Platyhelminthes Lab - Biology 205
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what is cephalization
development of head end
how many embryonic germ layers do platyhelminthes have
3
Is GVC complete or incomplete
incomplete
do platyhelminthes have a coelom?
No, they are acoelomate
are they monoecious or dioecious, and what does it mean
Monoecious: each individual can produce both sperm and egg
State the 3 free living platyhelminthes
Tricladida, Polycladida, and Rhabdocoela
Main identifier(s) of Tricladida
2 eye spots, cylindrical pharynx, 3 branches GVC
What is a pharyngeal pouch?
space that holds pharynx when retracted
What is the space that holds pharynx when retracted
pharyngeal pouch
What are rhabdities
small, dark spots in epidermis that produce mucus
What cells produce mucus in tricaldida
rhabdities
Main identifier(s) of Polycladida
ruffled pharynx, many tiny eyespots, GVC with many branches
Main identifier(s) of Rhabdocoela
bulbous pharynx, sac like GVC (no branches)
What are neodermata?
parasitic flatworms with modified epidermis called tegument
what is a tegument?
type of epidermis in neodermata (parasitic flatworms) that do not have cilia and are fused together
Which platyhelminthes have shell glands
neodermata
What do shell glands do
location where yolk is deposited into a shell with egg, also stores sperm
Give two examples of Trematoda
Fasciola and Echinostoma
Main identifier(s) of Trematoda
Oral and ventral suckers, uterus with shelled eggs
Name the life cycle stages of Fasciola (Trematoda)
egg to miracidium to sporocyst to rediate to 2nd gen rediae to cercaria to immature flukes to adult flukes
What are miracidum
life cycle stage of Fasciola that burrow through skin of snail
What do miracidium develop into
sporocyst
What do sporocysts do
produce many redia through asexual reproduction
What do rediae do
feed on snail tissue, produce 2nd generation of rediae
What do 2nd gen rediae do
produce many cercaria
What do cercaria do
leave the snail, attach to aquatic vegetation
What happens when a mammal eats aquatic vegetation with cercaria
immature flukes are released
What do immature flukes turn into
adult flukes
How are eggs released in the Fasciola (Trematoda) life cycle?
through feces
Main identifier(s) of Cestoda
no GVC, scolex, proglottids
What are sexually mature proglottids
segments with a complete set of male and female reproductive organs
What are gravid proglottids
segments with only female eggs
What is the life cycle of Cestoda
gravid proglottids are released into intestine, release eggs into environment, develops into onchosphere, eats by pig and developed into cysticercus, humans eat and scolex attaches to intestine
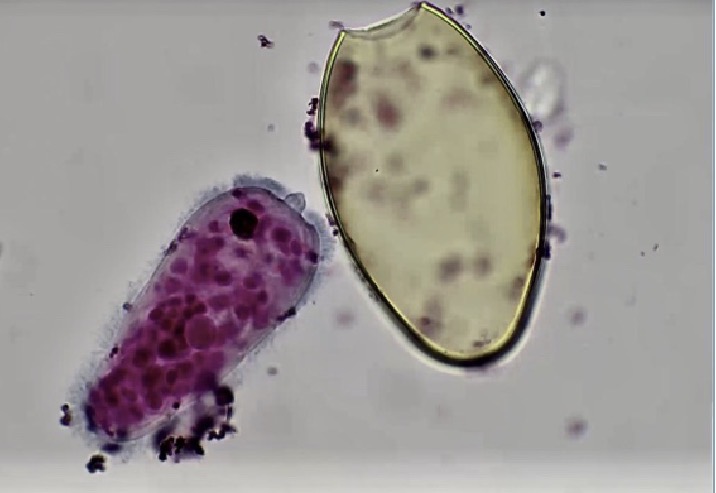
What is this, what does it do
miracdium, hatches from egg and burrows inside snail
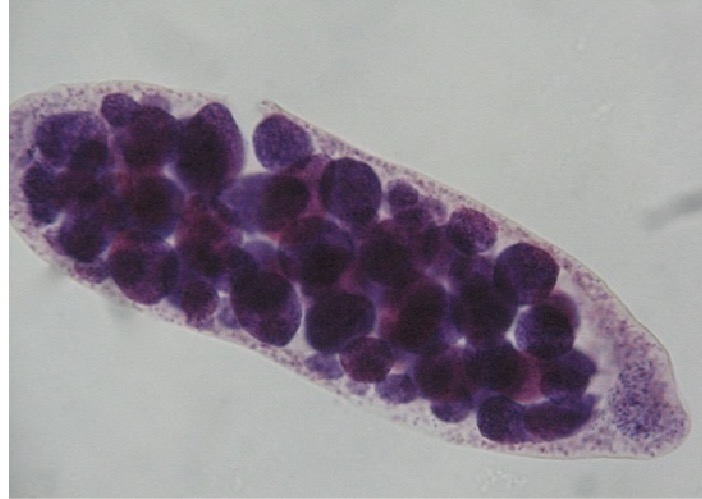
What is this, what does it do
Rediae, undergoes asexual reproduction in snail digestive gland

What is this, what does it do
Cercaria, free swimming and attach to vegetation