Bio Exam 3- Ecology
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
295 Terms
biotic
living components (organisms)
abiotic
nonliving components (temperature, pH, water, wind, salinity, etc.)
trail following
ants mark the way with pheromones (tells that food lies ahead on pathways)
path integration
on an outbound trop, any monitors length and direction of each segment and puts information together on the way home
orientation
adopting a path relative to an environmental cues (sun compass, polarization compass, magnetic compass)
honeybee waggle dance
first part of dance directs orientation, second part indicated how far to fly
migration
movement between locations, remain for a substantial length of time before returning, and is often periodic
society
group of individuals of one species, organized in a cooperative manner
social behavior
includes individual's behaviors that integrate them, and group behaviors of entire societies
pros of living in a group
-less susceptible to predators
-generational learning
-sharing work
-discover resources quicker
-thermoregulation
cons of living in a group
-competing for resources
-disease
-reduced genetic diversity
-more visible to predators
eusociality
consists of nonreproductive adults that help other members of the group, usually their mother (honey bees)
altruism
cost to one individual which aiding another
home range
space occupied by an individual, but others are not excluded
territory
other occupants are actively excluded
hybridization
behavior can prevent ________
hybridization
the process of an animal or plant breeding with an individual of another species or variety
term associated with limited postnatal period for learning
behavioral imprinting
term associated with mechanistic explanation
proximate cause
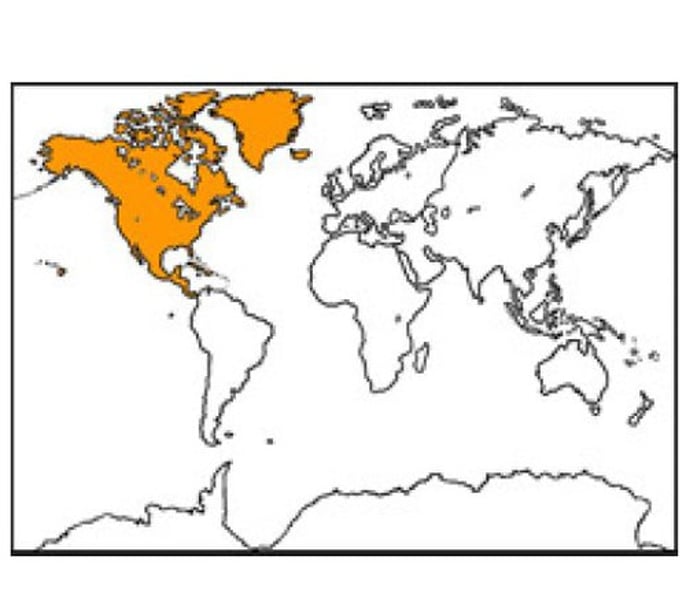
nearctic
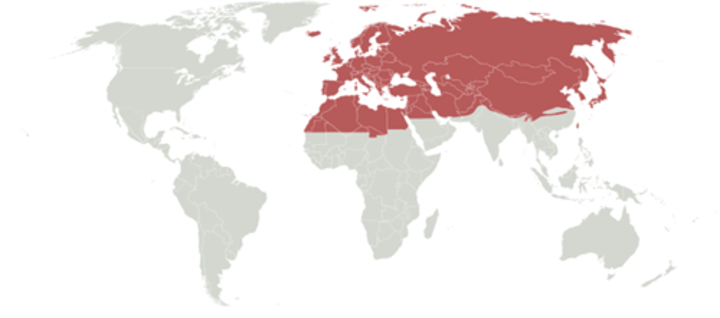
palearctic
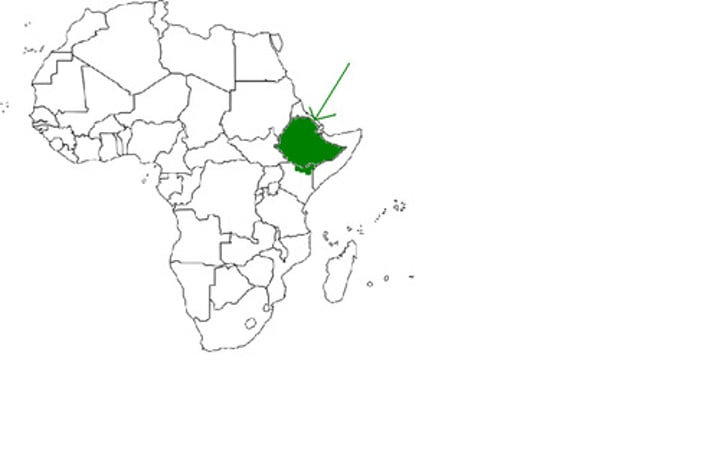
ethiopian
Africa
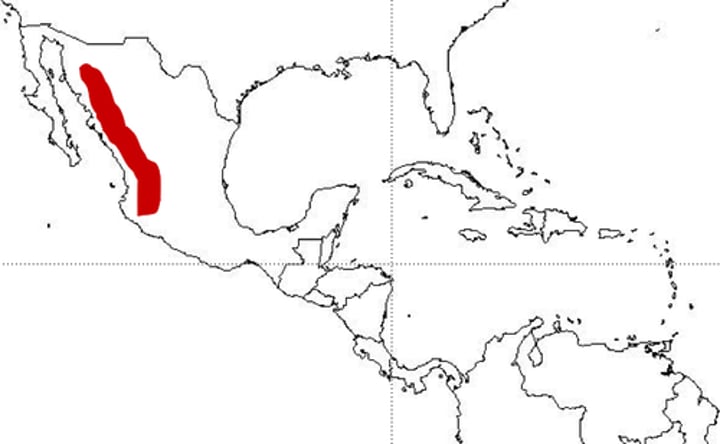
oriental
of, from, or characteristic of East Asia
australian
`
antarctic
scale of ecological organization
1. organism
2. population
3. community
4. ecosystem
5. biosphere
organism
survival, repro, and behavior
population
population dynamics, demography
community
interactions among populations, species diversity, trophic dynamics, competition, succession
ecosystem
FIRST LEVEL WITH ABIOTIC; living things and the environment in which they live
biosphere
all organisms on Earth and what they occupy
what drives global climate?
sunlight, movement of the planet, and atmospheric/ocean circulation
weather
short-term, day-to-day state of atmosphere (minutes to weeks)
climate
long-term behavior of the atmosphere (years to decades)
solar energy input varies with _____
latitude
sunlight is spread over the ______ (larger/smaller) surface area
larger
seasonality is a consequence of what two factors?
tilt and movement
revolution
circle external axis
rotation
turning on internal axis counterclockwise
tropical latitudes have more intense sunlight, causing air to...
rise and cool
adiabiotic cooling
compress gas expands, causing it to cool (more volume when hot, less when cool)
what happens to water in air as the air cools?
it condenses
Hadley cells
a large-scale atmospheric convection cell in which air rises at the equator and sinks at medium latitudes, typically about 30° north or south.
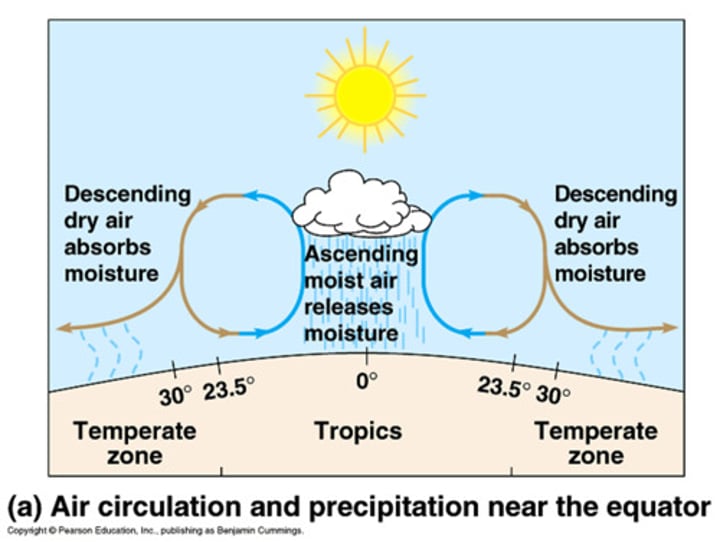
what causes prevailing winds?
Atmospheric circulation + the earth's rotation (near equator flows faster)
if air is moving towards the equator, it is going from ____ to ____, so it will fall behind
slow, fast
topography
variation in elevations (can alter regional climate)
upwelling
the upward movement of ocean water toward the surface as a result of diverging currents
water has a _____ (high/low) heat capacity, causing the temperature to fluctuate ____ (more/less) than land
high; less
growing season
when the temperature is warm enough for plants to grow
biogeography
spatial distributions of species
physical geography
spatial distribution of earth's climates
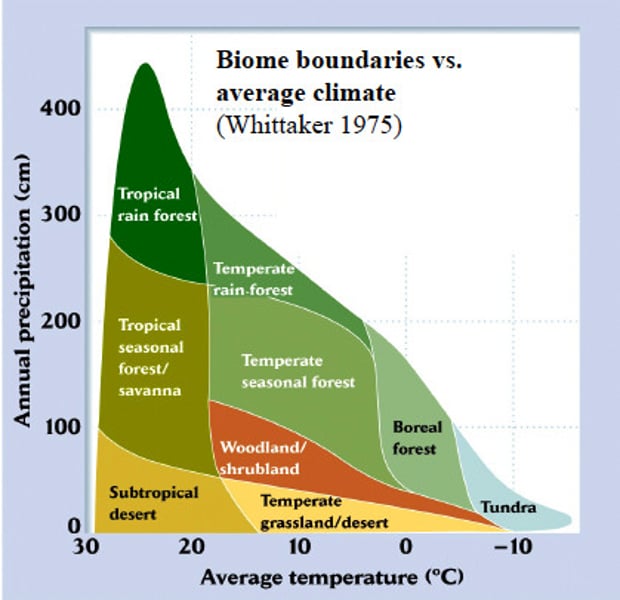
biome
a distinct physical environment that is inhabited by ecologically similar organisms with similar adaptations
terrestrial biomes
usually distinguished by the dominant type of vegetations
what determines a biome?
temp, precipitation, seasonality, siols, and disturbance
global climate patterns are linked to
biomes
should be able to recreate and label this graph?
aquatic biomes
climate less important, abiotic factors (water depth, temperature, pressure ,salinity, oxygen) more important
intertidal zone
Portion of the shoreline that lies between the high and low tide lines
hydrothermal vent
an opening in the sea floor out of which heated mineral-rich water flows (can have primal repro)
conservation ecology
understand and prevent extinction of vulnerable species
restoration ecology
restore health of damaged ecosystems
population ecology
study of births and deaths and dynamic forces that regulate the population
two ways of describing populations
spatial (density and dispersion) and temporal (rates of B/D)
density
# of individuals per unit area of volume
dispersion
pattern of spacing among individuals usually within the boundaries of the population
mark recapture method (CMR, capture-marker-recapture)
1. capture critters
2. cark critters
3. recapture of marked individuals
4. do math
N(est) =
M1 * Ns2 / M2
(# marked on day 1 * # captured on second day) / # marked on day 2
main dispersion patterns
clumped, random, uniform
clumped
social patterns and resource distribution
random
less common in nature; most likely a result of wind dispersion (tends to occur in plants)
uniform
equal spacing; variability less; due to allelopathy, territoriality, or competition
allelopathy
plants excrete toxic substance to limit competition
demography
study of processes that influence births, deaths, and population growth rate
principle of allocation
how can you allocate resources to different things than reproduction
what is always first priority of resource acquisition?
maintenance
semelparous species
expend their energy in a single, immense reproductive effort (all eggs in one basket)
interoparous species
exhibit repeated reproductive cycles
life history (traits that make up an organism's schedule of repro) examples
age at first repro, frequency and duration of repro, total number of offspring, life expentancy
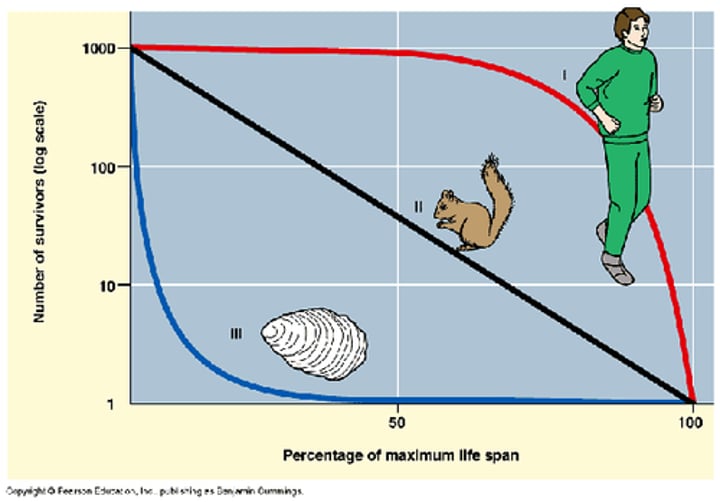
Type I survivorship curve
humans; parental care ,few offspring, ensures early years survival
Type II survivorship curve
birds 9c-strategist); average chance of surviving every year they live, some parental care, intermediate # of offspring
Type III survivorship curve
plants (r-strategists); no parental care, many offspring , most die early but ones that survive live long
survivorship curve
log scale on y axis
BD model
N/t = B-D
n = pop size
t = time
B = births
D = deaths
per capita
expressed on a per individual basis
birth rate equation
B = bN
B= # of births
b= per capita birth rate
N = population
death rate equation
D = dN
D = number of deaths
d = per capita death rate
N = population
per capita rate of increase formula
N/t = rN
r = b-d
r max
used when resources are unlimited; remains constant
if r remains constant, population doubling time will
also remain constant
carrying capacity (K)
max pop size that an environment can support
logistic growth model
N/t = r(max)N(K-N/K)
growth rate modifier
K-N/K
when N=0, the growth rate modifier is
1
when N = K, the growth rate modifier is
0
per capita growth rate
r - r(max) * (K-N/K)
assumptions of logistic model
-no immigration or emigration
-all individuals contribute equally (rmax is constant)
-environment (k) is constant
biotic factors
operate in a density-dependent manner (parasitism, disease ,competition, predation)
abiotic factors
operate in a density-independent manner (precipitation, natural disaster, habitat, temperature)
r-strategists
large numbers of offspring, limited parental care (unstable environments) (ex. rabbits)
k-strategists
few offspring, a lot of parental care (stable, predictable environments) (ex. elephants)