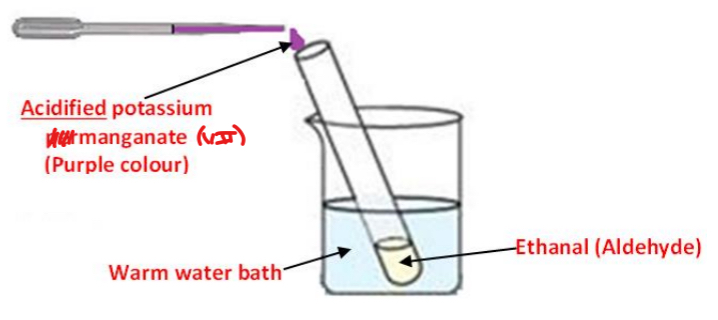
To show the reaction between ethanol and acidified potassium manganate (VII)
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Theory
• Acidified potassium permanganate, Fehling’s reagent and ammoniacal silver nitrate are all oxidising agents
• They will cause aldehydes to be oxidised to a carboxylic acid
• Ketones will not be oxidised under the same conditions
Note: These reactions test for aldehydes/distinguish between aldehydes and ketones i.e. prove a certain substance is an aldehyde and not a ketone
Important: If asked to show that an aldehyde can be ‘EASILY’ oxidised, a weak oxidising agent must be chosen i.e. Fehling’s reagent or ammoniacal silver nitrate
Procedure
• The ethanal (aldehyde) is placed in a test tube in a warm water bath
• Using a dropper, acidified dilute potassium manganate (VII) is added to the ethanal
Result: The purple colour of potassium manganate (VII) turns colourless
Note: When repeated with propanone (ketone) in place of ethanal, no colour change is observed
Write the half reactions that occur when acidified potassium manganate (VII) is added to ethanal (aldehyde)
1) image
2) MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- —[R]→ Mn2+ + 4H2O
Mn7+: purple
Mn2+: colourless
![<p>1) image</p><p>2) MnO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup> + 8H<sup>+</sup> + 5e<sup>-</sup> —[R]→ Mn<sup>2+</sup> + 4H<sub>2</sub>O</p><p>Mn<sup>7+</sup>: purple</p><p>Mn<sup>2+</sup>: colourless</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2453cd04-4db4-465b-9543-60f3d91943f9.jpg)
Explain the colour change that occurs when acidified potassium permanganate is reacted with ethanal
• MnO4- contains Mn7+ ions causing a purple colour
• When reacted with ethanal in an acidic environment, Mn7+ ions are reduced (gain 5 e–) to Mn2+ ions
• Mn2+ ions are colourless