lec 7.1 - transcription in eukaryotes
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
transcription in eukaryotes - general features
happens in nucleus unlike prokaryotes which don’t have nucleus
must open chromatin structure (push histones/nucleosomes away)
RNA polymerase in eukaryotes can NOT read DNA to find promoter sequence (unlike prokaryotes) - need transcription factors
3 different RNA polymerase - bacteria only employs one
nucleolus
area of genome that has rRNA genes
RNA pol I responsibilities
responsible for transcribing large rRNA precursors, 16S and 28S
situated wherever rRNA genes are transcribed (nucleolus)
happens in nucleolus - most active site for rRNA synthesis
RNA pol II responsibilities
responsible for transcribing most of all protein encoding genes
makes heterogenous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) aka pre-mRNA, which gets processed and becomes mature mRNA
happens in nucleoplasm/nucleus
RNA pol III responsibilities
responsible for transcribing genes for tRNAs,
snRNAs, 5S rRNA and other smaller functional RNAs
happens in nucleoplasm/nucleus
Eukaryotic RNA polymerase has
many basal factors – these bind to DNA – usually only needed for initiation
eukaryotic promoter composition
has core region that binds RNA polymerase which binds at start point
enhancer sequences - either upstream or downstream of start site
bind activators that activate RNA pol to usually stimulate transcription
silencer sequences - either upstream or downstream of start site
usually repress transcription
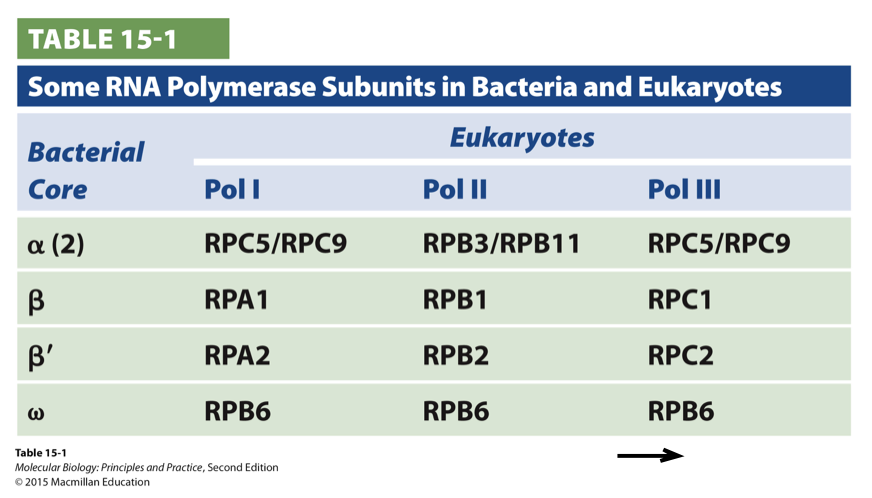
RNA pol subunits in bacteria and eukaryotes
some subunits are common to all classes of eukaryotic RNA polymerases and some are related to bacterial RNA polymerase
in terms of eukaryotic transcription, what component is homologous to sigma in prokaryotes?
transcription factors
they bind to specific genes to decide what gets transcribed