Computer Science - 1.2.3: Software Development
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
System Development Life Cycle
- Analysis/requirements
- Design
- Develop
- Test
- Deploy
Loops
Software development methodologies
- Waterfall
- Spiral
- Rapid Application Development
- Agile
- Extreme programming
These methods are just ways of going through the life cycle of software development.
Document Focused
documents with the requirements are constantly referred and added to.
Stages of the development are documented - proof.
Code focused
System based, looking more at code functionality, working in line with user requirements and having the users involved at all points.
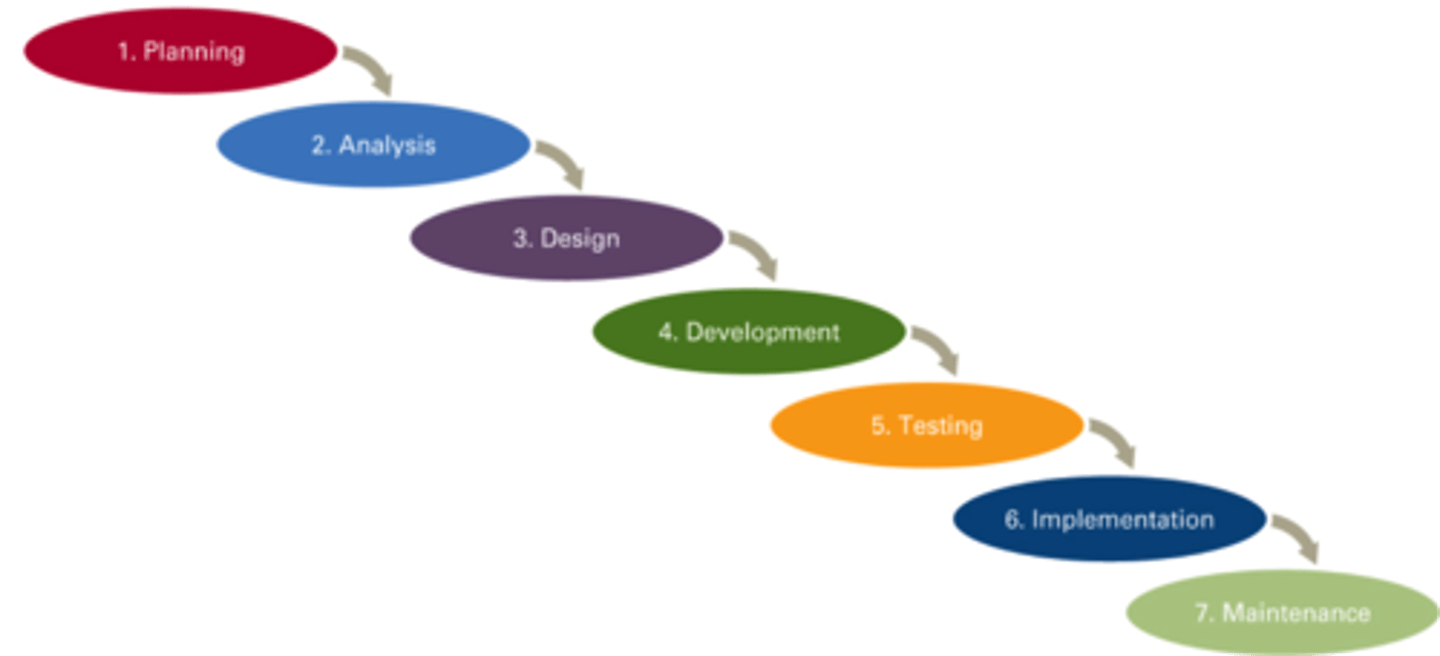
What is the waterfall methodology
Linear
Document focused
development team work through each stage of the life cycle in turn until the project is completed, following the rigid structure - once a section is finished it's difficult to go back if there are any errors.
Waterfall adv
good for keeping control of a project and meeting deadlines
Workers are clear on what their roles are.
Waterfall disadv
difficult to know if the end product meets user requirements since there's no product to show until the end.
If there are problems, won't know until testing at the end of the project.
When is waterfall used
If the user requirements are clearly understood, specified and unchanging.
Suitable for simple projects - not complex.
Large projects.
Rapid Application Methodology (RAD)
working through the life cycle focusing on the front end of the software and creating a 'prototype'. Get client/consumer feedback. Implement in next prototype. Continue until client/consumer is happy with it (less time for testing).
Go and finish the back end of the software.
User requirements gathered using focus groups. Used when these requirements are unclear.
RAD Adv
good usability due to continuous feedback from client
focus groups can be used
small team
low cost
RAD Disadv
can't tell what time and budget would be
fast development so could have lots of bugs
When is RAD used
Uncertain requirements
small/medium sized project
user interaction is important
quick development
Agile methodology
A collection of methodologies which aim to improve the flexibility of software development and adapt to changes in user requirements faster.
Sprints are structured as follows: design, develop, user feedback, refine. And this repeats. Analysis is done before sprints begin.
Each sprint is an entire life cycle, each sprint adds another feature to the program.
Best for small - medium projects, but larger projects can be decomposed so work can be allocated across multiple teams and managed separately.
Agile Adv
Focuses on the product and gets versions of working software to the client to ensure that their requirements are met.
If their requirements change, it is flexible enough to adapt - due to the focus on coding (and not documentation)
have working features of code that can be tested
Agile Disadv
Can be difficult to control agile projects which could end up taking longer than originally thought. This can cause budgeting issues.
Problems can be found later on since there wasn't as much time spent on analysis
When can agile be used
where client requirements change and flexibility is required.
small-medium sized. can be for large if broken down but will take time.
Extreme programming
Type of agile that focuses on getting high quality code, almost ready to be the final product quickly.
Two programmers working on the same set of code - catch mistakes easily. Quick development and feedback. Pair programming where one person programs and the other critiques.
Extreme programming adv
error avoidance through pair programming
changes can be made at short notice
Code is clear and comprehensible at all times
Extreme programming disadv
customer must participate
relatively large time investment
higher risk - problems found later as programming is prioritised
When is extreme programming used
where speed of product delivery and high quality is necessary
mall to medium-sized teams. However, it can be adapted for use in larger projects by scaling its practices and principles to fit the needs of the larger team and project.
What is the spiral method?
The spiral model has four quadrants:
determine objectives, where the developer determines the main objectives for the iteration and identifies any alternative solutions.
identify and manage risk, where the developer identifies the highest risk features of the program and mitigates them by planning or creating alternative solutions
develop and test, where the developer programs part of the project and test it
review and plan next iteration, where developer gains client feedback and plans any modifications for the next iteration.
Client feedback then informs future development and prototypes which feedback into future revisions.
Spiral adv
Focuses on risk
ensure client is happy
better for efficient use of resources by evaluating risk early on
Spiral disadv
It can be a lengthy process due to the evaluative nature
when is spiral used
large-scale, high-risk projects. These might be projects where technologies are unproven or multiple organisations are involved.