Integumentary System
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Integumentary system
Skin, hair, and nail
Functions of the integumentary system
1. Protection
2. Prevention of water loss and water gain
3. Temperature regulation
4. Metabolic regulation
5. Immune defense
6. Sensory reception
7. Secretion
2 main parts of the integumentary system
1. Skin
2. Skin accessories
Skin accessories
1. Hair
2. Nails
3. Glands
4. Sensory receptors
2 major layers of skin
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
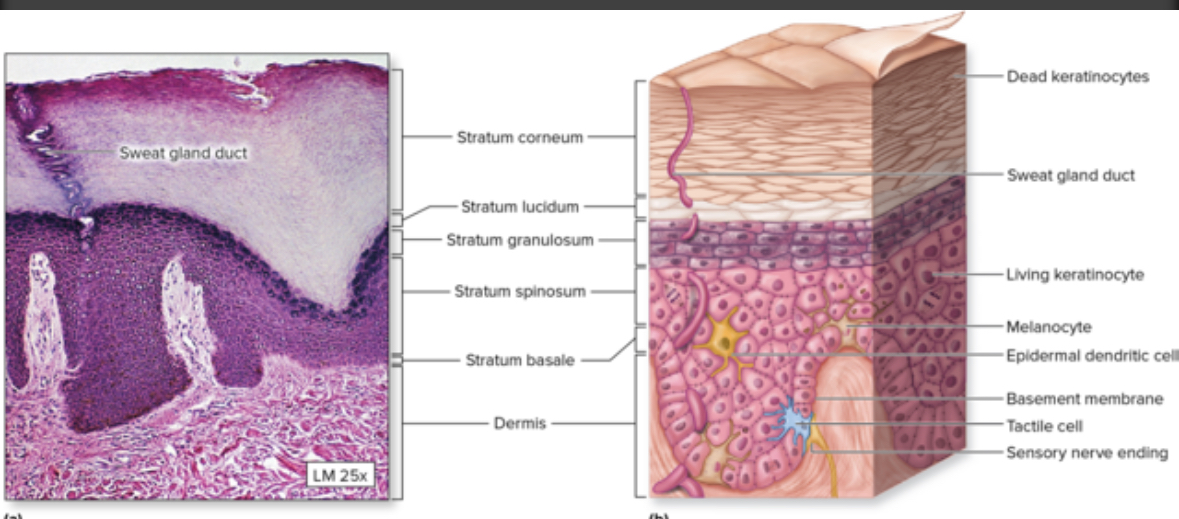
Epidermis
Structure: Outer layer of skin.
Keratinized stratified squamous ET
Avascular.
Consists of layers
Layers of the epidermis
1. Stratum basale
2. Stratum spinosum
3. Stratum granulosum
4. Stratum lucidum
5. Stratum corneum
Stratum basale
Deepest layer of the epidermis.
As upper layer of sloth off, makes new skin cells to replace and move upward
2 cell types:
1. Stem cells
2. Melanocytes
Keratinocytes
Produce keratin
Melanocytes
Produce melanin
Melanin
A pigment molecules that prevents damage to the skin by absorbing UV light
Stratum spinosum
2nd layer from the bottom layer.
2 types of cells:
Keratinocytes - alive
Dendritic cells
Dendritic cells
Eat bacteria and microbes.
Immune cells, like macrophages
Stratum granulosum
3rd layer from bottom layer
Cells:
Keratinocytes - dying, further from source of nutrients
Creates more room for packing of keratin
Secretes glycolipids - hydrophobic, prevent water loss
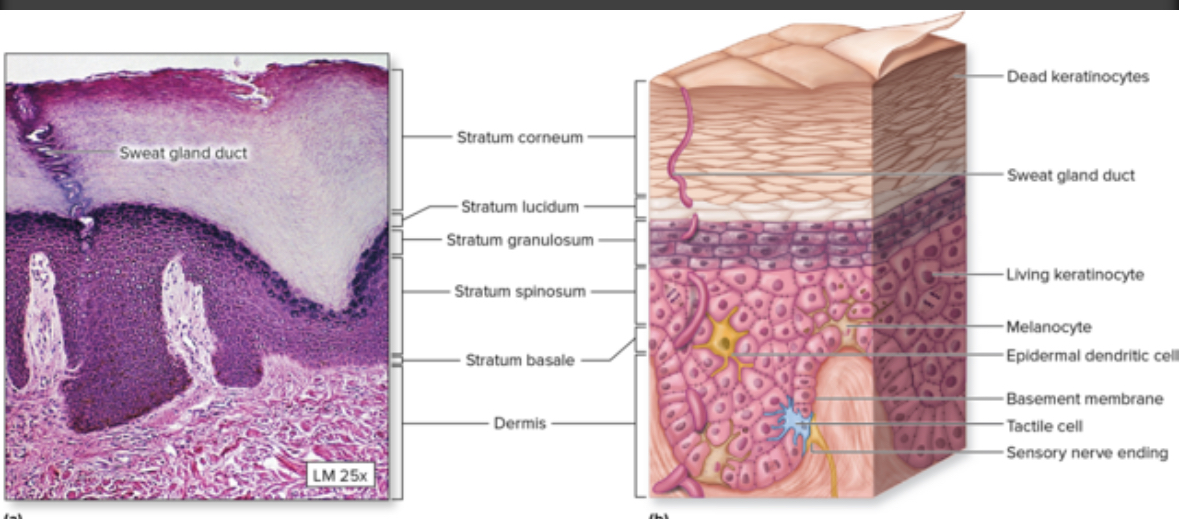
Stratum lucidum
4th layer from bottom layer
Cells:
Keratinocytes, dead
Contain maturing keratin
Looks clear
Lucid = clear
Function: extra strength
Layer only found in thick skin
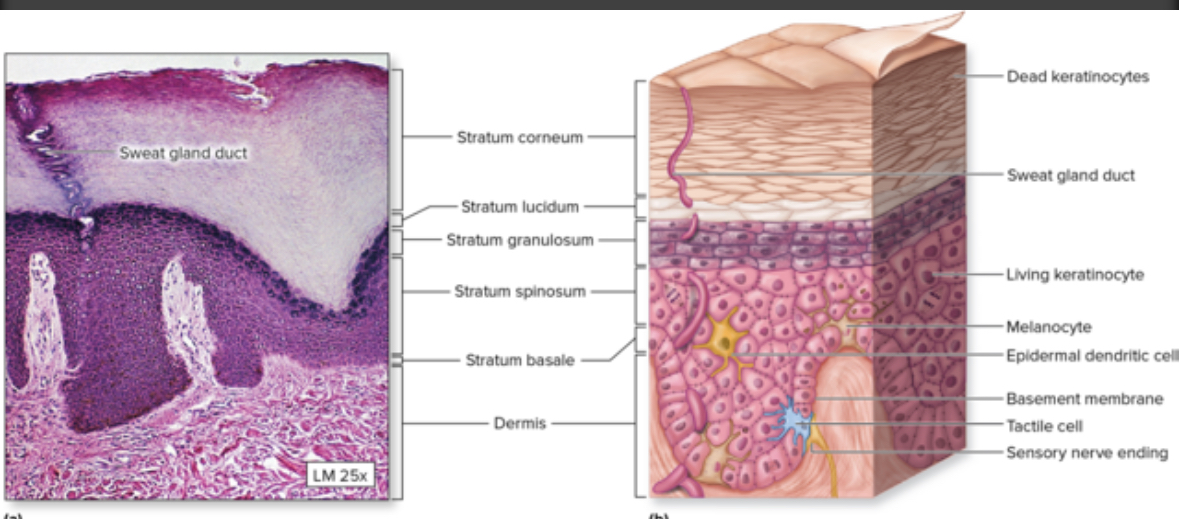
Stratum corneum
5th layer
Most superficial layer
Flaky
Cells:
Keratinocytes = dead
Flakes are collections did dead keratinocytes
Skin exposed to a lot of friction builds thicker layer = Calus = protection from damage
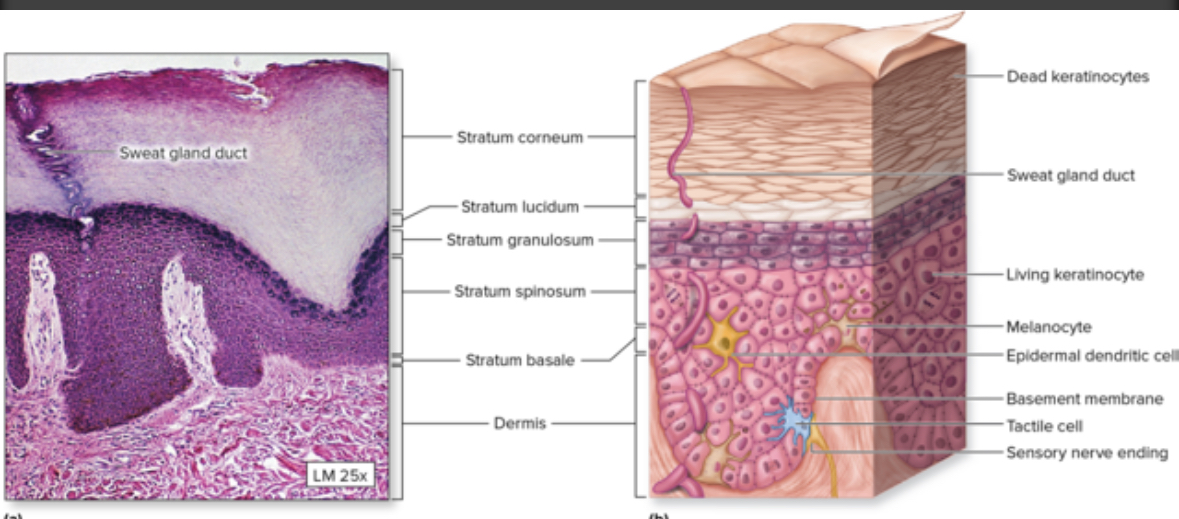
2 types of skin
Thin
Thick
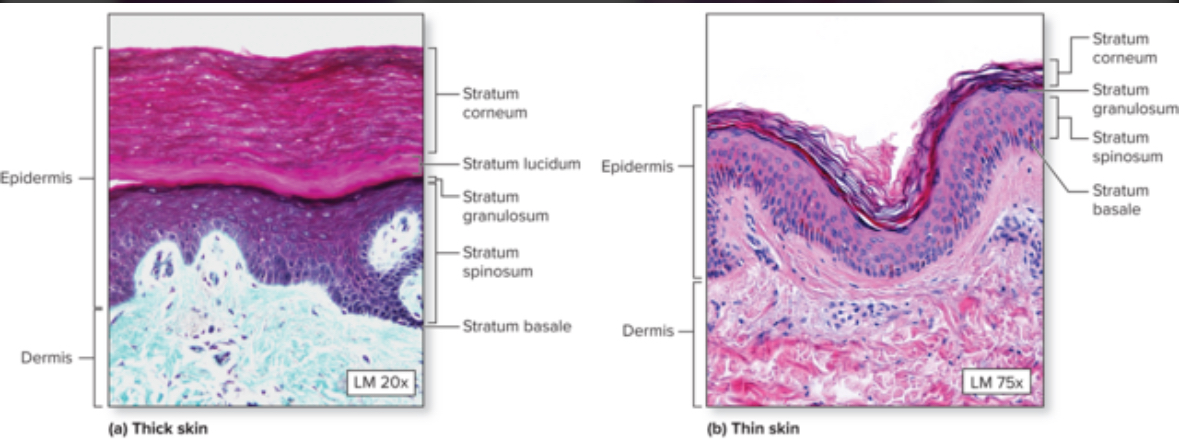
Thick skin
Each skin layer is thicker and has one extra layer = stratum lucidum
Epidermis ridge present
Location: fingertips, palms of hands, soles of feet
Epidermal ridges
Fingerprints
Thin skin
Most skin on the body.
Has hair.
Has 4 layers.
Dermis
Areolar CT And dense irregular CT
Function: support and nourishment of epidermis
2 layers of the dermis
Papillary layer
Reticular layer
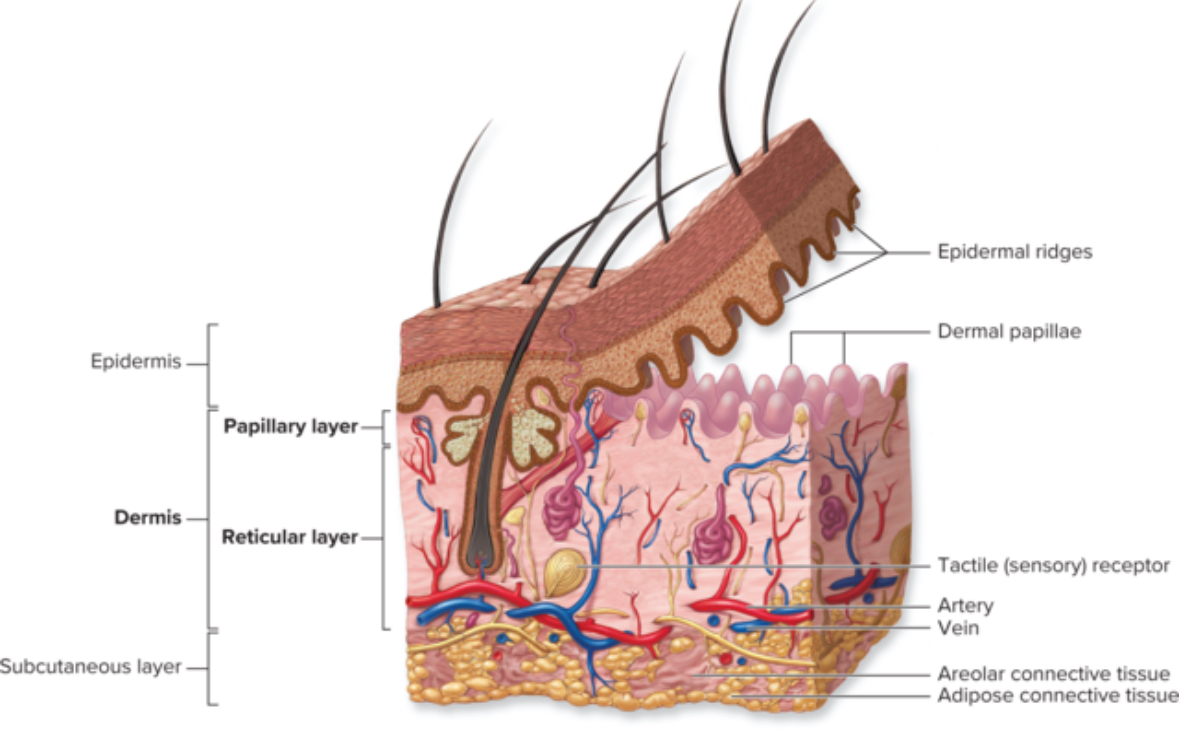
Papillary layer
Contains projections into epidermis
Areolar CT
Function: metabolic support and thermoregulation
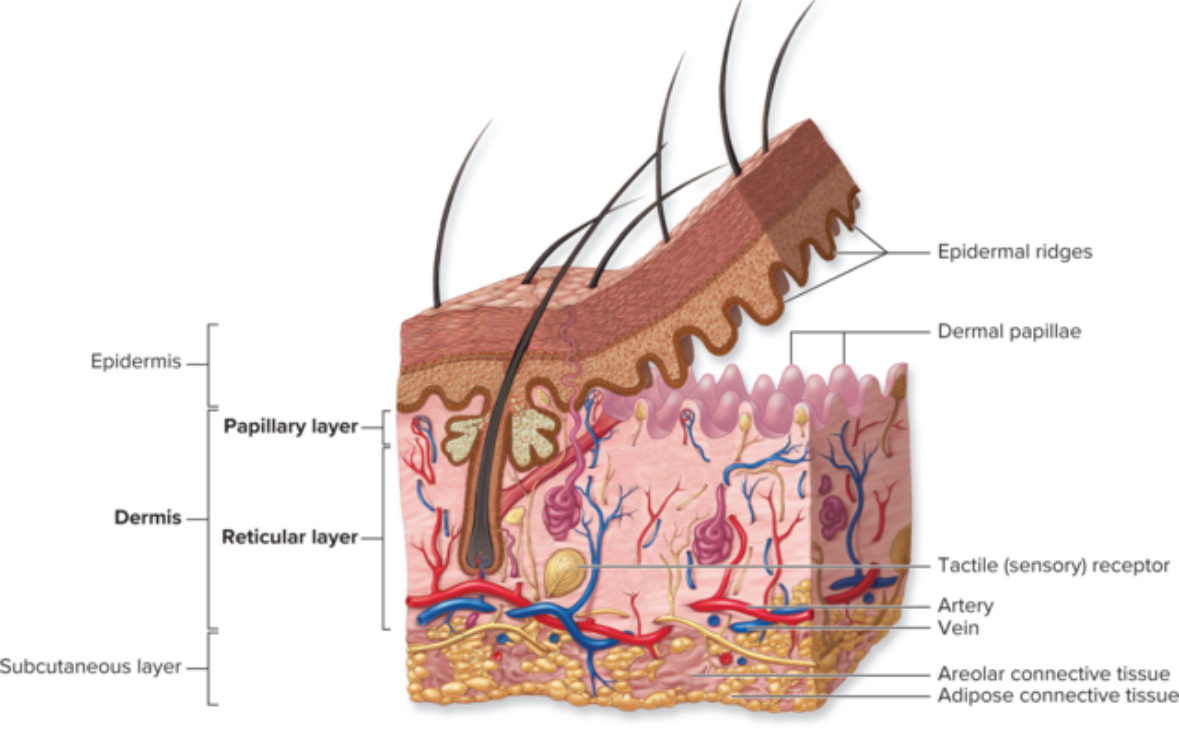
Reticular layer
Dense irregular CT
Function: support for structure from collagen and elastic fibers for elasticity
Reticular = network not reticular fibers
Hypodermis
Below the skin
AKA subcutaneous layer
Adipocytes
Adipose CT
Function: insulation, energy storage
Nails
Modified stratum corneum
Hard keratin
Hair
Column of dead keratinocytes with hard keratin
Grows from the hair follicle
Derivative of the epithelium
Function of hair
Protection
Heat retention
Sensory reception
Visual identification
Hair shaft
Portion of the hair that extends beyond the skin surface
Hair root
Embedded in the skin
Below the surface of the skin
Hair follicle
An oblique tube that surrounds the hair root
Extends into the dermis and sometimes into the subcutaneous layer
Function: produce new hair
Hair bulb
Consists of epithelial cells
A swelling at the base where the hair originates in the dermis
Arrector pili
Muscle
Extends from the dermal papillae to the mid region of the hair follicle
Thin ribbons of smooth muscle
Stimulated in response to an emotional state
Upon stimulation, the muscle contracts pulling on the follicle and elevating the hair to produce cutis anserina, aka goose bumps
Function: helps squeeze sebaceous gland to secrete sebum
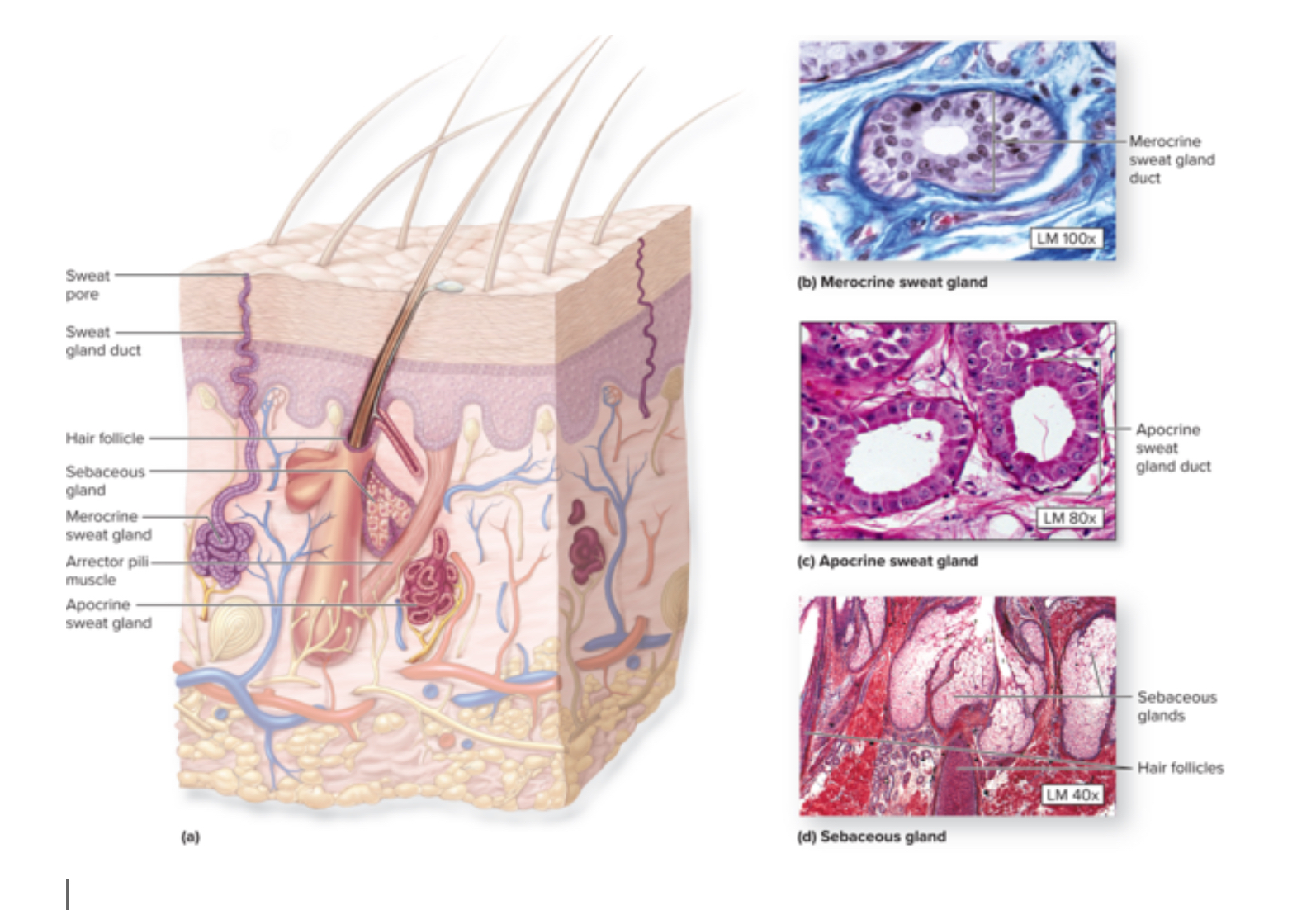
Sebaceous glands
Function: produce and secrete sebum for lubrication and antibacterial activity
Location: hair follicles
Sebum
Produced by the sebaceous glands
Lipid material which coats the epidermis and shaft of hair
Acne
Inflamed hair follicle due to sebum secretion
Merocrine sweat glands AKA eccrine sweat glands
Function: produce nonviscous watery secretion, normal sweat, regulates body temperature = thermoregulation,
Location: throughout the body
Gland —> duct—> surface of skin
Apocrine sweat glands
Location: axillary, anal, Areolar, and pubic regions
Function: produce viscous complex secretion
Influenced by hormones
Stinky sweat
Modified sweat glands
Cerumnous glands = ear wax
Mammary glands = milk
Sensory receptors
Meissner’s corpuscles
Free nerve ending
Pacinian corpuscles
Ruffini corpuscles
Meissner’s corpuscles
Location: Dermal layer
Structure: Coiled spring
Function: Detects soft fine touch
Free nerve endings
Location: Papillary layer
Function: Sense temperature and pain
Ruffini corpuscles
Function: Sense stretch
Location: reticular layer
Pacinian corpuscles
Structure: looks like an onion slice
Location: reticular layer of the dermis
Function: detects pressure and vibration