nurs320 - periop + perianesthesia
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
diagnostic surgery
exploratory surgery
palliative surgery
pt. has terminal illness - surgery to make patient life more comfortable
cosmetic surgery
enhance appearance
elective surgery
patient choosing to complete surgery
urgent surgery
patient needs surgery but not ASAP
emergency surgery
patient needs surgery ASAP
surgical risk factors
age
nutrition status
fluid and electrolyte balance
general health status
medications
what assessments should the nurse complete pre-op to ensure the patient is ready for surgery?
H&P exam
height and weight
teaching
medications
labs & diagnostic tests
operative site marked by physician
questions answered
emotional support
what teachings should the nurse complete pre-op?
know how to manage a drain or walk on crutches so after surgery nurse only needs to RETEACH!
informed consent that needs to completed before surgery
surgery consent
anesthesia consent
blood consent
who can consent to surgery?
adults
minors
emancipated minors
witness to consent - nurse watches pt. sign consent
emergency situations - in pt. notes to bring pt. for surgery without consent for life-threatening situation
immediate pre-op assessments
baseline vital signs
provide oral hygiene, remove dentures, record loose teeth
remove nail polish, cosmetics, hair pins, prostheses
have patient void
check name band
review consent
administer pre-op medications if ordered
elevate side rails
complete pre-op checklist
members of surgical team
surgeon - resident, med student
surgical assistant
anesthesiologist or CRNA
circulating nurse
scrub nurse/surg tech
speciality nurse - RNFA
what is “time out” for intra-operative phase?
team verifies for right person, right procedure, right site
ASA classifications
ASA 1 - healthy (no medical problems)
ASA 2 - one medical problem (i.e. high BP)
ASA 3 - more than one medical problem
ASA 4 0 severe systemic disease
ASA 5 - not expected to survive without surgery
ASA 6 - organ harvest (brain dead)
general anesthesia essential nursing assessments and interventions post-op
breathing tube - airway management
cardiovascular - hypotension, dysrhymias, MI
hypothermia - temp less than 95 (OR is cold!!)
malignant hyperthermia
malignant hyperthermia definition
chain reaction of abnormalities
pharmacogenetic disease of skeletal muscle
inherited disorder - single defective gene
malignant hyperthermia labs
caffeine/halothane contracture test
malignant hyperthermia triggering agents
inhalation agents and depolarizing muscle relaxant
malignant hyperthermia s/s
early signs - muscle rigidity, tachycardia, dysrhymias
cutaneous changes
tachypnea
pyrexia - hallmark of disease but late sign
malignant hyperthermia interventions
** immediate treatment!!
discontinue anesthesia/surgery
administer 100% oxygen
administer Dantrolene ASAP - reconstitute with 60CC of sterile water
patient cooling - cool IV fluid and ice
monitored anesthesia care (MAC)
administered by anesthesia provider
all IV anesthesia
patient able to maintain own airway
many types of agents available
moderate sedation
administered by non-anesthesia provider who has received special training
all IV anesthesia
patient able to maintain own airway
limited agents available for use
state laws can vary
assessments when patient enters PACU
airway, O2
VS
anesthesia report
LOC
I/O
pain/comfort
dressings
labs
communication hand-off from PACU nurse to med surg nurse
type and extent of surgical procedure
type of anesthesia
Pt. tolerance of anesthesia + surgical procedure
allergies
pathologic condition
status of VS
type and amount of IV fluids and medications administered
incisions, dressings, tubes, drains, catheters
estimated blood loss (EBL)
any intraoperative complications
pertinent past medical history
postoperative care assessments
airway first!! check rate, depth, rhythm; then check VS
respiratory
rate + pattern
breath sounds
patient’s color
use of accessory muscles
oxygen
pulse oximetry
neurological - LOC, ability to obey verbal commands, motor/sensory
renal/urinal system - track I/O
IV
GI system - nausea/vomit, GI peristalsis delayed
NG tube drainage to decompress and drain stomach
promote GI rest
allow lower GI tract to heal
pain assess
pain management - oral, IM, IV, patient controlled analgesia
mobilization
sit up in bed and dangle legs post op night for many surgeries
diet
progress from NPO → liquids → soft → house as tolerated
incentive spiromtery
breathing device to achieve maximal ventilation
measures respiratory flow or volume
sitting or semi-fowler
exhale normally, inhale as slowly and deeply as possible
5-10 times every hour
potential complications post-op and nursing care for complications/preventing
atelectasis, pneumonia, embolus
turn, cough, deep breathing
maintain hydration
early ambulation
incentive spirometer
thrombophlebitis
leg exercises while in bed, early ambulation
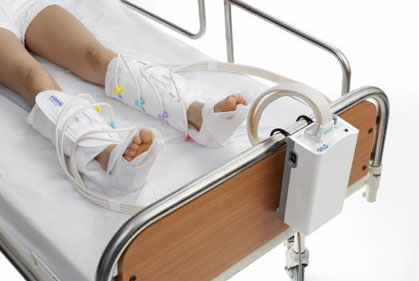
TED stockings, sequential hose (machine blows air into cloth around legs and promotes blood flow)
low dose heparin
first dressing change post-op is performed by who?
by physician
hemovac
self-suction
canister
used for orthopedic surgeries
penrose drain
half of tube inside site, half out
drains excess fluids
t-tube drain
used for some abdominal surgeries
hooked up to gravity bag
wound dehiscence
separation of the wound edges
more likely with vertical incisions
may be caused by a bacterial infection or poor wound healing
just some of the skin layers tear open
evisceration
organs with pink, serous drainage come out of wound
more likely in clients who are older, obese, diabetic, or malnourished
emergency
prevention of wound complications (dehiscence + evisceration)
splint incision when coughing
monitor for signs for infection, malnutrition, dehydration