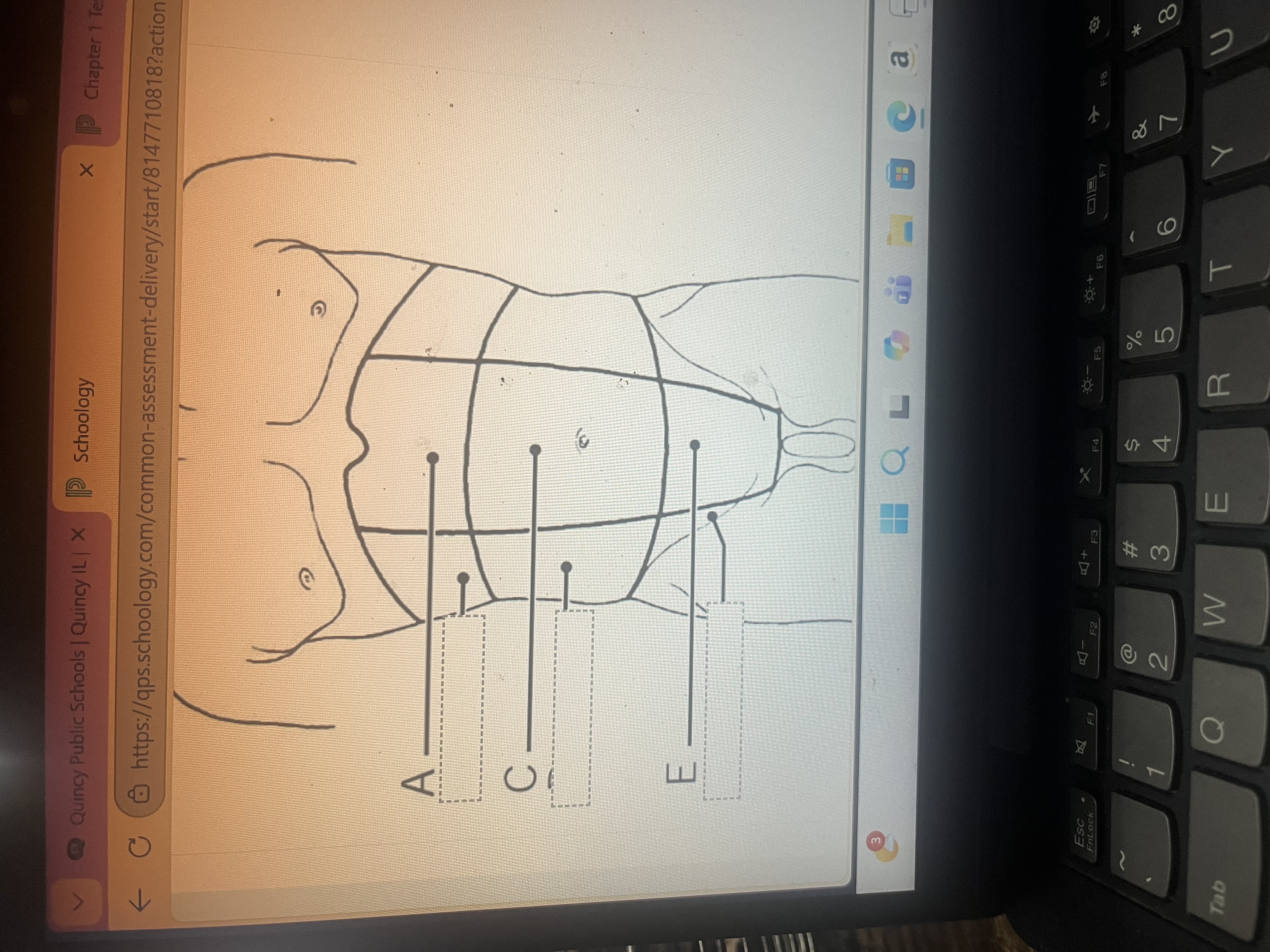
A- right hypochondriac region
B- right lumbar region
C- right iliac region
which of these regions is not associated with the ventral (anterior) portion of the head?
occipital
skeletal system
bones, ligaments, and cartilage
muscular system
skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscles
the nose is ____ to the ears
medial
The olecranon is _____ to the carpal
proximal
The antecubital region is _____ to the elbow
anterior
the knee is ____ to the thigh
distal
The occipital region is_____ to the nasal region
posterior
The tarsal region is _____ to the femoral region
distal
The cervical region is______ to the thoracic region
superior
the type of muscle found in the walls of hallow organs, such as the stomach, and in the walls of blood vessels
smooth
Striated and Voluntary
Skeletal muscle tissue
Striated and Involentary
cardiac muscle tissue
Intercalated discs between cells
Cardiac muscle tissuee
most suited more rapid diffusion
simple squamous
lines the walls of the bladder and capable of stretching
transitional
best suited for areas that are subject to friction
stratified squamous
Bone is best described as ____
ossepous tissue
Which type of tissue is situated in the lining of the urinary bladder and urethra where stretching occurs
Transitional
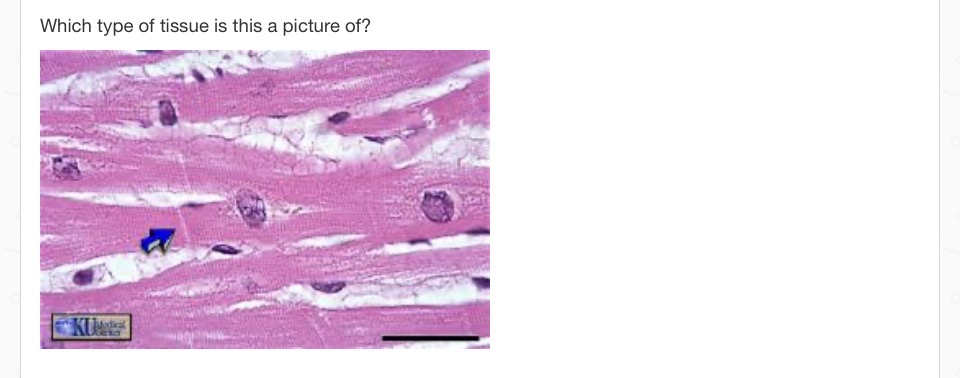
cardiac muscle tissue (picture)
Which of these characteristics best describes cardiac muscle tissue?
movement is involentary and cell’s striated
Many layers of flattened cells should be termed ________ epithelial tissue
stratified squamous
Identify the type of connective tissue that is found in the spleen
reticular
makes up the intervertebral discs
fibrocartilage
forms your hip bone
osseous
tendons and ligaments
dense regular
appears glassy and smooth
hyaline cartilage
Type of tissue that consists of living cells surrounded by an extracellular matrix
connective tissue
Type of tissue that is specialized to CONTRACT and produce movement
muscle tissue
Type of tissue that is found in the brain and spinal cord
nervous tissue
Type of tissue that can be described as voluntary or involuntary.
muscle tissue
Type of tissue that contains collagen, elastic, or reticular fibers
connective tissue
Type of tissue that is common in glands and their ducts, linings, and coverings of the body.
epithelial tissue
Type of tissue that supports, protects, and binds tissues together
connective tissue
Type of tissue that is the most abundant and diverseType of tissue that is the most abundant and diverse
connective tissue
Alexis tore her Achilles (calcaneal) tendon during a recent track meet. She has injured ________.
dense regular connective tissue
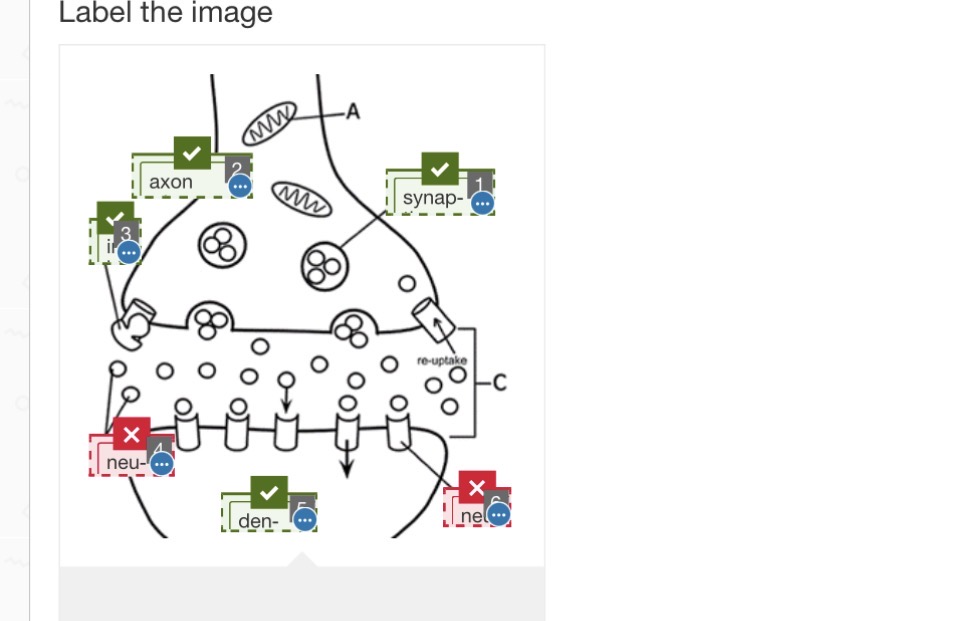
neurotransmitters, and neurotransmitter receptors
Put the following in order for the pathway of a nerve impulse
stimulus happens
sensory neurons
CNS
motor neurons
effector
response happens
What are the 2 structural divisions of the entire nervous system
CNS and PNS
Put the steps of the action potential being created in order.

Put in order the steps of neurotrassmision across a synapse
action potential reaches the axon terminal, the electrical charge opens calcium channels
calcium enters and, in turn, causes the synaptic vesicles containing the neurotransmitters to fuse with the axon membrane
porelike openings form, releasing the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft
The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the membrane of the next neuron
f enough neurotransmitter is released, a graded potential will be generated and eventually an action potential (nerve impulse) will occur in the neuron beyond the synapse
the neurotransmitter is quickly removed from the synapse either by reuptake or by enzymatic activity
During the resting state, a neuron is ________.
polarized with more sodium ions outside the cell and more potassium ions inside the cell
An action potential (nerve impulse) is caused by an influx of these ions into the cell ________.
sodium
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of events that correlates to the sequence of events of a nerve impulse?
1. the membrane becomes depolarized
2. sodium channels open and sodium ions diffuse inward
3. the membrane becomes repolarized
4. potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse (passively) outward
2,1,4,3
Which of the following is the correct sequence in neurotransmitter signaling
Action potential → Neurotransmitter release → Receptor binding
During an action potential, which of the following occurs
Sodium ions flow into the neuron followed by potassium ions flowing out
All of the following are components of a chemical synapse EXCEPT
Myelin sheath
Which of the following represents the correct pathway of spinal reflexes
Sensory neuron → Interneuron → Motor neuron → Muscle
Neurotransmitters are typically stored in
synaptic vesicles
During the repolarization phase of an action potential, which of the following occurs
Sodium channels close and potassium channels open
The sodium-potassium pump (Na⁺/K⁺) contributes to the resting membrane potential by
Pumping three Na⁺ ions out of the cell and two K⁺ ions into the cell
What ion channel is primarily responsible for the initial depolarization during an action potential?
sodium channels
An action potential reaches the axon terminal. What is the next step in neurotransmission?
calcium ions enter the presynaptic terminal
Which of the following best describes the synaptic cleft
The gap between a presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron
Which of the following is NOT a type of neuroglia in the central nervous system?
Scwann cells
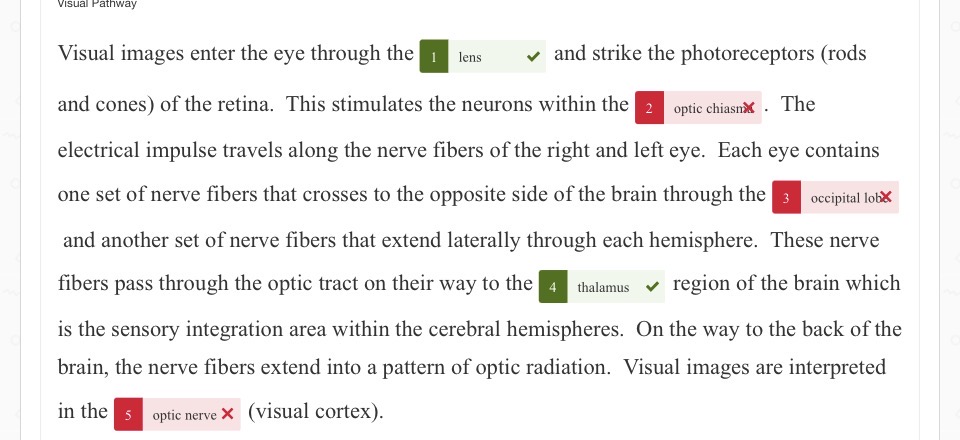
optic nerve, optich chaisma, occiptial lobe
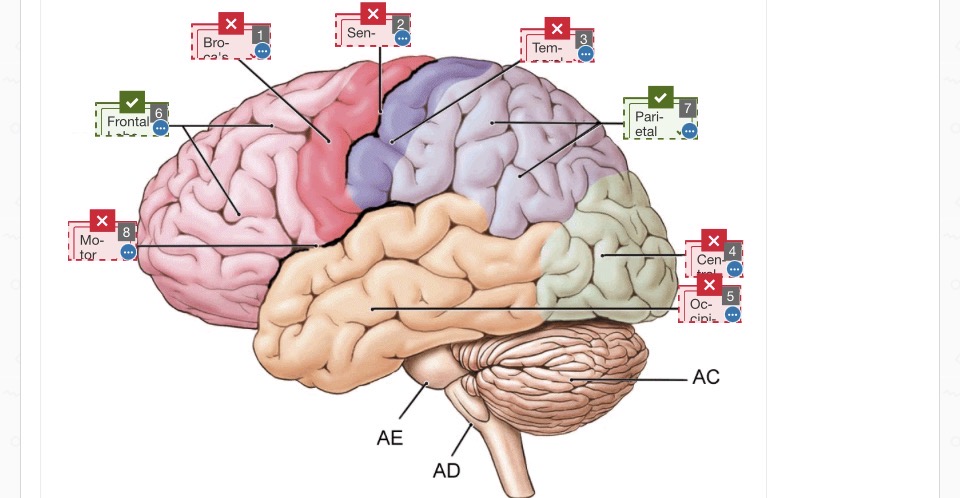
pink: motor cortex
between pink and purple: central sulcus
purple: sensory cortex
orange: temporal lobe
green: occipital lobe
between pink and orange: brochaes area
Which cranial nerves control eye movement?
cranial nerve III, IV, VI



retina 4. choroid
olfactory
optic
ocularmotor
trochlear
trigmenal
abducens
facial
vestibulacholear
gloss o pharyngeal
vagus
accesory
hypogolssal

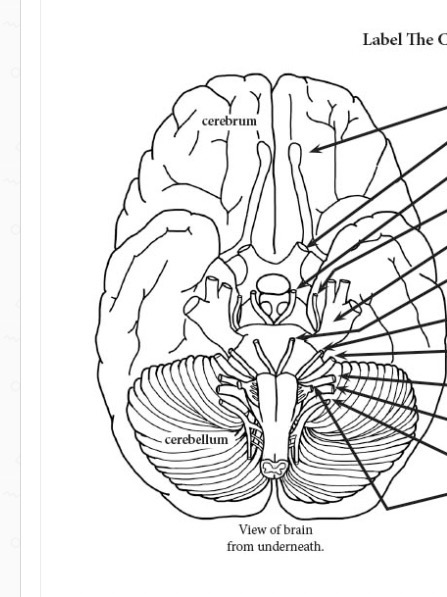
1 pineal gland 4 hypothalamus
8 fourth ventricle 9 spinal cord
10 medulla oblongata
12 midbrain 14 optic chaisma

2 fat 3 eye muscle
The brain and spinal cord are protected and cushioned by three connective tissue membranes that are collectively called ________.
meninges
corpus callosum
large nerve fiber tract that allows communication between 2 cerebral hemispheres
parietal lobe of cerebrum
houses the primary somatic sensory cortex
diencephalon
composed of thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
frontal lobe of cerebrum
houses the primary motor cortex
brainstem
composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
cerebellum
responsible for muscle coordination and balance
ventricles
cavities where cerebrospinal fluid is formed and is housed
thalamus
relay station for sensory impulses traveling to sensory cortex of cerebrum
limbic system
the emotional-visceral center of the brain
medulla oblongata
responsible for heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, swallowing, and vomiting
pons
rounded protrusion just below midbrain that includes nuclei invovled in control of breathing; "bridge"
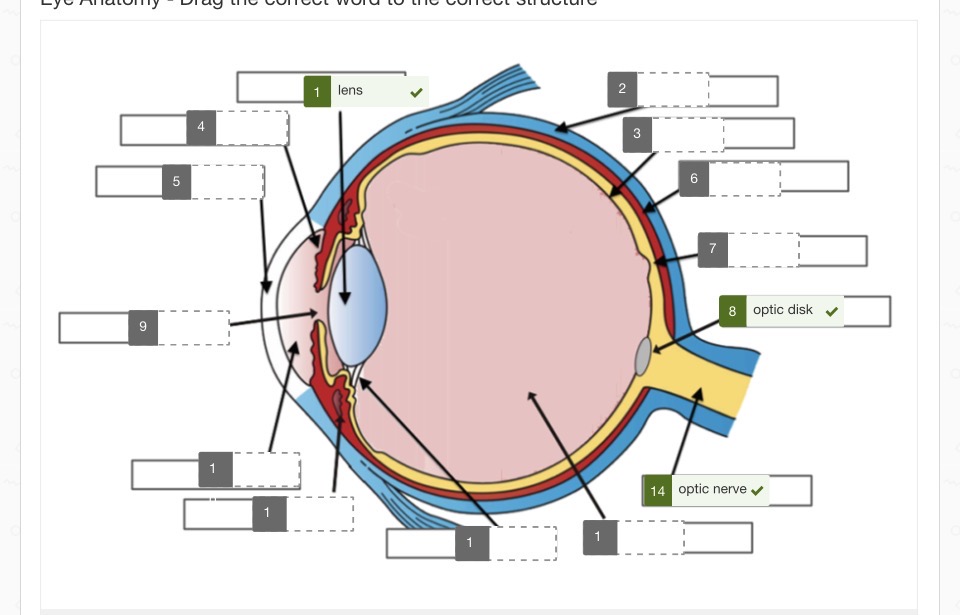
2 sclera 3 retina 4 iris 5 cornea 6 choroid 7 fovea centralisis 9 pupil
10 aquaous humor 11 ciliary body
12 zonules (suspensory ligaments) 13 viterous humor
Which cranial nerve descends into the thoracic and abdominal cavities to regulate heart rate and promote digestive activity?
vagus
The only pair of cranial nerves to extend to the thoracic and abdominal cavities is the ________ nerves.
Vagus
Which system produces chemical messengers known as hormones?
endocrine