Biology 251 - Practical 2 Study Guide
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
What is the longest wavelength of UV radiation?
UV-A
What is the most damaging wavelength?
UV-C (100-280 nm)
What is the wavelength of UV-B?
280-315 nm
At what wavelength is UV lethal to cells and causes DNA damage?
254-260 nm
Natural Antibiotics
chemical metabolites produced by some fungi and bacteria to kill or stop the growth of nearby bacterial competitors
Semi-synthetic antibiotics
produced chemically in the lab by keeping the active moiety intact but modifying an R (side chain) group
Synthetic antibiotics
entirely produced inside laboratories, such as sulfonamides.
Bactericidal
antibiotics that kill bacteria
Bacteriostatic
antibiotics only inhibit the growth but does not actually kill the bacterial cells. They work in combination with your immune system to eliminate an infectious disease
Narrow spectrum antibiotics
target a specific gram class of bacteria
Broad spectrum antibiotics
target both Gram types of bacteria
Antibiotic high selective toxicity
drug targets bacteria and not humans (very specific)
Antibiotic low selective toxicity
cause more serious side effects in humans (not very specific for bacterial cell membranes).
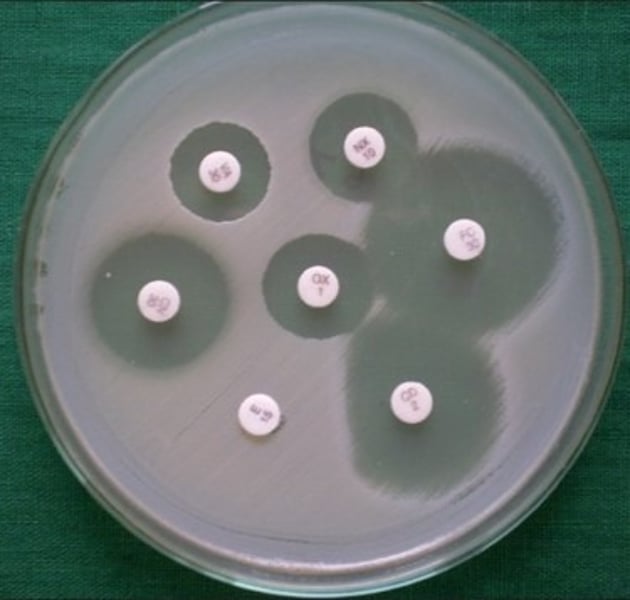
What is the zone of inhibition?
area around the disk in which no bacteria grow
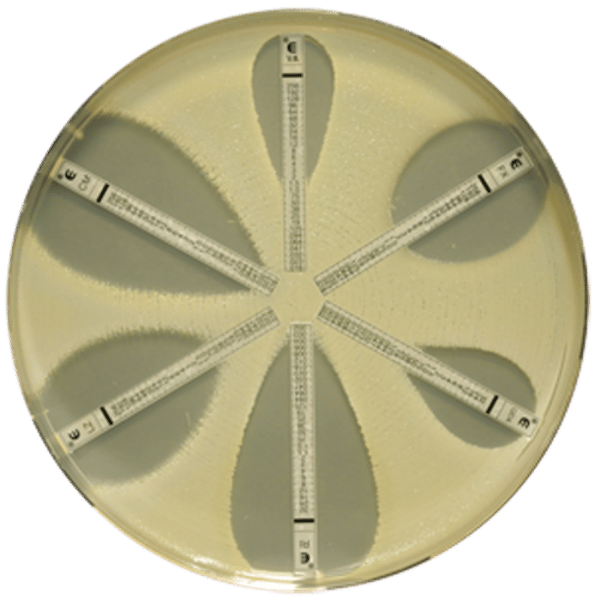
What does a E-TEST determine? (2 parts)
Antimicrobial susceptibility; Determines the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotics.
What antibiotic sensitivity test is the image showing? (Know how to measure the diameter in mm)
Kirby Bauer
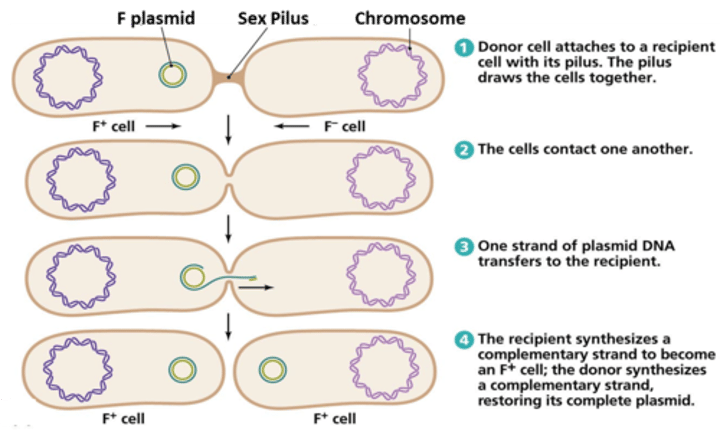
What are the two types of conjugation?
Vertical transmission & Horizontal gene transfer
What is vertical transmission?
when genetic information is passed from the parent cell to the daughter cells as a result of binary fission.
What is horizontal gene transfer?
occurs when genetic information is passed between unrelated cells.
What antibiotic sensitivity test is the image showing? (Know how to read the MIC)
E-TEST
What are plasmids?
small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules that usually exist extra-chromosomally (outside of the bacterial chromosome).
True or false: Plasmids have non-essential genes that can provide antibiotic resistance genes
TRUE
What are the three types of methods of horizontal gene transfer that bacteria can use
Conjugation, transformation, & transduction
Transformation, conjugation, and transduction all share ONE characteristic. What is it?
They must all require a donor (external source of DNA) and a recipient (acquires the DNA)
What is conjugation?
is the process of transferring genetic information (in the form of a plasmid) from one donor bacterial cell to a recipient cell through a sex pilus.
What does it mean for a host cell to be transduced?
A transduced recipient host cell has received a plasmid from a former donor host cell and has expressed genes that were brought in by the phage.
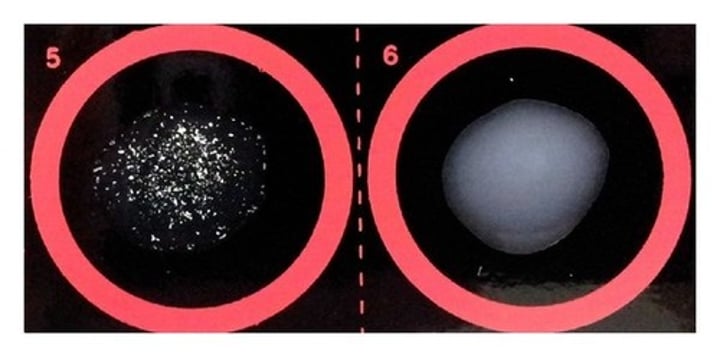
This image shows the results of a latex agglutination assay. Which sample (5 or 6) show a positive result?
5 has clumps, showing a positive result
What type of agar is necessary for the Kirby-Bauer test?
Mueller-Hinton agar
What is the SOS system?
It is the bacterial DNA repair system when UV damages DNA
What is this image showing?
What is the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)?
The lowest amount of an antibiotic that will inhibit the growth of organisms
Fill in the blanks: Conjugation is the transfer of genetic information, usally in the form of a __________ , from a __________ bacterium to a __________ through a specialized structure like a __________.
PLASMID; DONOR; RECIPIENT; SEX PILUS
What is transformation?
a cell takes in genetic material from its surroundings and incorporates it into its own DNA
What is transduction?
the process of introducing foreign DNA into a cell by a virus or viral vector (ex: bacteriophage)
What does it mean for a bacterium to be sensitive?
The bacterium IS susceptible to the effects of an antibiotic (killed or inhibited growth)
What does it mean for a bacterium to be resistant?
The bacterium is NOT susceptible to the antibiotic
What does it mean for a bacteria to be considered as intermediate?
means that the bacteria may be gaining resistance to the antibiotic. In these instances, another concentration or multiple antibiotics (polypharmacy) is necessary to affect the cell.
True or False: The smaller the diameter of the zone of inhibition, the more sensitive the bacteria are to a particular antibiotic
FALSE, the LARGER the zone of inhibition, the more sensitive the bacteria is to a particular antibiotic
What type of gene transfer does this image show?
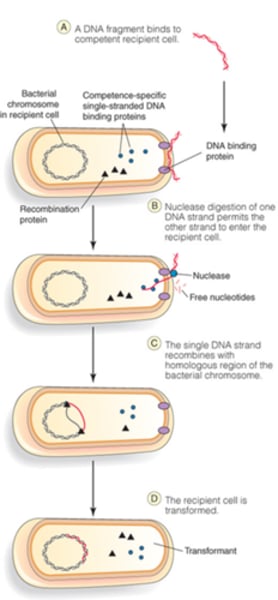
Are competent cells rare in nature?
Yes
What are competent cells?
bacterial cells that are able to take up foreign DNA from it's surroundings
What are Enterobacteriaceae?
a group of short, Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic rods that ferment glucose; Can be apart of normal GI microbiota; opportunists; pathogens
What is a nosocomial infection? Can it cause resistance to antibiotics?
Healthcare-acquired infections.; Yes, it can cause a resistance to multiple antibiotics
What are the four different types of differential media tests we used?
1. Triple Sugar Citrate Agar (TSA)
2. Sulfide-Indole-Motility (SIM) medium
3. Simmon's Citrate Agar (SCA)
4. Urea Agar
What three sugars in are in TSI?
Glucose, sucrose, lactose
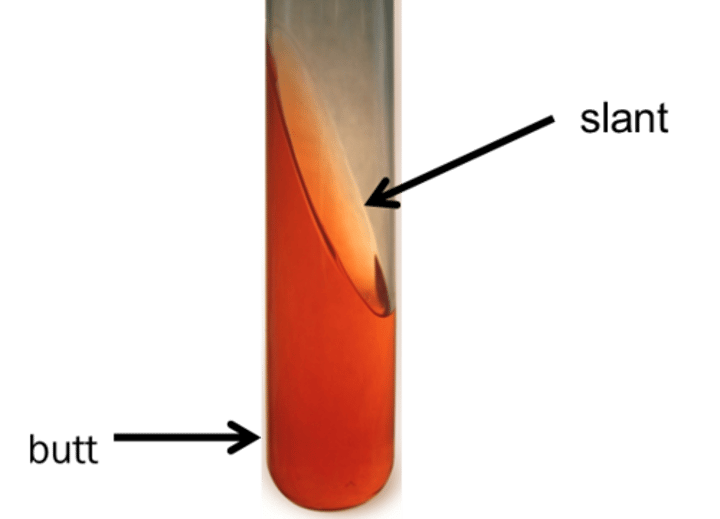
In TSI, what color is the agar if it is acidic pH?
Yellow
In TSI, what color is the agar if it is alkaline pH?
Pink-red
In TSI, where can glucose fermentation be observed?
Since glucose fermentation does not require oxygen, it can be observed in the bottom of the tube
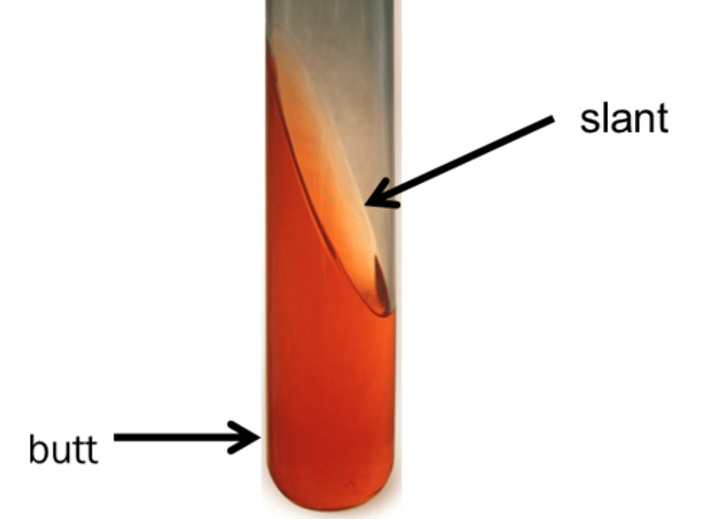
Where can sucrose and lactose fermentation be observed in TSI?
Both sucrose and lactose fermentation require oxygen so it can be observed on the slant
What does a yellow bottom and pink slant indicate in TSI?
It means that the bacteria has fermented the glucose but was not able to use either lactose or sucrose (K/A)
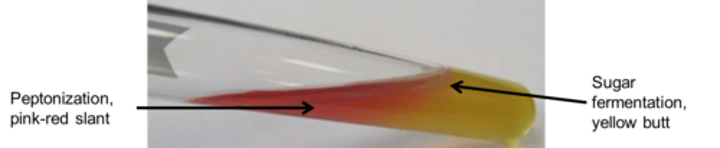
What does it mean that if both the bottom and slant are red in TSI?
It means that the bacteria did not ferment any sugars and only peptones were used (K/K). The bacteria are not Enterobacteriaceae also known as alkaline reversion/conversion
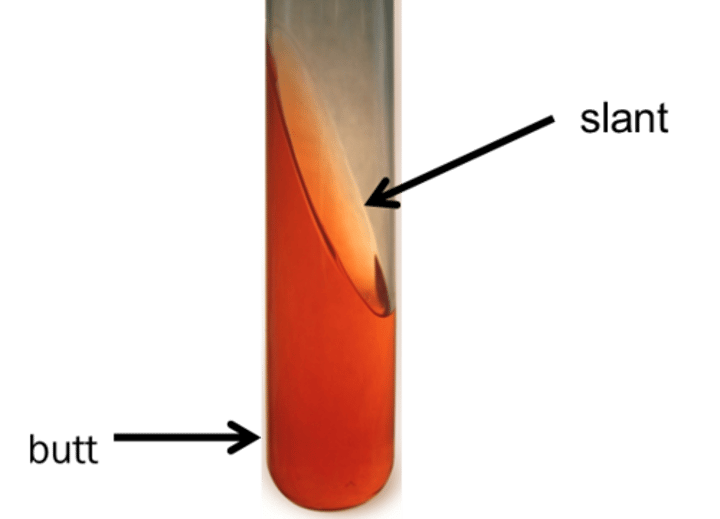
What is Alkaline reversion/conversion
It occurs when the bacteria initially rapidly ferment all the sugars, turning the media yellow. After depleting the sugars, the bacteria then use the amino acids for food and the media turns red.
In the TSI test, how can you tell if the bacteria can remove Sulfur?
It will have a black bottom
In SIM media, what does the enzyme tryptophanase hydrolyze? What does it produce?
It hydrolyzes tryptophan to produce indole and pyruvate
In the TSI test, how can you tell if the bacteria produced gas?
If there is breaks or air spaces in the agar
In SIM medium, how would you know if the bacteria had reduced sulfur?
Black precipitate will form in the media
In SIM medium, how would you know if the bacteria DID NOT reduce sulfur?
The media would be clear
True or False: Tryptophanase found in SIM medium can hydrolyze the amino acid tryptophan and produce indole and pyruvate
TRUE
What reagent is added to SIM to detect indole?
Kovac's reagent
How do you know if SIM medium is positive for indole?
It will turn cherry red
How do you know if the SIM medium is negative for indole?
It will remain the same color (yellow)
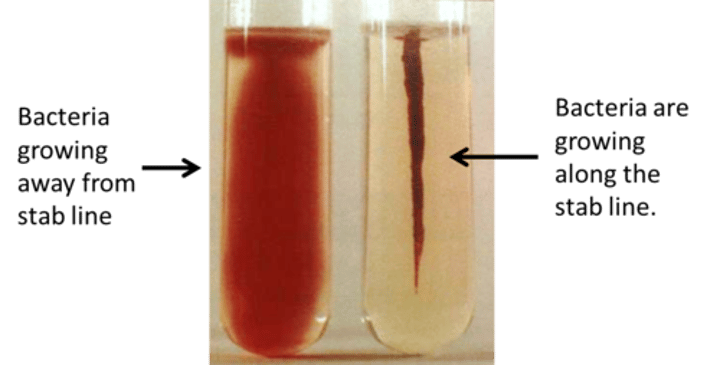
How do you know if the SIM medium has motility?
Bacteria will grow away from the stab line (line of inoculation)
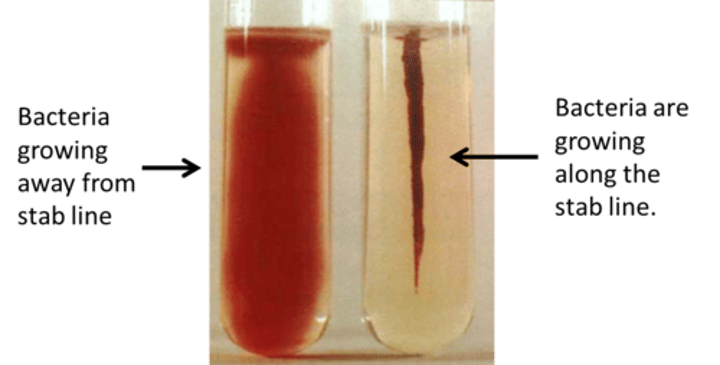
How do you know if the SIM medium DOES NOT have motility?
Bacteria will only grow along the stab line (line of inoculation)
True or False: Simmon's Citrate Agar (SCA) contains sodium citrate as it's only available carbon source
TRUE
Can citrase use sodium citrate and nitrogen to produce ammonia?
Yes
In SCA, what color will the agar be if it is positive for citrase activity?
Blue because of the pH indicator, bromothymol blue
In SCA, if the bacteria cannot use citrate then what color will the agar be?
It will remain green which is negative for any citrate activity
What is urea agar composed of?
Urea, peptones, glucose, and phenol red (indicator)
In Urea when ammonia is produced, what is the pH? Is it detected by phenol red?
The pH becomes alkaline; it is detected by phenol red
In Urea, if bacteria have urease enzymes and hydrolyzes urea to ammonia, what color would show this?
The agar will turn a bright pink medium (positive)
In Urea, if the bacteria cannot use urea, what color will the agar be?
The agar will remain it's original color (orange) and will be negative.
What is chromagar?
differentiate many members of the Enterobacteriaceae based on color; is capable of differentiating and detecting more than one population and even small numbers of microbes in a clinical specimen
What does "potable" mean?
safe to drink; free from contamination with microbes
What are coliforms?
Gram-negative bacillus (rod-shaped) are facultative anaerobes, ferment lactose-producing acid and gas, and only live in the gastrointestinal tract of animals.
What two dyes does Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) have?
Eosin Y and Methylene Blue
What causes EMB medium to turn to a pink-dark purple color?
Coliforms producing acid from lactose fermentation
True or false: E.coli on a EMB medium will turn a metallic green sheen bacteria because of excessive acid production
TRUE
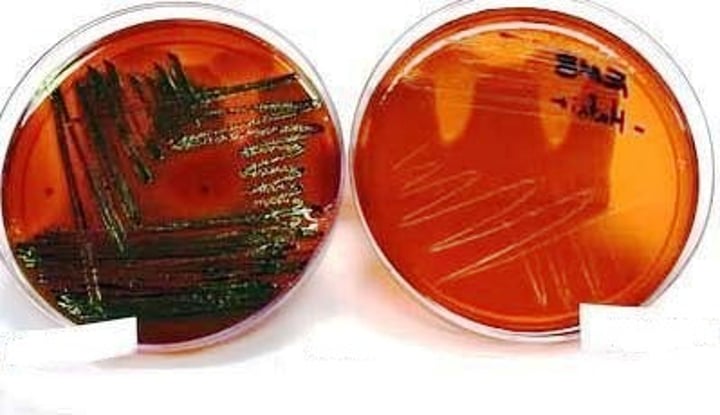
True or False: Non-coliforms ferment lactose
FALSE; Non-coliforms cannot ferment lactose, only coliforms can
If there is no lactose fermentation present on EMB, what does this mean? What color will it be?
This means there are no coliforms present but non-coliforms are growing. The agar will remain red and the bacteria will be clear.
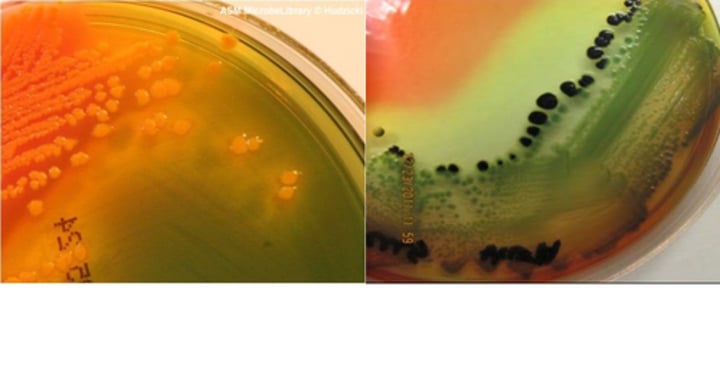
Bile salts
inhibit the growth of most Gram-positive bacteria and 3 sugars: lactose, sucrose, and salicin.
What color will the media be if HEA is fermenting either lactose, sucrose, or salicin? Are coliforms or non-coliforms present?
Yellow-pinkish-orange; Coliforms are present (E.coli present)
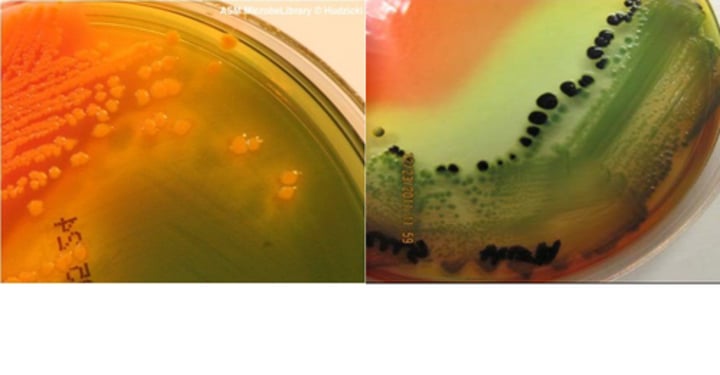
In HEA, if no fermentation occurs, what color will the media be? Is there coliforms or non-coliforms present?
The media will be blue-green; there is non-coliforms present (Salmonella present)
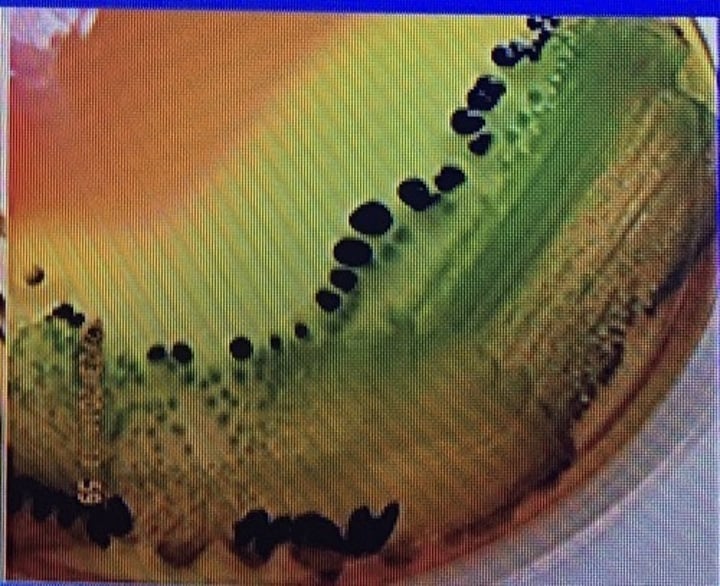
What causes HEA media to become black?
Sodium thiosulfate (sulfur) and ferric ammonium citrate. They react with H2S gas to produce ferrous sulfide. Indication of Salmonella
What does MacConkey agar contain? (MCA) (3)
bile salts, crystal violet, neutral red
What color will the media be if lactose fermentation occurs in MCA? Are coliforms or non-coliforms present?
The media will be pink; coliforms are present
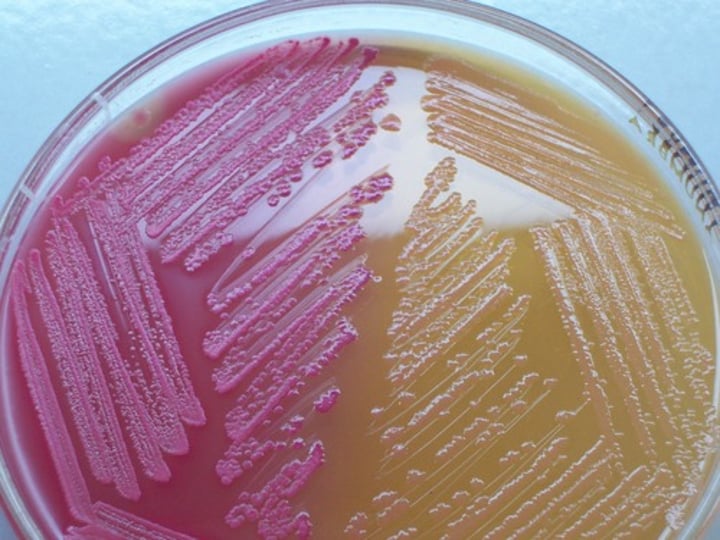
If there is no fermentation, what color will the MCA media be? Are there coliforms or non-coliforms present?
The media will be colorless; non-coliforms are present
What does Rapid'E. coli 2 agar detect?
Selective chromogenic medium used to detect E. coli and other coliforms in food and water.
Fill in the blank: Coliforms________ form ________ colonies; E.coli ________ form ________ to ________ colonies.
GAL+/GLU-; BLUE/GREEN; GAL+/GLU-; VIOLET; PINK
What is a bacteriophage?
A virus that infects and replicates inside bacteria
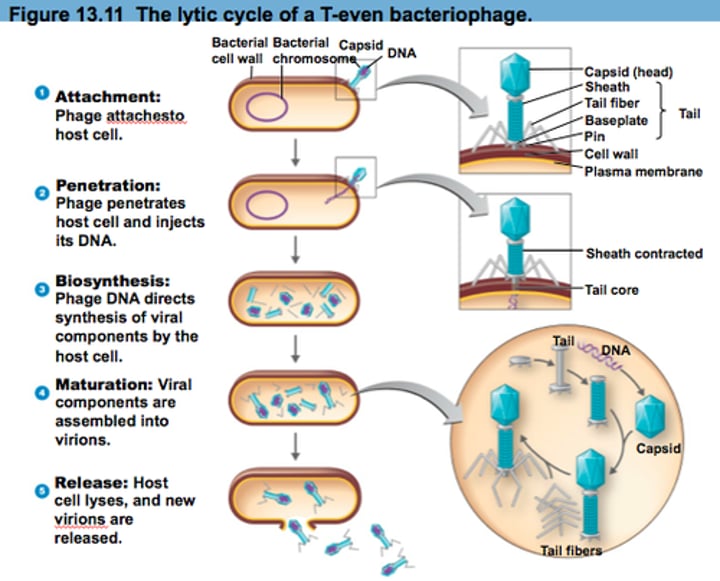
What is the difference between a lytic and a lysogenic cycle?
In the lytic cycle, the viral genome does not incorporate into the host genome. In the lysogenic cycle, the viral genome incorporates into the host genome and stays there throughout replication until the lytic cycle is triggered.
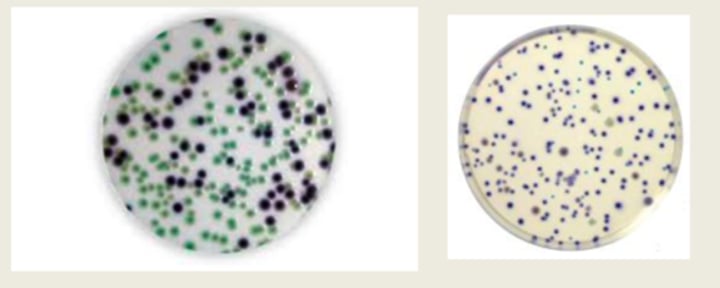
On the Rapid E'coli Agar 2 Plate, what color will Coliforms turn?
Blue/green
On the Rapid E'coli Agar 2 Plate, what color will Non-Coliforms turn?
Clear/white
On the Rapid E'coli Agar 2 Plate, what color will E'coli turn?
purple/pink
Is staphylococcus aureus gram positive or negative?
gram positive cocci
Is staphylococcus responsible for great numbers of nosocomial infections and antibiotic resistance genes?
Yes
What is staphylococcus?
pyogenic (pus-forming) causing abscesses and can invade tissues to cause systematic diseases like acute endocarditis, necrolytic pneumonia, and toxic shock syndrome.
Does Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) cause thousands of death annually in the U.S.?
Yes
What is staphylococcus saprophyticus?
may be normal flora in the vaginal tract and it is associated with urinary tract infections.
What is staphylococcus epidermidis?
a common member of the skin flora, but it may be associated with nosocomial infections of the blood.
What is enterococcus?
can cause blood stream infections and be resistant to antibiotics such as vancomycin resistant Enterococcus (VRE).