Topic 3.5 - Alcohols
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the functional group
of an alcohol?
Hydroxyl group -OH
What is the general formula
of an alcohol?
C n H 2n+1 OH
How do you name alcohols
(one prefix, one suffix)?
Hydroxyl- or -OH
What kind of intermolecular
forces do alcohols have?
Why?
Hydrogen bonding, due to the electronegativity
difference in the OH bond
How do alcohols’ m.p. And
b.p. Compare to other
hydrocarbons’ of similar C
chain lengths? Why?
Higher, because they have hydrogen bonding →
stronger than Van der Waals forces
Are alcohols soluble in
water? Why does solubility
depend on chain length?
Soluble when short chain - OH hydrogen bonds
to hydrogen bond in water
Insoluble when long chain - non-polarity of C-H
bond takes precedence
What makes an alcohol
primary?
C bonded to OH is only bonded to one other C
atom
What makes an alcohol
secondary?
C bonded to OH is bonded to two other C atoms
What makes an alcohol
tertiary?
C bonded to OH is bonded to three other C
atoms
How can ethanol be made
from crude oil?
Hydration of ethene via electrophilic addition
(phosphoric acid catalyst H₃PO₄)
What are the advantages
and disadvantages of this
method?
Advantages - fast, continuous process, ethanol
has a high purity
Disadvantages - not renewable as from crude oil
How can ethanol be made
by fermentation?
Plant carbohydrates broken down and
fermented by enzymes in yeast →
ethanol
What conditions are needed
for this reaction to take
place?
Enzymes in yeast as catalyst, 35°C, anaerobic
conditions
Write an equation for the
reaction which takes place.
C 6 H 12 O 6 (aq) → 2C 2 H 5 OH + 2CO 2
What are the advantages
and disadvantages of this
method?
Advantages - renewable as from plants
Disadvantages - slow, batch process, enzymes
stop working at 15% alcohol so solution is not
pure, needed to be fractionally distilled
In the future, how might
most ethene be made? Why
is it not made like this at the
moment?
Dehydrate ethanol made by fermentation →
ethene
Not economical at the moment
Define carbon neutral
No net addition of CO 2 to the atmosphere -
carbon dioxide released when combusted =
carbon dioxide absorbed as a plant
Explain how using ethanol
in petrol engines could be
considered to be carbon
neutral.
Carbon dioxide released in fermentation and
combustion = carbon dioxide absorbed when
growing
Why would it probably not
be entirely carbon neutral to
use ethanol?
Other “carbon costs” associated with it e.g.
Transport
What is a commercial fuel
that uses ethanol? What
else does it contain and
why?
Methylated spirits - methanol (toxic, so it can't be
drunk)
Write an equation for the
combustion of ethanol.
C 2
H 5
OH (l) + 3O 2 (g) → 2CO 2 (g) + 3H 2
O (l
What is an elimination
reaction?
The removal of a smaller molecule from
a larger one
Which group leaves the
parent molecule in the case
of alcohols?
OH and a H (to form water)
What physical conditions
are needed for the
elimination reaction from
alcohols to alkenes? (2
alternatives)
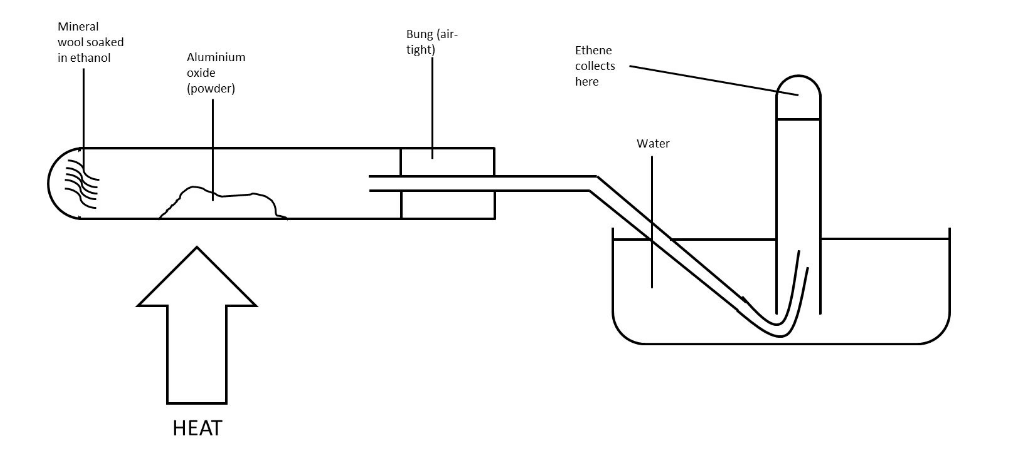
Excess hot concentrated sulphuric acid or pass
vapour over hot aluminium oxide
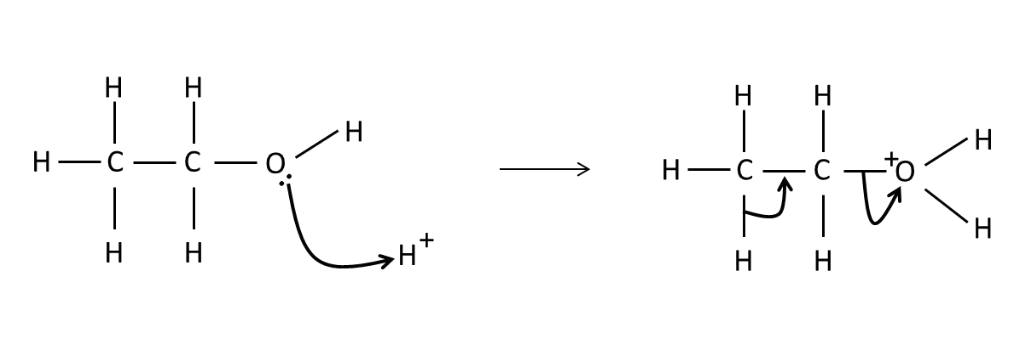
Draw a mechanism for the
dehydration of ethanol.
Draw a method for
dehydration of ethanol in the
lab.
What forms if you partially
oxidise a primary alcohol?
An aldehyde
What conditions are needed
to partially oxidise a primary
alcohol?
Dilute sulphuric acid, potassium
dichromate (VI), distill product as it’s
produced, gentle heating
Write an equation for the
partial oxidation of ethanol
CH 3
CH 2
OH (l) + [O] → CH 3
CHO (g) + H 2
O (l)
What forms if you fully
oxidise a primary alcohol?
A carboxylic acid
What conditions are needed
for this reaction?
Concentrated sulphuric acid, potassium
dichromate (VI), reflux for about 20 mins, strong
heating
Write an equation for the full
oxidation of ethanol
CH 3
CH 2
OH (l) + 2[O] → CH 3
COOH (g) + H 2
O (l)
What forms if you oxidise a
secondary alcohol?
A ketone
Why can it not be oxidised
further and why can’t a
tertiary alcohol be oxidised?
A carbon-carbon bond would have to break
What conditions are needed
for the oxidation of a
secondary alcohol?
Concentrated sulphuric acid, potassium
dichromate (VI), reflux for about 20 mins, strong
heating
Write an equation for the
oxidation of propan-2-ol.
CH 3 CH(OH)CH 3 (l) + [O] → CH 3 COCH 3 (g) + H 2 O (l)
What is an aldehyde? What
is its functional group?
Molecule with C=O group at the end of a carbon
chain, carbonyl functional group (C=O)
How do you name
aldehydes? Give an
example.
Suffix -al
e.g. ethanal
What is a ketone? What is
its functional group?
Molecule with C=O group in the middle of a carbon chain,
carbonyl functional group (C=O)
How do you name ketones?
Give an example?
Suffix -one
e.g. propanone
What is a carboxylic acid?
What is its functional group?
Molecule with a COOH group, which has to be at
the end of a carbon chain.
Carboxyl functional group (made up of carbonyl
C=O and hydroxyl -OH group)
How do you name
carboxylic acids? Give an
example
Suffix -oic acid
e.g. propanoic acid
What does the Tollens’ test
give a positive result for?
aldehydes
What is in Tollens’ reagent?
How does this react with the
substance to be tested?
Silver nitrate in NH 3 (aq) - oxidises aldehydes but
not ketones
Complex silver (I) ions reduced to Ag(s)
How do you carry out the
Tollens’ test?
Add equal volumes of substance being tested
and tollen’s reagent to a test tube, leave in water
bath for 10mins and observe any changes
What is the result of the
Tollen’s test for aldehydes
and ketones?
Aldehydes - silver mirror forms (solid Ag)
Ketones - no visible change
What does Fehling’s
solution give a positive test
result for?
aldehydes
What is in Fehling’s? How
does this react with the
substance to be tested?
Blue copper (II) complex ions - gentle oxidising
agent
Reduced to Cu + ions (brick red)
What conditions do you
need to use the Fehling’s
solution?
Heat
What result do aldehydes
and ketones give in the
fehlings test?
Aldehydes- brick red ppt
Ketones- no visible change