kin 221 - mod g1 biomechanics tissue properties
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:05 PM on 9/8/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
tolerance
what a tissue can withstand
2
New cards
exposure
the load/stress a tissue is exposed to
3
New cards
time dependent injuries
loads are repeated/constant causing a decrease in tolerance overtime
4
New cards
true
at low exposure, the risk of injury is still high
t or f
t or f
5
New cards
false
at low exposure, risk of injury is low
t or f
t or f
6
New cards
geometric properties
properties described in terms of load and deformation
7
New cards
false
a different load application causes different deformation with samples that have a larger CSA
8
New cards
material properties
properties described in terms of stress and strain
9
New cards
stress
normalized load (force/CSA)
10
New cards
pascals
stress is expressed in
11
New cards
strain
normalized deformation (change in length/original length)
12
New cards
elastic region
the area where when applying a load to a tissue, it will go back to its original state
13
New cards
yield point
the point of the stress-strain and load-deformation curve becomes non-linear
14
New cards
plastic region
area of the load-deformation and stress-strain curve where there is permanent deformation when a load is removed
15
New cards
ultimate failure
where the load/stress reaches it maximum value and the tissue fails
16
New cards
stiffness
the slope component of the load-deformation curve
17
New cards
young’s modulus
the slope/change in stress over strain in the stress-strain curve
18
New cards
true
the area under the load-deformation curve is the energy needed to cause failure
t or f
t or f
19
New cards
false
load deformation curve is a normalized version of the stress-strain curve
t or f
t or f
20
New cards
true
structural properties depends on shape and size of the tissue
t or f
t or f
21
New cards
bending
this loading type uses the moment of inertia
22
New cards
torsion
this loading type uses the polar moment of inertia
23
New cards
deformations
a tissue that has a longer length but the same CSA as another will withstand higher ______________
24
New cards
loads
a tissue that has a larger CSA but the same lengths as another will withstand higher _______
25
New cards
true
the black line has the stiffest tissue
t or f
t or f
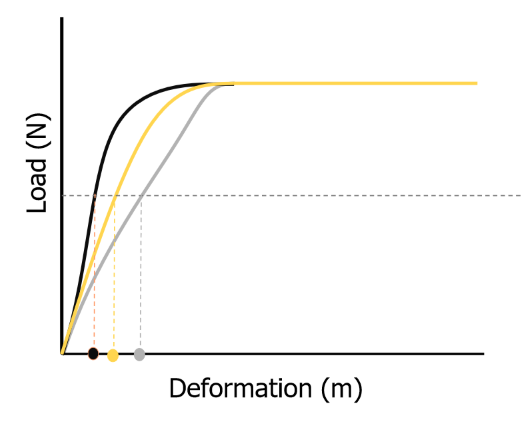
26
New cards
false
the yellow line has the stiffest tissue
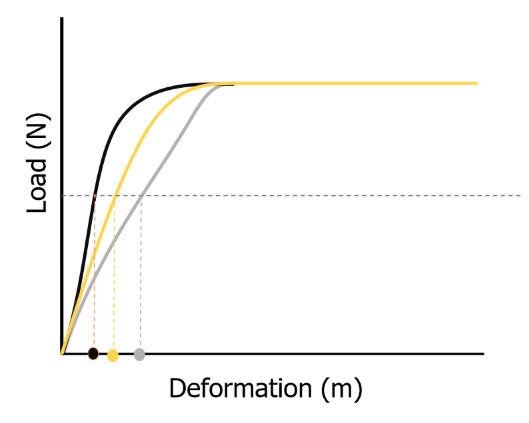
27
New cards
high
a material with a high young modulus will have a ____ amount of stress for a given strain
28
New cards
low
a material for a given stress and a high young modulus will have a ___ amount of strain
29
New cards
nanoindentation
bone samples with small indenter pushed into it with known forces and area of contact to measure young modulus
30
New cards
microindentation
a controversial method using live people have probes inserted through the skin to indent bones
31
New cards
standardized tension/compressive tests
destructive tests using machines to test materials with known stresses
32
New cards
toe region
common in ligaments/tendons and is a non-linear start of the load deformation curve
33
New cards
collagen
the toe region of a load deformation curve is due to __________ stretching
34
New cards
sample
load-deformation curves are specific to a
35
New cards
material
stress strain are generalizable to a ___________
36
New cards
false
you can use either stress strain or load deformation to see the differences in muscles with varying lengths and CSA
t or f
t or f