Platyhelminthes and Nematodes
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
The Bilateria are characterized by what and it allows for what?
characterized by bilateral symmetry which allows for specialization
What phylum do flatworms belong to?
Platyhelminthes
What are characteristics of Platyhelminthes (flatworms)?
acelomates
soft bodied
1 mm to many meters
many parasitic, others free-living
move by ciliated ventral epithelial cells
musculoskeletal
Flatworms typically want to move to what type of environment?
To the dark
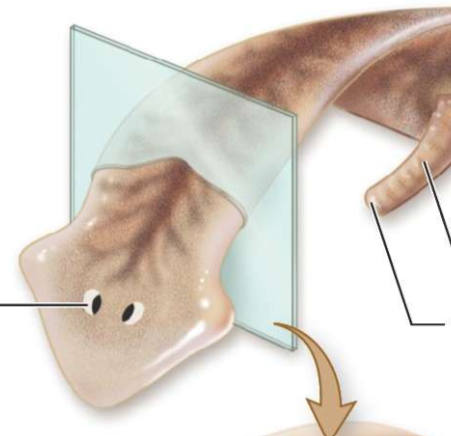
What is the left most line?
eye spot
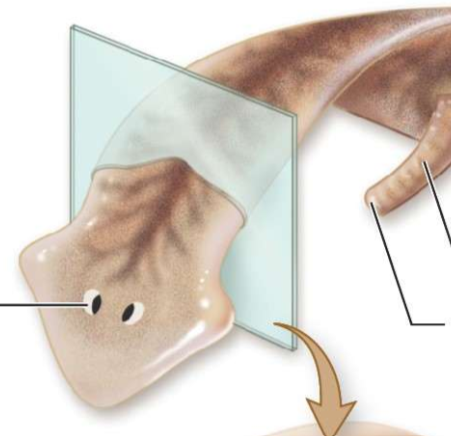
What is the middle line?
mouth
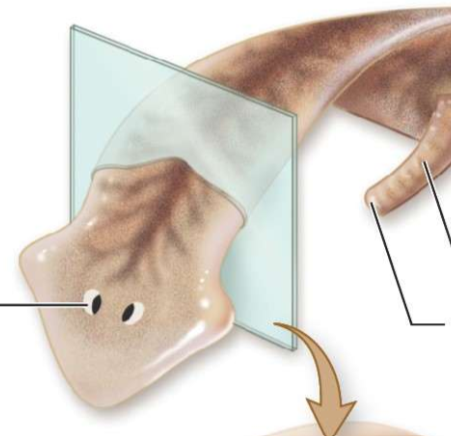
What is the right most line?
protruding pharynx
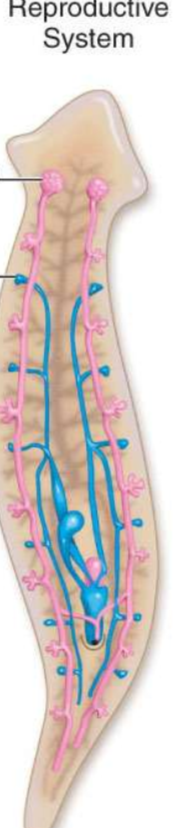
What is the top left(#1)?
testis

What is number 2
oviduct

what is number 3?
sperm duct
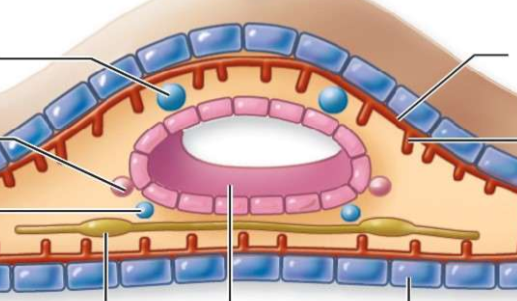
What is number 4?
nerve cord (runs along ventral side)
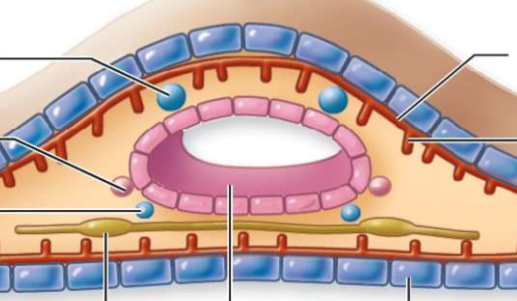
What is number 5?
intestine

What is number 6?
epidermis
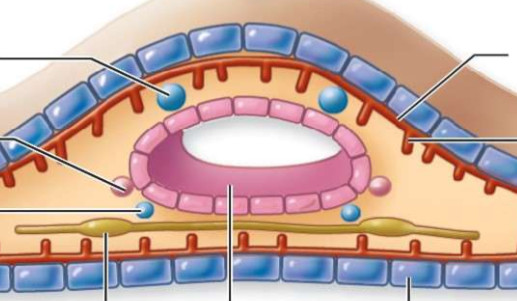
What is number 7?
parenchymal muscle
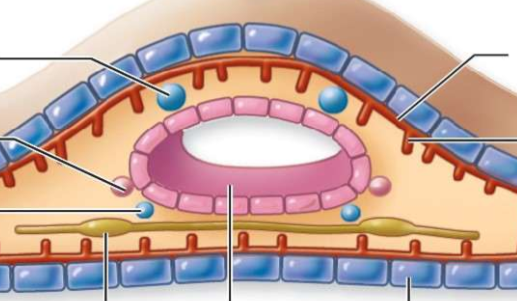
what is number 8?
longitudinal muscles
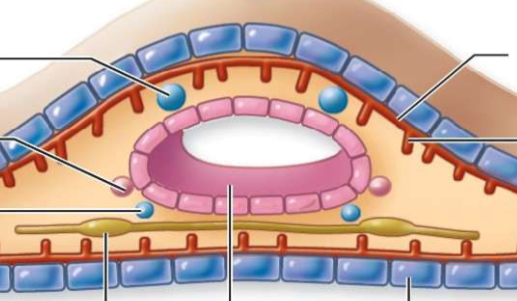
what is number 9?
circular muscles
flatworms are _____ in most cases
hermaphrodites
What is the arrow pointing to?
Intestine
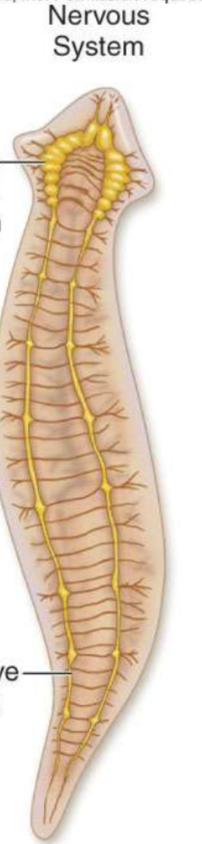
What is the top arrow pointing to?
anterior cerebral ganglion
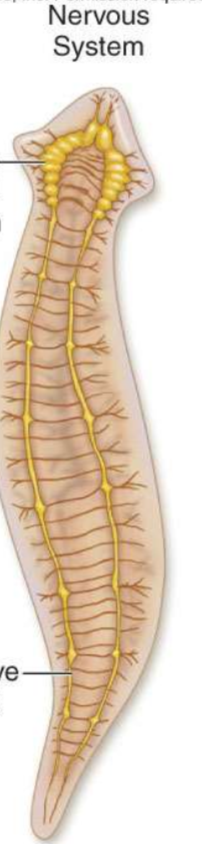
What is the bottom arrow pointing to?
Nerve chord
What is the top arrow pointing to?
ovary
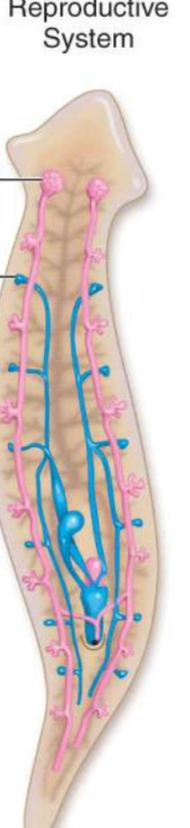
What is the bottom arrow pointing to?
Testis
Platyhelminthes have a ____ gut with a ______ ________
blind, ventral opening
What type of digestion do you have if you have a blind gut?
incomplete digestive system
What allows food to be torn into small bits in platyhelminthes?
muscular contractions in the pharynx
True or False: Platyhelminthes have some extracellular digestion
True
What does the phagocytosis?
cells that line the gut
What worm lacks mouths and digestive systems?
Tapeworms (parasitic flatworms)
How do tapeworms get food?
Absorb food directly through body walls and live in the intestines
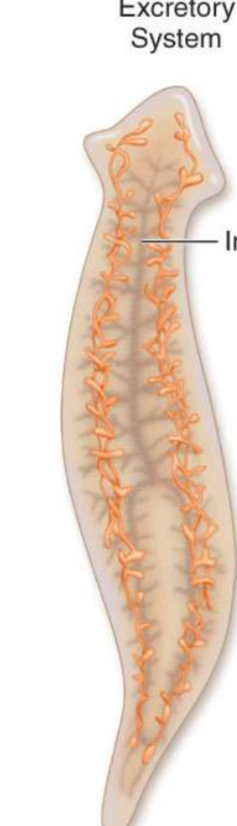
Platyhelminthes have what two main systems?
Excretory and Osmoregulatory systems
Describe the physical parts of the systems
network of fine tubules runs through body
flame cells located on the side branches of tubules
Describe the process of water movement
internal cilia move water and excretion into tubules
then removed through pores between epidermal cells
What is the primary function?
water balance
what is the secondary function?
excretion
Most ________ diffuses into ________ and eliminated through _______
metabolic waste, the gut, the mouth
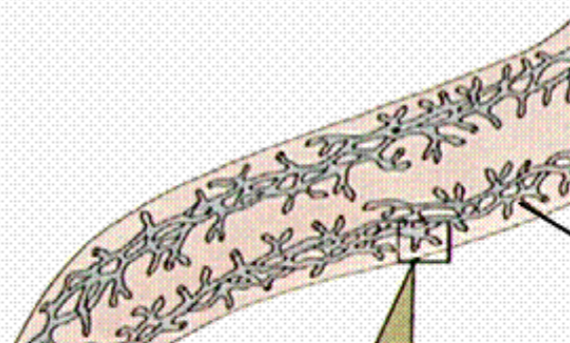
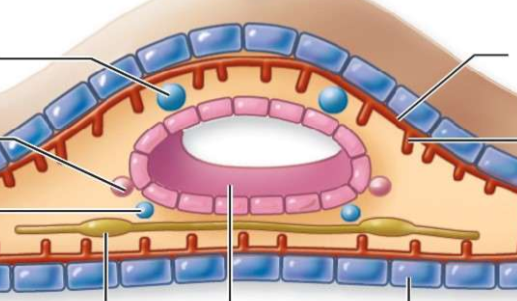
What is the black line pointing to?
excretory canal
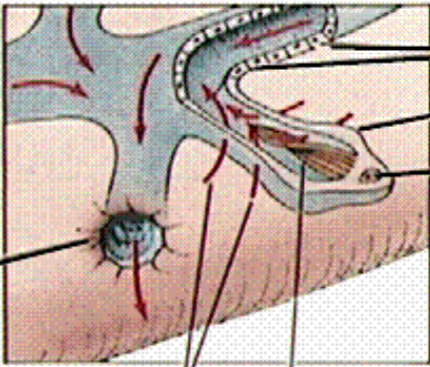
What is this an image of?
insides of a platyhelminthe

What is line 1 pointing to?
excretory pore
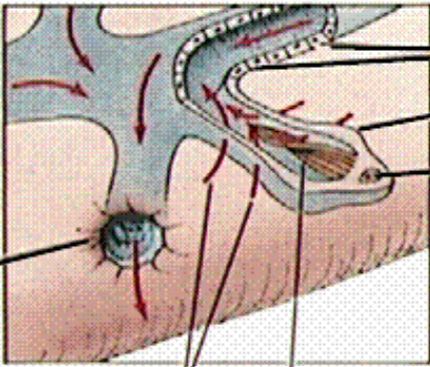
what are lines 2 and 3 pointing at?
fluid movement
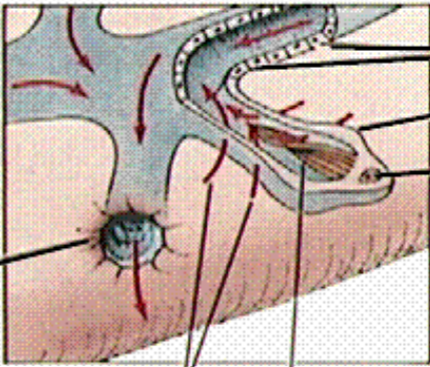
what is the 4th line pointing to?
cilia (in others it can be flagella too)
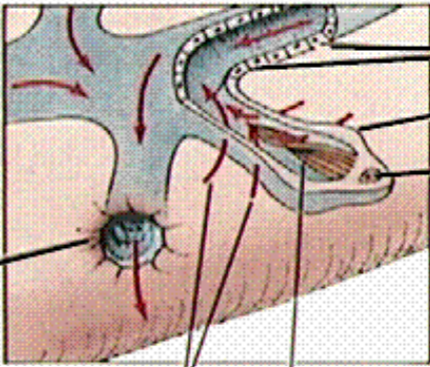
What is line 5 pointing to?
Nucleus
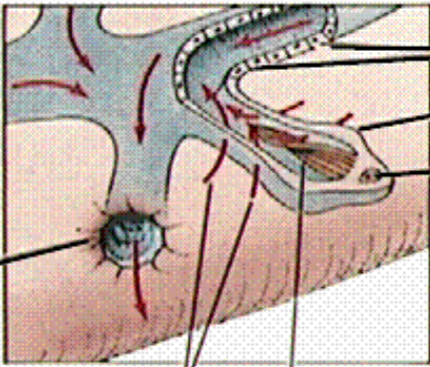
What is line 6 pointing to?
flame cell
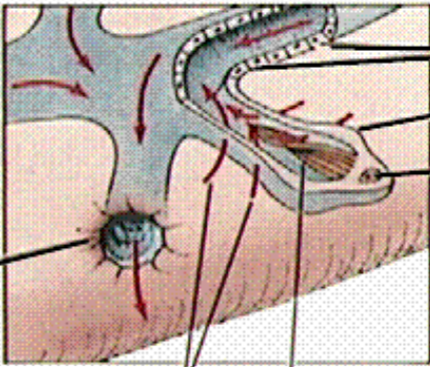
What are the last two lines pointing to?
Tubule cells
Respiration
gas diffuses between cells and the air
What does a simple nervous system consist of?
anterior cerebral ganglion
bilateral ventral nerve cords with transverse connections (like ladder rungs)
eyespot can distinguish light from dark
Characteristics of reproduction in platyhelminthes
most hermaphroditic with cross fertilization
many have internal fertilization
direct and indirect development
regeneration
What is internal fertilization?
sperm is delivered inside
What is direct development and what type of animals have it?
embryo directly develops into an adult, found in freshwater worms
What is indirect development and what animals have it?
has a larval stage, occurs usually in marine animals
What are the two major groups of platyhelminthes?
turbellaria and neodermata
Turbellaria
free living platyhelminthes
ex: planaria
Neodermata
parasitic platyhelminthes
can be endo or ectoparasites
in endoparasites, they are resistant to hosts digestive enzymes in order to survive
endo parasites also have no eyespots
What are the two major Neodermata subgroups?
class trematoda and class cestoda
Trematoda (Flukes)
1mm to 8cm small
endoparasites (feeds off of RBCs)
takes food in through mouth
most life cycles have multiple hosts
Step 1 Fluke Life Cycle
Numerous eggs are put in the environment through feces that contain miracidium and into the water
Step 2 Fluke Life Cycle
miracidium hatches after being eaten by a snail
Step 3 Fluke Life Cycle
sporocyst forms (inside snail)
Step 4 Fluke Life Cycle
redia forms (inside snail)
Step 5 Fluke Life Cycle
Cercaria burrows inside of muscles of fish after leaving the snail
Step 6 Fluke Life Cycle
metacercarial cysts in fish muscles form
Step 7 Fluke Life Cycle
raw, infected fish is consumed by humans or other mammals
What are the terms associated with the asexual reproduction of the oriental liver fluke?
miracidium, rediae, cercaria
What is the latin name for the oriental liver fluke?
clonorichis sinensis
miracidium
ciliated stage in egg
rediae
non-ciliated larvae produced within sporocyst
cercaria
tadpole-like larval stage
What happens in the second part of the complex life cycle of the liver fluke?
larval maturation in fish (2nd intermediate host)
then sexual maturation and reproduction in humans (primary hosts)
What is the 1st intermediate host for a liver fluke?
snails
metacercaria
juvenile stage produce within cysts
What are some common characteristics of liver flukes?
lives in bile ducts of liver of humans, cats, dogs, and pigs
common in Asia
individual flukes can live 15-30 years in the liver
What are some facts about what happens when the liver fluke enters a human body?
typically asymptomatic
heavy infestation can lead to cirrhosis and death
increases chances of liver cancer
What is cirrhosis?
scarring of the liver
What is the genus name for blood flukes?
schistosoma
How many species of what type of animal can cause the disease schistosomiasis?
3 species of blood flukes
What organism carries schistosomiasis?
freshwater snails
where do blood flukes usually live?
in blood vessels associated with the intestine or bladder
what are the symptoms of blood fluke infestation?
itchy or skin rash after 1st contact (Burrow into RBCs)
1-2 months: fever, chills, muscle aches, cough
chronic: damage to intestine and bladder
How do the worms keep themselves from being detected by the immune system?
worms coat themselves with the host’s own antigens which makes them immunologically invisible
What class do tapeworms belong to?
cestoda
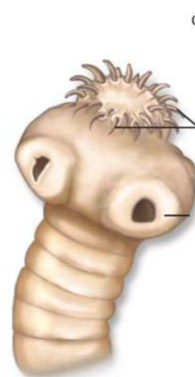
What part of what organism is shown here?
The scolex of a tapeworm
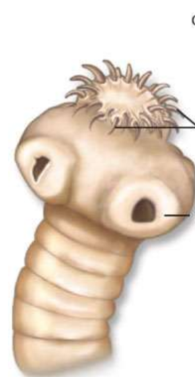
What are the top two arrows pointing at?
hooks
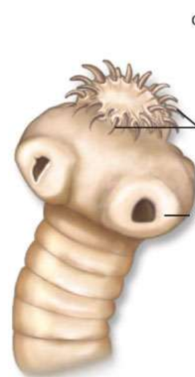
What is the middle arrow pointing at?
the sucker
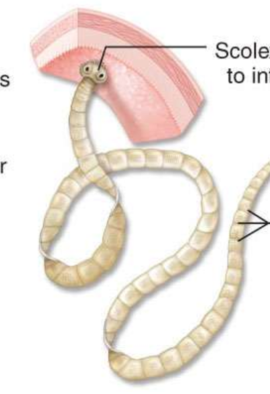
What is the top arrow pointing at and showing?
shows that the scolex is attached to the intestinal wall
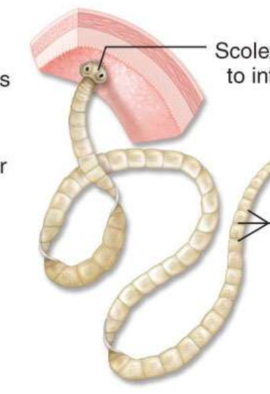
What are the bottom three arrows pointing at?
Repeated proglottid sections

What is this a zoomed in picture of and on what animal?
One proglottid region on a tapeworm

What is the top arrow pointing at?
uterus

What is the middle arrow pointing at?
genital pore
What are some basic characteristics of tapeworms?
most species live in the intestines of vertebrates
no digestive cavity or enzymes
long flat bodies divided into three zones
What are the names of the three zones in a tapeworm?
scolex, neck, and proglottids
Scolex
attachment organ, almost like suckers or clips to hold on to the intestine walls
no mouth
Neck
unsegmented portion of the tapeworm
Proglottids
repetitive sections of the tapeworm
Characteristics of proglottids
each a complex hermaphroditic unit
active growing zone in neck
posterior proglottids form mature eggs
What is the name of the beef tapeworm?
taenia saginata
How does the beef tapeworm get passed to humans?
juvenile in cattle muscle and burrow through instestines to muscles
passed to humans when eating undercooked beef
becomes adult in human intestines and pass between humans to cows through feces
How long are the tapeworms viable in feces?
up to 5 months
What is a pseudocoelomate?
they have a pseudocoel, which is a cavity between the mesoderm and endoderm
What does the pseudocoel serve as?
a hydrostatic skeleton against which the animal’s muscles can work
What do pseudocoelomates lack and what makes up for it?
they lack a defined circulatory system which is covered for by fluids which move within the pseudocoel
What phylum do roundworms belong to?
nematoda