6.3.2 Spectroscopy (incomplete)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What does NMR stand for?
nuclear magnetic resonance
How is NMR used in medicine?
MRI scans
Give 2 types of NMR
C-NMR
H1-NMR
What region of the electromagnetic spectrum is NMR involved in?
low energy radio waves
What are the 2 main features of carbon NMR spectrums?
peak position
number of peaks
What does position of the peak tell you?
the type of carbon
What does the number of peals tell you?
the nuber of different carbon environments
What may the area under a C NMR peak tell you?
the relative ratio of carbons in that environment
Why may area under a peak not be representatuve in C-NMR?
only 1% of carbon atoms are C-13 atoms
What is chemical shift of C-NMR relative to?
TMS (tetramethylsilane)
What is the formula of tetramethylsilane
(CH3)4Si
Draw TMS
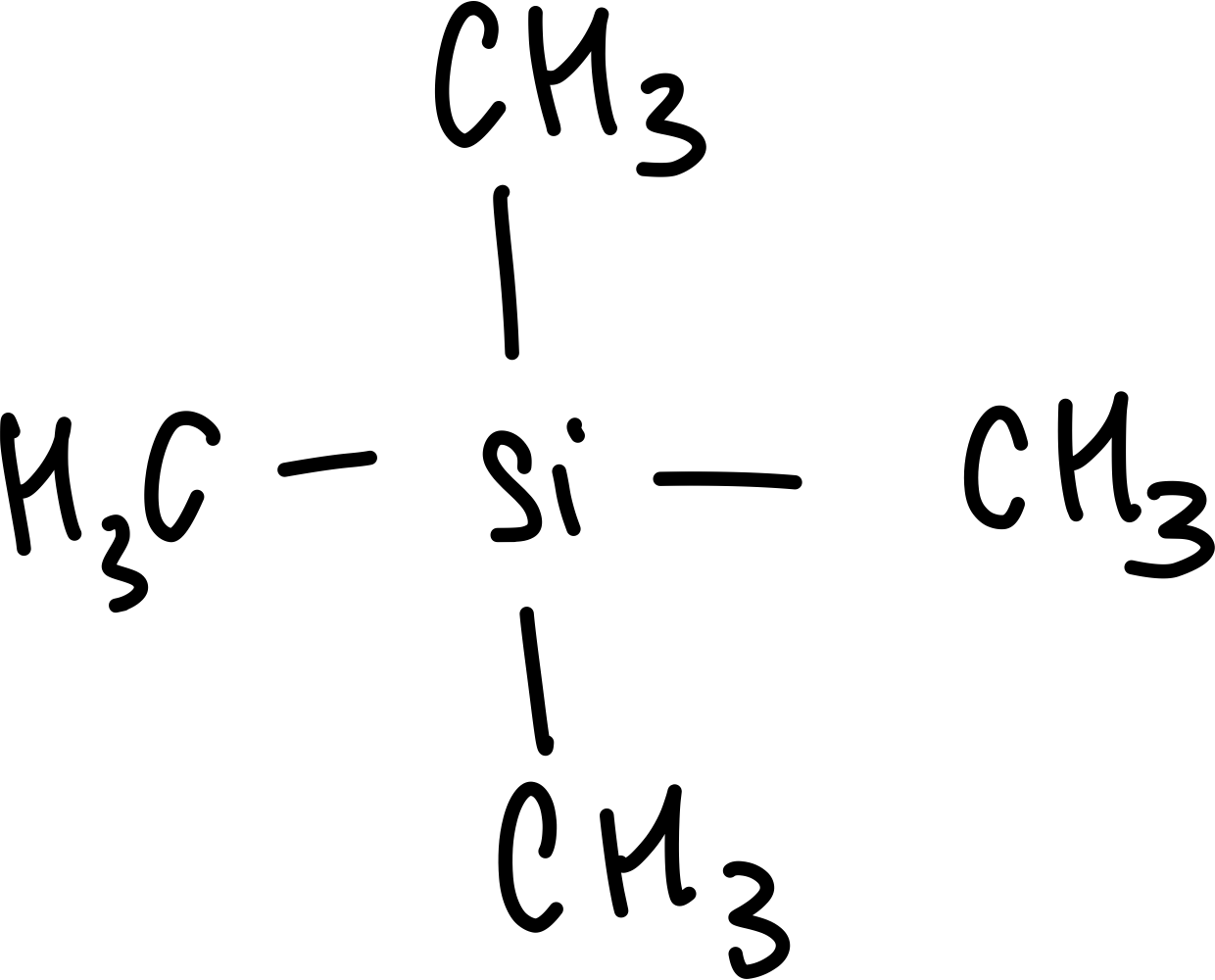
Why is TMS the internal standard?
all 4 carbons are in the same environment
all 12 hydrogens are in the same environment
What does TMS produce on a C-NMR spectrum?
singe peak where shift = 0