Neuro Exam 1
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
Neuron doctrine
brain composed of independent cells, signals transmitted from cell to cell across gaps (synapses)
Unipolar neuron
single extension branches in two directions, forming a receptive pole and an output zone
biopolar neuron
one axon, one dendrite
multipolar neuron
one axon, many dendrites, most common type
“star” brain cells
neurons
sensory neurons
respond to environment; light, odor, touch (PNS)
motoneurons
contact muscles or glands (PNS)
interneurons
receive input from and send input to other neurons, integration (most neurons in CNS)
glial cells
support the brain, non neuronal, in CNS and PNS, four kinds
astrocytes
glial cells, star shaped, fill spaces between neurons for support, provide blood-brain barrier, regulate composition of the EC.
oligodendrocytes
wrap axons with myelin sheaths inside brain and spinal cord, wrap several axons, form segments of myelin sheath; nodes of ranvier where axon membrane is exposed
multiple sclerosis
glial cells, oligodendrocyte injury from autoimmune attack
microglia
glial cells, cells move around, clean up debris from dying neurons and glia
ependymal cells
glial cell, line ventricles, secrete and absorb cerebral spinal fluid
AIDS encephalitis
brain damage in patient from neurotoxins glutamate and nitric oxide from viral activated microglia (glial cell)
dendritic spines
increase surface area and can CHANGE, they have neural plasticity, number and structure rapidly altered by experience
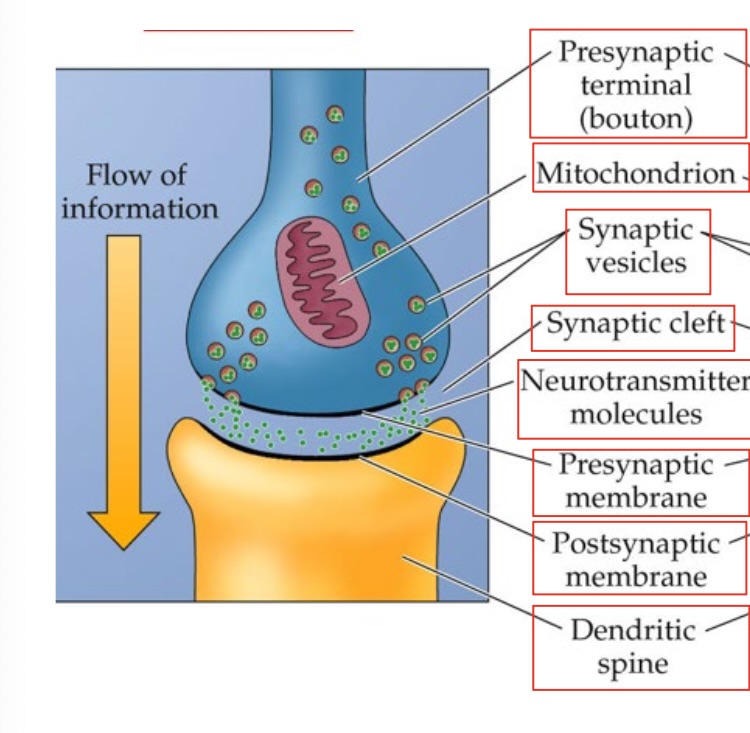
Synapse
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
cranial nerves, spinal nerves
autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, brainstem and spinal cord
sympathetic nervous system
prepares body for action, spinal cord
parasympathetic nervous system
brainstem and bottom of spinal cord, rests and digests
basal ganglia
movement control, center of the brain, contains the thalamus
limbic system
emotional memory, regulation, olfactory bulb, amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus
cerebellum
very back, lower end of brain, motor coordination and learning
horizontal, separates brain from top to bottom
sagitall, slices brain down the midline
coronal, separates brain from front to back, butterfly
medial
towards the middle
ipsilateral
same side
anterior
head end (FRONT)
proximal
center
dorsal
towards the back
lateral
side
contralateral
opposite side
posterior
tail end
ventral
towards stomach
afferent
carries neural information TOWARDS region of interest (sensory)
efferent
carries neural information AWAY from region of interest (motor)
white matter
composed of axon bundles, appear white because myelin sheaths (white fatty tissue) covers the axons
gray matter
composed of clusters of neuron cell bodies, dark gray appearance
reticular formation
part of mid brain, sleep, arousal, body temperature
meninges
brain wrappings
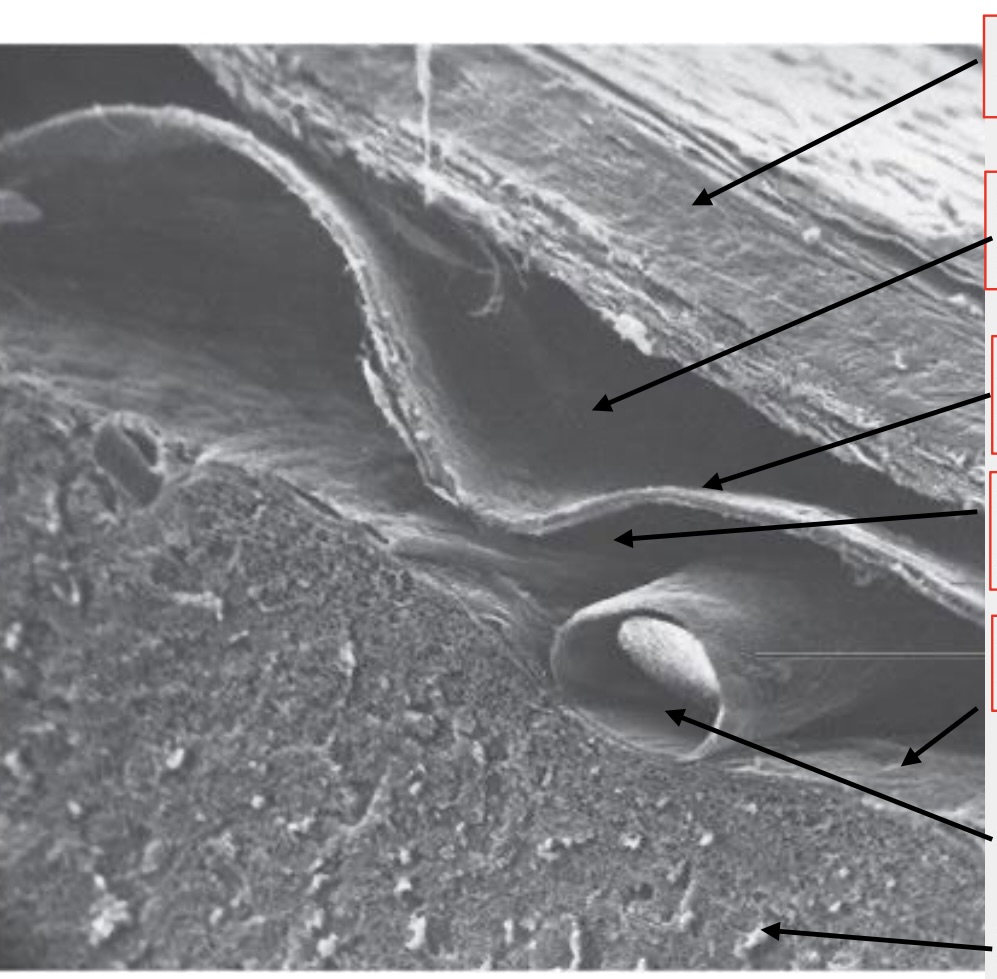
top arrow
dura mater
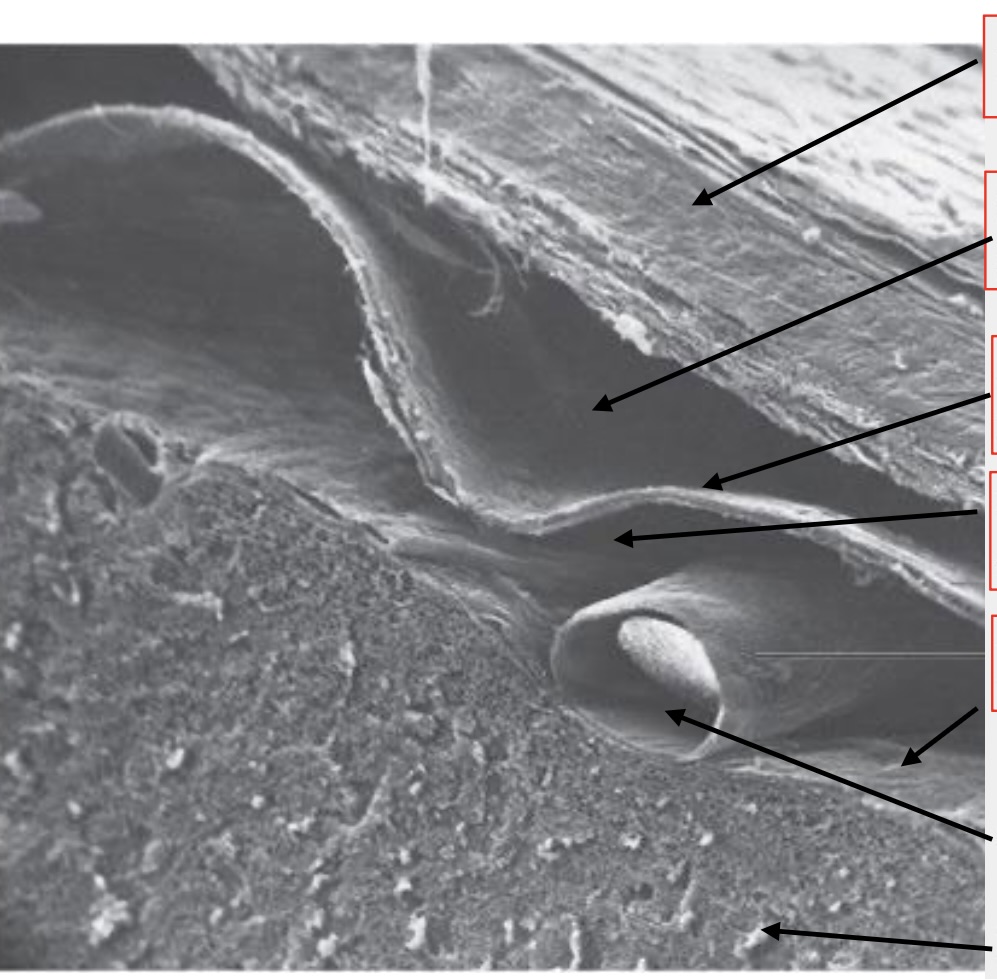
second arrow
subdural space
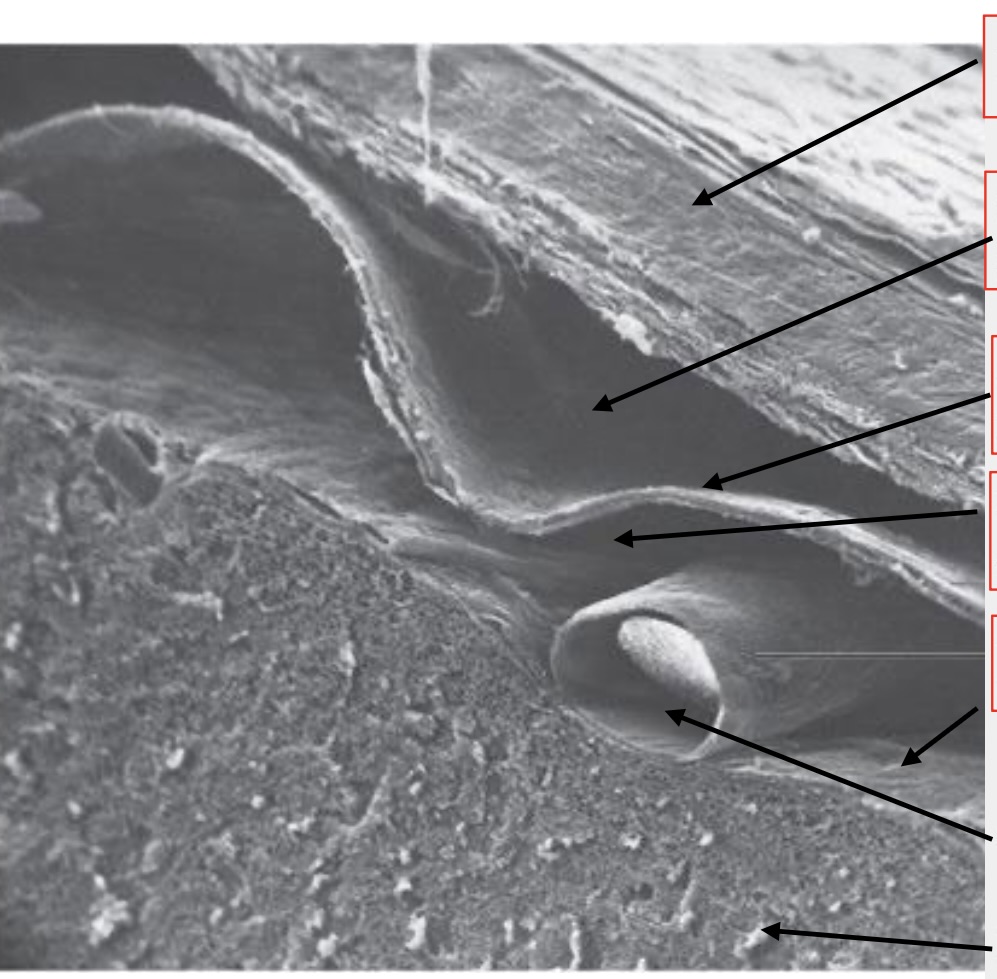
third arrow
arachnoid membrane
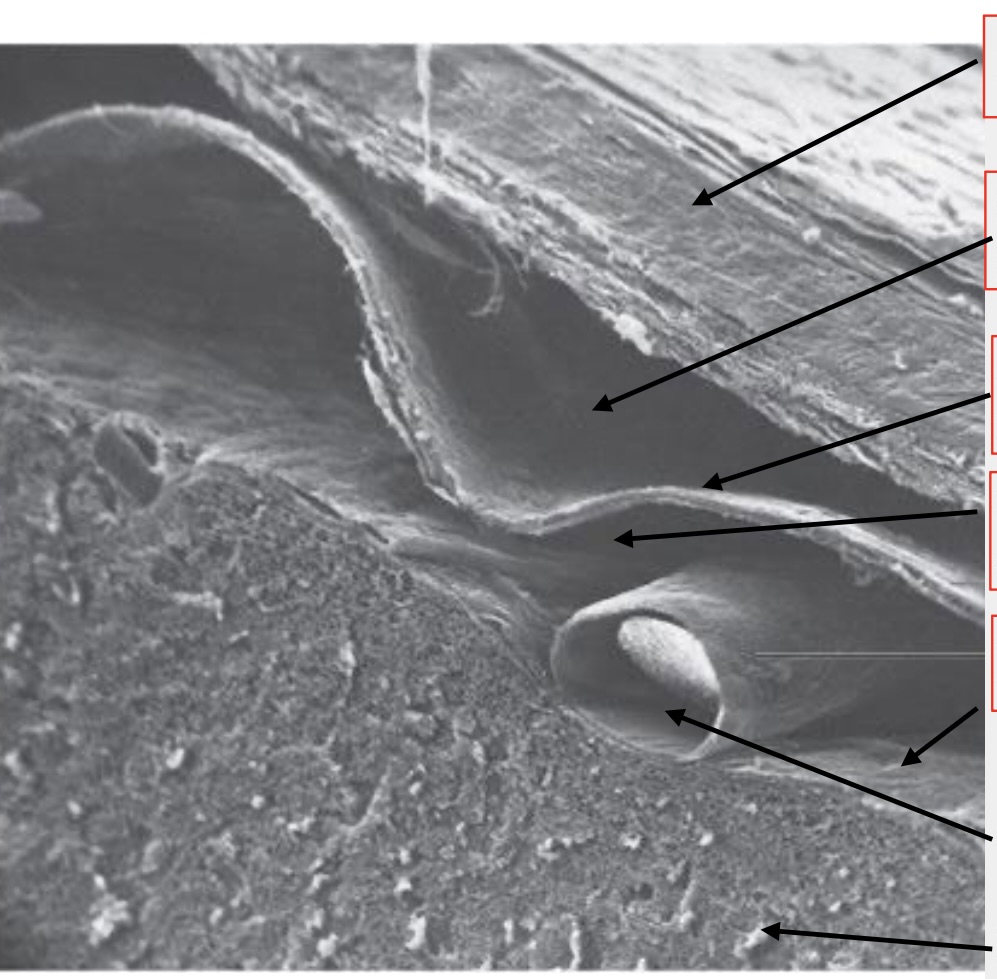
fourth arrow
subarachnoid space
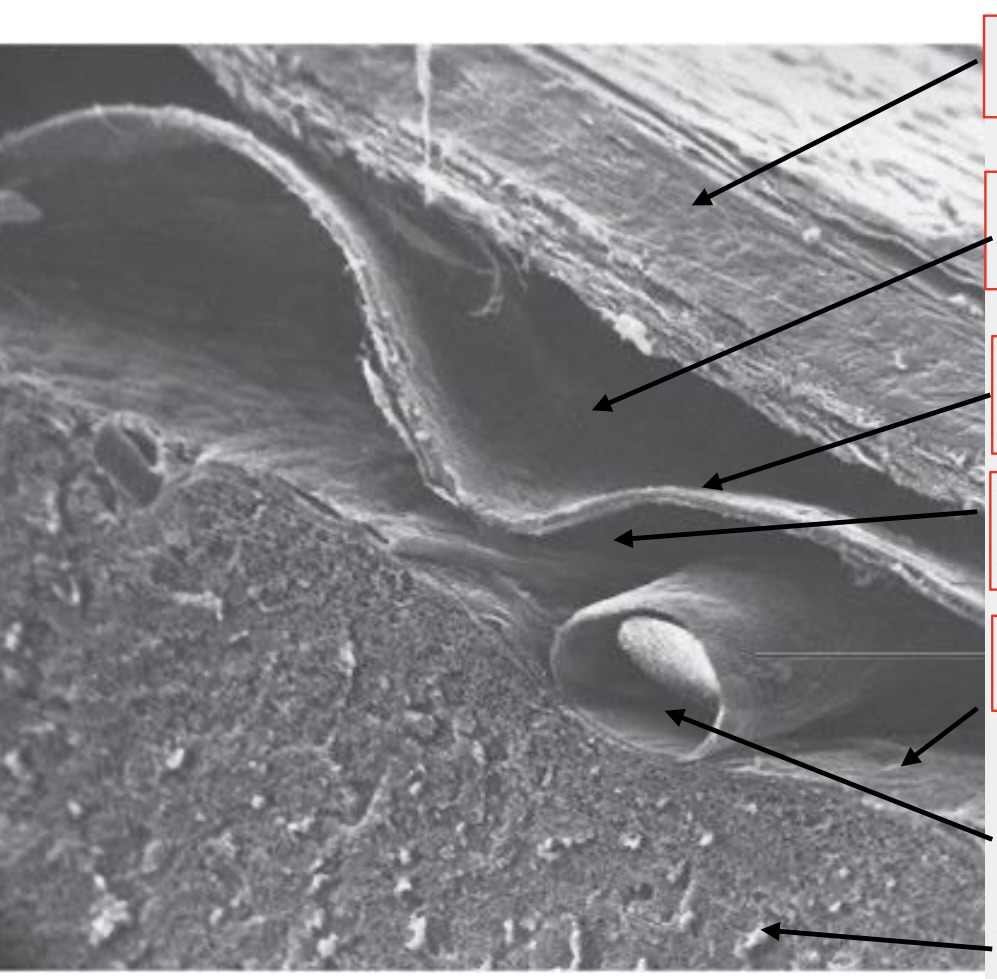
fifth (tiny) arrow
pia mater
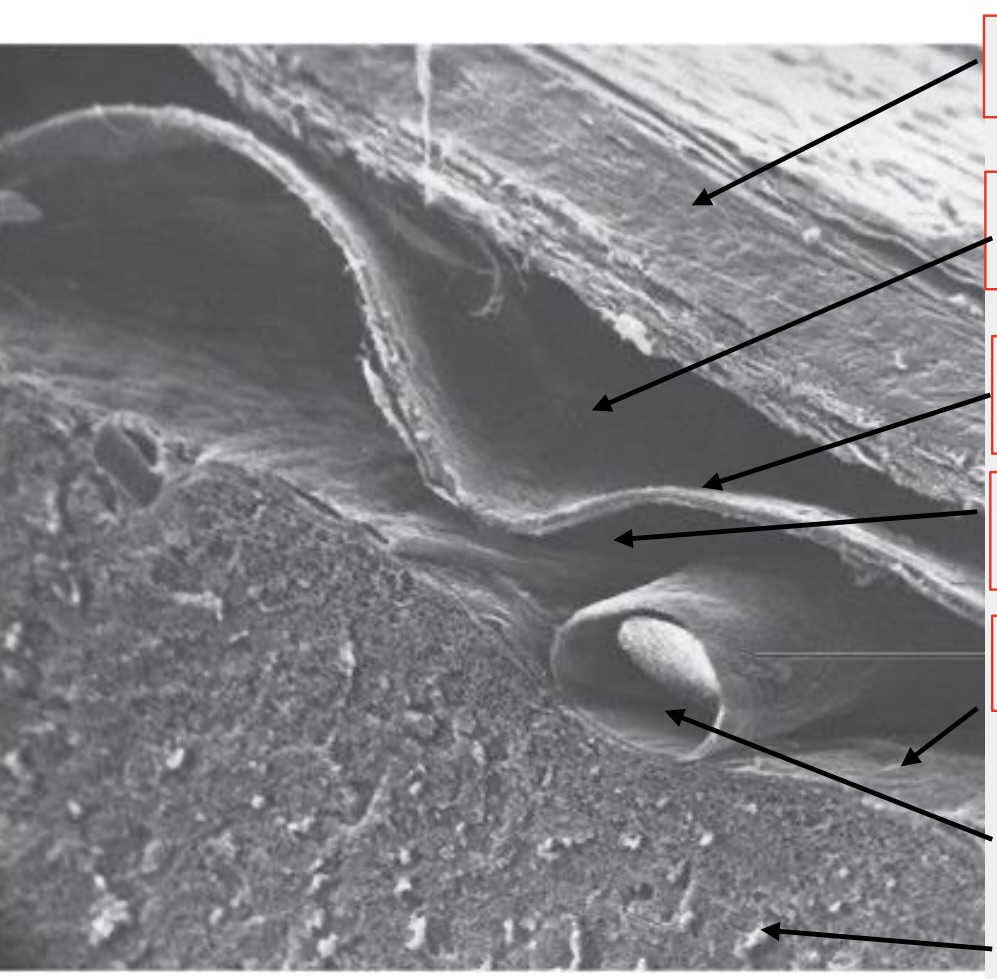
second to last arrow
artery
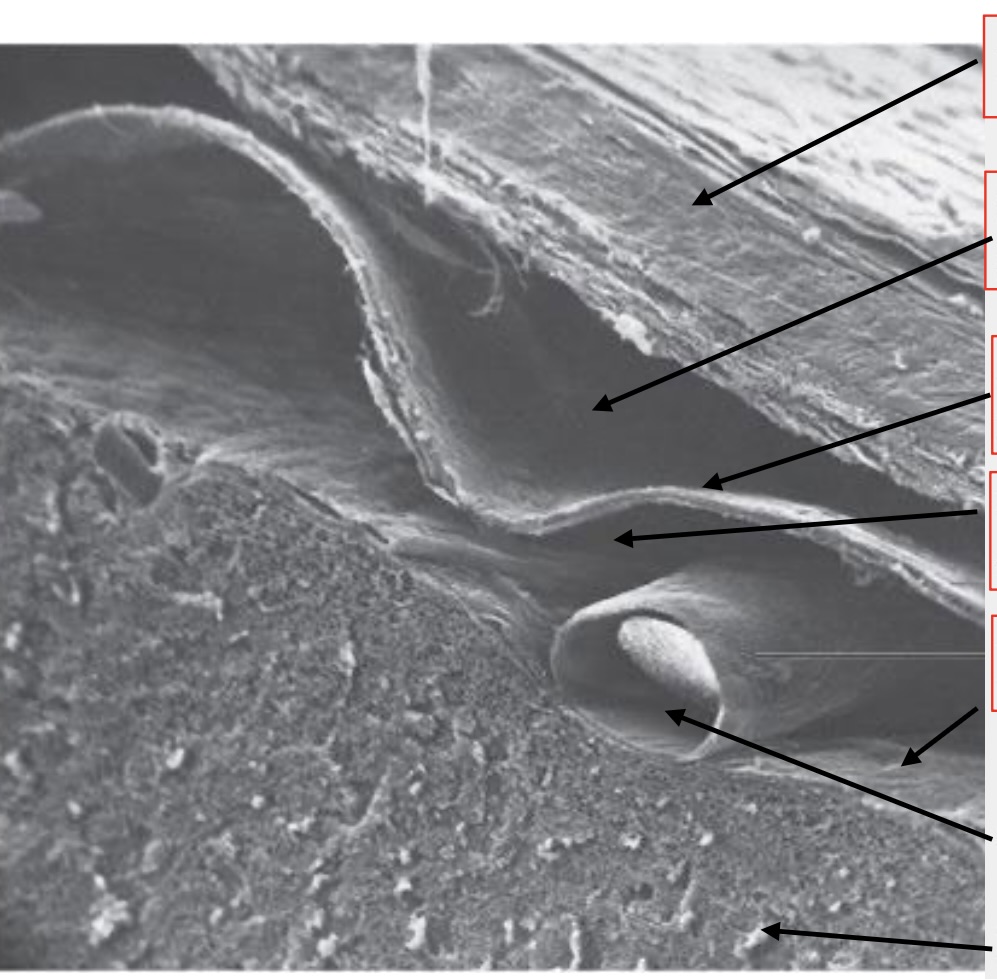
last arrow
brain
subdural hematoma
collection of blood between the brain and dura mater, caused by head trauma
cerebral ventricles
make CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)- surrounds and cushions brain
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) flow
produced inside the brain, circulates around the border from front to back and exits the brain
hydrocephalus
CSF circulation failure, too much CSF, swollen head
white matter tracts
connect brain areas, short and long distance
CT scan
black and white, shows tissue density, whiter means denser, view from above the head
MRI
protons line up in parallel, pulse of radio waves knocks protons over, they reconfigure, emitting radio waves differing by tissue density
PET scan
brain activity, inject radioactive chemicals to map their destinations, few clinical uses
functional MRI (fMRI)
brain activity, detects change in brain metabolism like oxygen use, shows how networks of brain structures collaborate, shows all views of brain (3D)
DTI
images of axons of neurons, showing brain connections, up and down axons are BLUE, front to back of brain axons are GREEN
soma
cell body
rough ER
membranes with ribosomes (rough/bumpy) protein synthesis site, surrounds nucleus
smooth ER
regulates cytoplasm, no bumps on it
Golgi apparatus
stacks of flat membrane compartments, packages products for shipment in cell
neuron membrane
lipid bilayer, surrounds cell and separates cytoplasm from ECF
intrinsic proteins
receptors, ion channels, give neurons the necessary properties for signaling
cytoskeleton
structural support, microtubules, neurofilament, microfilament
microtubules
20nm tubes straight up and down look like hollow circles inside neuron
neurofilaments
10nm twisted cables, static support structures, look like tiny dots
anterograde transport
material moved from soma to terminals along microtubules using kinesis as enabling protein
retrograde transport
material moved from terminals towards soma via dynein as enabling protein
MELAS syndrome
Mitochondrial, Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, Stroke: mitochondrial energy failure
neuron size
matters, larger neurons cover larger distance, more complex, and faster
semipermeable membrane
screen door, only allows certain things through
diffusion
ions flow from high to low concentration along their concentration gradient
electrostatic pressure
causes ions to flow towards OPPOSITELY charged ions. positive and negative go together
inside axon
negative charge
outside axon
positive charge
ion channels
proteins spanning the cell membrane so ions can pass in and out. neuronal cell membrane repels water and ions are surrounded by water so they can only enter through a channel
gated ion channels
open/close in response to voltage change, chemicals, mechanical action
neuron equilibrium
-60mV, negatively charged proteins inside, neurons are most permeable to K+, positively charged potassium (K+) moves into cell through potassium channels
sodium potassium pump
pumps Na+ out and K+ in to maintain -60mV
tetrodoxin
comes from fugu fish, blocks nerve action by blocking pores of sodium channels in neuron membranes, kills you because nerves can’t fire=no breathing or movement
graded potential
occurs in dendrites, as graded potentials spread across membrane, they diminish, bigger stimulus bigger response
action potential
graded potentials can turn into action potentials if the membrane reaches threshold, inside of the cell becomes briefly positive, occurs in the axon hillock- right next to the soma
all or none action potential
neurons fire at full amplitude or not at all
action potential first step
voltage gated Na+ channels open in response to initial depolarization
action potential second step
more voltage gated channels open and more Na+ ions rush in all at once until membrane potential hits +40mV
action potential third step
voltage gated Na+ channels close, action potential is achieved at +40mV
action potential fourth step
because of the Na+ the inside of the cell is more positive so voltage gated K+ channels open
action potential final step
K+ moves out and resting potential is restored
absolute refractory phase
+40mV, maximum, no more action potentials can be produced
relative refractory phase
the period after the absolute refractory phase when only a strong stimulation can produce an action potential, mV is on the decline
Na+ refractory period
inactivation gate locks during absolute refractory period and opens during action potential
nodes of ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath on the axon, sodium and potassium channels are found
synapse signaling
electrical signal > chemical signal > electrical signal
chemical synapse transmission
action potential travels down axon to axon terminal, calcium channels open halfway down so Ca+ enters, synaptic vesicles fuse with membrane and release transmitter into the cleft
after transmitter is released into cleft
transmitter binds to postsynaptic receptor, causing EPSP or IPSP
EPSP
excitatory, depolarization, pushes cell closer to threshold, results from Na+ ions entering the cell making inside more positive, integrated by axon hillock
IPSP
inhibitory, hyper polarization, pushes cell away from threshold, results from Cl- ions entering cell, makes inside more negative, integrated by axon hillock