Microeconomics Theme 3 <3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
1
New cards
1 niche market
2 diseconomies of scale
3 conflicting objectives (family business)
2 diseconomies of scale
3 conflicting objectives (family business)
why firms stay small
2
New cards
1 higher profits
2 economies of scale
3 increased market share and price setting power
2 economies of scale
3 increased market share and price setting power
why firms grow big
3
New cards
1 internal growth (use profits to increase output)
2 external growth (merger or takeover)
2 external growth (merger or takeover)
how firms grow big
4
New cards
1 financial constraints
2 size of market
3 regulation
4 competition
2 size of market
3 regulation
4 competition
what stops growth
5
New cards
combination of two or more companies into a single firm
merger
6
New cards
horizontal and vertical
2 types of mergers
7
New cards
a merger that occurs in the same stage of production
horizontal integration
8
New cards
a merger at different stages of the production away from the consumer
backward vertical integration
9
New cards
a merger at different stages of the production closer to the consumer
forward vertical integration
10
New cards
two completely different firms merging
conglomerate integration
11
New cards
1 reduce competition
2 economies of scale
3 monopoly power
2 economies of scale
3 monopoly power
advantages of horizontal integration
12
New cards
1 dis economies of scale
2 lack of synergy
2 lack of synergy
disadvantages of horizontal integration
13
New cards
1 control of the supply chain
2 improved access to raw materials
2 improved access to raw materials
advantages of vertical integration
14
New cards
1 no expertise in the industry
2 lack of synergy
2 lack of synergy
disadvantage of vertical integration
15
New cards
1 reduced risk by diversitification
2 increased consumer base
2 increased consumer base
advantage of conglomerate integration
16
New cards
1 lack of synergy
2 no expertise in the market
2 no expertise in the market
disadvantage of conglomerate integration
17
New cards
When a firm splits into two or more independent firms
demergers
18
New cards
1 reduce diseconomies of scale
2 new separate firms can specialise
3 a firm can sell one of its demerged divisions and its assets to increase SNP
4 reduce conflicts between different cultures within a firm
2 new separate firms can specialise
3 a firm can sell one of its demerged divisions and its assets to increase SNP
4 reduce conflicts between different cultures within a firm
Reasons for demergers
19
New cards
business - in SR, there is cost of administration and in LR high returns so increases AC
workers - job losses, increase in managers
consumers - impact on price depends on scale of competiton
workers - job losses, increase in managers
consumers - impact on price depends on scale of competiton
impacts of demergers
20
New cards
maximising profits
private sector
21
New cards
maximising welfare of citizens
public sector
22
New cards
An organisation whose main objective is not to make money e.g. charity
non profit organisation
23
New cards
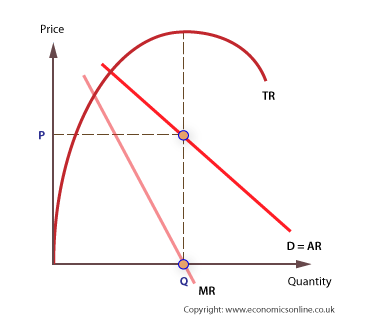
price x quantity
total revenue
24
New cards
total revenue increases
elastic good price decreases
25
New cards
total revenue decreases
inelastic good price decreases
26
New cards
total revenue/quantity
average revenue formula
27
New cards
the revenue you receive per unit of output
average revenue
28
New cards
additional revenue received from one extra unit of output
marginal revenue
29
New cards
MC=MR
profit maximisation point
30
New cards
MR=0
revenue maximisation point
31
New cards
AR=AC
sales maximisation point
32
New cards
fixed costs + variable costs
total cost formula
33
New cards
total cost/quantity
average cost formula
34
New cards
(AR-AC) x quantity
profit formula
35
New cards
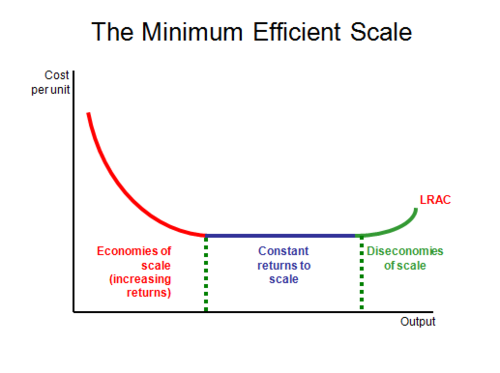
all factors of production is variable
long run average cost
36
New cards
at least one factor of production is fixed (usually capital)
short run cost curve
37
New cards
an additional factor of production will result in a smaller increase in output
the law of diminishing marginal returns
38
New cards
output increasing as cost per unit decreases
economies of scale
39
New cards
1 managerial
2 financial
3 commercial
4 technical
5 marketing
2 financial
3 commercial
4 technical
5 marketing
5 types of economies of scale
40
New cards
employ specialist managers
increase division of labour
increase efficiency
decrease LRAC
increase division of labour
increase efficiency
decrease LRAC
managerial EofS
41
New cards
bigger firms are perceived as less risky by financial institutions
lower interest rates when taking a loan
decrease lRAC
lower interest rates when taking a loan
decrease lRAC
financial EofS
42
New cards
bulk buying decreases LRAC
commercial EofS
43
New cards
specialist capital decreases LRAC
technical EofS
44
New cards
lower unit cost for advertising as the firm expands
marketing EofS
45
New cards
output increases as cost per unit increase
diseconomies of scale
46
New cards
1 lack of motivation
2 loss of coordination
3 poor communication
4 organisational slack
2 loss of coordination
3 poor communication
4 organisational slack
4 types of diseconomies of scale
47
New cards
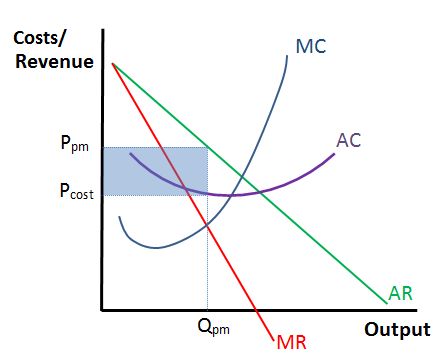
a firm with a lot of market share so they have price setting power
price maker
48
New cards
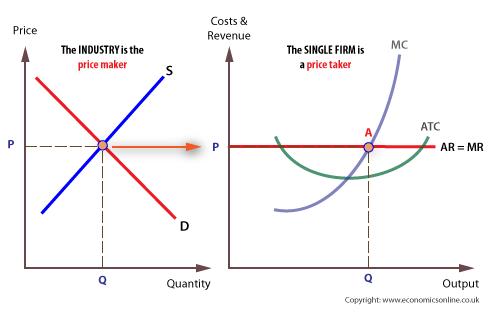
firms that accept the market price
price taker
49
New cards
1 no barriers to entry or exit
2 infinite amount of buyers and sellers
3 homogeneous good
4 perfect information
2 infinite amount of buyers and sellers
3 homogeneous good
4 perfect information
Characteristics of perfect competition
50
New cards
in the SR they make SNP
new firms enter the market as profits act as a signal
supply increases
in the LR firms make no SNP
new firms enter the market as profits act as a signal
supply increases
in the LR firms make no SNP
price takers making profit in the short run
51
New cards
in the SR they make a loss
firms leave the market as loss acts as a signal
supply decreases
in the LR firms make no SNP
firms leave the market as loss acts as a signal
supply decreases
in the LR firms make no SNP
price takers making a loss in the short run
52
New cards
AR shifts with the dependants of demand PACIFIC
what shifts AR
53
New cards
AC shifts when fixed costs changes but MC does not
AC and MC shifts when variable costs shift
AC and MC shifts when variable costs shift
what shift AC
54
New cards
the production of any particular good in the least costly way (lowest point on the AC curve)
productive efficiency
55
New cards
(P=MC)
allocative efficiency
56
New cards
uses SNP to innovate
dynamic efficiency
57
New cards
(any point on the AC curve)
x efficiency
58
New cards
AVC is higher than AR then the firm leaves the market immediately
shut down point
59
New cards
1 low barriers to entry of exit
2 many buyers and sellers
3 slightly differentiated goods
4 firms aim to profit maximise
2 many buyers and sellers
3 slightly differentiated goods
4 firms aim to profit maximise
characteristics of monopolistic competition
60
New cards
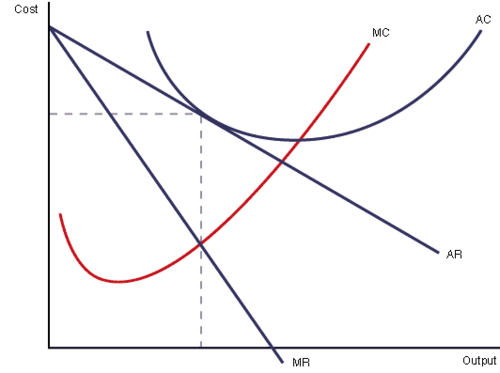
SNP acts as a signal
new firms enter the market
increase in competition
increase in AC (marketing)
decrease in AR
no SNP
new firms enter the market
increase in competition
increase in AC (marketing)
decrease in AR
no SNP
firms in monopolistic competition in the LR
61
New cards
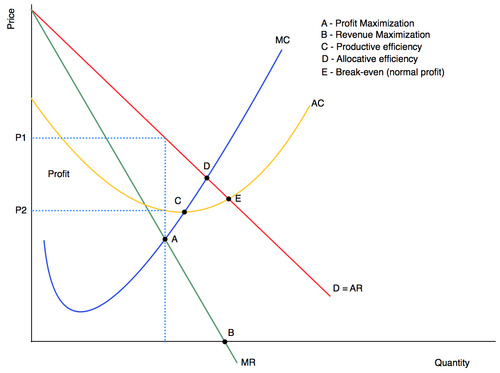
1 5 firms have 60% market share
2 high barriers to entry and exit
3 slightly differentiated goods
4 firms aim to profit maximise
5 firms are interdependent
2 high barriers to entry and exit
3 slightly differentiated goods
4 firms aim to profit maximise
5 firms are interdependent
oligopoly characteristics
62
New cards
high concentration ratio in the market and the demand is inelastic
oligopoly
63
New cards
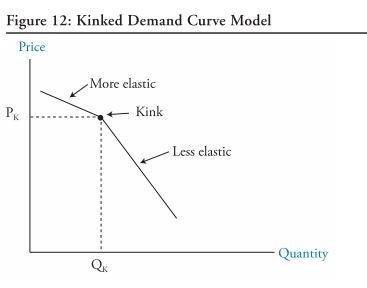
price rigidity
if a firm increases their price, then other firms will not (demand is elastic)
if a firm decreases their price, then other firms will decrease prices (demand is inelastic)
if a firm increases their price, then other firms will not (demand is elastic)
if a firm decreases their price, then other firms will decrease prices (demand is inelastic)
kinked demand curve
64
New cards
two existing firms with high market share engage in price fixing or quality fixing (illegal)
collusion
65
New cards
firms openly speak and cooperates on explicit price fixing
overt collusion
66
New cards
firms indirectly cooperates on price fixing
tacit collusion
67
New cards
1 small number of firms
2 demand is inelastic
3 firms output can be monitored easily
4 incomplete information
2 demand is inelastic
3 firms output can be monitored easily
4 incomplete information
collusion characteristics
68
New cards
1 enforcement problems
2 falling market demand
3 successful entry of non cartel firms into the market
4 market regulators
5 whistle blowers
2 falling market demand
3 successful entry of non cartel firms into the market
4 market regulators
5 whistle blowers
why collusion breaks down
69
New cards
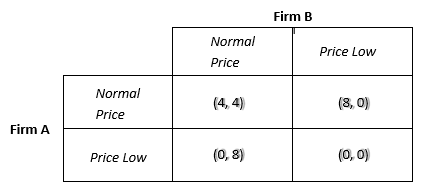
the payoff firms get if they increase price or decrease price
pay off matrix
70
New cards
firms collude and set a high price to gain joint SNP
joint profit maximisation
71
New cards
while colluding a firm could decrease price and break the agreement to gain more SNP while the other firm gain less profit
first movers advantage
72
New cards
one firm supplying the only good or service dominating the market with 100% concentration
pure monopoly
73
New cards
one firm has 25% or more concentration ratio
legal monopoly
74
New cards
one firm has 40% concentration ratio
dominant monopoly
75
New cards
1 one firm in the market
2 high barriers to entry
3 firms aim to profit maximise
4 price setting OR quantity setting power but not both
2 high barriers to entry
3 firms aim to profit maximise
4 price setting OR quantity setting power but not both
monopoly characteristics
76
New cards
government - corporation tax, compete on international market
worker - increase job security, bonuses and perks
consumers - innovation in the market
other firms - secure outlet for suppliers, constant quality for firms
worker - increase job security, bonuses and perks
consumers - innovation in the market
other firms - secure outlet for suppliers, constant quality for firms
benefits of monopoly
77
New cards
government - often avoid tax
workers - low bargaining power, low job security (increase in capital)
consumers - less choice, higher prices, lower quality
other firms - monopsony set low prices for the supplier
workers - low bargaining power, low job security (increase in capital)
consumers - less choice, higher prices, lower quality
other firms - monopsony set low prices for the supplier
costs of monopoly
78
New cards
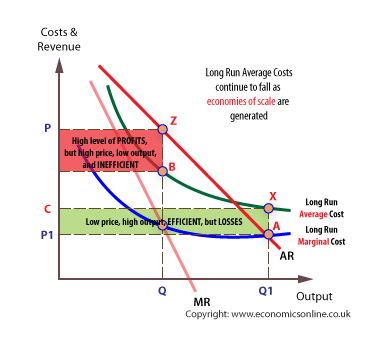
sunk costs are high so economies of scale is constant
natural monopoly
79
New cards
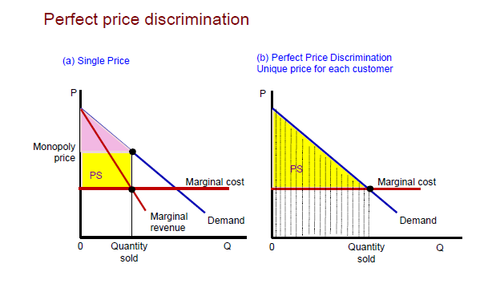
monopolies can discriminate on price on different consumers who have different PED to increase their SNP
price discrimination
80
New cards
demand is inelastic
demand is irresponsive to a change in price
train firms charge higher prices
demand is irresponsive to a change in price
train firms charge higher prices
peak traveller (commuter)
81
New cards
demand is elastic
demand is responsive to a change in price
train firms charge lower prices
demand is responsive to a change in price
train firms charge lower prices
off peak travellers (leisure)
82
New cards
a firm which is the sole buyer of resources or supplies
pure monopsony
83
New cards
firms have some control over their supplier
monopsony power
84
New cards
supplier - secure revenue stream
monospony - increase bargaining power
consumer -
monospony - increase bargaining power
consumer -
benefits of monopsony
85
New cards
supplier - reduced bargaining power
monopsony - suppliers may shut down
consumer -
monopsony - suppliers may shut down
consumer -
costs of monopsony
86
New cards
ease of which firms enter or exit the market
contestability
87
New cards
1 low barriers to entry or exit
2 good information
3 low sunk costs
2 good information
3 low sunk costs
what affects contestability
88
New cards
1 limit pricing or predatory pricing
2 economies of scale and product differentiation
3 patents, copyrights and licensing requirements
2 economies of scale and product differentiation
3 patents, copyrights and licensing requirements
types of barriers of entry or exit
89
New cards
1 no physical location
2 consumers can be reached easily
3 brand awareness reaches further
4 disrupting existing markets
this increases contestability
2 consumers can be reached easily
3 brand awareness reaches further
4 disrupting existing markets
this increases contestability
technology reducing contestability
90
New cards
the additional quantity of output produced by an additional unit of labour
marginal physical product of labour (MPPL)
91
New cards
the additional revenue received by a firm by using an additional unit of labour
marginal revenue product of labour (MRPL)
92
New cards
MPPL x MR
MRPL formula
93
New cards
each additional unit of labour, brings less additional productivity because capital is fixed
the law of diminishing marginal productivity
94
New cards
labour is homogenous
prefect information
perfect labour mobility
workers and firms are price takers and they must accept the industry wage rate
no barriers to entry or exit
prefect information
perfect labour mobility
workers and firms are price takers and they must accept the industry wage rate
no barriers to entry or exit
perfectly competitive labour market
95
New cards
there is an inverse relationship between w/r and quantity of labour
how w/r affects demand for labour
96
New cards
when the w/r is low the capital will be substituted for labour as the labour is cheaper
labour substitution
97
New cards
when the w/r is high the labour will be substituted for capital as the capital is cheaper
capital substitution
98
New cards
capital becoming expensive
deregulation
PACIFIC
deregulation
PACIFIC
shifts in the demand for labour curve
99
New cards
the demand of labour is dependant on the demand of the good
derived demand
100
New cards
we cant workout individual productivity as people work in teams
criticism of the law diminishing marginal productivity