Chapter 6: Genetic Linkage and Mapping in Eukaryotes
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
Each species must contain hundreds to thousands of genes, yet?
Most have at most a few dozen chromosomes
Each chromosome is therefore likely?
To carry many hundred or even thousands of different genes
What does the transmission of genes close to one another on the same chromosome violate?
Mendel’s law of independent assortment
In eukaryotic species, each linear chromosome is comprised of?
A long piece of DNA that typically contains many hundred or even a few thousand different genes
What is Synteny?
Two or more genes are located on the same chromosome and are physically linked
What is Genetic Linkage?
The phenomenon that genes close together on a chromosome tend to be transmitted as a unit, which influences inheritance patterns
Chromosomes are called?
Linkage groups
Why are chromosomes called linkage groups?
They contain a group of genes that are linked together
The number of linkage groups is the?
Number of types of chromosomes of the species
What are examples of number of linkage groups?
In humans
22 autosomal linkage groups
An X chromosome linkage group
A Y chromosome linkage group
What is a two-factor cross?
Studies linkage between two genes
What is a three-factor cross?
Studies linkage between three genes
Genes that are far apart on the same chromosome may independently assort from each other are due to?
Crossing over
In 1905, William Bateson and Reginald Punnett conducted?
A cross in sweet pea involving two different traits
What are 2 characteristics that Bateson and Punnett studied?
Flower color and pollen shape
What was the ratio Bateson and Punnett found?
The expected 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation for this two-factor cross was surprisingly not obtained
Independent Assortment does not?
Always occur
What did Bateson/Punnett cross look like?
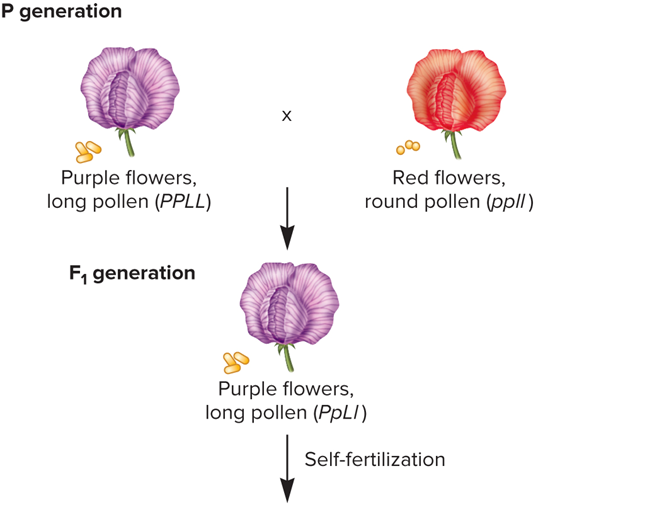
What was the four phenotypes in the F2 generation produced by Bateson/Punnett
Purple flowers, long pollen
Purple flowers, round pollen
Red flowers, long pollen
Red flowers, round pollen
What was the observed #, Ratio, Expected # and Ratio of Purple flowers, long pollen?
Observed #: 296
Ratio: 15.6
Expected #: 240
Ratio: 9
What was the observed #, Ratio, Expected # and Ratio of Purple flowers, round pollen?
Observed #: 19
Ratio: 1.0
Expected #: 80
Ratio: 3
What was the observed #, Ratio, Expected # and Ratio of Red flowers, long pollen?
Observed #: 27
Ratio: 1.4
Expected #: 80
Ratio: 3
What was the observed #, Ratio, Expected # and Ratio of Red flowers, round pollen?
Observed #: 85
Ratio: 4.5
Expected #: 27
Ratio: 1
What did Bateson/Punnett suggest?
That the transmission of the two traits from the parents was somehow coupled
What did Bateson/Punnett find?
The two traits are not easily assorted in an independent manner
They did not realize that the coupling is due to the linkage of the two genes on the same chromosome
In diploid eukaryotic species, linkage can be altered during meiosis as a result of?
Crossing over
When is linkage that can be altered during meiosis from crossing over occur?
During prophase I of meiosis
Replicated sister chromatid homologues associate as?
Bivalents
Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes exchange?
DNA segments
What may crossing over produce?
Recombinant genotypes
What happens when crossing over doesnt occur?
Linked genes segregate together
What do haploid cells contain?
The same combination of alleles as the original chromosomes
True or false, The arrangement of linked alleles has not been altered in the gametes?
True
What does Meiosis look like?
Crossing over and chiasma formation
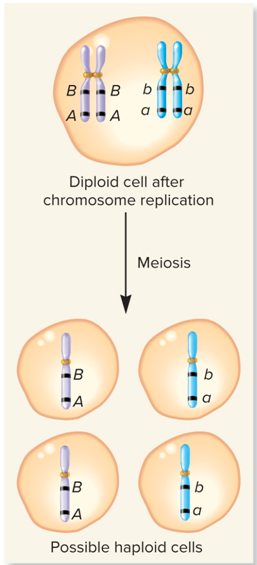
Crossing over can?
Reassort alleles
What are nonparental or recombinant cells?
Haploid cells that contain a combination of alleles NOT found in the original chromosomes
What are Recombinant offspring?
Produced by the exchange of DNA between 2 homologous chromosomes during meiosis in one or both parents, leading to a novel combination of genetic material
What is the definition of Recombinant offspring from chap 6?
Those that have been produced due to a crossover event during gamete formation in (at least) one of their parents
Morgan had evidence for?
X-linked genes
Who had the first direct evidence of linkage?
Studied that Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted
What did Morgan investigate?
Different traits that followed an X-linked pattern of inheritance in Drosophila
What different traits did Morgan find that were x-linked in Drosophilia?
Body color
Eye color
Wing length
What did Morgan’s Three-factor cross look like?
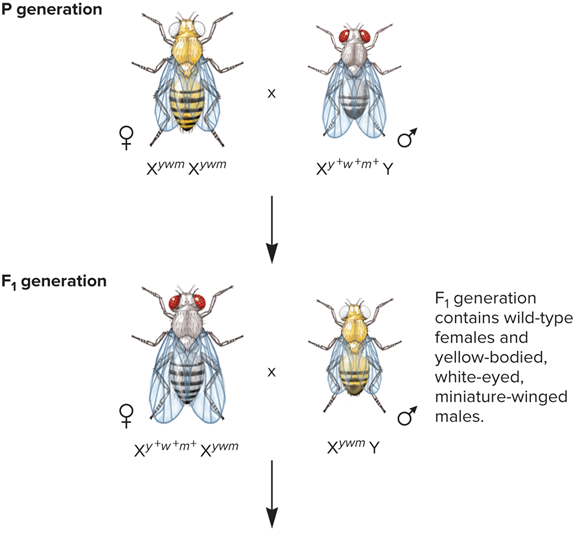
What are the phenotypes found in Morgan’s Three factor cross?
Gray body, red eyes, long wings
Gray body, red eyes, miniature wings
Gray body, white eyes, long wings
Gray body, white eyes, miniature wings
Yellow body, red eyes, long wings
Yellow body, red eyes, miniature wings
Yellow body, white eyes, long wings
Yellow body, white eyes, miniature wings
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Gray body, red eyes, long wings?
Females: 439
Males: 319
Total: 758
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Gray body, red eyes, miniature wings?
Females: 208
Males: 193
Total: 401
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Gray body, white eyes, long wings
Females: 1
Males: 0
Total: 1
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Gray body, white eyes, miniature wings?
Females: 5
Males: 11
Total: 16
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Yellow body, red eyes, long wings?
Females: 7
Males: 5
Total: 12
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Yellow body, red eyes, miniature wings?
Females: 0
Males: 0
Total: 0
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Yellow body, white eyes, long wings?
Females: 178
Males: 139
Total: 317
How many females, males and total amount of flies had Yellow body, white eyes, miniature wings?
Females: 365
Males: 335
Total: 700
What 2 key observations did Morgan interpet?
Why did the F2 generation have a significant number of recombinant offspring?
Why was there a quantitative difference between the different types of F2 recombinant offspring?
What did Morgan observe?
A much higher proportion of the combinations of traits found in the parental generation
What was Morgan’s explanation for higher proportions of traits found in the parental generation?
All three genes are located on the X chromosome
The three genes tend to be transmitted together as a unit
What was Morgan’s Data?
Morgan considered the previous studies of the cytologist F.A. Janssens to explain these data
Janssens had microscopically observed chiasmata and proposed that crossing over involves a physical exchange between homologous chromosomes
Morgan realized that crossing over between homologous X chromosomes was consistent with his data
He assumed crossing over did not occur between the X and Y chromosome (The three genes were not found on the Y chromosome)
What were Morgan’s 3 important hypotheses to explain his results?
The genes for body color, eye color and wing length and all located on the x-chromosome, so their alleles will tend to be inherited together
Due to crossing over, the homologous X chromosomes (in the female) can exchange pieces of the chromosomes, resulting in new combinations of alleles
The likelihood of crossing over depends on the distance between the two genes and is more likely to occur between two genes that are far apart from each other
What is the 1st set of Recombinant offspring from Morgan’s Data?
Gray body, red eyes; 1159
Yellow body, white eyes; 1017
Gray body, white eyes; 17
Yellow body, red eyes; 12
Total: 2205
What is the 2nd set of Recombinant offspring from Morgan’s Data?
Red eyes, long wings; 770
White eyes, miniature wings; 716
Red eyes, miniature wings; 401
White eyes, long wings; 318
Total: 2205
What does no Crossing over/Nonrecombinant offspring look like?
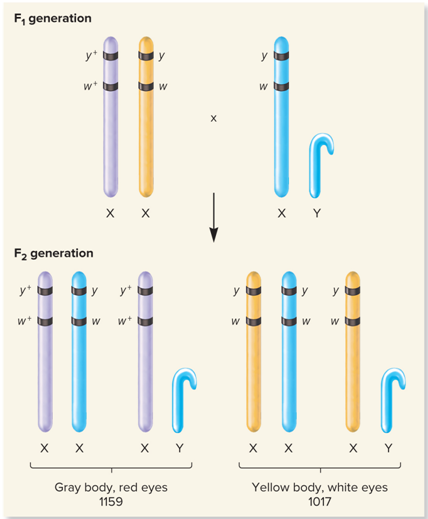
What does Crossing over/Recombinant offspring look like?
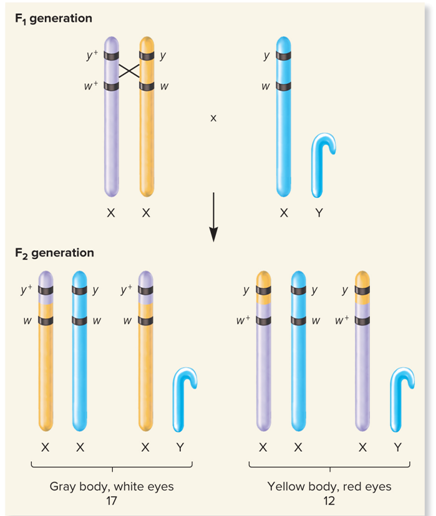
What did no crossing over in this region, very common look like?
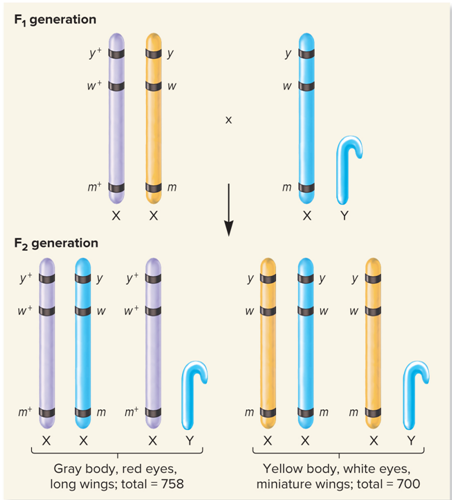
What did Cross over between eye color and wing length genes, fairly common look like?
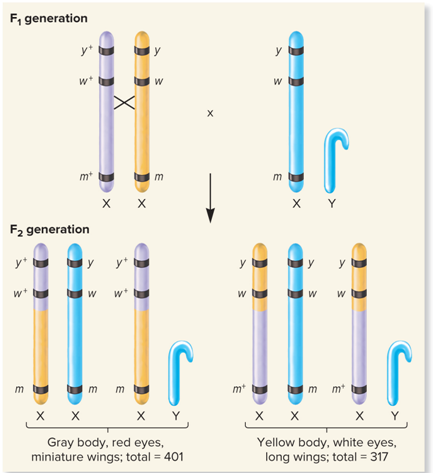
What did Crossover between body color and eye color genes, uncommon look like?
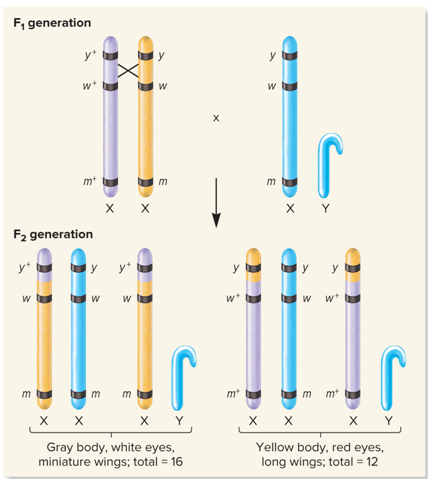
What did Double crossover, very common look like?
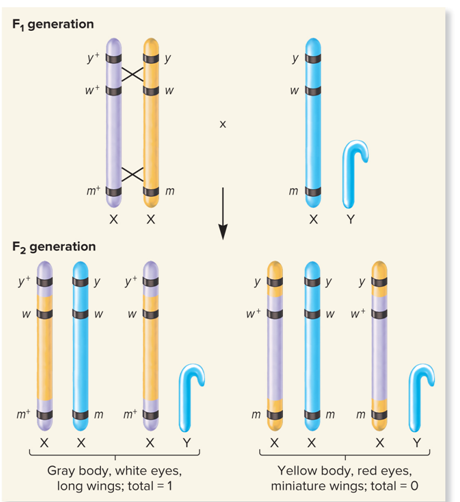
Each gene has its own?
Unique locus
What is Genetic Mapping (gene mapping or chromosome mapping?
Performed to determine the linear order of linked genes along the same chromosome
What are the 6 uses of Genetic Maps?
They allow us to understand the overall complexity and genetic organization of a particular species
They can help molecular geneticists to clone genes
They improve our understanding of the evolutionary relationships among different species
They can be used to diagnose, and perhaps, someday to treat inherited human diseases
They can help in predicting the likelihood that a couple will produce children with certain inherited diseases
They provide helpful information for improving agriculturally important strains through selective breeding programs
What does Genetic Maps allow us to do?
Estimate the Relative Distances Between Linked Genes
What is the relative distance between linked genes based on?
The likelihood that a crossover will occur between them
What happens experimentally with genetic maps?
The percentage of recombinant offspring is correlated with the distance between the two genes
What do Genes that are far apart result in?
Many recombinant offspring
What do Close genes result in?
Very few recombinant offspring
What is the formula for Map Distance?
(# of recombinant offspring)/(total # of offspring) x100%
For Map distance, what are map units (mu)?
The units of distance, also called centiMorgans (cM)
What is One mu equivalent to?
1% recombination frequency (RF)
What is the relationship between Testcross and Genetic Linkage Map?
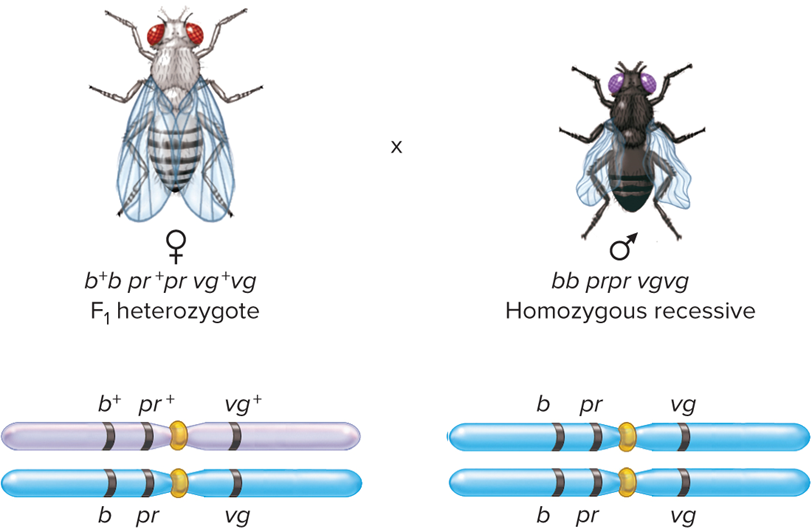
Genetic mapping experiments are typically accomplished by a conducting a testcross, where an individual that is heterozygous for two or more genes is crossed to one that is homozygous recessive for the same genes
What is an example of the relationship between Testcross and Genetic Linkage Map?
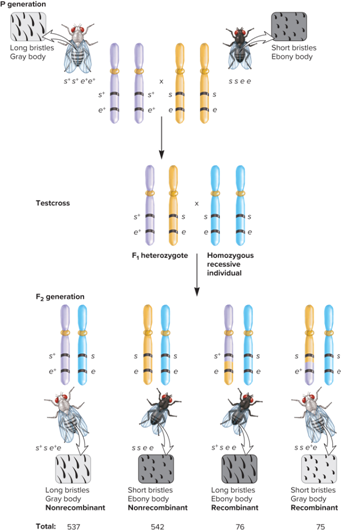
Testcross with two linked genes (s and e) affecting bristle length and body color in fruit flies
s = short bristles and s+ = normal bristles
e = ebony body color and e+ = gray body color
What does the Testcross to Distinguish Recombinant and Nonrecombinant Offspring look like?
What is the relationship between recombination and map distance?
Multiple crossovers set a quantitative limit on measurable recombination frequencies as the physical distance increases
A testcross is expected to yield a maximum of only 50% recombinant offspring
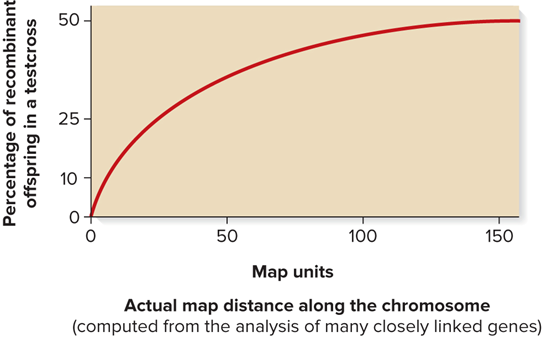
What is testcross data used for?
Can be used to estimate the distance between the two genes
How many map units were in theTestcross to Distinguish Recombinant and Nonrecombinant Offspring diagram?
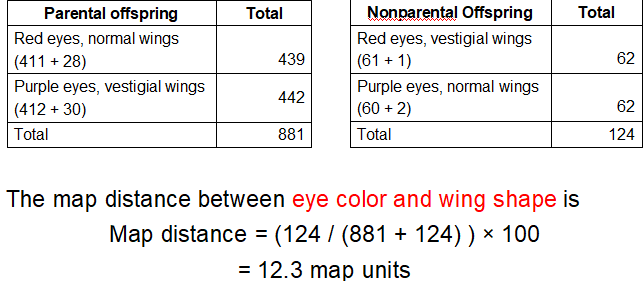
Map distance= (75+76)/(542+537+76+75) x100= 12.3 map units
In theTestcross to Distinguish Recombinant and Nonrecombinant Offspring diagram, how many map units are s and e genes apart?
The s and e genes are 12.3 map units apart from each other along the same chromosome
What are characteristics of Three-Factor Crosses?
Data from three-factor crosses can also yield additional information about map distance and gene order
The following experiment outlines a common strategy for using three-factor crosses to map genes
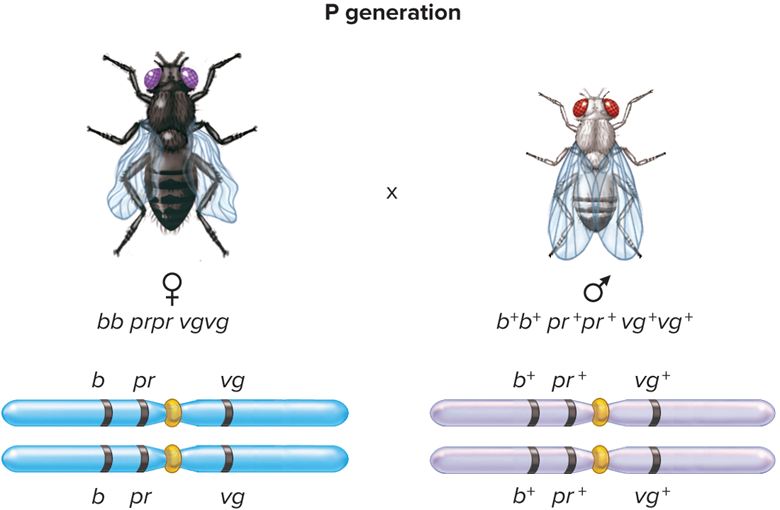
In this example, fruit flies that differ in body color, eye color and wing shape are considered
b = black body color
b+ = gray body color
pr = purple eye color
pr+ = red eye color
vg = vestigial wings
vg+ = long wings
What does Step 1: Crossbreed flies homozygous for 3 alleles look like?
What does Step 2: perform test cross look like?
What is Step 3: Collect Data from a Three-factor cross look like?
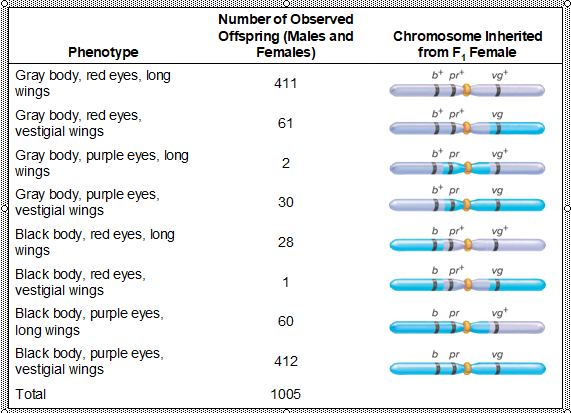
What does the analysis of the F2 generation flies allow you to do?
Map the three genes
The 3 genes exist as?
2 alleles each
Since 3 genes exist as 2 alleles each, there are how many possible combinations of offspring?
2³ = 8 possible combinations of offspring
What happens if the genes assort independently?
All eight combinations would occur in equal proportions
What is obvious from the F2 data?
That they are far from equal
What are 3 characteristics In the offspring of crosses involving linked genes?
Nonrecombinant phenotypes occur most frequently
Double crossover phenotypes occur least frequently
Single crossover phenotypes occur with “intermediate” frequency
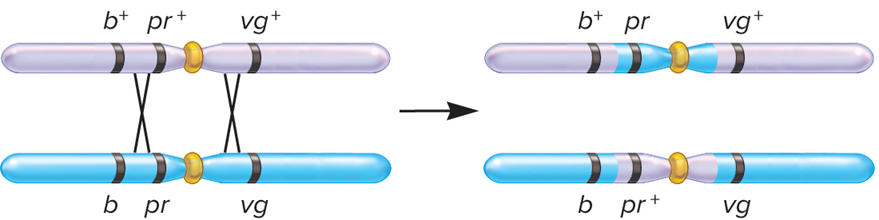
What are four characteristics of Double Crossover?
The combination of traits in the double crossover tells us which gene is in the middle
A double crossover separates the gene in the middle from the other two genes at either end
In the double crossover categories, the recessive purple eye color is separated from the other two recessive alleles
Thus, the gene for eye color lies between the genes for body color and wing shape
What does Double Crossover look like?
What is Step 4: Calculate the Map Distance Between Pairs of Genes?
One strategy is to regroup the data according to pairs of genes
From the P generation, we know that the dominant alleles are linked, as are the recessive alleles
(Nonrecombinant F2 offspring have a pair of dominant or a pair of recessive alleles, Recombinant F2 offspring have one dominant and one recessive allele)
The regrouped data will allow us to calculate the map distance between the two genes
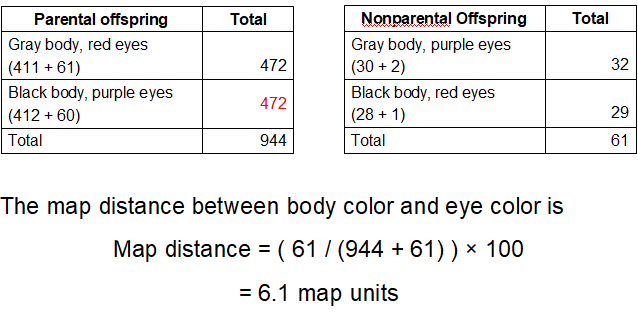
What does Step 4 look like for body color and eye color and what is the map distance?
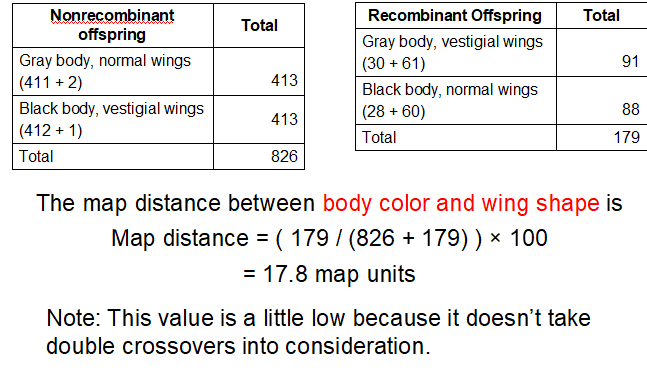
What does Step 4 look like for body color and wing shape and what is the map distance?
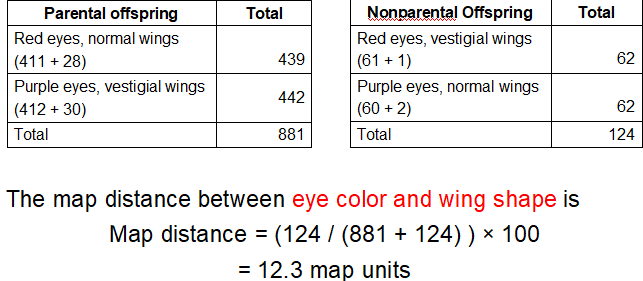
What does Step 4 look like for eye color and wing shape and what is the map distance?
What is Step 5: Construct the map?
The body color and wing shape genes are farthest apart based on the map unit calculation
The eye color gene is in the middle
The data are consistent with the map being drawn as
b − pr − vg (from left to right)