ap econ exam review
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
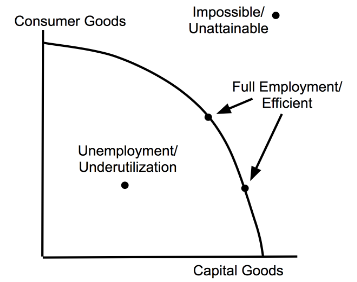
Production Possibilities Curve
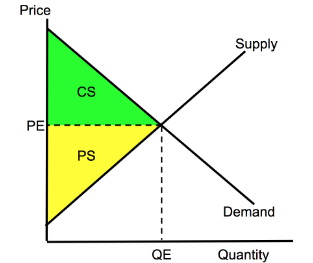
Supply and Demand (CS+PS)
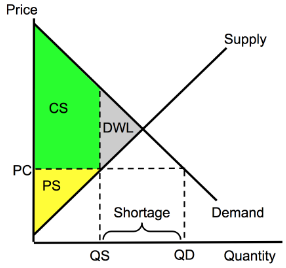
Price Ceiling (CS,PS,DWL)
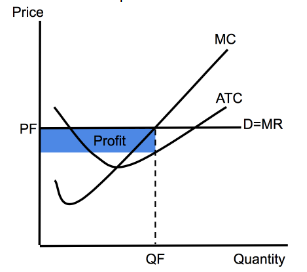
Perfect Competition (Firm,Profit)
Perfect Competition (Firm,Long-run)
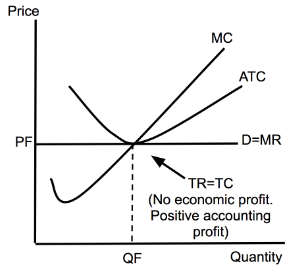
Monopoly (Profit,DWL)
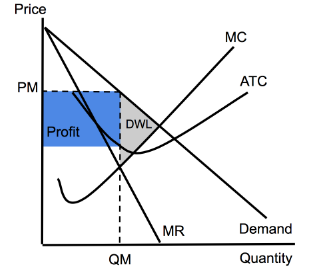
Monopolistic Comp (Long-run)
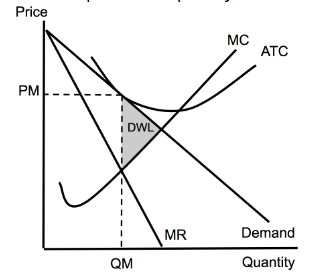
Perfectly Competitive Labor (Firm)
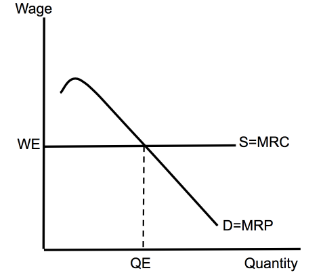
Negative Production Externality (DWL)
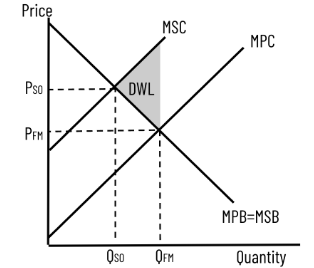
Positive Consumption Externality (DWL)
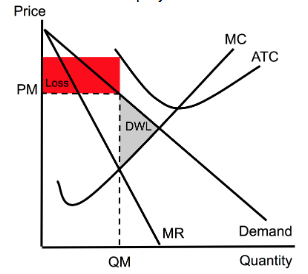
Monopoly (Loss)
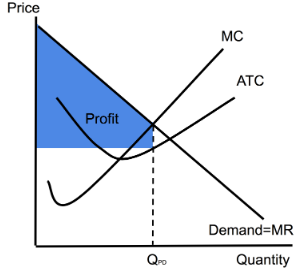
Perfect Price Discrimination (Profit)
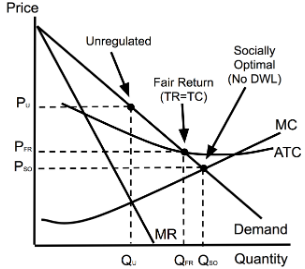
Natural Monopoly
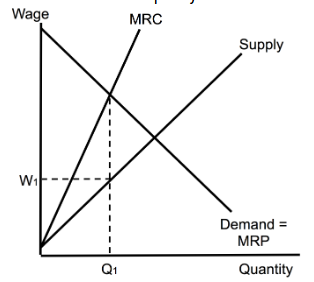
Monopsony
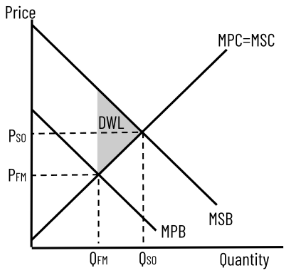
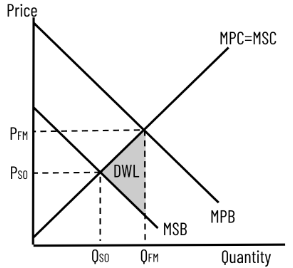
Negative Consumption Externality (DWL)
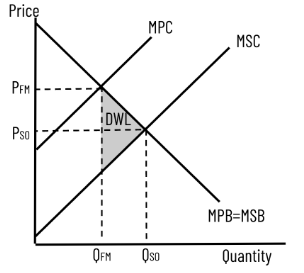
Positive Production Externality (DWL)
Negative externalities: The free market makes too much output where the MSC is___________ MSB.
greater than
Positive externalities: The free market doesn't make enough output where the MSC is ___________ MSB
less than
Comparative advantage: A country should specialize, if they have a lower ___________ than another country
opportunity cost
When the cross-price elasticity is positive, the two goods are
substitutes for each other.
When the cross-price elasticity is negative, the two goods are
complements to each other.
Total revenue test: When demand is inelastic, a _______ in the price will increase the total revenue
increase
Accounting profit
TR - Explicit Costs
Economic Profit
TR - (Explicit costs + implicit costs)
Shifters of demand
T: astes and preferences
R: elated goods (substitutes and complements)
I: ncome
B: uyer expectations
E: xpectations of the supplier
**Number of buyers
Shifters of supply
R: esources (input costs)
O: ther good prices (prices of inputs)
T: axes
T: echnology
E: xpectations of the supplier
N: umber of competitors
The law of demand
a higher price leads to a lower quantity demanded and that a lower price leads to a higher quantity demanded
The law of supply
an increase in the price of goods or services results in an increase in the quantity that suppliers make available to the market