Anatomy and Physiology: Identifying Bones Quiz
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Types of bones, Different Splits of the Skeleton
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Long bones
longer than they are wide (with heads at each end)
Long bones example
Humerus (in upper arm), femur(in upper leg), phalanges

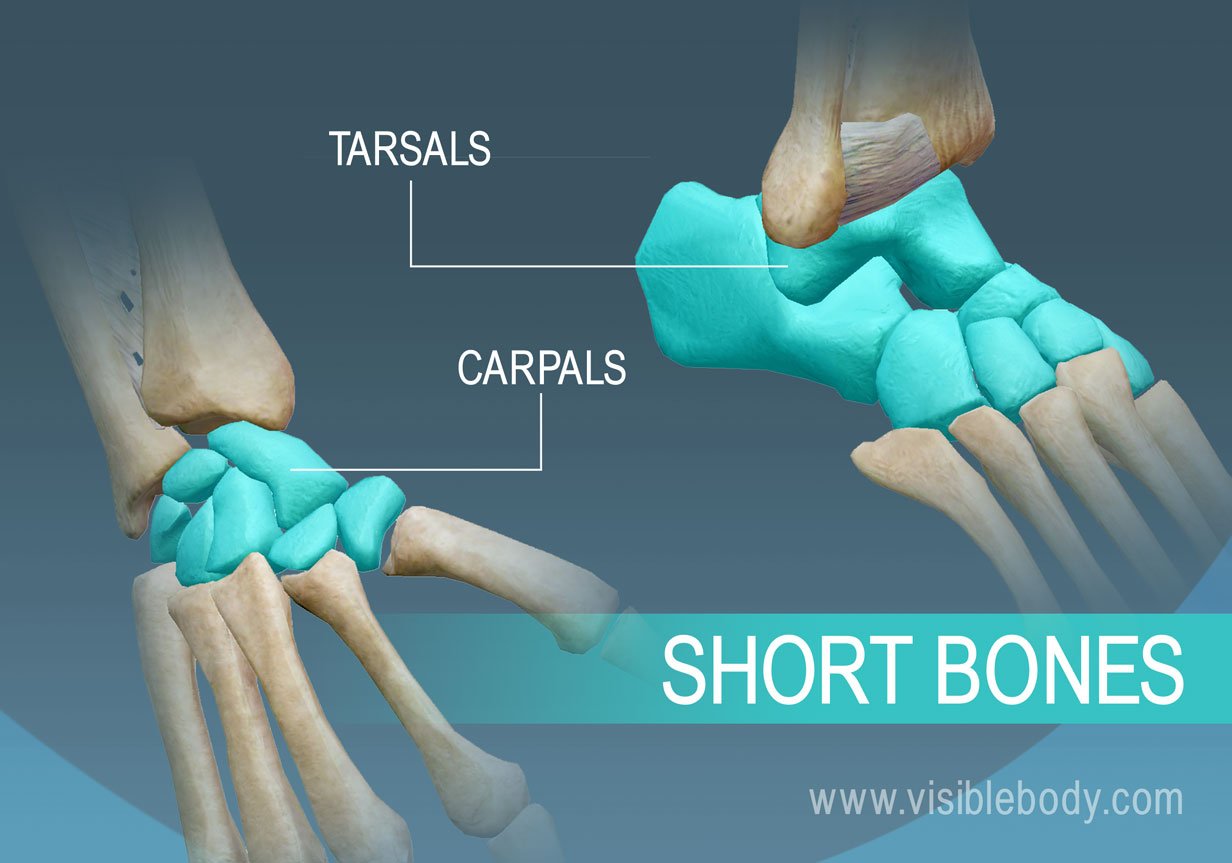
Short bones
often cube shaped and contain higher amounts of spongy bone
Short bones example
Carpals (small bones that make up wrist), tarsals (small bones that form ankle and heel)
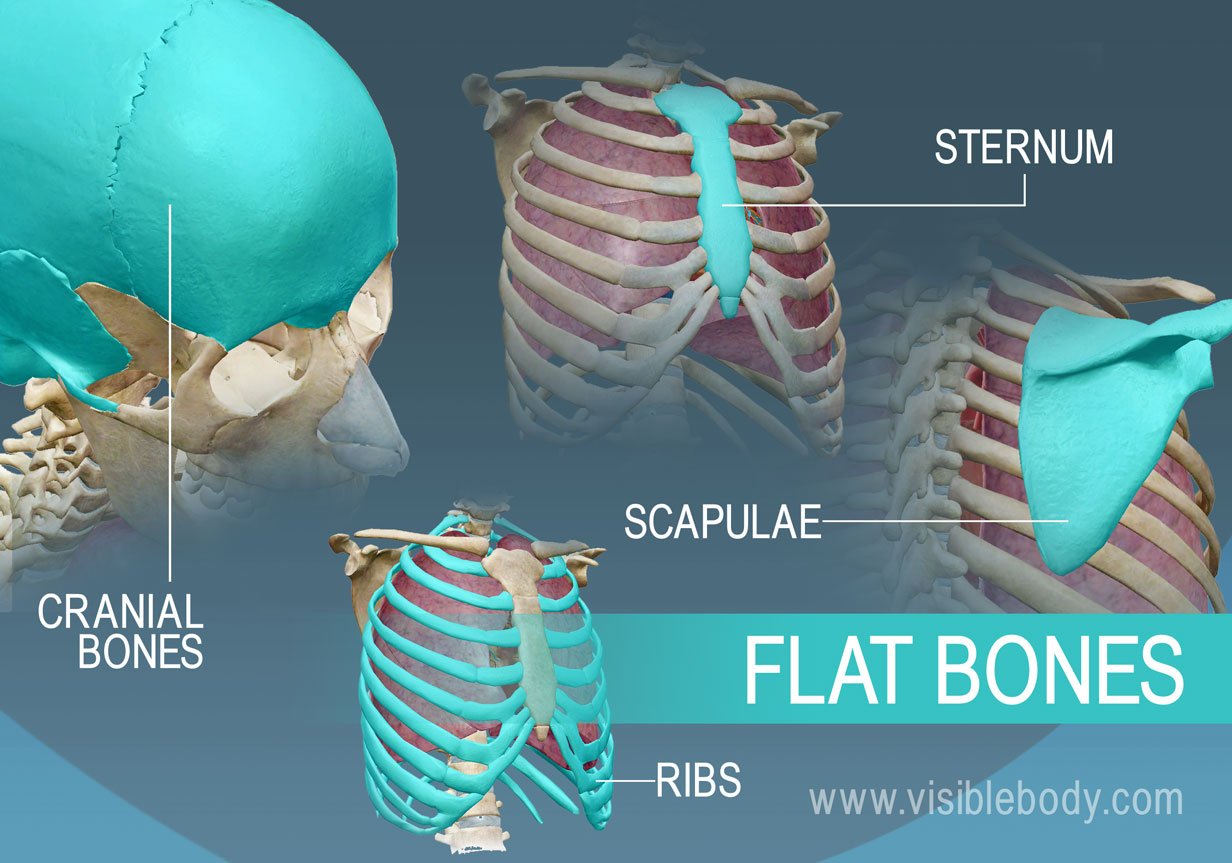
Flat bones
thin and often curved, flattened
Flat bone example
skull bones, pelvic bones, ribs, sternum (a.k.a. breastbone)
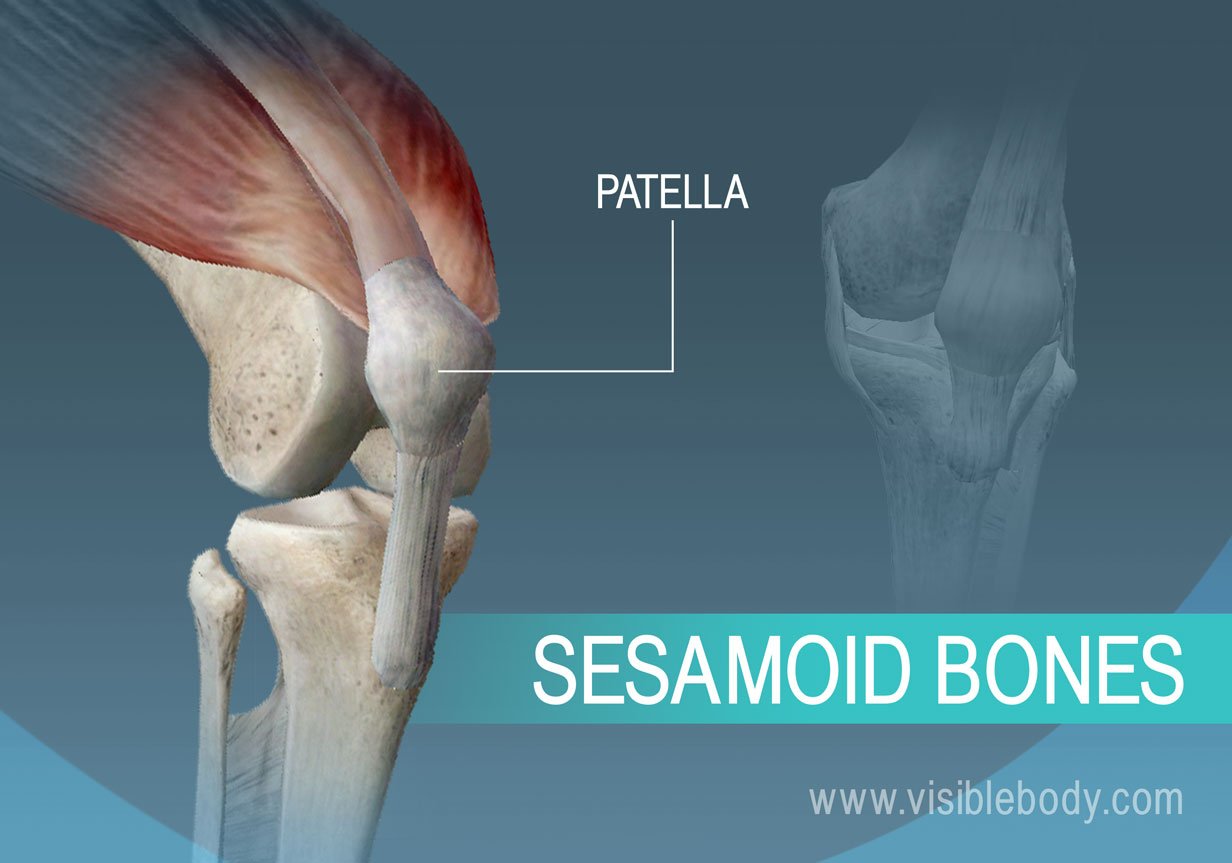
Seasmoid
round and embedded within a tendon
Seasmoid example
patella (located at the front of the knee joint)
Irregular bones
do not fit into any of the other categories due to their unnatural shape
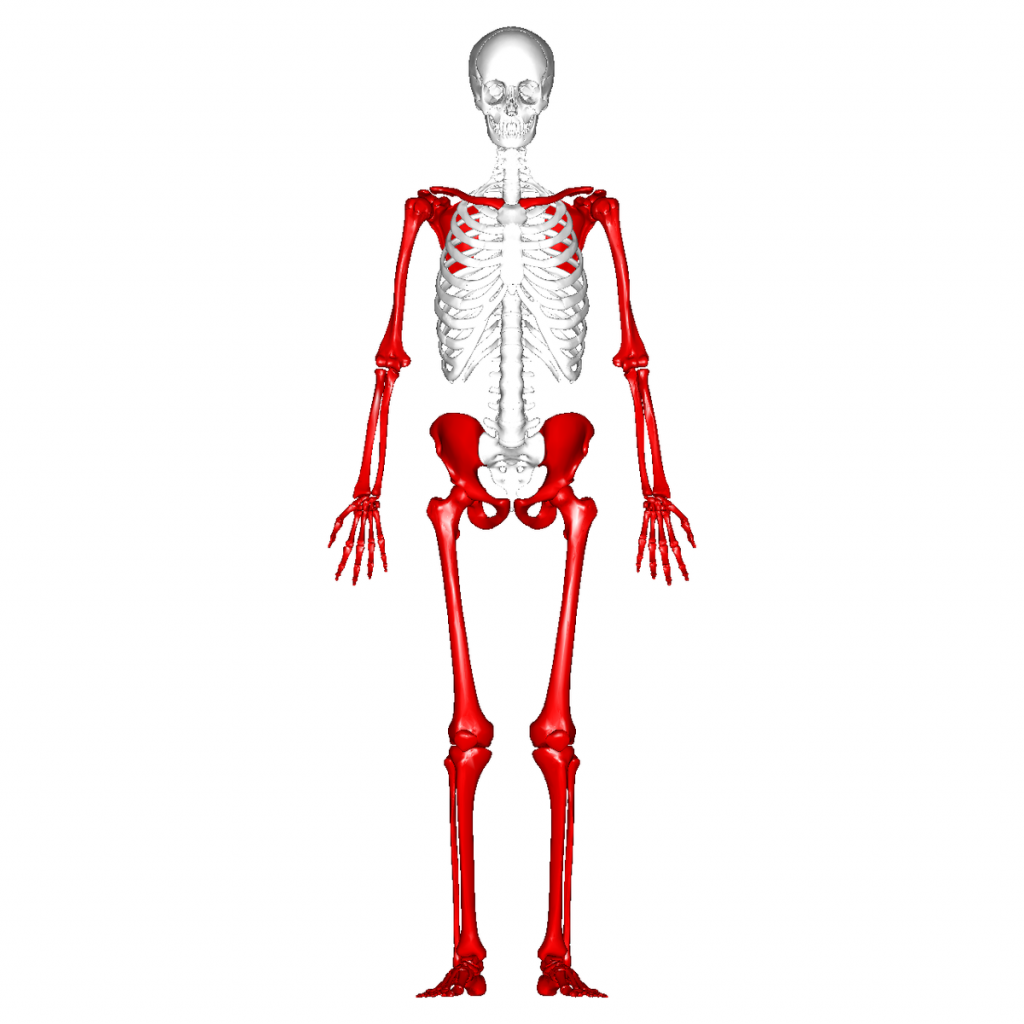
Axial skeleton
central core of the human skeleton that provides structural support for the body and protects essential organs (skull, vertebral column, rib cage, sternum)
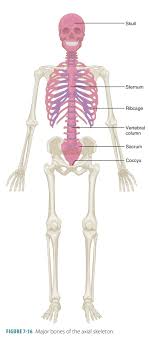
Appendicular skeleton
refers to the bones that make up the limbs (arms and legs), and their supporting structures that aid in movement (shoulder bones, upper limb bones, pelvic bones, lower limb bones)