IBESS Topic 7
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
Energy Security
The ability to secure affordable, reliable and sufficient energy supplies for the needs of a particular country.
2
New cards
Energy Crisis
A significant bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy.
3
New cards
Energy Choice factors
\
1. Availability of the supply (domestic or international)
2. Technology developments (does it already exist? Is there potential?)
3. Politics (lead to conflict?)
4. Economics (cheaper to import or produce)
5. Cultural Attitudes (love of the SUV)
6. Sustainability
7. Environmental Considerations
1. Availability of the supply (domestic or international)
2. Technology developments (does it already exist? Is there potential?)
3. Politics (lead to conflict?)
4. Economics (cheaper to import or produce)
5. Cultural Attitudes (love of the SUV)
6. Sustainability
7. Environmental Considerations
4
New cards
Why is more money going to finding more oil & gas?
\
1. Transnational corporations are committed to carbon economy. Scale of change would be massive.
2. Cheaper to produce electricity from fossil fuels currently.
3. Many countries are locked into their energy choice by trade agreements or convenience.
4. All renewable source are location dependent - can’t work for everyone.
1. Transnational corporations are committed to carbon economy. Scale of change would be massive.
2. Cheaper to produce electricity from fossil fuels currently.
3. Many countries are locked into their energy choice by trade agreements or convenience.
4. All renewable source are location dependent - can’t work for everyone.
5
New cards
What does the Greenhouse Effect do (short version)?
Keep the earth warm at night (when there’s no sunlight --think of the hot and cold side of the moon)
6
New cards
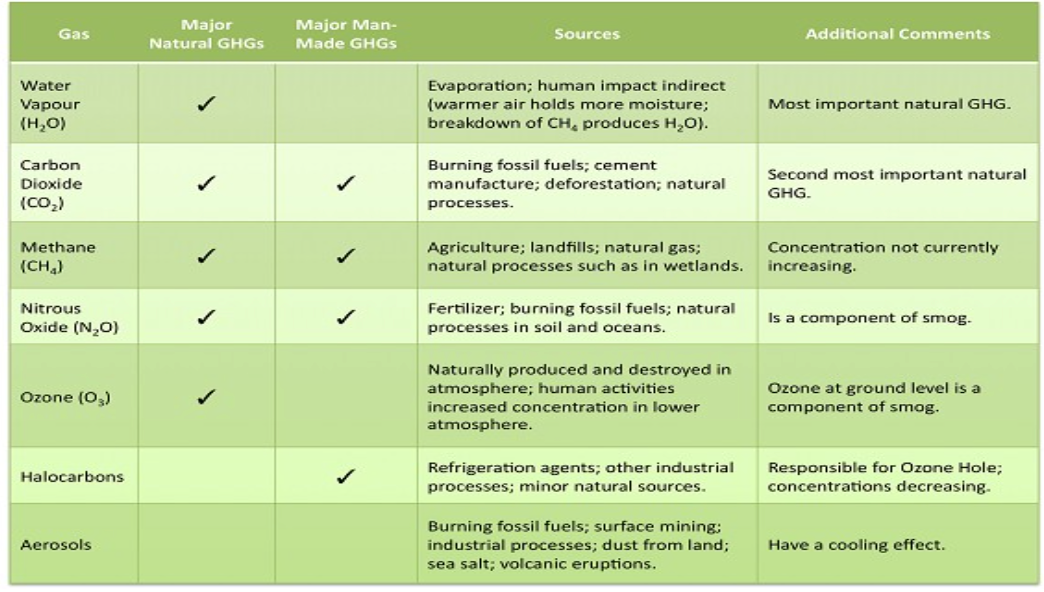
Greenhouse Gases
water vapour (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxides (N2O), ozone (O3) & CFC’s/HCFC’s
7
New cards
What is the primary type of incoming radiation that strikes the Earth causing it to warm?
Longwave infrared radiation
8
New cards
What is the type of radiation released by any object (including the Earth) that has a temperature?
Thermal radiation → transferred in the form of electromagnetic waves
9
New cards
Human Influence on the Greenhouse Effect
Through the combustion of fossil fuels, raising of large amounts of livestock, and deforestation humans have increased the amount of GHGs…EGE (enhanced greenhouse effect)
10
New cards
Weather
The daily result of changes in temperature, pressure and precipitation in the environment
11
New cards
Climate
The average weather pattern that has been established over a long period of time.
12
New cards
What two gases have the greatest contribution to the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect?
Carbon dioxide & Methane
13
New cards
Why are Carbon dioxide levels increasing?
Burning fossil fuels & Deforestation/Land Alteration prevents carbon sequestration due to reduced photosynthesis by vegetation
14
New cards
Why are Methane levels increasing?
Increased animal agriculture (notably cattle), Melting permafrost which allows trapped methane to escape, increased rice production, increased waste that is decomposing in anaerobic environments (landfills).
15
New cards
Mitigation
Attempts to reduce (or maintain current levels) the effects of climate change
16
New cards
Mitigation involves
The reduction of GHG concentrations in the atmosphere by:
1. reducing the source
2. increasing the number of GHG sinks
1. reducing the source
2. increasing the number of GHG sinks
17
New cards
Mitigation techniques
Carbon taxes, carbon trading & carbon offset
18
New cards
Carbon taxes
* Introduced by some countries like Britain
* Pollution tax → fee on the production, distribution or use of fossil fuels based on how much carbon is emitted
* Tax makes dirty fuels more expensive
* Pollution tax → fee on the production, distribution or use of fossil fuels based on how much carbon is emitted
* Tax makes dirty fuels more expensive
19
New cards
Carbon trading
* trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought
* governments set targets for the amount of carbon dioxide that can be emitted by industries and divide these between plants/companies
* governments set targets for the amount of carbon dioxide that can be emitted by industries and divide these between plants/companies
20
New cards
Carbon offset
* when you buy an offset, you fund projects that reduce **greenhouse gas** (GHG) emissions (restore forests, update power plants or increase energy efficiency in transport)
* you can pay to reduce the global GHG total instead of making radical reductions of your own
* you can pay to reduce the global GHG total instead of making radical reductions of your own
21
New cards
Adaptation involves
making attempts to adjust lifestyles to overcome problems associated with climate change
22
New cards
Adaptation techniques
* infrastructure to deal with sea level rise/flooding, developing strategies to increase freshwater in areas that are expected to experience droughts, and changing agricultural practices to adapt to climate and soil quality
23
New cards
Adaptations to Climate Change: Equality
* Economic inequalities restrict the adaptive options available to LEDCs
* Adaptive measures are hampered by inequalities around the world
* Adaptive measures are hampered by inequalities around the world
24
New cards
International Efforts/Conferences to Address Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Climate Change
IPCC → Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (science related to CC)
NAPAs →National Adaptation Programmes of Action (urgent and immediate needs/assessment of vulnerability to current climate and extreme events)
UNFCCC → United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
NAPAs →National Adaptation Programmes of Action (urgent and immediate needs/assessment of vulnerability to current climate and extreme events)
UNFCCC → United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
25
New cards
International Efforts to Address Climate Change
Kyoto Protocol & Paris Agreement
26
New cards
Kyoto Protocol
* 1997/2005 - Countries pledged to reduce GHG levels to 1990 levels (about a 5% reduction) within 15 years
* No country met the target (most countries saw an increase in GHGs)
* Lacked support from US which doomed the agreement
* No country met the target (most countries saw an increase in GHGs)
* Lacked support from US which doomed the agreement
27
New cards
Paris Agreement
* 2015 - Countries pledged to reduce GHG levels so that there would be at most a 2°C increase in global temperature during the 21st century
* Current predictions show a 3.2 C increase in global temperatures
* Current predictions show a 3.2 C increase in global temperatures
28
New cards
Positive Feedback Mechanism
Albedo, Deforestation, Methane Accumulation in Atmoshere
29
New cards
Albedo
* the measure of how much light is reflected back into space by earth’s surface
* less snow, the more heat that is absorbed by the planet, increasing the temperature (and cycle repeats)
* less snow, the more heat that is absorbed by the planet, increasing the temperature (and cycle repeats)
30
New cards
Deforestation
\
* Trees are a carbon sink which means they are able to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis.
* Fewer trees, means vegetation can take less carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere, more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere means higher temperatures, higher temperatures mean more evaporation and less suitable climate for further tree growth.
* Trees are a carbon sink which means they are able to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis.
* Fewer trees, means vegetation can take less carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere, more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere means higher temperatures, higher temperatures mean more evaporation and less suitable climate for further tree growth.
31
New cards
Methane Accumulation in Atmosphere
* A warmer planet melts permafrost which releases methane that is trapped underground.
* Methane is a greenhouse gas which means higher concentrations lead to more warming, which melts more permafrost, which leads to more methane being released
* Methane is a greenhouse gas which means higher concentrations lead to more warming, which melts more permafrost, which leads to more methane being released
32
New cards
Negative Feedback Mechanisms
Increase plant growth & Increased cloud cover
33
New cards
Increased plant growth
\
* A warmer planet allows for more plants to grow. More plant growth can remove more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to restrict future increases in temperature.
* A warmer planet allows for more plants to grow. More plant growth can remove more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to restrict future increases in temperature.
34
New cards
Increased Cloud Cover
* A warmer planet produces more evaporation, which leads to more cloud formation. Clouds are able to block incoming visible and UV light, thus helping to “shade” the Earth.
35
New cards
How can money/influence minimize climate change?
\
* Better medical care
* More stringent environmental protection laws
* Infrastructure to control flooding
* Greater priority to restore infrastructure if systems go down
* Better medical care
* More stringent environmental protection laws
* Infrastructure to control flooding
* Greater priority to restore infrastructure if systems go down
36
New cards
Fossil Fuels
Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Oil Sands, Oil Shale, Fracking (a process of obtaining Natural Gas and oil) & Coal
37
New cards
Fossil Fuel Disadvantages
* Greenhouse gas (primarily CO2) emissions are driving global warming
* Coal mining has huge environmental impact (creates runoff problems, acid mine drainage, destruction of habitat)
* Infrastructure (roads, homes, pipelines) needs to put in place for new extraction sites
* Fossil fuels pollute water as well (oil spills)
* Coal mining has huge environmental impact (creates runoff problems, acid mine drainage, destruction of habitat)
* Infrastructure (roads, homes, pipelines) needs to put in place for new extraction sites
* Fossil fuels pollute water as well (oil spills)
38
New cards
Nuclear Energy
\
* Fission chain reaction – Neutrons fired into heavy nuclei cause them split into smaller nuclei (this continues to occur)
* When the heavy nuclei split, energy is released (thermal energy)
* This thermal energy is used to spin a turbine that then generates electricity
* Fission chain reaction – Neutrons fired into heavy nuclei cause them split into smaller nuclei (this continues to occur)
* When the heavy nuclei split, energy is released (thermal energy)
* This thermal energy is used to spin a turbine that then generates electricity
39
New cards
Biomass
* + : Renewable, Carbon Neutral, and Available worldwide
* - : Low energy return per input, cultivating land for biofuels is intensive and relies on fertilizers and pesticides, demand for biofuels made from staple crops may increase world hunger and prices for stable crops
* - : Low energy return per input, cultivating land for biofuels is intensive and relies on fertilizers and pesticides, demand for biofuels made from staple crops may increase world hunger and prices for stable crops
40
New cards
Geothermal
\
* Radioactive decay that is occurring deep within the Earth releases thermal energy.
* This energy can be tapped to generate steam to turn turbines, thus generating electricity, or to directly supply thermal energy to homes.
* Radioactive decay that is occurring deep within the Earth releases thermal energy.
* This energy can be tapped to generate steam to turn turbines, thus generating electricity, or to directly supply thermal energy to homes.
41
New cards
Geothermal Energy Summary
* + : Renewable & Carbon Neutral
* - : Availability is limited & high costs related to corrosion of equipment
* - : Availability is limited & high costs related to corrosion of equipment
42
New cards
Wind Energy Summary
* + : Renewable, Carbon neutral, high energy return on investment, can be placed in remote areas and surrounded by crops
* - : Winds are unpredictable, not all areas well suited to wind farms due to lack of consistent winds, kills birds
* - : Winds are unpredictable, not all areas well suited to wind farms due to lack of consistent winds, kills birds
43
New cards
Hydroelectric Energy Summary
* + : Renewable, Carbon neutral, high energy return on investment
* - : Habitat destruction, damns interfere with migratory fish species, thermal pollution of water downstream from dam, sedimentation buildup behind dam
* - : Habitat destruction, damns interfere with migratory fish species, thermal pollution of water downstream from dam, sedimentation buildup behind dam