Lecture 10 - Genetic Engineering
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Genetic Engineering
the direct manipulation of DNA to alter an organism's characteristics in a particular way.
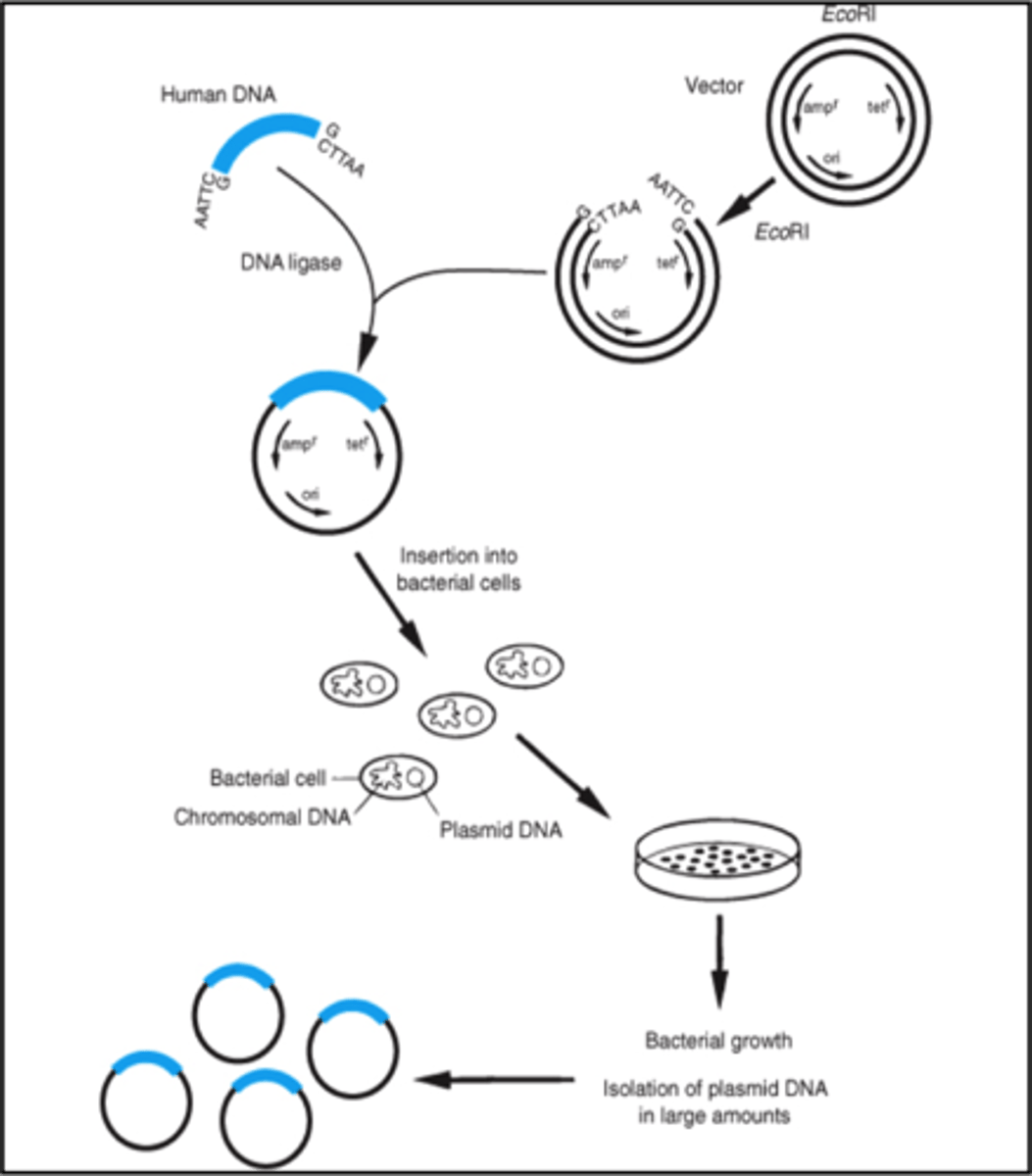
How to clone a human gene (insulin) into a bacterium:
1. Purify plasmid
2. Make many copies of target gene DNA (insert)
3. Use restriction enzymes* to cut insert and plasmid
4. Ligate cut insert into cut plasmid with DNA ligase*
5. Transform cells with recombinant plasmid
6. Induce expression of gene
7. Purify products
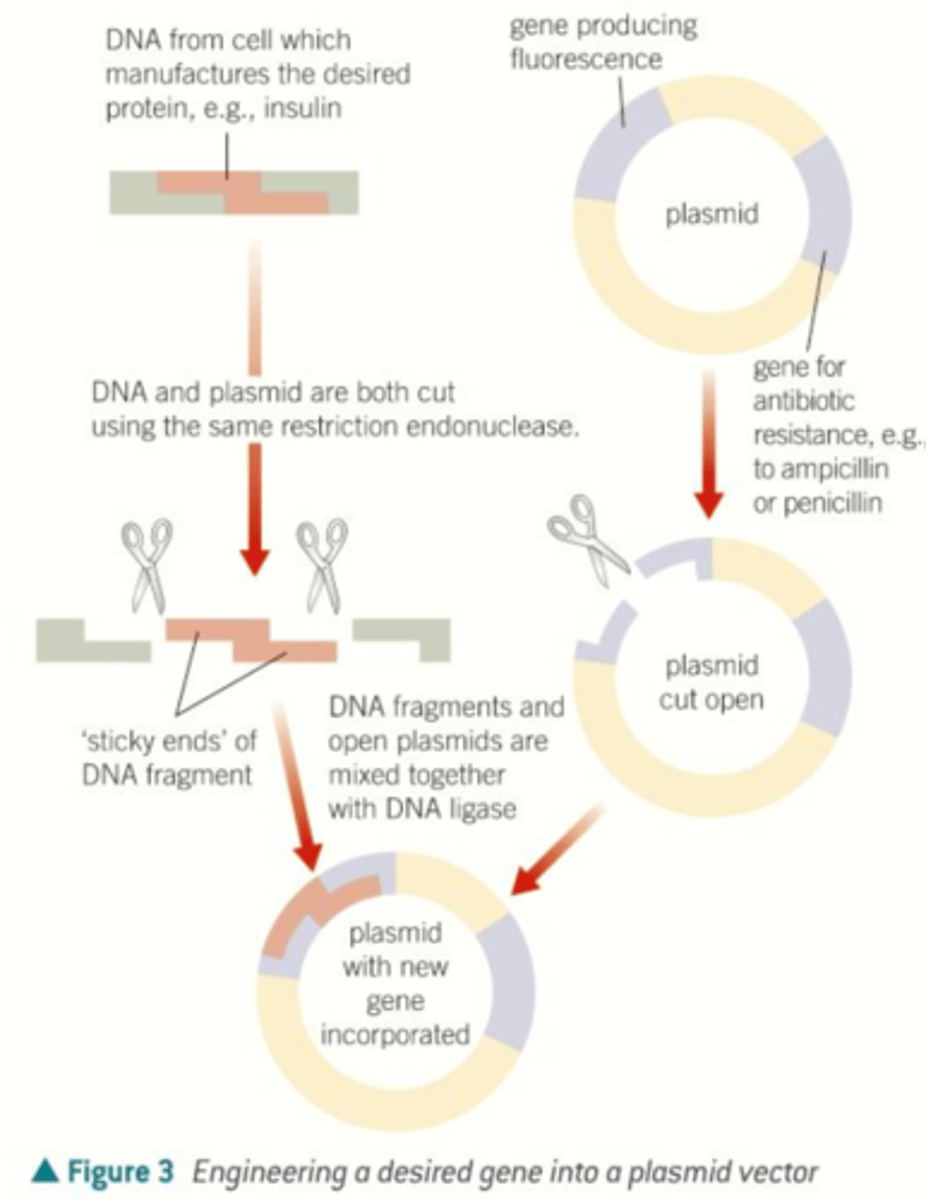
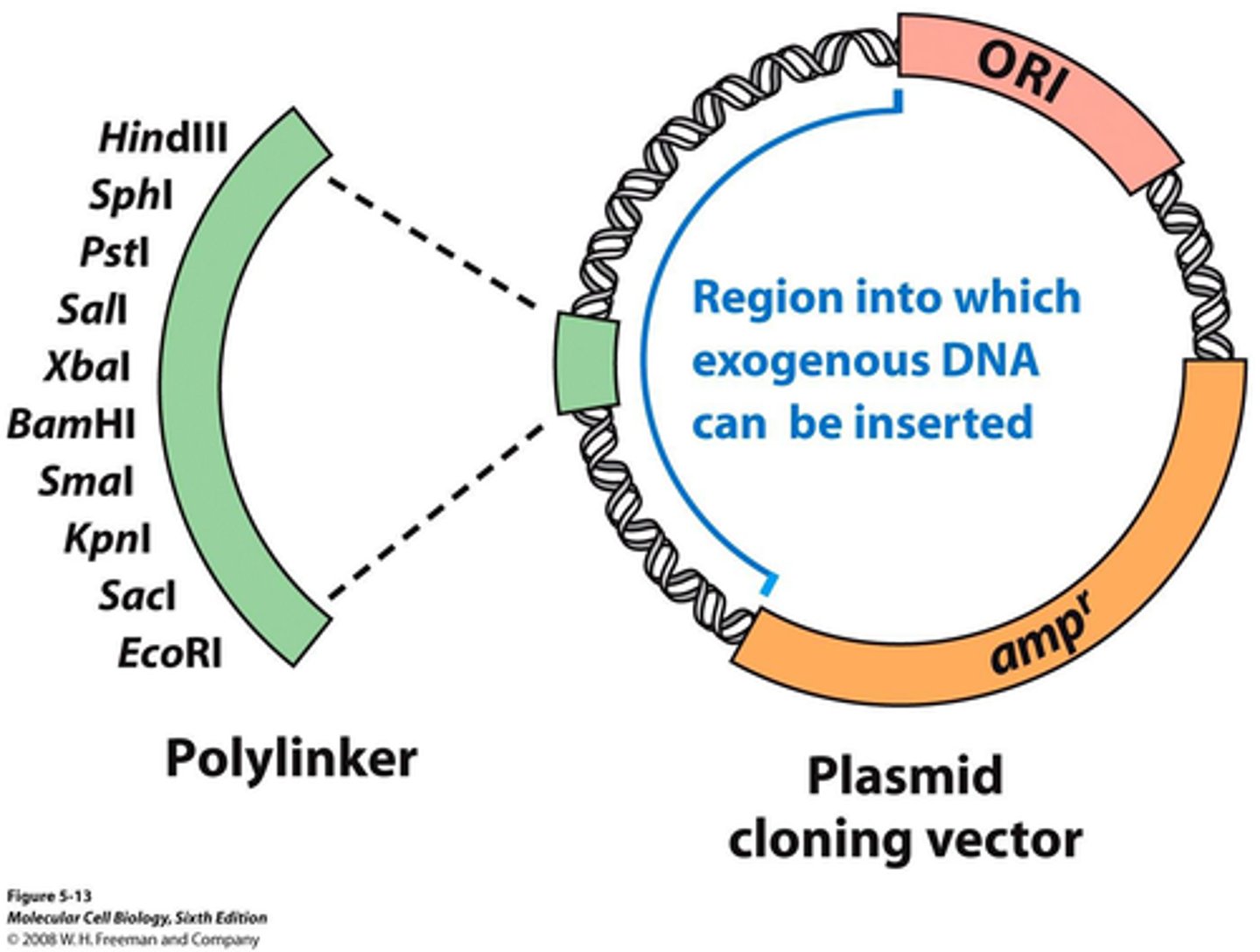
1. Purifying Plasmid
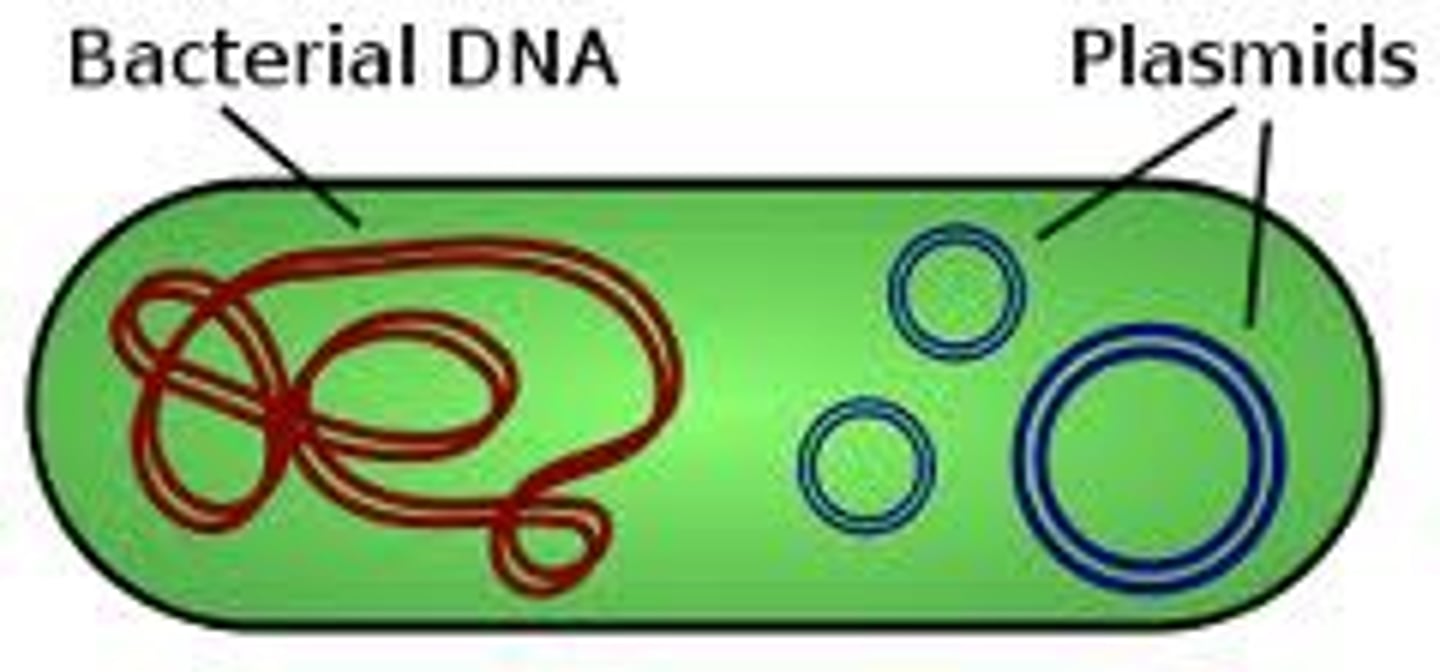
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
Vectors
small pieces of DNA that can be stably maintained by the recipient
can introduce foreign fragments to encode new properties
they have direction; trasmit genes from one organism to another
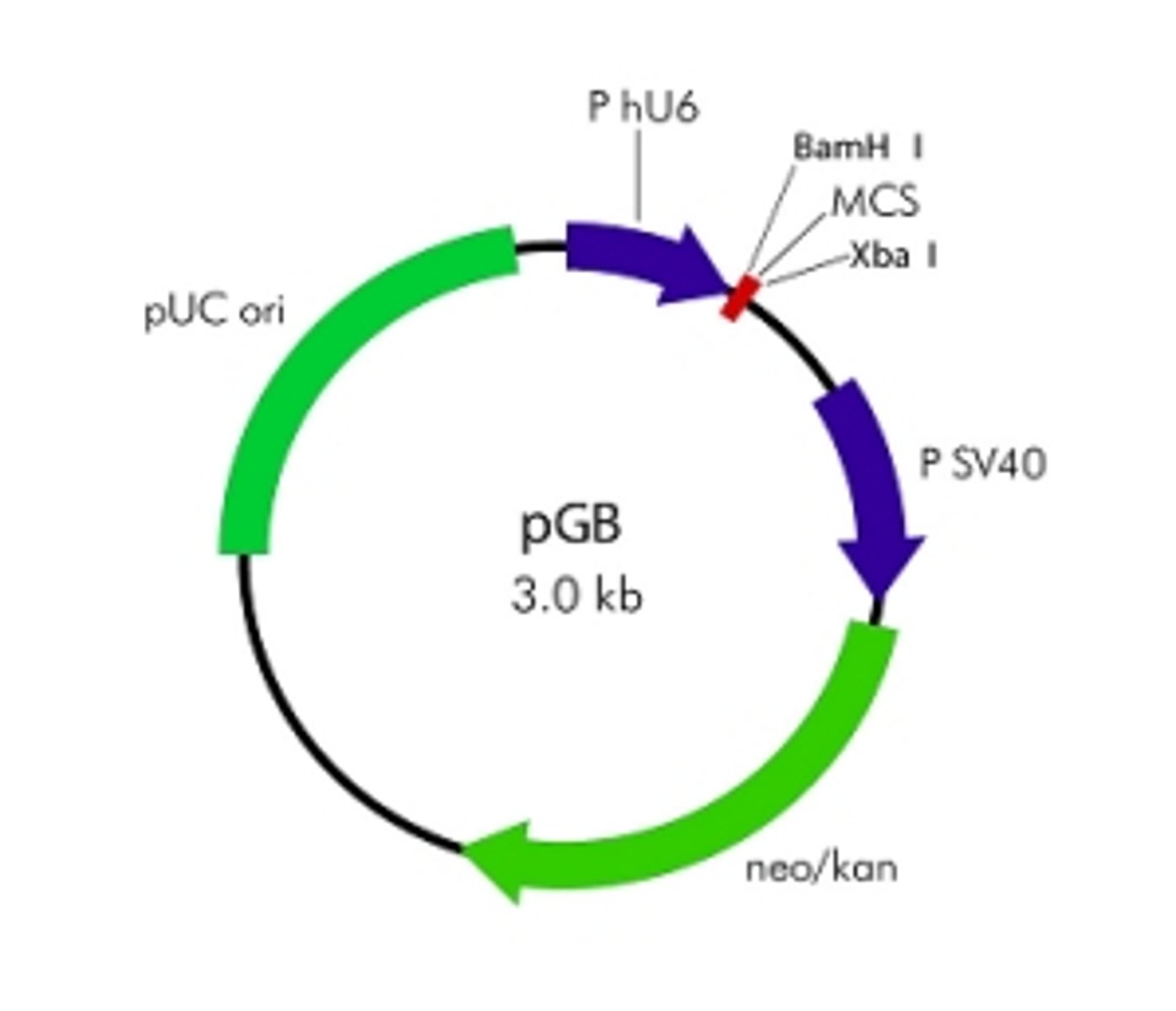
Cloning Vector
a DNA molecule used to carry and deliver foreign genetic material into a host cell, enabling the replication and amplification of that DNA.
Plasmid Properties
contains a origin of replication
selectable marker (AbxR)
restriction enzyme cut sites
high copy number
small size
2. Make many copies of target gene DNA (insert)
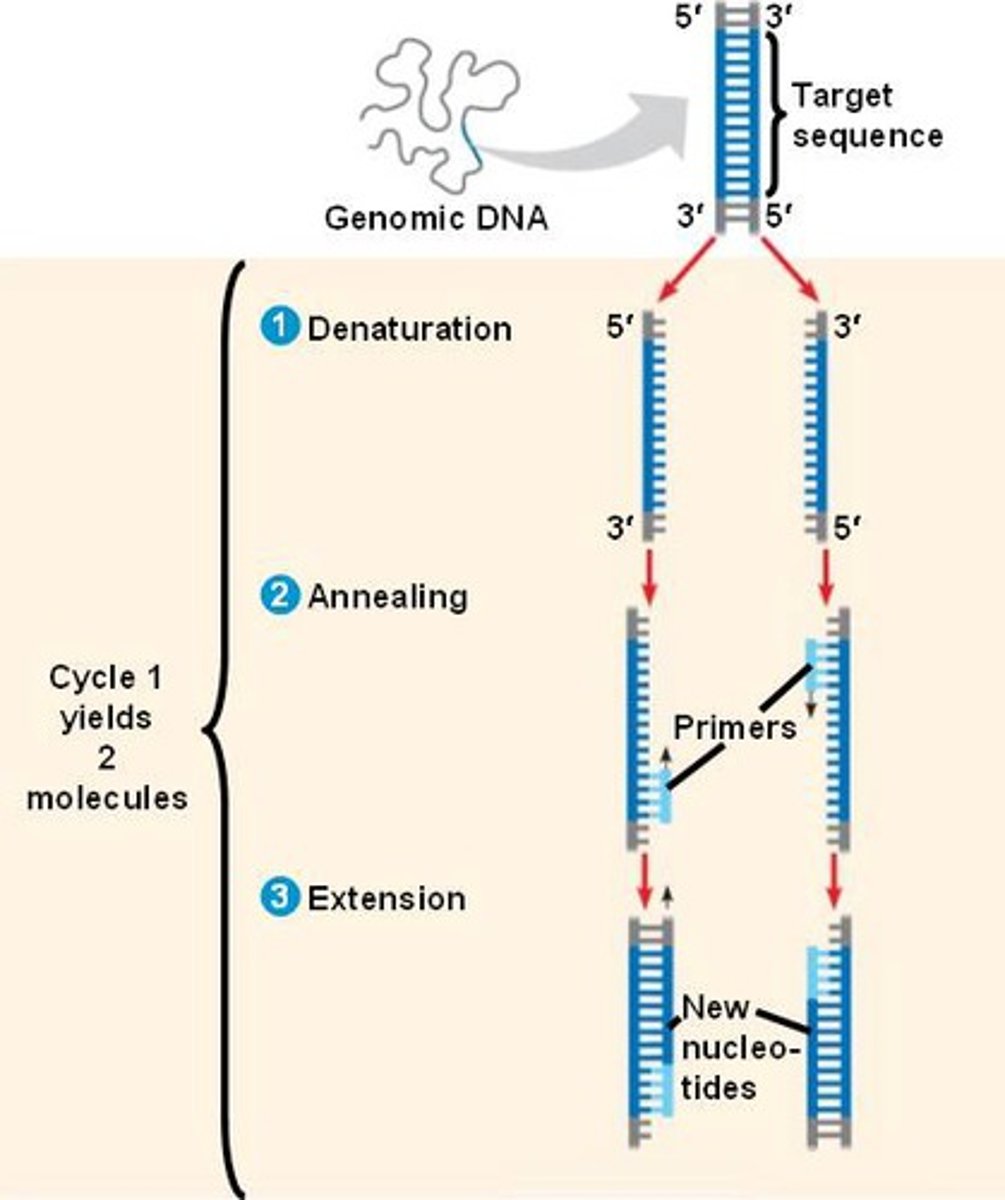
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
an in-vitro method of amplifying DNA replication of an insert to produce a bunch of copies
PCR X Insulin
insulin gene contains introns so it must be converted to cDNA
Complementary DNA (cDNA)
reverse transciptase performs reverse transcription on mRNA (introns are spliced out) to make DNA without any introns
Distinguish the process to "clone" a prokaryotic gene and a eukaryoticgene into a prokaryote.
Prokaryotic DNA: already intron free
Eukaryotic DNA: has introns, must do reverse transcription (must DNA → mRNA → cDNA)
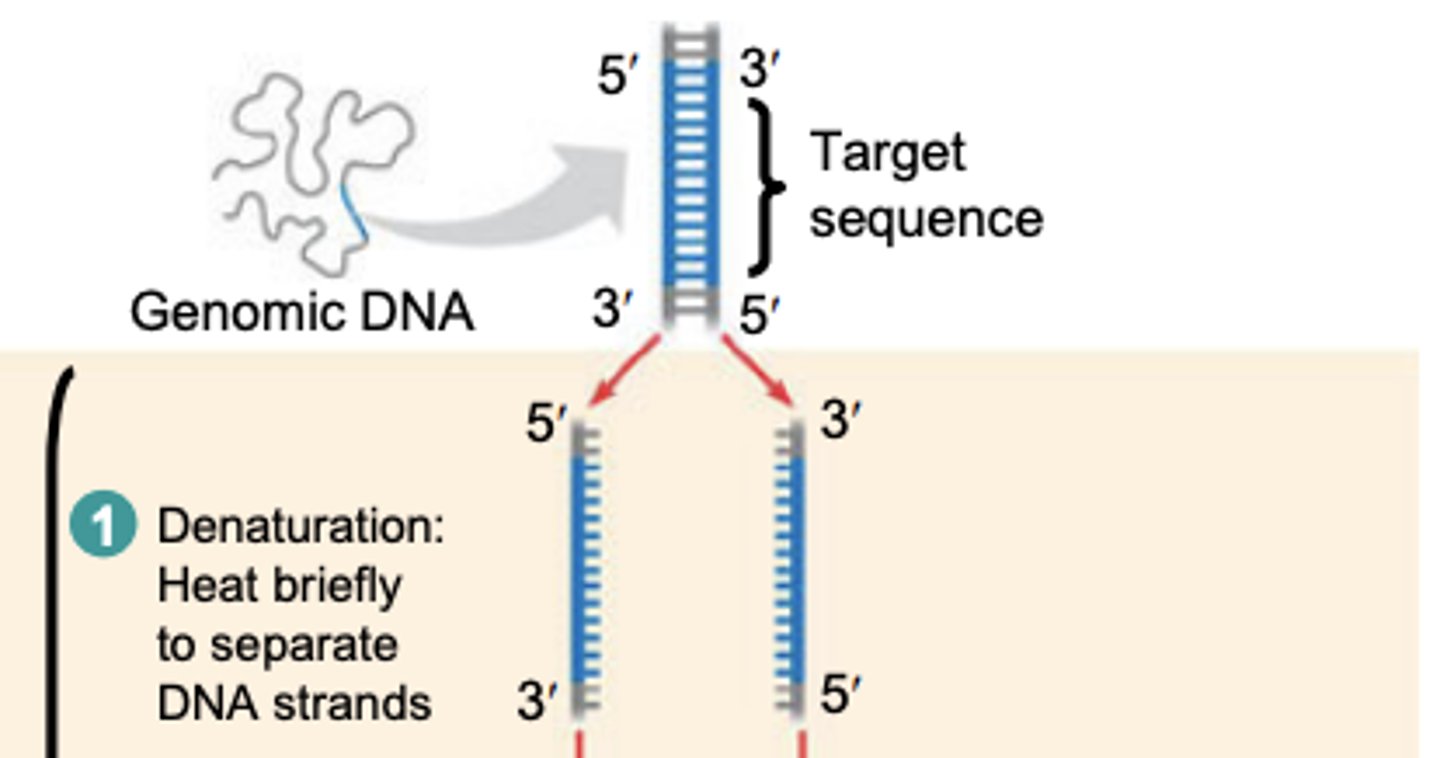
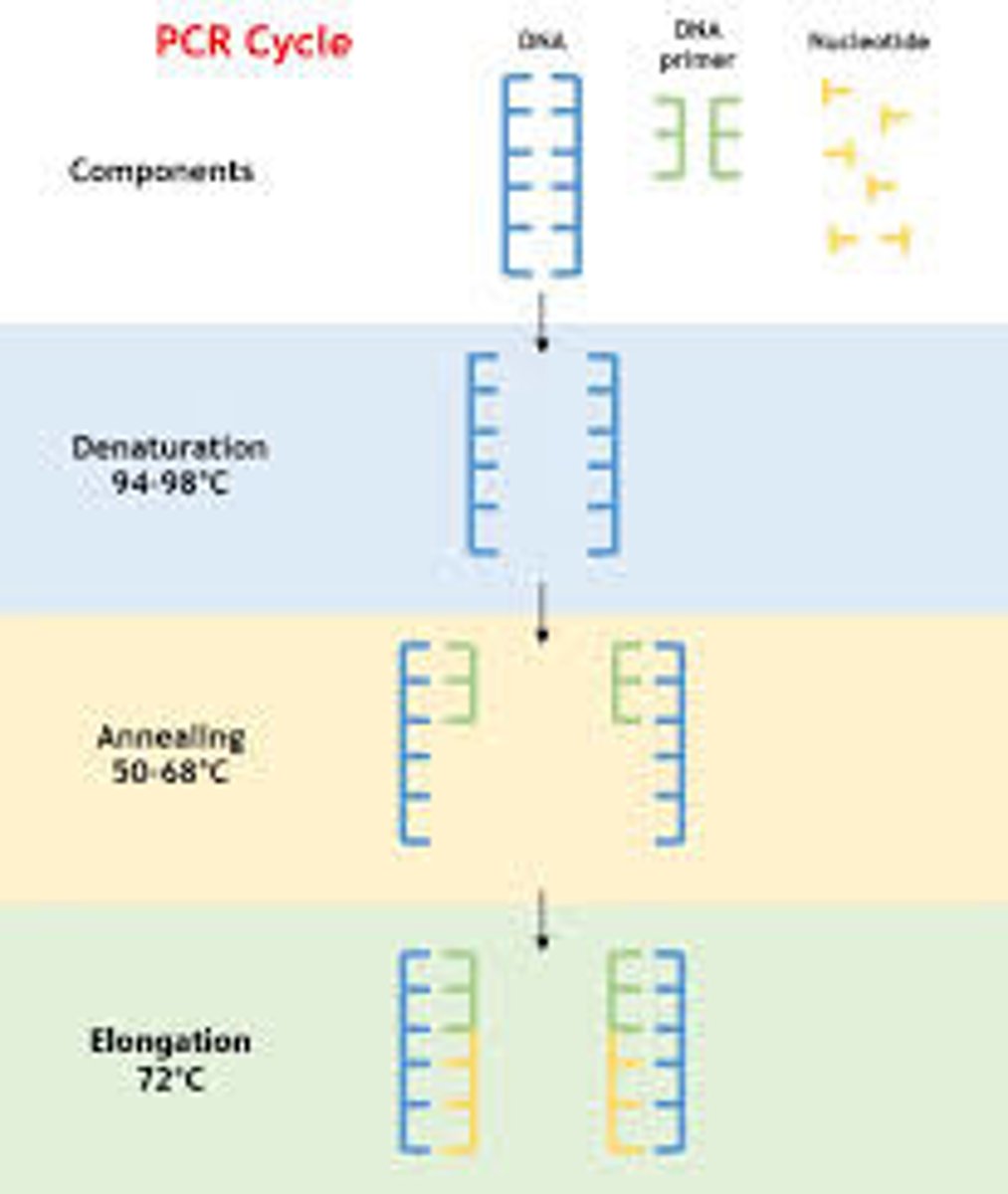
PCR: Denaturation
Heat (95C) briefly to separate DNA strands
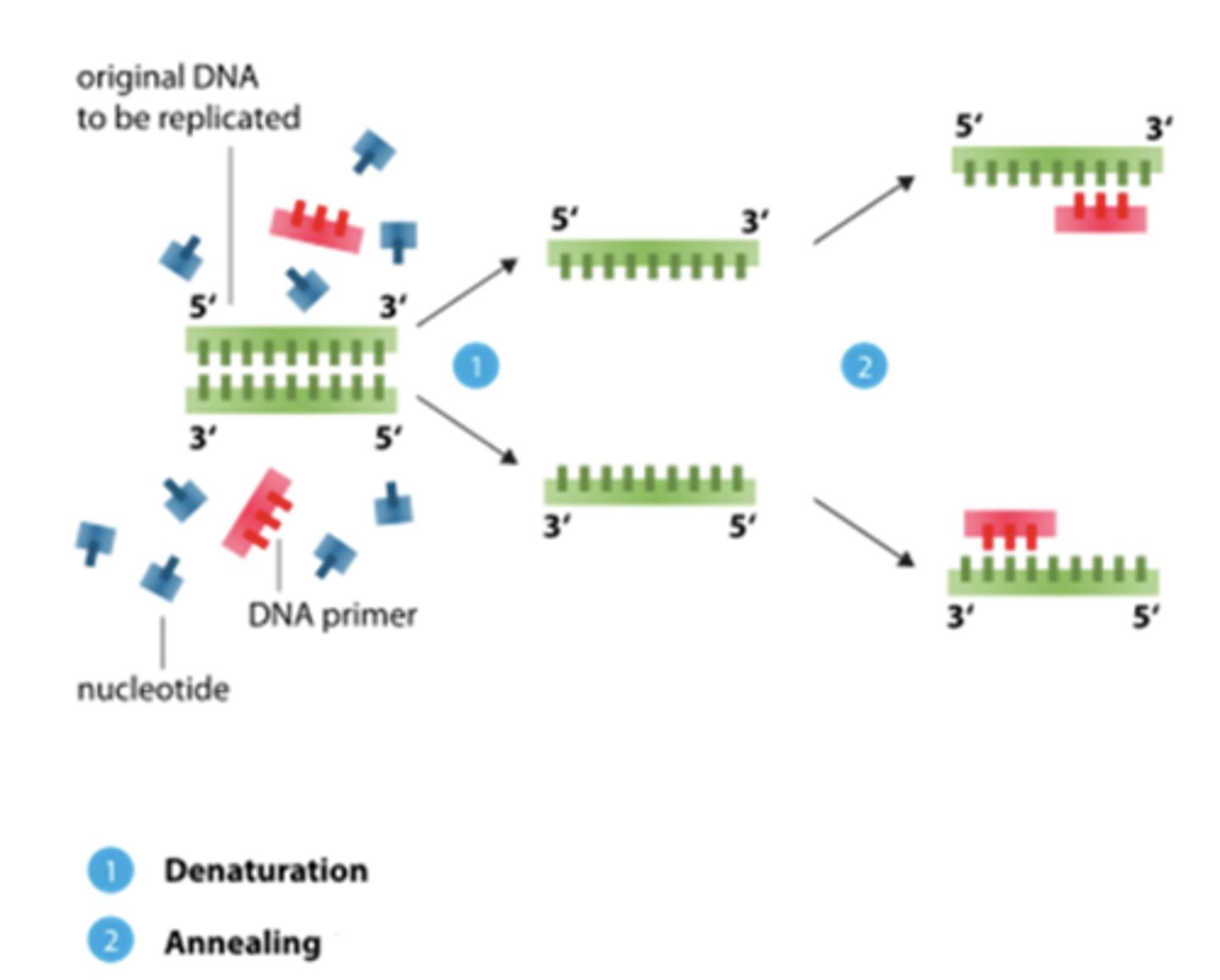
PCR: Annealing
DNA sample is cooled (60C) allowing primers to attach to opposite ends of the target sequence
PCR: Extension
increase temperature - add DNA polymerase and nucleotides to produce two complete strands
3. Use restriction enzymes to cut insert and plasmid
Restriction Enzymes (RE)
endonucleases that cut (hydrolyze the phosphodieester bond of) the phosphate-sugar backbone of dsDNA at specific sequences
Endonuclease
cut inside a DNA strand (e.g., restriction enzymes in defense, or in repair).
Exonucleases
chew DNA from the ends (important in repair and DNA processing)
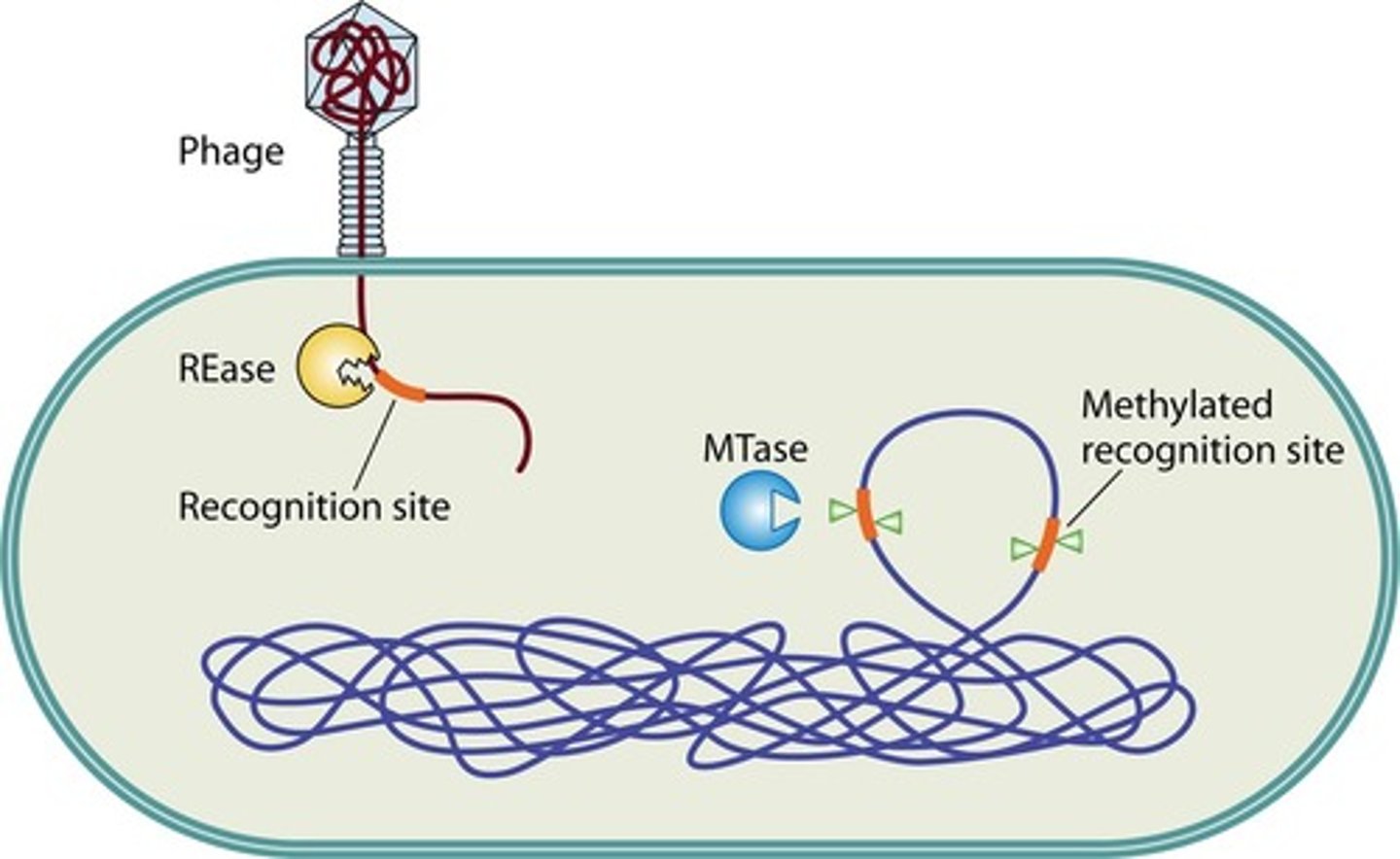
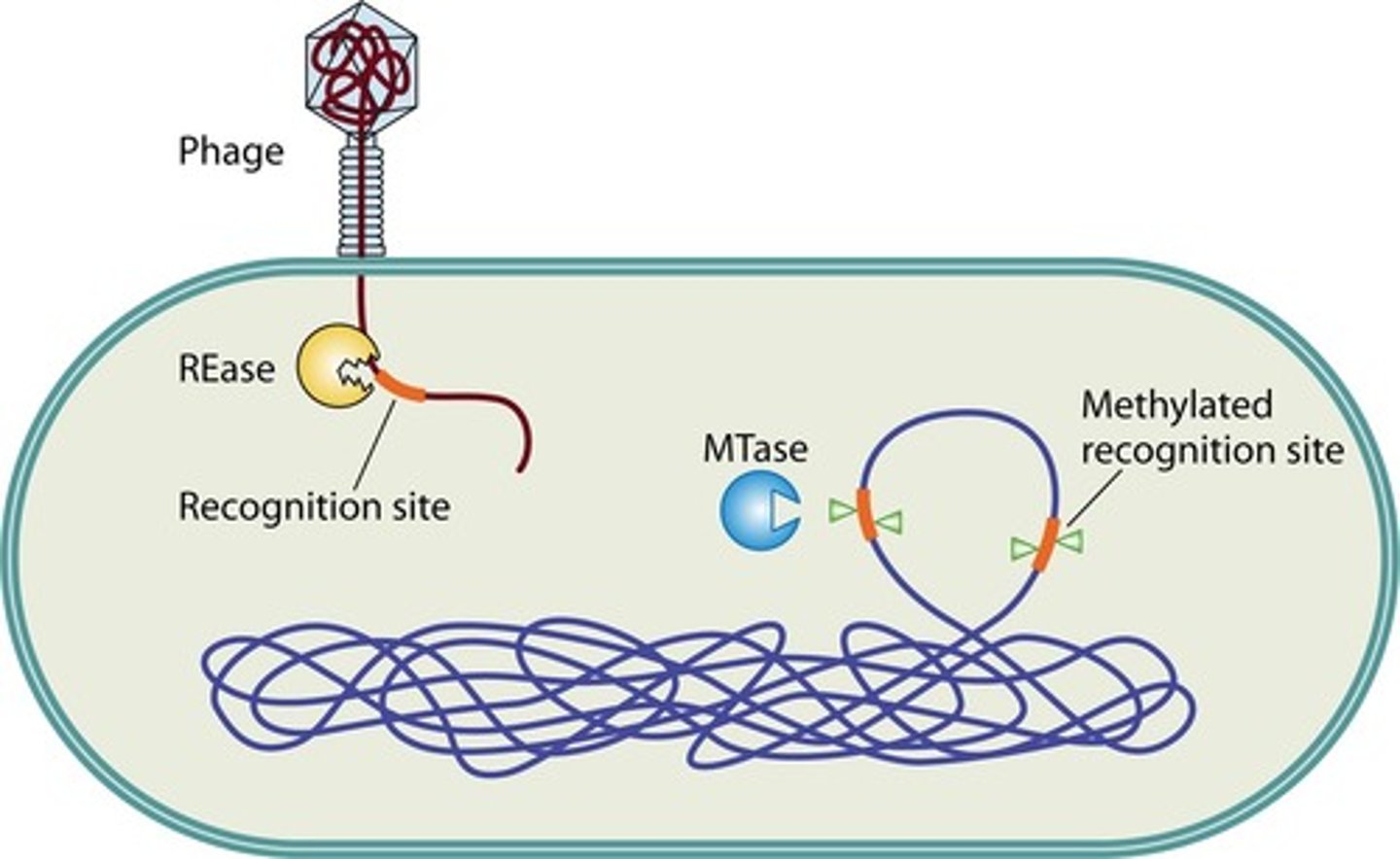
Restriction-Modification (RM) System
to protect aaginst phase infection
to protect host DNA with recognition sequence
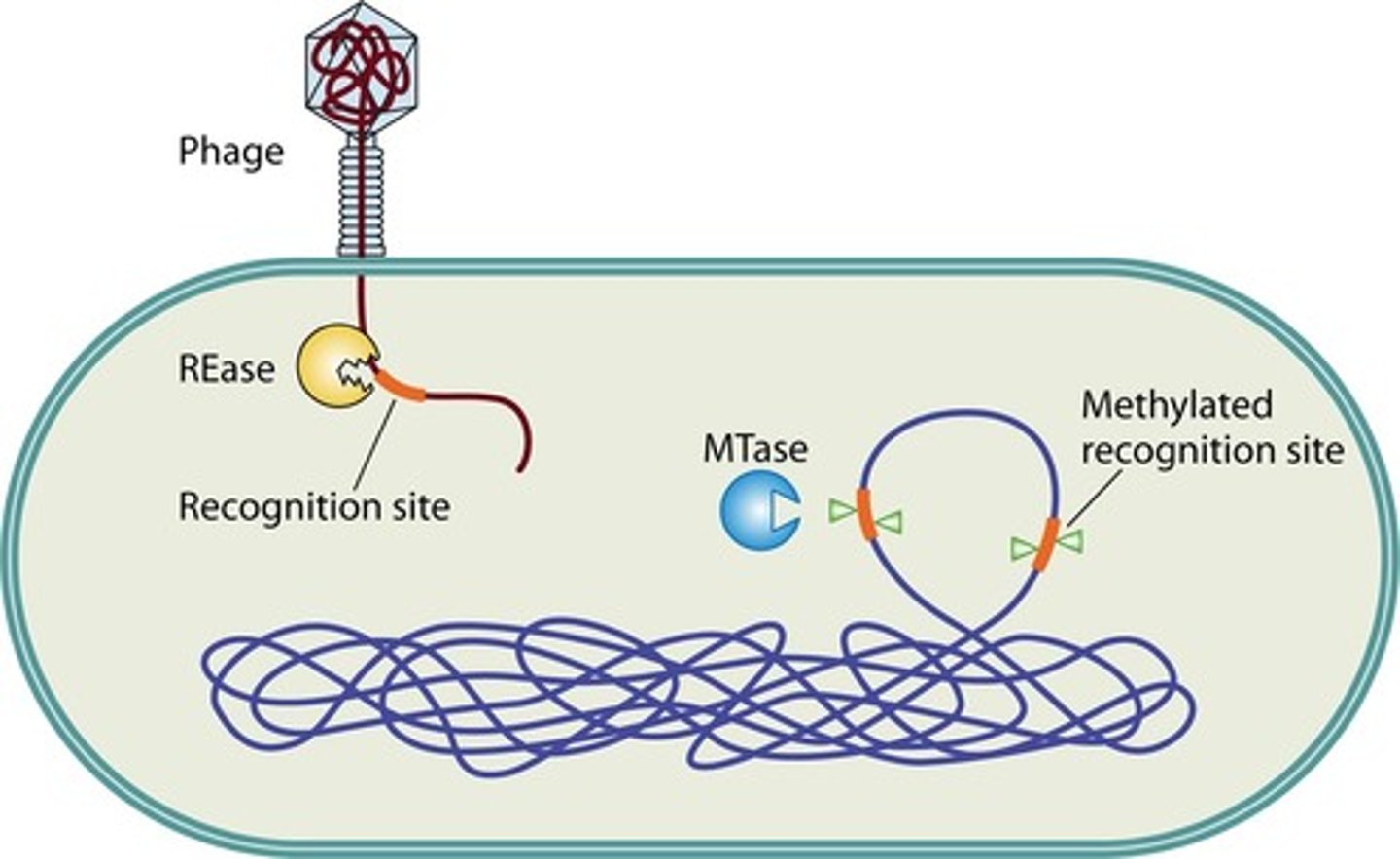
RM System: Enzymes
Restriction Enzymes (RE)
Methylase
To protect against phage infection
a RE cuts dsDNA (e.,g viral genomes) that carry the RE's recognition sequence, which prvents replication of the viral genome
To protect host DNA with the recognition sequence
A methylase that recognizes the same DNA sequence as its RE partner modifies the DNA by adding a methyl group; methylation at its recognition site inhibits the partner RE from cutting the DNA
Gel Purification
isolates the DNA segment that was cut ("insert")
Electrophoresis
A process where DNA fragments are separated according to size using electrical charges, separating the insert
4. Ligate cut insert into cut plasmid with DNA ligase*
DNA ligase joins together stickey ends of the DNA insert and the plasmid = recombinant plasmid
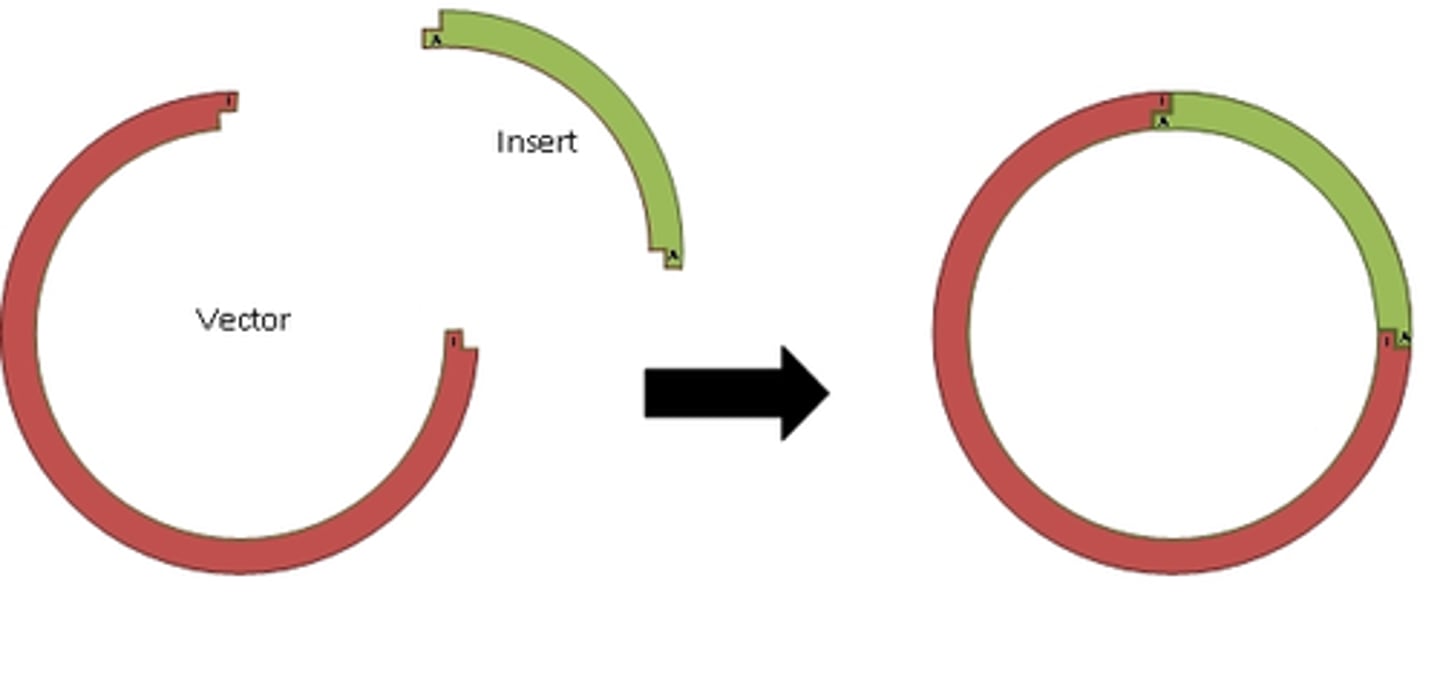
5. Transform cells with recombinant plasmid
perform artificial transformation with recombinant plasmid. then, plate treated cells onto media with selection (e.g., antibiotic) to select for transformants carrying the selectable marker (e.g.,abxR)
Methylation
chemical tag that marks host DNA as "self," and also signals during replication/repair
CRISPR
clustered, regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
CRISPR-Cas
a system of bacterial immune defense
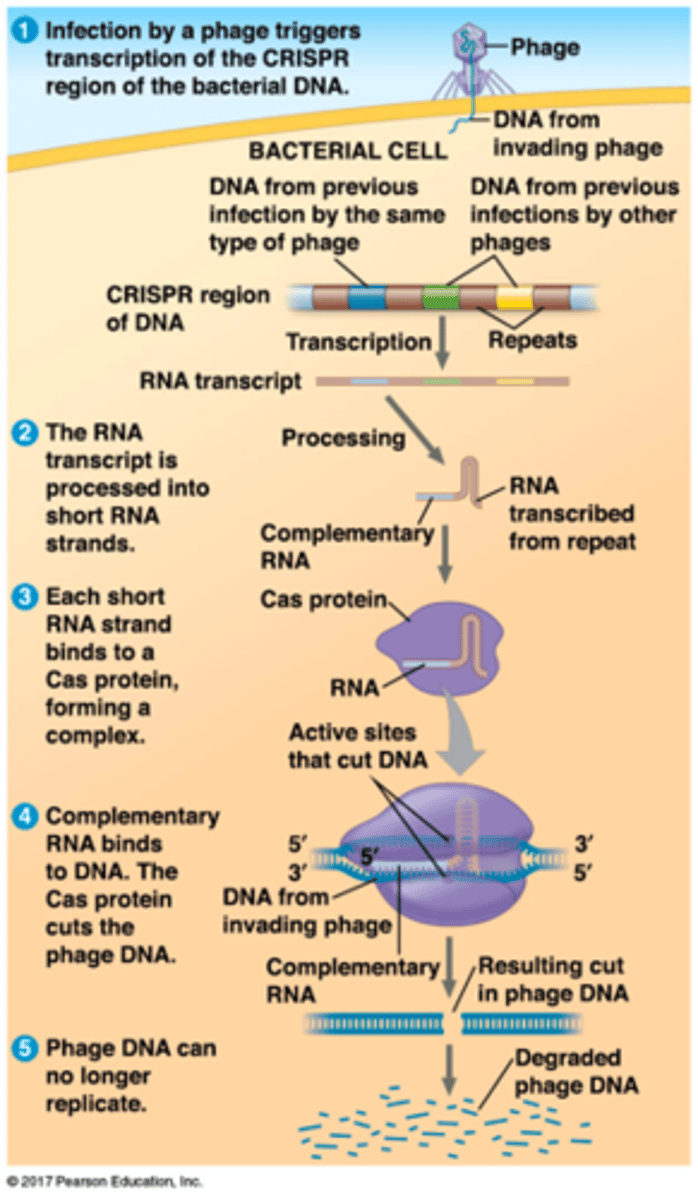
CRISPR-Cas Mechanism
1. Spacers
2. crRNA
3. Cas9
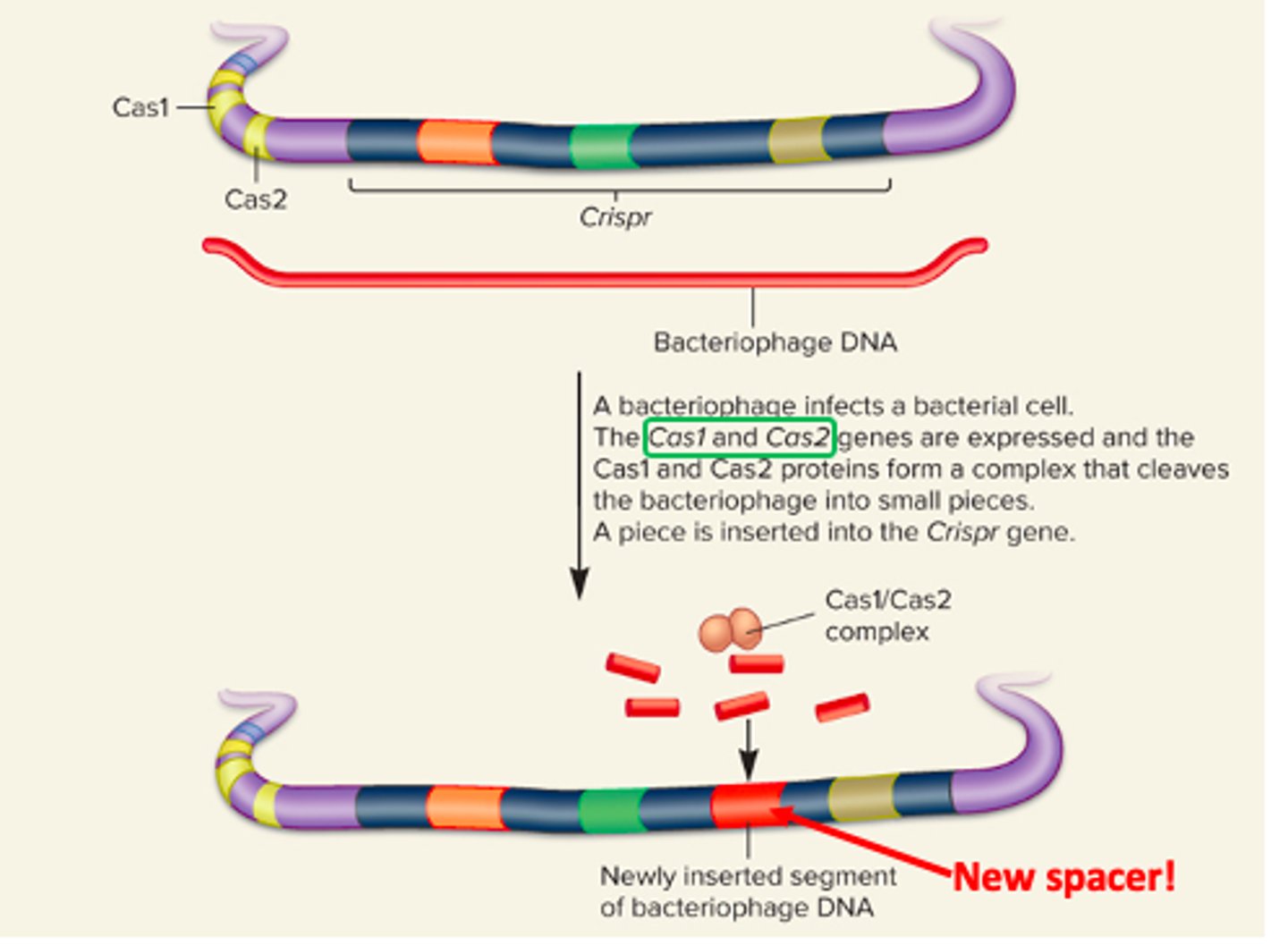
Spacers
CRISPR array is assembled on bacterial chromosome by the insertion of phage sequences (spacers) and a CRISPR-specific repeated sequence
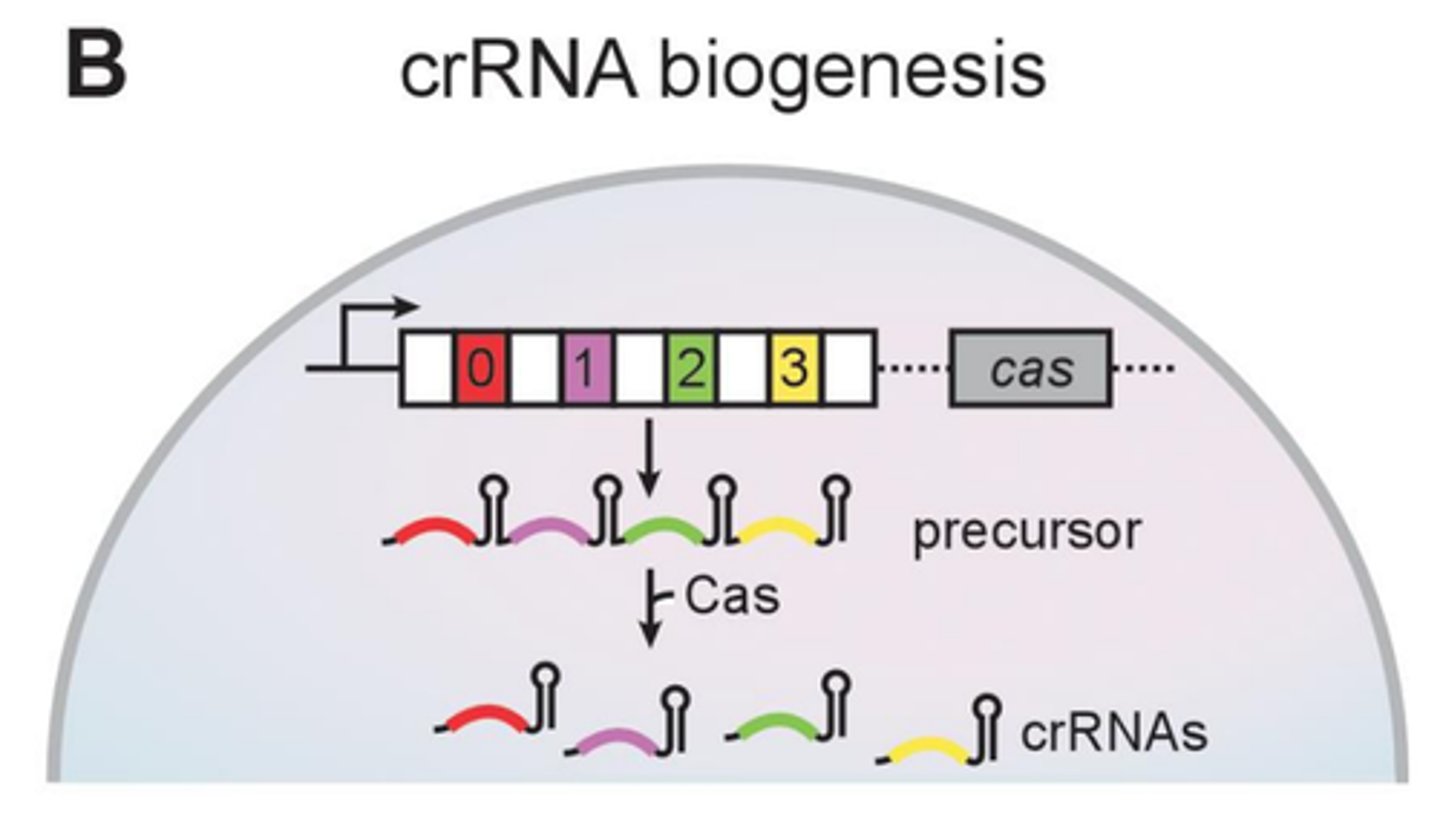
crRNA
CRISPR array is transcribed to produce precursor RNA (pre-crRNA)
3. Cas9
crRNA that match viral sequence recruits Cas9 which cuts the viral genome, preventing phage replication
CRISPR/Cas9 X Genome Editing
Use Cas9 to cut a specific section of DNA to precisely delete, insert, or modify a gene