CTE Exam Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/354
Last updated 7:31 PM on 1/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
355 Terms
1
New cards
Sagittal Plane
divides body into left & right
2
New cards
Coronal (frontal) Plane
divides body into anterior & posterior
3
New cards
Transversal Plane
divides body into superior & inferior
4
New cards
Supine
patient lies flat on the back
5
New cards
Prone
patient lies on the abdomen w/ head turned to either side
6
New cards
Trendelenburg
patient lies on the back w/ feet elevated
7
New cards
Types of Connective Tissues
adipose, ligaments, tendons, & cartilage
8
New cards
Adipose
stores fat cells
9
New cards
Ligaments
strong, flexible, bands that hold bones firmly together by the joints
10
New cards
Tendons
white bands that attach skeletal muscle to bone
11
New cards
What systems are lined by mucous membranes?
digestive, respiratory, & urinary
12
New cards
Serous membrane
double walled membrane that produces serous fluid
13
New cards
What does the pleural membrane line?
lines thoracic cavity & protects lung
14
New cards
Cyanosis
skin turns blue due to lack of oxygen
15
New cards
Hemorrhage
the release of blood from a broken blood vessel
16
New cards
Osteoblasts
synthesizes bone matrix protein & minerals
17
New cards
Osteocytes
lines the inside of fully formed bones & maintain bone tissue
18
New cards
Osteoclasts
degrade bone to initiate bone remoldeling
19
New cards
Bursae
fluid-filled sac that works as a cushion between tissues in joints
20
New cards
Foramen
a hole through which nerves and blood vessels pass
21
New cards
Hematopoiesis
the formation of blood
22
New cards
Fontanel
soft spot on a baby’s head
23
New cards
Synovial fluid
lubricating substance in joints
24
New cards
Where are ball & socket joints found?
shoulders & hips
25
New cards
Where are hinge joints found?
knees, elbows, & joints of the fingers
26
New cards
Where are pivot joints found?
radius & ulna, axis & atlas
27
New cards
Where are gliding joints found?
vertebrae
28
New cards
Bunion
a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe
29
New cards
Hammertoe
a foot condition in which the toe has an abnormal bend in the middle joint
30
New cards
Gout
a common form of inflammatory arthritis caused by hyperuricemia (too much uric acid in the body)
31
New cards
Osteomalacia
softening of the bones due to a lack of vitamin D & calcium
32
New cards
Osteoporosis
bones become weak & brittle due to lack of calcium
33
New cards
Rickets
imperfect calcification, softening, and distortion of bones
\
sx-delayed growth, bow legs weakness
causes- lack of vitamin D in children
tx- supplements
\
sx-delayed growth, bow legs weakness
causes- lack of vitamin D in children
tx- supplements
34
New cards
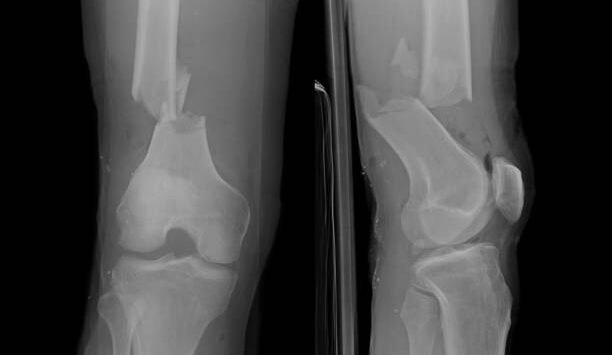
Comminuted Fracture
a fracture resulting in bone splinters
35
New cards
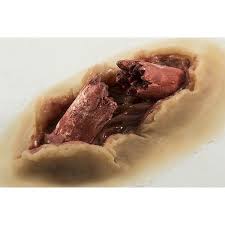
Compound Fracture
fracture where the bone breaks skin
36
New cards
Compression Fracture
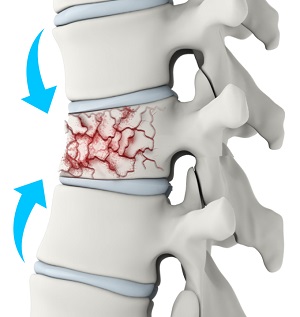
37
New cards
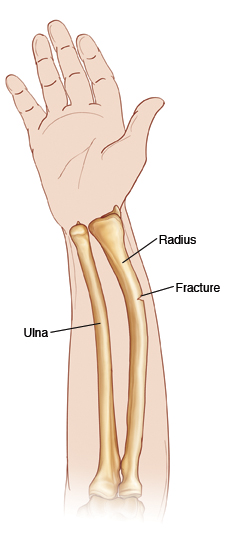
Greenstick Fracture
fracture due to the bending of the bone
38
New cards
Simple Fracture
bone is broken but skin is intact
39
New cards
Stress Fracture
tiny cracks in bone due to repetitive force
40
New cards
Kyphosis
exaggerated forward rounding of the upper back
41
New cards
Lordosis
excessive inward curvature of the spine; common in pregnant women
42
New cards
Scoliosis
side-ways curvature of the spine
43
New cards
Spina Bifida
a birth defect in which the spine fails to develop properly
44
New cards
Arthritis
inflammation of the joints
45
New cards
osteoarthritis
a type of arthritis where the flexible tissue of a joint breaks down
46
New cards
rheumatoid arthritis
an autoimmune disorder that attacks the joints
47
New cards
Abduction
the movement of a limb away from the midline of the body
48
New cards
Adduction
movement of a limb toward the midline of the body
49
New cards
Anaerobic
without oxygen
50
New cards
Fascia
a thin causing of connective tissue that surrounds and holds every organ, blood vessel, bone, nerve fiber, and muscle in place
51
New cards
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
smooth, skeletal, & cardiac
52
New cards
Skeletal muscle
voluntary & striated muscle tissue that are attached to bone by tendons
53
New cards
Smooth muscle
involuntary & visceral muscle that is found in the walls of the digestive system, uterus & blood vessels
54
New cards
Cardiac
involuntary muscle found in the heart
55
New cards
Sphincter
circular muscles in openings of esophagus & stomach, stomach & small intestine, anus, urethra, & mouth
56
New cards
Contractibility
the ability of a muscle to reduce the distance between the parts of its contents or the space it surrounds (to flex)
57
New cards
Excitability (irritability)
to the ability to respond to certain to certain stimuli
58
New cards
Extensibility
the ability to be stretched
59
New cards
Elasticity
ability of muscle to return to its original length when relaxing
60
New cards
Origin
the part of a skeletal muscle that is attaches to a fixed bone (it moves the least)
61
New cards
Insertion
the art of the skeletal muscle that moves during contractions
62
New cards
Synaptic cleft
neuromuscular junction
63
New cards
Fibromyalgia
a chronic condition that causes pain & tenderness throughout the body; more common in older aged women
64
New cards
Hernia
intestinal organ pushed through an opening in the muscle lining
65
New cards
Muscle spasms
sudden involuntary contractions of a muscle; usually caused by overuse of muscle & dehydration
66
New cards
Muscle Strain
tear to the muscle fibers or tendon; RICE for treatment
67
New cards
Tendonitis (tendinopathy)
inflammation of a tendon
68
New cards
Muscular Dystrophy
a genetic condition that causes progressive weakness & loss of muscle mass; usually affects boys
69
New cards
Tetanus (lockjaw)
serious illness caused by clostridium bacteria (found on rusty metals)
70
New cards
Abrasion
superficial injuries of the skin & visceral linings of the body
71
New cards
Albinism (achromasia)
a genetic disorder that is characterized by little or no melanin production; causes white hair, pale skin, & red or grey eyes
72
New cards
Alopecia arcata
an autoimmune disorder that causes damage to hair follicles which results in hair loss
73
New cards
Boils (carbuncles)
a group of pus-filled bumps forming a connected area of infection under the skin
74
New cards
Dermatitis
inflammation of the skin
75
New cards
Gland
an organ that produces & releases substances with specific purposes
76
New cards
Impetigo
a highly contagious but mild infection that is characterized by yellow crust; usually in children
77
New cards
Keratin
a protein that helps form hair, nails & epidermis
78
New cards
Macule
a flat, distinct, discolored area of the skin; freckles, flat moles, & port-wine stains
79
New cards
Melanin
a substance that produces pigmentation in hair, eyes & skin
80
New cards
Melanocyte
a cell found in melanosomes that produces melanin
81
New cards
MRSA
a cause of staph infections that is very difficult to treat due to its resistance to antibiotics
cx- staphylococcus bacterium
sx- bumps that are red, swollen, painful, pus filled & accompanied by a fever
tx- oral clindamycin or IV vancomycin
cx- staphylococcus bacterium
sx- bumps that are red, swollen, painful, pus filled & accompanied by a fever
tx- oral clindamycin or IV vancomycin
82
New cards
Papule
a solid or cystic raised spot on the skin
83
New cards
Puritis
itchy skin
84
New cards
Psoriasis
a skin disease that causes a rash with itchy & scaly patches; most common on the knees, elbows, trunk & scalp
85
New cards
Pustule
pus-filled bump (pimple)
86
New cards
Sebum
an oily substance produced in the sebaceous glands; forms a protective coating on the skin’s surface
87
New cards
Stratum corneum
the most outer layer of the skin that acts as a barrier from water exciting & bacteria; waterproof due to keratin
88
New cards
Stratum germinativum (basale)
the deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basal lamina & is attached to it by hemidesmosomes
89
New cards
Tumor
a swelling of a part of the body causes by an abnormal growth of tissue
90
New cards
Ulcer
a sore on the visceral lining of an organ
91
New cards
Urticaria (hives)
a raised itchy rash
92
New cards
Vesicles
a thin-walled sac filled with a fluid
93
New cards
Verrucae (plantar warts)
hard growths on the heel or balls of the feet caused by HPV
94
New cards
Stratum lucidum
a translucent layer of the epidermis that regulates temperature & amount of water released into the environment
95
New cards
Stratum granulosum
a thin layer of cells in the epidermis that accumulates dense basophilic keratohyalin granules that forma waterproof layer
96
New cards
Stratum spinosum
a layer of the epidermis that makes the skin strong & flexible
97
New cards
Papillae
ridges in stratum basale that arise from dermis that help with grip
98
New cards
Cortex
Outer layer of hair
99
New cards
Medulla
inner layer of hair
100
New cards
Arrector pili
a tiny muscle that attaches to the base of a hair follicle at one end and to dermal tissue on the other end